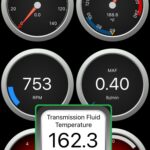
The 2006 Ford F250 Obd2 system is a crucial tool for diagnosing and maintaining your truck; OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN provides expert insights into leveraging this technology for peak performance. By understanding your F250’s diagnostic capabilities, you can ensure optimal functionality and longevity. We offer solutions to address your truck’s diagnostic needs, from understanding diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) to utilizing suitable scan tools.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the 2006 Ford F250 OBD2 System
- 1.1. Key Components of the OBD2 System
- 1.2. Benefits of Understanding Your F250’s OBD2 System
- 2. Essential OBD2 Tools for Your 2006 Ford F250
- 2.1. OBD2 Scanners: Basic vs. Advanced
- 2.2. Recommended OBD2 Scanners for 2006 Ford F250
- 2.3. Software Options: FORScan and More
- 3. Reading and Interpreting 2006 Ford F250 OBD2 Codes
- 3.1. Connecting Your Scanner and Retrieving Codes
- 3.2. Understanding the Structure of OBD2 Codes
- 3.3. Common OBD2 Codes for 2006 Ford F250 and Their Meanings
- 4. Diagnosing and Repairing Common 2006 Ford F250 Issues Using OBD2
- 4.1. Step-by-Step Diagnostic Process
- 4.2. Case Studies: Using OBD2 to Solve Real-World Problems
- 4.3. When to Seek Professional Help
- 5. Maintaining Your 2006 Ford F250’s OBD2 System
- 5.1. Regular OBD2 Scans for Preventative Maintenance
- 5.2. Keeping Your Truck in Good Condition
- 5.3. Addressing Issues Promptly
- 6. Advanced OBD2 Diagnostics for the 2006 Ford F250
- 6.1. Live Data Streaming and Analysis
- 6.2. Bidirectional Control
- 6.3. Manufacturer-Specific Codes and Data
- 7. Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using OBD2 on Your 2006 Ford F250
- 7.1. Misinterpreting Codes
- 7.2. Neglecting Basic Troubleshooting
- 7.3. Clearing Codes Without Repairing the Problem
- 8. The Future of OBD2 and Diagnostics
- 8.1. OBD3 and Enhanced Monitoring
- 8.2. Integration with Mobile Devices and Cloud Services
- 8.3. The Role of AI and Machine Learning
- 9. Resources for 2006 Ford F250 OBD2 Information
- 9.1. Online Forums and Communities
- 9.2. Repair Manuals and Technical Documentation
- 9.3. Professional Diagnostic Services
- 10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About 2006 Ford F250 OBD2
1. Understanding the 2006 Ford F250 OBD2 System
What exactly is the OBD2 system in your 2006 Ford F250?
The On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD2) system in your 2006 Ford F250 is a standardized system that monitors various components and systems within your vehicle, providing valuable insights into its operational health. It’s essentially your truck’s internal health monitor, constantly checking sensors and systems to ensure everything is running as it should. First introduced in the mid-1990s, OBD2 became mandatory for all vehicles sold in the United States by 1996, as stated by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA).
Understanding OBD2 involves grasping its key functions:
- Monitoring Vehicle Systems: The OBD2 system monitors a wide array of vehicle systems, including the engine, transmission, emissions control system, and more.
- Detecting Malfunctions: When the system detects a malfunction or a reading outside of the acceptable range, it stores a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) and illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL), commonly known as the “check engine light.”
- Providing Diagnostic Information: The OBD2 system provides a standardized method for accessing diagnostic information, allowing technicians and vehicle owners to diagnose and repair problems effectively.
According to a study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), understanding the OBD2 system is fundamental for efficient vehicle maintenance and repair. The OBD2 system is located under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
1.1. Key Components of the OBD2 System
What are the vital parts that make up the OBD2 system in your F250?
The 2006 Ford F250 OBD2 system consists of several key components working together to monitor and diagnose vehicle health. These components include:
- Sensors: Numerous sensors are strategically placed throughout the vehicle to monitor various parameters such as engine speed, coolant temperature, oxygen levels in the exhaust, and throttle position.
