The 2006 Pontiac Grand Prix Obd2 Port Fuse is essential for diagnostics; let’s locate it with the help of OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN and understand its function, potential issues, and troubleshooting. Understanding its location and how to address related problems is crucial for maintaining your vehicle’s performance and ensuring accurate diagnostic readings. By the end of this guide, you’ll be well-equipped to handle fuse-related issues affecting your OBD2 port, enhancing your vehicle maintenance toolkit and troubleshooting abilities.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the OBD2 Port and Its Importance
- 1.1. Why the OBD2 Port Fuse Matters
- 2. Locating the OBD2 Port Fuse in a 2006 Pontiac Grand Prix
- 2.1. Step-by-Step Guide to Finding the Fuse
- 2.2. Common Fuse Locations
- 3. Identifying a Blown Fuse
- 3.1. Visual Inspection
- 3.2. Using a Multimeter
- 4. Replacing a Blown Fuse
- 5. Common Causes of a Blown OBD2 Port Fuse
- 6. Troubleshooting a Non-Functional OBD2 Port
- 7. Advanced Diagnostic Tools and Techniques
- 8. Preventative Measures to Protect Your OBD2 Port
- 9. OBD2 Port and Aftermarket Devices
- 10. OBD2 Compliance and Regulations
- 11. Understanding OBD2 Codes
- 11.1. Common OBD2 Codes
- 12. How OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN Can Help
- 13. Conclusion
- 14. FAQ: 2006 Pontiac Grand Prix OBD2 Port Fuse
- 14.1. Where is the OBD2 port located in a 2006 Pontiac Grand Prix?
- 14.2. What does the OBD2 port fuse protect?
- 14.3. What is the amperage rating of the OBD2 port fuse in a 2006 Pontiac Grand Prix?
- 14.4. How do I check if the OBD2 port fuse is blown?
- 14.5. What are the common causes of a blown OBD2 port fuse?
- 14.6. Can I use a fuse with a higher amperage rating to replace a blown OBD2 port fuse?
- 14.7. What should I do if the new OBD2 port fuse blows immediately after replacement?
- 14.8. What tools do I need to replace the OBD2 port fuse?
- 14.9. How can I prevent future issues with my OBD2 port?
- 14.10. What should I do if the OBD2 port is not working, even after replacing the fuse?
- 15. Key Terminologies
1. Understanding the OBD2 Port and Its Importance
The On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD2) port is a standardized interface used to access a vehicle’s computer system for diagnostics and monitoring. This port, typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side, allows mechanics and car owners to connect diagnostic tools, such as OBD2 scanners, to read trouble codes, monitor engine performance, and perform various tests. The OBD2 system was mandated in the United States for all cars manufactured after 1996 to standardize emissions testing and provide better diagnostic capabilities. Its implementation has transformed automotive repair, making it more efficient and accurate.
The OBD2 port serves several critical functions:
-
Retrieving Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): When a problem arises in your vehicle, the engine control unit (ECU) stores a DTC. The OBD2 scanner reads these codes, providing a starting point for diagnosing the issue.
-
Monitoring Real-Time Data: The OBD2 port allows you to monitor various parameters in real-time, such as engine speed (RPM), vehicle speed, coolant temperature, and oxygen sensor readings. This data helps identify anomalies and potential problems.
-
Performing System Tests: Some advanced OBD2 scanners can perform system tests, such as an oxygen sensor test or an evaporative emissions system (EVAP) test, to verify the functionality of specific components.
-
Clearing Trouble Codes: After repairing a problem, you can use the OBD2 scanner to clear the stored DTCs, turning off the check engine light.
1.1. Why the OBD2 Port Fuse Matters
The OBD2 port fuse protects the diagnostic port from electrical surges and short circuits. Like any electrical component, the OBD2 port is vulnerable to damage from voltage spikes or faulty wiring. A blown fuse can render the OBD2 port non-functional, preventing you from using diagnostic tools to read codes or monitor your vehicle’s performance.
