Unlocking your 2006 Toyota Highlander’s hidden data is now easier than ever with the proper OBD2 PID list, empowering you to diagnose and optimize your vehicle’s performance; OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN is dedicated to providing you with the most accurate and comprehensive information, enabling you to troubleshoot issues, monitor key parameters, and ensure your Highlander runs smoothly for years to come by using a scan tool, diagnostic tool, trouble code. Explore insightful solutions for effective vehicle maintenance and data interpretation.
Contents
- Table of Contents
- 1. Understanding OBD2 PIDs for Your 2006 Toyota Highlander
- 1.1. What are OBD2 PIDs?
- 1.2. Why are PIDs Important for Your 2006 Toyota Highlander?
- 1.3. Standard vs. Manufacturer-Specific PIDs
- 2. Key OBD2 PIDs for the 2006 Toyota Highlander
- 2.1. Engine-Related PIDs
- 2.2. Fuel System PIDs
- 2.3. Transmission-Related PIDs
- 2.4. Other Important PIDs
- 3. Accessing OBD2 PIDs with an OBD2 Scanner
- 3.1. Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner
- 3.2. Connecting the OBD2 Scanner
- 3.3. Navigating the Scanner Software
- 3.4. Using the OBDLink App
- 4. Essential Steps Before You Begin
- 4.1. Verify Scanner Compatibility
- 4.2. Prepare Your Vehicle
- 4.3. Understand OBD2 Basics
- 4.4. Gather Necessary Tools
- 4.5. Set Up a Clean Workspace
- 5. Step-by-Step Guide to Reading PIDs
- 5.1. Connect the OBD2 Scanner
- 5.2. Power On and Navigate the Scanner
- 5.3. Select the PIDs to Monitor
- 5.4. Read and Record the Data
- 5.5. Using the OBDLink App (if applicable)
- 5.6. Save and Analyze Data
- 6. Interpreting OBD2 PID Data
- 6.1. Understanding Normal Ranges
- 6.2. Recognizing Abnormal Readings
- 6.3. Using PID Data for Diagnostics
- 6.4. Practical Examples
- 7. Advanced PID Monitoring and Diagnostics
- 7.1. Monitoring Manufacturer-Specific PIDs
- 7.2. Data Logging and Analysis
- 7.3. Comparative Analysis
- 7.4. Case Studies
- 7.5. Resources for Advanced Diagnostics
- 8. Troubleshooting Common Issues
- 8.1. Scanner Connection Issues
- 8.2. Inaccurate or Missing Data
- 8.3. Communication Errors
- 8.4. OBDLink App Issues (if applicable)
- 9. Benefits of Monitoring OBD2 PIDs
- 9.1. Improved Fuel Efficiency
Table of Contents
- Understanding OBD2 PIDs for Your 2006 Toyota Highlander
- Key OBD2 PIDs for the 2006 Toyota Highlander
- Accessing OBD2 PIDs with an OBD2 Scanner
- Essential Steps Before You Begin
- Step-by-Step Guide to Reading PIDs
- Interpreting OBD2 PID Data
- Advanced PID Monitoring and Diagnostics
- Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Benefits of Monitoring OBD2 PIDs
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About 2006 Toyota Highlander OBD2 PIDs
- Need Immediate Assistance?
1. Understanding OBD2 PIDs for Your 2006 Toyota Highlander
What are OBD2 PIDs and why are they important for your 2006 Toyota Highlander? OBD2 PIDs, or On-Board Diagnostics Parameter IDs, are codes used to request data from your vehicle’s computer; understanding these codes allows you to monitor various parameters, diagnose issues, and optimize your Highlander’s performance, giving you greater control over your vehicle’s health.
OBD2 PIDs serve as a standardized way to access real-time data from your vehicle’s engine control unit (ECU) and other modules; these parameters include engine temperature, RPM, vehicle speed, fuel trim, and numerous other sensor readings, giving you insights into how your vehicle is performing. According to a study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE) in 2022, utilizing OBD2 scanners and understanding PIDs can reduce diagnostic time by up to 40%, making it an invaluable tool for both professional technicians and DIY enthusiasts.
1.1. What are OBD2 PIDs?
OBD2 PIDs are essentially codes that your OBD2 scanner uses to request specific information from your vehicle’s computer; each PID corresponds to a particular sensor reading or calculated value within the vehicle’s system, allowing you to monitor a wide range of parameters.
1.2. Why are PIDs Important for Your 2006 Toyota Highlander?
Monitoring PIDs allows you to:
- Diagnose Problems: Identify the root cause of issues by observing abnormal readings.
- Monitor Performance: Keep track of critical parameters to ensure your Highlander is running efficiently.
- Preventative Maintenance: Detect potential problems before they become major repairs.
- Optimize Fuel Economy: Fine-tune your driving habits based on real-time data.
1.3. Standard vs. Manufacturer-Specific PIDs
It’s essential to understand the difference between standard and manufacturer-specific PIDs:
- Standard PIDs: These are defined by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) and are common across most OBD2-compliant vehicles, including the 2006 Toyota Highlander; standard PIDs cover basic parameters such as engine RPM, vehicle speed, and coolant temperature.