- Electronic Control Unit (ECU): The ECU, also known as the Powertrain Control Module (PCM), is the brain of the OBD2 system. It receives data from the sensors, analyzes it, and makes adjustments to engine operation as needed.
- Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): When a sensor reading falls outside of the specified range, the ECU stores a DTC, which is a standardized code that identifies the specific problem area.
- Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL): The MIL, or “check engine light,” illuminates when a DTC is stored in the ECU, alerting the driver to a potential problem.
- Data Link Connector (DLC): The DLC is a standardized connector, usually located under the dashboard, that allows technicians to access the OBD2 system with a scan tool.
1.2. Benefits of Understanding Your F250’s OBD2 System
What advantages do you gain by knowing how your F250’s OBD2 system works?
Understanding the OBD2 system in your 2006 Ford F250 provides numerous benefits, empowering you to take better care of your truck and save money on repairs.
- Early Problem Detection: By regularly monitoring your vehicle’s OBD2 system, you can detect potential problems early on, before they escalate into major repairs.
- Informed Decision-Making: Knowing the DTCs and their meanings allows you to make informed decisions about necessary repairs, avoiding unnecessary work and expenses.
- Improved Fuel Efficiency: Addressing issues detected by the OBD2 system, such as a faulty oxygen sensor, can improve your truck’s fuel efficiency, saving you money at the pump.
- Reduced Emissions: A properly functioning OBD2 system ensures that your vehicle meets emissions standards, helping to protect the environment.
- Enhanced Resale Value: A well-maintained vehicle with a clean OBD2 history is more attractive to potential buyers, increasing its resale value.
According to a report by the American Automobile Association (AAA), proactive vehicle maintenance, including monitoring the OBD2 system, can significantly reduce the likelihood of breakdowns and costly repairs.
2. Essential OBD2 Tools for Your 2006 Ford F250
What are the must-have OBD2 tools for your 2006 Ford F250?
Having the right OBD2 tools is essential for diagnosing and maintaining your 2006 Ford F250. These tools allow you to access the data stored in your truck’s computer, read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), and monitor various engine parameters.
2.1. OBD2 Scanners: Basic vs. Advanced
What are the differences between basic and advanced OBD2 scanners, and which is right for you?
OBD2 scanners come in a range of options, from basic code readers to advanced diagnostic tools. Understanding the differences between them is crucial for selecting the right tool for your needs.
- Basic OBD2 Scanners: These scanners are designed to read and clear DTCs. They typically display the code number and a brief description of the problem. Basic scanners are inexpensive and easy to use, making them suitable for DIYers and vehicle owners who want to quickly identify and clear minor issues.
- Advanced OBD2 Scanners: These scanners offer a wider range of features, including the ability to display live sensor data, perform advanced diagnostics, and even program certain vehicle functions. Advanced scanners are typically used by professional technicians and experienced DIYers who need more in-depth diagnostic capabilities.
| Feature | Basic OBD2 Scanner | Advanced OBD2 Scanner |
|---|---|---|
| Code Reading | Reads and clears DTCs | Reads and clears DTCs, including manufacturer-specific codes |
| Live Data | May display limited live data | Displays comprehensive live sensor data, including graphs and charts |
| Advanced Diagnostics | Limited diagnostic capabilities | Performs advanced diagnostics such as bidirectional control, component testing, and system resets |
| Programming | No programming capabilities | May offer limited programming capabilities, such as key programming or ECU reflashing |
| Price | Typically under 100 USD | Typically 200 USD or more |
| User Level | DIYers, vehicle owners | Professional technicians, experienced DIYers |
2.2. Recommended OBD2 Scanners for 2006 Ford F250
Which OBD2 scanners are highly recommended for use with your 2006 Ford F250?