Several reasons highlight the importance of the OBD2 port fuse:
-
Diagnostic Accessibility: A working OBD2 port is essential for diagnosing engine problems, emissions issues, and other mechanical faults. Without it, identifying the cause of a check engine light or performance issue becomes significantly more difficult.
-
Emissions Testing: In many states, a functioning OBD2 port is required to pass emissions testing. If the port is not working due to a blown fuse, your vehicle will fail the test.
-
Safety: Some diagnostic codes can indicate safety-related issues, such as problems with the anti-lock braking system (ABS) or airbags. Early detection through the OBD2 port can prevent accidents and ensure your vehicle is safe to drive.
-
Preventing Further Damage: Addressing issues early through OBD2 diagnostics can prevent minor problems from escalating into major repairs.
2. Locating the OBD2 Port Fuse in a 2006 Pontiac Grand Prix
To locate the OBD2 port fuse in your 2006 Pontiac Grand Prix, you will need to consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual. The manual provides detailed diagrams and descriptions of the fuse box locations and the specific fuses related to different systems. The OBD2 port fuse is usually located in one of two fuse boxes:
-
Instrument Panel Fuse Block: This fuse box is typically located inside the vehicle, often under the dashboard on the driver’s side. It contains fuses for various interior electrical components, including the OBD2 port, radio, and interior lights.
-
Underhood Fuse Block: This fuse box is located in the engine compartment, usually near the battery. It houses fuses for critical engine components, such as the fuel pump, ignition system, and cooling fans.
2.1. Step-by-Step Guide to Finding the Fuse
-
Consult the Owner’s Manual:
- The owner’s manual is your primary resource for identifying the exact location of the fuse boxes and the OBD2 port fuse. Look for a section titled “Fuses” or “Electrical System.”
-
Locate the Instrument Panel Fuse Block:
- This fuse box is commonly found under the dashboard on the driver’s side. You may need to remove a small panel or access door to reveal the fuse box.
-
Inspect the Fuse Diagram:
- Once you’ve located the fuse box, examine the diagram printed on the inside of the cover or in the owner’s manual. The diagram labels each fuse and its corresponding system.
- Look for a fuse labeled “OBD,” “DLC” (Data Link Connector), or “Diagnostic Port.” The amperage rating of the fuse (e.g., 10A, 15A) will also be indicated.
-
If Not in the Instrument Panel Fuse Block, Check the Underhood Fuse Block:
- If you cannot find the OBD2 port fuse in the instrument panel fuse block, check the underhood fuse block. This fuse box is located in the engine compartment, typically near the battery.
- Refer to the fuse diagram to identify any fuses related to the diagnostic system.
-
Use a Fuse Puller:
- Once you’ve identified the correct fuse, use a fuse puller (usually included in the fuse box) to gently remove it. If you don’t have a fuse puller, you can use needle-nose pliers, but be careful not to damage the fuse or surrounding components.
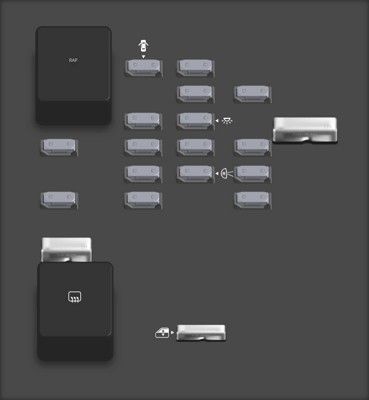 Instrument Panel Fuse Block Diagram
Instrument Panel Fuse Block Diagram
2.2. Common Fuse Locations
While the exact location can vary, the OBD2 port fuse in a 2006 Pontiac Grand Prix is often found in the instrument panel fuse block. It may be labeled as “OBD,” “DLC,” or “Diagnostic Port.” The amperage rating is typically between 10A and 15A. Always verify the location and rating with your owner’s manual to ensure accuracy.