- Manufacturer-Specific PIDs: These are unique to each vehicle manufacturer and provide access to more detailed information; for your 2006 Toyota Highlander, Toyota-specific PIDs can offer insights into transmission temperature, individual sensor readings, and other proprietary data.
Understanding both types of PIDs ensures you can get a comprehensive view of your vehicle’s performance.
 OBD2 Scanner Connected to Car
OBD2 Scanner Connected to Car
Image: An OBD2 scanner connected to a car, illustrating the tool’s use in accessing vehicle data.
2. Key OBD2 PIDs for the 2006 Toyota Highlander
What are the most useful OBD2 PIDs to monitor for your 2006 Toyota Highlander? Monitoring key PIDs can provide valuable insights into your vehicle’s engine, transmission, and overall health; some of the most essential PIDs include engine coolant temperature (ECT), mass airflow (MAF), fuel trims, and oxygen sensor readings, helping you identify potential issues and maintain optimal performance.
Key OBD2 PIDs are critical for diagnosing and monitoring your 2006 Toyota Highlander effectively; according to a 2023 report by J.D. Power, vehicles that undergo regular OBD2 monitoring experience 20% fewer mechanical issues over their lifespan; let’s explore the must-know PIDs:
2.1. Engine-Related PIDs
These PIDs provide insights into the engine’s performance and efficiency:
- Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT):
- PID: 05
- Description: Monitors the engine’s operating temperature.
- Importance: Ensures the engine is not overheating, which can cause severe damage.
- Mass Airflow (MAF) Sensor:
- PID: 10
- Description: Measures the amount of air entering the engine.
- Importance: Critical for proper fuel-air mixture and combustion.
- Engine RPM:
- PID: 0C
- Description: Indicates the engine’s rotational speed.
- Importance: Helps diagnose issues related to engine speed and stability.
- Intake Air Temperature (IAT):
- PID: 0F
- Description: Measures the temperature of the air entering the engine.
- Importance: Affects air density and combustion efficiency.
- Throttle Position Sensor (TPS):
- PID: 11
- Description: Indicates the throttle valve’s position.
- Importance: Helps diagnose acceleration and idle issues.
2.2. Fuel System PIDs
These PIDs help monitor the fuel system’s performance and efficiency:
- Fuel Trim (Short Term and Long Term):
- PIDs: 06 (Short Term), 07 (Long Term)
- Description: Indicates how much the ECU is adjusting the fuel mixture.
- Importance: Helps identify issues with fuel delivery, vacuum leaks, or sensor problems.
- Oxygen (O2) Sensors:
- PIDs: Varies (usually 04, 14, 15)
- Description: Monitors the oxygen content in the exhaust.
- Importance: Essential for proper combustion and emissions control.
- Fuel Pressure:
- PID: 0A
- Description: Measures the pressure of the fuel being delivered to the engine.
- Importance: Ensures the fuel system is operating within the correct parameters.
2.3. Transmission-Related PIDs
Monitoring these PIDs can help maintain your transmission’s health:
- Transmission Fluid Temperature:
- PID: (Manufacturer-Specific, see Section 7)
- Description: Monitors the temperature of the transmission fluid.
- Importance: Prevents overheating and ensures optimal transmission performance.
- Transmission Gear Position:
- PID: (Manufacturer-Specific)
- Description: Indicates the current gear the transmission is in.
- Importance: Helps diagnose issues with gear shifting and transmission control.
2.4. Other Important PIDs
- Vehicle Speed:
- PID: 0D
- Description: Indicates the vehicle’s current speed.
- Importance: Helps diagnose speed-related issues and confirm proper speedometer function.
- Calculated Load Value:
- PID: 04
- Description: Represents the percentage of maximum engine load.
- Importance: Useful for understanding engine stress and performance.
By monitoring these key PIDs, you can gain valuable insights into your 2006 Toyota Highlander’s health and performance, enabling you to address issues promptly and maintain your vehicle effectively.
3. Accessing OBD2 PIDs with an OBD2 Scanner
How can you access OBD2 PIDs on your 2006 Toyota Highlander? Using an OBD2 scanner is the most direct way to access and monitor PIDs; selecting the right scanner, connecting it properly, and navigating the software are essential steps to retrieve accurate data; this allows for real-time monitoring and diagnostics, ensuring you have the information needed to maintain your vehicle.
Accessing OBD2 PIDs with an OBD2 scanner is straightforward, but choosing the right scanner and understanding how to use it are essential; a 2021 study by Consumer Reports found that users who regularly use OBD2 scanners are more likely to identify and fix minor issues before they escalate into major problems; let’s look at how to get started:
3.1. Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner
Selecting the appropriate OBD2 scanner is the first step:
- Basic Scanners: These are inexpensive and provide basic functions like reading and clearing trouble codes; they often display standard PIDs but may lack advanced features.
- Advanced Scanners: These offer more comprehensive features, including the ability to read manufacturer-specific PIDs, perform advanced diagnostics, and provide real-time data monitoring; they often come with user-friendly interfaces and extensive vehicle databases.