Several OBD2 scanners are highly recommended for use with the 2006 Ford F250, offering a balance of features, performance, and value. Here are a few options to consider:
- FORScan with OBDLink MX+ or BAFX Adapter: FORScan is a powerful software program specifically designed for Ford vehicles. When paired with a compatible OBD2 adapter like the OBDLink MX+ or BAFX adapter, it provides access to advanced diagnostic features, including the ability to read manufacturer-specific codes, perform bidirectional control, and program certain vehicle functions.
- ScanGauge II: The ScanGauge II is a compact and versatile OBD2 scanner that displays live data, reads and clears DTCs, and monitors vehicle performance. It’s easy to install and use, making it a popular choice for monitoring your F250’s vital signs while driving.
- Torque Pro (with suitable adapter): Torque Pro is an Android app that turns your smartphone or tablet into a powerful OBD2 scanner. When paired with a compatible Bluetooth OBD2 adapter, it can display live data, read and clear DTCs, and even record data logs for later analysis.
2.3. Software Options: FORScan and More
What software options are available for enhancing your OBD2 diagnostics on your F250?
In addition to OBD2 scanners, several software options can enhance your diagnostic capabilities and provide more in-depth insights into your 2006 Ford F250’s performance.
- FORScan: FORScan is a highly recommended software program specifically designed for Ford vehicles. It offers advanced diagnostic features, including the ability to read manufacturer-specific codes, perform bidirectional control, and program certain vehicle functions. FORScan is available for Windows PCs and as a “lite” version for mobile devices.
- Torque Pro: Torque Pro is a popular Android app that turns your smartphone or tablet into a powerful OBD2 scanner. It can display live data, read and clear DTCs, and even record data logs for later analysis.
- OBDwiz: OBDwiz is a Windows-based software program that provides comprehensive OBD2 diagnostic capabilities. It can display live data, read and clear DTCs, perform advanced diagnostics, and generate reports for analysis.
According to a study by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), using specialized software like FORScan can significantly improve the accuracy and efficiency of vehicle diagnostics.
3. Reading and Interpreting 2006 Ford F250 OBD2 Codes
How do you read and understand the OBD2 codes from your 2006 Ford F250?
Once you have an OBD2 scanner, the next step is to learn how to read and interpret the diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) that your 2006 Ford F250 may generate. Understanding these codes is crucial for accurately diagnosing and repairing problems with your vehicle.
3.1. Connecting Your Scanner and Retrieving Codes
What is the process for connecting your scanner to your F250 and retrieving the stored DTCs?
Connecting your OBD2 scanner to your 2006 Ford F250 and retrieving the stored DTCs is a straightforward process:
- Locate the DLC: Find the Data Link Connector (DLC) on your F250. It’s typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Connect the Scanner: Plug your OBD2 scanner into the DLC.
- Turn on the Ignition: Turn the ignition key to the “on” position, but do not start the engine.
- Power on the Scanner: Turn on your OBD2 scanner and follow the on-screen prompts to establish a connection with your vehicle’s computer.
- Retrieve Codes: Select the option to “Read Codes” or “Retrieve DTCs” from the scanner’s menu. The scanner will then display any stored DTCs.
3.2. Understanding the Structure of OBD2 Codes
What does each part of an OBD2 code signify?
OBD2 codes follow a standardized format, making it easier to understand their meaning. Each code consists of five characters:
-
First Character: Indicates the system being affected:
- P: Powertrain (engine, transmission)
- B: Body (interior, exterior)
- C: Chassis (brakes, suspension)
- U: Network (communication systems)
-
Second Character: Indicates whether the code is generic or manufacturer-specific:
- 0: Generic (SAE) code
- 1: Manufacturer-specific code
-
Third Character: Indicates the specific subsystem affected:
- 0: Fuel and air metering
- 1: Fuel and air metering (injector circuit)
- 2: Fuel and air metering (injector circuit)
- 3: Ignition system or misfire
- 4: Auxiliary emission controls
- 5: Vehicle speed control, idle control system
- 6: Computer output circuit
- 7: Transmission
- 8: Transmission
-
Fourth and Fifth Characters: Specify the exact fault within the subsystem.
For example, the code P0300 indicates a generic (0) powertrain (P) code related to misfires (3), with the last two digits (00) indicating a random or multiple cylinder misfire.