3. Identifying a Blown Fuse
Once you’ve located the OBD2 port fuse, the next step is to determine if it’s blown. A blown fuse is easy to identify through a visual inspection.
3.1. Visual Inspection
-
Remove the Fuse: Use a fuse puller or needle-nose pliers to carefully remove the fuse from the fuse box.
-
Examine the Fuse: Hold the fuse up to the light and look for a break in the metal filament inside the fuse. If the filament is broken or the fuse appears black or charred, it is blown and needs to be replaced.
-
Check the Fuse Rating: Ensure that the replacement fuse has the same amperage rating as the original. Using a fuse with a higher rating can damage the electrical system.
3.2. Using a Multimeter
A multimeter provides a more precise method for checking a fuse’s condition.
-
Set Up the Multimeter: Set the multimeter to the continuity setting (indicated by a sound wave symbol or an arrow pointing to a diode symbol).
-
Test the Fuse: Touch one probe of the multimeter to each of the metal contacts on the fuse. If the multimeter beeps or displays a reading close to zero ohms, the fuse is intact. If there is no beep or the reading is very high (indicating an open circuit), the fuse is blown.
4. Replacing a Blown Fuse
Replacing a blown fuse is a straightforward process. Follow these steps to ensure a successful replacement:
-
Purchase a Replacement Fuse: Buy a new fuse with the same amperage rating as the blown fuse. You can find replacement fuses at most auto parts stores.
-
Turn Off the Ignition: Before replacing the fuse, turn off the vehicle’s ignition to prevent electrical surges.
-
Insert the New Fuse: Use the fuse puller or needle-nose pliers to carefully insert the new fuse into the fuse slot. Ensure it is fully seated and makes good contact.
-
Test the OBD2 Port: After replacing the fuse, test the OBD2 port by plugging in a diagnostic scanner. If the scanner powers on and can read data, the fuse replacement was successful.
-
If the Fuse Blows Again: If the new fuse blows immediately or shortly after replacement, there may be an underlying electrical problem, such as a short circuit. In this case, it is best to consult a qualified mechanic to diagnose and repair the issue.
5. Common Causes of a Blown OBD2 Port Fuse
Understanding the common causes of a blown OBD2 port fuse can help you prevent future issues. Here are some typical reasons why this fuse might blow:
-
Short Circuit in the OBD2 Port: A short circuit in the OBD2 port or its wiring can cause the fuse to blow. This can be due to damaged wires, corrosion, or loose connections.
-
Faulty OBD2 Scanner: A malfunctioning or poorly designed OBD2 scanner can draw excessive current, causing the fuse to blow. Always use reputable scanners and ensure they are compatible with your vehicle.
-
Wiring Issues: Problems with the vehicle’s wiring harness, such as chafed or damaged wires, can lead to short circuits that affect the OBD2 port.
-
Overload: Connecting multiple devices to the OBD2 port simultaneously or using devices that draw too much power can overload the circuit and blow the fuse.
-
Moisture or Corrosion: Exposure to moisture or corrosion can damage the fuse box and its components, leading to fuse failures.
6. Troubleshooting a Non-Functional OBD2 Port
If you’ve checked the fuse and it’s not blown, but the OBD2 port still isn’t working, there may be other underlying issues. Here are some troubleshooting steps to follow:
-
Check the OBD2 Port Connections:
- Inspect the OBD2 port for any signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections. Clean the contacts with a contact cleaner if necessary.
- Ensure that the OBD2 port is securely mounted and that the wiring harness is properly connected.
-
Inspect the Wiring Harness:
- Examine the wiring harness connected to the OBD2 port for any signs of damage, such as cuts, chafing, or exposed wires.
- Repair or replace any damaged wiring to ensure proper electrical continuity.