3.3. Common OBD2 Codes for 2006 Ford F250 and Their Meanings
What are some common OBD2 codes you might encounter on your 2006 Ford F250, and what do they mean?
Here are some common OBD2 codes that you might encounter on your 2006 Ford F250, along with their possible meanings and potential causes:
| Code | Description | Possible Causes |
|---|---|---|
| P0171 | System Too Lean (Bank 1) | Vacuum leak, faulty oxygen sensor, dirty fuel injectors, low fuel pressure |
| P0174 | System Too Lean (Bank 2) | Vacuum leak, faulty oxygen sensor, dirty fuel injectors, low fuel pressure |
| P0300 | Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected | Faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, fuel injectors, vacuum leak, low compression |
| P0401 | Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Flow Insufficient Detected | Faulty EGR valve, clogged EGR passages, faulty differential pressure feedback (DPFE) sensor |
| P0420 | Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1) | Faulty catalytic converter, exhaust leak, faulty oxygen sensors |
| P0470 | Exhaust Pressure Sensor Malfunction | Faulty exhaust pressure sensor, wiring issue, PCM failure |
| P0603 | Internal Control Module Keep Alive Memory (KAM) Error | PCM failure, low battery voltage, wiring issue |
| P2263 | Turbocharger Boost System Performance | Leaks in the boost system, faulty turbocharger, faulty boost sensor, malfunctioning turbocharger control solenoid or actuator, incorrect air filter |
It’s important to note that these are just potential causes, and further diagnosis may be required to pinpoint the exact problem. Resources like the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) provide extensive information on vehicle safety and common issues.
4. Diagnosing and Repairing Common 2006 Ford F250 Issues Using OBD2
How can you use the OBD2 system to diagnose and fix common problems in your 2006 Ford F250?
The OBD2 system is a valuable tool for diagnosing and repairing a wide range of issues in your 2006 Ford F250. By understanding how to interpret the DTCs and use live data, you can effectively troubleshoot problems and get your truck back on the road.
4.1. Step-by-Step Diagnostic Process
What is the recommended process for diagnosing issues using your OBD2 scanner?
A systematic approach to diagnosing issues using your OBD2 scanner will help you identify the root cause of the problem efficiently:
- Retrieve DTCs: Connect your OBD2 scanner to the DLC and retrieve any stored DTCs.
- Record the Codes: Write down all the DTCs, including the code number and description.
- Research the Codes: Use online resources or a repair manual to research the possible causes and symptoms associated with each code.
- Inspect the Vehicle: Visually inspect the vehicle for any obvious signs of damage, such as loose wires, leaking fluids, or broken components.
- Gather more information: Talk to the customer/driver of the car to understand the issue(s) they are experiencing with the car and any information that could help diagnose the root cause.
- Verify the Problem: If possible, try to verify the problem by replicating the conditions under which the DTC was set.
- Test Components: Use your OBD2 scanner to monitor live data from relevant sensors and components. Compare the readings to the expected values to identify any discrepancies.
- Perform Further Testing: If necessary, perform additional tests, such as a compression test, fuel pressure test, or vacuum leak test, to further narrow down the problem.
- Repair the Problem: Once you have identified the root cause of the problem, perform the necessary repairs.
- Clear the Codes: After completing the repairs, clear the DTCs and test drive the vehicle to ensure that the problem has been resolved.
4.2. Case Studies: Using OBD2 to Solve Real-World Problems
Can you provide examples of how OBD2 has been used to resolve specific issues in a 2006 Ford F250?
Here are a couple of case studies demonstrating how the OBD2 system can be used to solve real-world problems in a 2006 Ford F250:
Case Study 1: Diagnosing a Misfire
A 2006 Ford F250 owner reported a noticeable misfire and a flashing check engine light. Using an OBD2 scanner, the technician retrieved the code P0300 (Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected).
- Diagnosis: The technician used the scanner to monitor live data from the engine sensors. The data revealed that the misfire was occurring primarily on cylinder number 5. Further testing revealed a faulty ignition coil on that cylinder.