-
Test the OBD2 Port Voltage:
- Use a multimeter to check the voltage at the OBD2 port. You should have approximately 12 volts between pin 16 (power) and pin 4 or 5 (ground).
- If there is no voltage, there may be a problem with the wiring or the power supply to the OBD2 port.
-
Check the Ground Connection:
- Ensure that the OBD2 port has a good ground connection. A poor ground can cause intermittent or complete failure of the port.
- Clean and tighten the ground connections to ensure proper grounding.
-
Consult a Professional:
- If you’ve checked the fuse, connections, wiring, and voltage, and the OBD2 port still isn’t working, it’s time to consult a qualified mechanic.
- A professional can diagnose and repair more complex electrical issues affecting the OBD2 port.
7. Advanced Diagnostic Tools and Techniques
For more advanced troubleshooting and diagnostics, consider using the following tools and techniques:
-
OBD2 Scanners with Advanced Features:
- Some OBD2 scanners offer advanced features such as live data streaming, bidirectional control, and system tests. These features can help you pinpoint specific problems and verify the functionality of various components.
- Examples include scanners from Autel, Snap-on, and Launch.
-
Wiring Diagrams:
- A wiring diagram for your 2006 Pontiac Grand Prix can provide valuable information about the OBD2 port’s wiring and connections to other systems.
- Wiring diagrams can be found in repair manuals or online databases.
-
Professional Diagnostic Software:
- Professional diagnostic software, such as GM Tech2 or specialized programs from aftermarket suppliers, can provide in-depth diagnostic capabilities and access to vehicle-specific data.
-
Oscilloscope:
- An oscilloscope can be used to analyze electrical signals in the OBD2 port and wiring harness, helping you identify intermittent problems or signal distortions.
8. Preventative Measures to Protect Your OBD2 Port
Taking preventative measures can help protect your OBD2 port and prevent future fuse failures or other issues:
-
Use High-Quality OBD2 Scanners:
- Invest in a high-quality OBD2 scanner from a reputable brand to ensure compatibility and prevent excessive current draw.
-
Avoid Overloading the Port:
- Do not connect multiple devices to the OBD2 port simultaneously, as this can overload the circuit and blow the fuse.
-
Protect the Port from Moisture:
- Keep the OBD2 port clean and dry to prevent corrosion and damage to the electrical contacts. Use a protective cover if necessary.
-
Regular Inspections:
- Periodically inspect the OBD2 port and its wiring for any signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections.
-
Professional Maintenance:
- Have your vehicle serviced by a qualified mechanic who can check the OBD2 port and electrical system as part of routine maintenance.
9. OBD2 Port and Aftermarket Devices
Many aftermarket devices, such as performance tuners, GPS trackers, and insurance monitoring devices, connect to the OBD2 port. While these devices can offer valuable features, they can also cause problems if not properly designed or installed.
-
Compatibility Issues: Ensure that any aftermarket device you connect to the OBD2 port is compatible with your vehicle. Check the manufacturer’s specifications and consult with a professional if necessary.
-
Power Consumption: Some aftermarket devices can draw excessive power from the OBD2 port, leading to fuse failures or battery drain. Choose devices with low power consumption or use an external power source.
-
Installation Quality: Poorly installed aftermarket devices can damage the OBD2 port or its wiring. Have the device installed by a qualified technician to ensure proper installation and prevent electrical problems.
-
Software Conflicts: Some aftermarket devices can interfere with the vehicle’s computer system, causing software conflicts or performance issues. Monitor your vehicle’s performance after installing an aftermarket device and remove it if you experience any problems.
10. OBD2 Compliance and Regulations
The OBD2 system is mandated by government regulations to ensure emissions compliance and provide diagnostic information for vehicle repairs. Understanding these regulations can help you maintain your vehicle and avoid issues with emissions testing.
-
EPA Regulations: The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) requires all cars manufactured after 1996 to be OBD2 compliant. This includes having a standardized OBD2 port and the ability to monitor emissions-related components.