- Solution: The technician replaced the faulty ignition coil, cleared the DTC, and test drove the vehicle. The misfire was gone, and the check engine light did not return.
Case Study 2: Resolving a Lean Condition
A 2006 Ford F250 owner complained of poor fuel economy and a rough idle. An OBD2 scan revealed the codes P0171 (System Too Lean, Bank 1) and P0174 (System Too Lean, Bank 2).
- Diagnosis: The technician suspected a vacuum leak. Using a smoke machine, they introduced smoke into the intake manifold and quickly located a leak in a vacuum hose.
- Solution: The technician replaced the leaking vacuum hose, cleared the DTCs, and test drove the vehicle. The fuel economy improved, and the idle smoothed out.
These case studies illustrate how the OBD2 system can be a powerful tool for diagnosing and repairing a wide range of issues in your 2006 Ford F250.
4.3. When to Seek Professional Help
When should you consult a professional mechanic instead of attempting to fix the problem yourself?
While the OBD2 system can empower you to diagnose and repair many issues with your 2006 Ford F250, there are times when it’s best to seek professional help. Consider consulting a qualified mechanic if:
- You are not comfortable working on your vehicle.
- You are unable to accurately diagnose the problem using the OBD2 system.
- The repair requires specialized tools or knowledge.
- The problem involves complex systems, such as the transmission or engine.
- You are unsure how to perform the necessary repairs safely and effectively.
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, automotive service technicians and mechanics require extensive training and expertise to diagnose and repair modern vehicles effectively.
5. Maintaining Your 2006 Ford F250’s OBD2 System
How can you keep your 2006 Ford F250’s OBD2 system in optimal condition?
Proper maintenance of your 2006 Ford F250’s OBD2 system is essential for ensuring accurate diagnostics and preventing potential problems.
5.1. Regular OBD2 Scans for Preventative Maintenance
How often should you scan your F250’s OBD2 system, even if there are no apparent issues?
Regular OBD2 scans can help you catch potential problems early on, before they escalate into major repairs. It’s recommended to scan your F250’s OBD2 system at least every six months, even if there are no apparent issues. This proactive approach can help you identify and address minor problems, such as a loose gas cap or a malfunctioning sensor, before they cause more serious damage.
5.2. Keeping Your Truck in Good Condition
What general maintenance practices contribute to a healthy OBD2 system?
Several general maintenance practices can contribute to a healthy OBD2 system in your 2006 Ford F250:
- Regular Oil Changes: Changing your engine oil according to the manufacturer’s recommendations helps to keep the engine running smoothly and prevent excessive wear.
- Properly Inflated Tires: Maintaining proper tire pressure improves fuel efficiency and reduces stress on the vehicle’s suspension and drivetrain.
- Clean Air Filter: A clean air filter ensures that the engine receives adequate air, improving performance and fuel economy.
- Well-Maintained Battery: A healthy battery is essential for reliable starting and proper operation of the vehicle’s electrical systems.
- Timely Spark Plug Replacement: Replacing spark plugs at the recommended intervals ensures proper ignition and prevents misfires.
5.3. Addressing Issues Promptly
Why is it crucial to address OBD2-detected issues as soon as possible?
Addressing issues detected by the OBD2 system promptly is crucial for preventing further damage and ensuring the longevity of your 2006 Ford F250. Ignoring a DTC or delaying necessary repairs can lead to more serious problems, such as engine damage, reduced fuel economy, and increased emissions. According to a study by the Car Care Council, neglecting routine maintenance can result in significantly higher repair costs over time.
6. Advanced OBD2 Diagnostics for the 2006 Ford F250
What advanced diagnostic techniques can you use with your F250’s OBD2 system?
For experienced DIYers and professional technicians, the OBD2 system offers advanced diagnostic capabilities that can help pinpoint even the most elusive problems.
6.1. Live Data Streaming and Analysis
How can you use live data to diagnose intermittent or performance-related issues?