-
State Emissions Testing: Many states require vehicles to pass emissions testing as part of their registration process. A functioning OBD2 port is essential for this testing, as it allows inspectors to access the vehicle’s diagnostic data.
-
Tampering Laws: It is illegal to tamper with or disable the OBD2 system or any emissions-related components. Doing so can result in fines and other penalties.
-
Right to Repair: The “Right to Repair” movement advocates for consumers’ and independent repair shops’ access to vehicle diagnostic and repair information. This ensures that vehicle owners have the freedom to choose where they have their cars serviced.
11. Understanding OBD2 Codes
OBD2 codes are standardized alphanumeric codes that provide information about specific problems detected by the vehicle’s computer system. Understanding these codes can help you diagnose and repair your vehicle more effectively.
-
Generic Codes: These codes are standardized across all makes and models and relate to common issues such as engine misfires, oxygen sensor failures, and evaporative emissions problems.
-
Manufacturer-Specific Codes: These codes are specific to a particular make or model and provide more detailed information about the problem.
-
Reading OBD2 Codes: Use an OBD2 scanner to read the stored trouble codes. The scanner will display the code along with a brief description of the problem.
-
Interpreting OBD2 Codes: Refer to a repair manual or online database to find a detailed explanation of the code and possible causes.
-
Clearing OBD2 Codes: After repairing the problem, use the OBD2 scanner to clear the stored codes and turn off the check engine light.
11.1. Common OBD2 Codes
Here are some common OBD2 codes and their possible causes:
| Code | Description | Possible Causes |
|---|---|---|
| P0171 | System Too Lean (Bank 1) | Vacuum leak, faulty oxygen sensor, MAF sensor problem, fuel delivery issue |
| P0300 | Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected | Faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, fuel injectors, vacuum leak, low compression |
| P0420 | Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold | Faulty catalytic converter, oxygen sensor problem, exhaust leak |
| P0442 | Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (Small Leak) | Loose or damaged gas cap, leaking EVAP hose, faulty purge valve |
| P0507 | Idle Air Control System RPM Higher Than Expected | Vacuum leak, faulty idle air control valve, throttle body problem |
12. How OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN Can Help
At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we understand the complexities of vehicle diagnostics and maintenance. Our mission is to provide you with the tools and information you need to keep your vehicle running smoothly. Here’s how we can assist you:
-
Expert Advice:
- Our team of experienced mechanics and automotive professionals is available to answer your questions and provide expert advice on OBD2 diagnostics, fuse-related issues, and vehicle maintenance.
-
Detailed Guides and Tutorials:
- We offer a comprehensive library of guides and tutorials that cover a wide range of topics, including OBD2 code interpretation, fuse box diagrams, and troubleshooting techniques.
-
Product Recommendations:
- We can recommend high-quality OBD2 scanners, diagnostic tools, and replacement parts that are compatible with your 2006 Pontiac Grand Prix.
-
Service Referrals:
- If you need professional assistance with your vehicle, we can refer you to trusted mechanics and repair shops in your area.
We are dedicated to helping you navigate the world of OBD2 diagnostics and vehicle maintenance. Whether you’re a seasoned mechanic or a car owner looking to learn more, OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN is your trusted resource.
13. Conclusion
Finding and maintaining the 2006 Pontiac Grand Prix OBD2 port fuse is essential for accurate vehicle diagnostics and maintenance. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can locate the fuse, identify common causes of failure, and troubleshoot related issues effectively. A functional OBD2 port ensures access to critical vehicle data, enabling timely repairs and preventing more significant problems. Remember to consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual, use the appropriate tools, and take preventative measures to protect your OBD2 system. With the right knowledge and resources, you can keep your vehicle running smoothly and efficiently.
Do you need further assistance with your 2006 Pontiac Grand Prix OBD2 port or any other vehicle diagnostics? Contact us at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN. Our expert team is here to provide the support and solutions you need. Call us at +1 (641) 206-8880, visit our website at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, or stop by our location at 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States. We’re here to help you keep your vehicle in top condition.