Live data streaming allows you to monitor real-time sensor readings and engine parameters while the vehicle is running. This can be invaluable for diagnosing intermittent issues or performance-related problems.
- Identifying Sensor Problems: By monitoring live data, you can identify sensors that are providing inaccurate readings or failing intermittently.
- Analyzing Engine Performance: Live data can help you analyze engine performance under different conditions, such as idle, acceleration, and deceleration. This can reveal problems with fuel delivery, ignition timing, or other engine parameters.
- Troubleshooting Intermittent Issues: Live data can be used to capture data when an intermittent problem occurs, providing valuable clues for diagnosis.
6.2. Bidirectional Control
What is bidirectional control, and how can it aid in diagnostics?
Bidirectional control allows you to send commands to the vehicle’s computer and activate specific components or systems. This can be useful for testing components, verifying repairs, and performing certain programming functions.
- Testing Components: Bidirectional control can be used to activate components such as fuel injectors, solenoids, and relays to verify that they are functioning properly.
- Verifying Repairs: After performing a repair, bidirectional control can be used to verify that the problem has been resolved.
- Performing Programming Functions: Some OBD2 scanners offer bidirectional control capabilities that allow you to perform certain programming functions, such as key programming or ECU reflashing.
6.3. Manufacturer-Specific Codes and Data
How do manufacturer-specific codes and data enhance diagnostic accuracy for your F250?
Manufacturer-specific codes and data provide more detailed information about problems that are unique to Ford vehicles. These codes and data can help you pinpoint the exact cause of a problem and avoid unnecessary repairs. FORScan is an excellent software tool for accessing manufacturer-specific codes and data on your 2006 Ford F250.
7. Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using OBD2 on Your 2006 Ford F250
What are some common pitfalls to avoid when working with the OBD2 system on your 2006 Ford F250?
To ensure accurate diagnoses and avoid potential problems, it’s important to be aware of common mistakes that people make when using the OBD2 system on their 2006 Ford F250.
7.1. Misinterpreting Codes
Why is it crucial to research codes thoroughly before taking action?
One of the most common mistakes is misinterpreting OBD2 codes. It’s essential to research the codes thoroughly before taking any action to ensure that you understand the possible causes and symptoms associated with each code. Relying solely on the code description can lead to misdiagnosis and unnecessary repairs.
7.2. Neglecting Basic Troubleshooting
Why should you always perform a visual inspection and basic tests before relying solely on the OBD2 system?
Don’t rely solely on the OBD2 system without performing basic troubleshooting steps. Always start with a visual inspection of the vehicle, checking for any obvious signs of damage, such as loose wires, leaking fluids, or broken components. Perform basic tests, such as checking the battery voltage and inspecting the spark plugs, before diving into more advanced diagnostics.
7.3. Clearing Codes Without Repairing the Problem
Why is it important to address the underlying issue before clearing the DTCs?
Clearing codes without repairing the underlying problem is a temporary fix that will only lead to the problem returning. Address the root cause of the issue before clearing the DTCs. After completing the repairs, test drive the vehicle to ensure that the problem has been resolved and that the check engine light does not return.
8. The Future of OBD2 and Diagnostics
How is OBD2 technology evolving, and what can we expect in the future?
The OBD2 system is constantly evolving to keep pace with advancements in automotive technology.
8.1. OBD3 and Enhanced Monitoring
What are the potential benefits of future OBD systems like OBD3?
OBD3 is a proposed future standard that would enhance the monitoring capabilities of the OBD system and provide real-time emissions data to regulatory agencies. This could lead to more effective emissions control and improved air quality. According to the EPA, future OBD systems will likely incorporate more sophisticated diagnostic algorithms and communication protocols.
8.2. Integration with Mobile Devices and Cloud Services
How will mobile devices and cloud services play a larger role in vehicle diagnostics?
Mobile devices and cloud services are already playing a larger role in vehicle diagnostics, and this trend is expected to continue. Mobile apps can provide access to diagnostic data, repair information, and even remote diagnostic services. Cloud-based platforms can store vehicle data, track maintenance history, and provide predictive maintenance alerts.
8.3. The Role of AI and Machine Learning
How might artificial intelligence and machine learning revolutionize vehicle diagnostics?
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning have the potential to revolutionize vehicle diagnostics. AI-powered diagnostic systems could analyze vast amounts of data from sensors and other sources to identify patterns and predict potential problems. Machine learning algorithms could be used to improve the accuracy and efficiency of diagnostic procedures.
9. Resources for 2006 Ford F250 OBD2 Information
Where can you find reliable information and resources about your F250’s OBD2 system?
Numerous resources are available to help you learn more about your 2006 Ford F250’s OBD2 system.
9.1. Online Forums and Communities
What are some valuable online communities for F250 owners and enthusiasts?
Online forums and communities can be a great source of information and support for F250 owners. These communities provide a platform for sharing experiences, asking questions, and getting advice from other enthusiasts. Some popular online forums for Ford F250 owners include Ford Truck Enthusiasts and PowerStroke.org.
9.2. Repair Manuals and Technical Documentation
Where can you find detailed repair manuals and technical documentation for your F250?
Repair manuals and technical documentation provide detailed information about your F250’s OBD2 system, including wiring diagrams, component locations, and diagnostic procedures. You can find repair manuals at auto parts stores, online retailers, and from the manufacturer.
9.3. Professional Diagnostic Services
When is it best to seek professional diagnostic services for your F250?
While the OBD2 system can empower you to diagnose and repair many issues with your 2006 Ford F250, there are times when it’s best to seek professional diagnostic services. If you are unable to accurately diagnose the problem using the OBD2 system, or if the repair requires specialized tools or knowledge, it’s best to consult a qualified mechanic. OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN offers professional diagnostic services to help you get your F250 back on the road.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About 2006 Ford F250 OBD2
Here are some frequently asked questions about the 2006 Ford F250 OBD2 system:
Q1: What is an OBD2 scanner?
An OBD2 scanner is a device used to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) from a vehicle’s computer, helping diagnose potential issues.
Q2: How do I locate the OBD2 port in my 2006 Ford F250?
The OBD2 port is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
Q3: What does the “check engine light” indicate?
The check engine light indicates that the OBD2 system has detected a problem and stored a diagnostic trouble code (DTC).
Q4: Can I clear the check engine light myself?
Yes, you can clear the check engine light using an OBD2 scanner, but it’s important to address the underlying issue first.
Q5: What is the difference between generic and manufacturer-specific OBD2 codes?
Generic codes are standardized across all vehicles, while manufacturer-specific codes are unique to a particular make and model.
Q6: What is FORScan, and why is it recommended for Ford vehicles?
FORScan is a software program specifically designed for Ford vehicles, offering advanced diagnostic features and access to manufacturer-specific codes.
Q7: How often should I scan my F250’s OBD2 system?
It’s recommended to scan your F250’s OBD2 system at least every six months, even if there are no apparent issues.
Q8: What are some common OBD2 codes for the 2006 Ford F250?
Some common codes include P0171 (System Too Lean, Bank 1), P0300 (Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected), and P0401 (EGR Flow Insufficient Detected).
Q9: Can I use my smartphone as an OBD2 scanner?
Yes, you can use a smartphone or tablet as an OBD2 scanner by pairing it with a compatible Bluetooth OBD2 adapter and using a suitable app like Torque Pro.
Q10: When should I seek professional help for OBD2-related issues?
Seek professional help if you are not comfortable working on your vehicle, are unable to accurately diagnose the problem, or if the repair requires specialized tools or knowledge.
Understanding and utilizing the OBD2 system in your 2006 Ford F250 can greatly enhance your vehicle’s performance and longevity. By following this comprehensive guide, you are well-equipped to handle most diagnostic needs.
For expert advice and assistance with your 2006 Ford F250 OBD2 system, contact OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN. Our team of experienced technicians is here to help you diagnose and repair any issues with your vehicle. Visit us at 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States, call us at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN. Contact us on Whatsapp for immediate assistance. We are committed to ensuring your vehicle runs smoothly and efficiently.