14. FAQ: 2006 Pontiac Grand Prix OBD2 Port Fuse
14.1. Where is the OBD2 port located in a 2006 Pontiac Grand Prix?
The OBD2 port in a 2006 Pontiac Grand Prix is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side. You may need to look closely, as it is often near the steering column or integrated into the lower dash panel.
14.2. What does the OBD2 port fuse protect?
The OBD2 port fuse protects the diagnostic port from electrical surges and short circuits. It ensures that the diagnostic port functions correctly and that diagnostic tools can safely communicate with the vehicle’s computer system.
14.3. What is the amperage rating of the OBD2 port fuse in a 2006 Pontiac Grand Prix?
The amperage rating of the OBD2 port fuse in a 2006 Pontiac Grand Prix is typically between 10A and 15A. Always verify the correct rating with your vehicle’s owner’s manual to ensure accurate replacement.
14.4. How do I check if the OBD2 port fuse is blown?
To check if the OBD2 port fuse is blown, remove the fuse from the fuse box and visually inspect it for a break in the metal filament. If the filament is broken or the fuse appears black or charred, it is blown and needs to be replaced. Alternatively, use a multimeter to test the fuse for continuity.
14.5. What are the common causes of a blown OBD2 port fuse?
Common causes of a blown OBD2 port fuse include short circuits in the OBD2 port or its wiring, faulty OBD2 scanners, wiring issues, overload, and moisture or corrosion.
14.6. Can I use a fuse with a higher amperage rating to replace a blown OBD2 port fuse?
No, you should never use a fuse with a higher amperage rating than the original. Using a fuse with a higher rating can damage the electrical system and potentially cause a fire. Always use a fuse with the same amperage rating as the original.
14.7. What should I do if the new OBD2 port fuse blows immediately after replacement?
If the new OBD2 port fuse blows immediately after replacement, there may be an underlying electrical problem, such as a short circuit. In this case, it is best to consult a qualified mechanic to diagnose and repair the issue.
14.8. What tools do I need to replace the OBD2 port fuse?
To replace the OBD2 port fuse, you will need a fuse puller (usually included in the fuse box) or needle-nose pliers, a replacement fuse with the correct amperage rating, and your vehicle’s owner’s manual for reference.
14.9. How can I prevent future issues with my OBD2 port?
To prevent future issues with your OBD2 port, use high-quality OBD2 scanners, avoid overloading the port, protect the port from moisture, perform regular inspections, and have your vehicle serviced by a qualified mechanic.
14.10. What should I do if the OBD2 port is not working, even after replacing the fuse?
If the OBD2 port is not working, even after replacing the fuse, check the OBD2 port connections, inspect the wiring harness, test the OBD2 port voltage, and check the ground connection. If the problem persists, consult a qualified mechanic for further diagnosis and repair.
15. Key Terminologies
- OBD2 Port: The standardized diagnostic port in vehicles that allows access to the vehicle’s computer system.
- Fuse: A safety device that protects electrical circuits from overcurrent.
- Amperage Rating: The maximum current a fuse can handle before blowing.
- Short Circuit: An abnormal connection between two points in an electrical circuit, resulting in excessive current flow.
- Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC): A code stored in the vehicle’s computer system that indicates a specific problem.
- Multimeter: An electronic instrument used to measure voltage, current, and resistance.
- Wiring Harness: A set of wires that transmit electrical power and signals throughout the vehicle.
- Ground Connection: A connection to the vehicle’s chassis that provides a return path for electrical current.
- EPA: The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, which regulates vehicle emissions.
- Aftermarket Device: A non-original equipment device installed in a vehicle, such as a performance tuner or GPS tracker.
By understanding these key terminologies, you can better navigate the complexities of vehicle diagnostics and maintenance.