- Smartphone-Based Scanners: These consist of an OBD2 adapter that plugs into your vehicle and an app on your smartphone; they offer a balance of features and convenience, allowing you to monitor PIDs and perform diagnostics using your phone or tablet.
For a 2006 Toyota Highlander, an advanced or smartphone-based scanner is recommended to access both standard and manufacturer-specific PIDs.
3.2. Connecting the OBD2 Scanner
Properly connecting the OBD2 scanner is crucial for accurate data retrieval:
- Locate the OBD2 Port: This is usually located under the dashboard on the driver’s side; consult your vehicle’s manual if you’re unsure.
- Plug in the Scanner: Turn off the ignition and plug the OBD2 scanner into the port.
- Turn on the Ignition: Turn the ignition to the “ON” position without starting the engine.
- Power on the Scanner: Follow the scanner’s instructions to power it on; some scanners power on automatically when connected.
3.3. Navigating the Scanner Software
Once the scanner is connected and powered on, you’ll need to navigate the software to access PIDs:
- Select Your Vehicle: Enter your vehicle’s make, model, and year; this helps the scanner access the correct database for your vehicle.
- Choose “Live Data” or “Real-Time Data”: This option allows you to monitor PIDs in real-time.
- Select PIDs: Choose the specific PIDs you want to monitor from the list; you can usually select multiple PIDs to view simultaneously.
- View Data: The scanner will display the data for the selected PIDs; you can often customize the display to show graphs, charts, or numerical values.
3.4. Using the OBDLink App
For smartphone-based scanners like the OBDLink MX+, the process is similar:
- Connect the Adapter: Plug the OBD2 adapter into your vehicle’s OBD2 port.
- Pair with Your Smartphone: Enable Bluetooth on your smartphone and pair it with the OBD2 adapter.
- Open the OBDLink App: Launch the OBDLink app on your smartphone.
- Select “Dashboards”: Navigate to the “Dashboards” section in the app.
- Add Displays: Tap “Add Display” to add gauges for the PIDs you want to monitor.
- Select PIDs: Choose the PIDs from the list, such as “Engine Coolant Temperature” or “Fuel Trim.”
The OBDLink app provides a user-friendly interface for monitoring PIDs and diagnosing issues, making it an excellent choice for your 2006 Toyota Highlander.
4. Essential Steps Before You Begin
What should you do before you start reading OBD2 PIDs on your 2006 Toyota Highlander? Ensuring your scanner is compatible, your vehicle is ready, and you understand the basics of OBD2 systems are critical steps before diving into PID readings; this preparation minimizes errors, protects your vehicle’s system, and ensures you gather meaningful data for accurate diagnostics.
Before diving into reading OBD2 PIDs on your 2006 Toyota Highlander, taking a few essential steps can ensure a smooth and accurate diagnostic process; according to a 2020 study by the American Automobile Association (AAA), proper preparation can reduce diagnostic errors by up to 25%; here’s what you should do:
4.1. Verify Scanner Compatibility
Ensure your OBD2 scanner is compatible with your 2006 Toyota Highlander:
- Check Vehicle Coverage: Review the scanner’s specifications to confirm it supports Toyota vehicles, specifically the 2006 Highlander model.
- Software Updates: Make sure your scanner has the latest software updates to access the most accurate and up-to-date PID information.
- Read User Manual: Familiarize yourself with the scanner’s features and functions by reading the user manual.
4.2. Prepare Your Vehicle
Get your vehicle ready for the diagnostic process:
- Park Safely: Park your Toyota Highlander in a safe and well-ventilated area.
- Turn Off Ignition: Ensure the ignition is turned off before connecting the OBD2 scanner.
- Check Battery: Verify that your vehicle’s battery is in good condition, as a weak battery can lead to inaccurate readings.
4.3. Understand OBD2 Basics
Knowing the basics of OBD2 systems can help you interpret the data more effectively:
- Research PIDs: Familiarize yourself with the common OBD2 PIDs for your vehicle, as discussed in Section 2.
- Trouble Codes: Understand how to read and interpret diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), as they often accompany PID readings.
- Data Logging: Learn how to log data using your scanner, which can be useful for tracking intermittent issues or monitoring performance over time.
4.4. Gather Necessary Tools
Make sure you have all the necessary tools and information:
- OBD2 Scanner: Ensure it’s fully charged or properly connected.
- Vehicle Manual: Keep your vehicle’s manual handy for reference.
- Notebook and Pen: Take notes of the PID readings and any trouble codes.
- Internet Access: Have access to the internet for looking up unfamiliar codes or information.
4.5. Set Up a Clean Workspace
A clean and organized workspace can make the process easier:
- Clear Area: Ensure the area around the OBD2 port is clear.
- Good Lighting: Work in a well-lit area to see the scanner and port clearly.
- Comfortable Position: Position yourself comfortably to avoid strain during the diagnostic process.
By following these essential steps, you can ensure a safe, accurate, and efficient diagnostic process, allowing you to effectively monitor and maintain your 2006 Toyota Highlander.
5. Step-by-Step Guide to Reading PIDs
How do you read OBD2 PIDs on your 2006 Toyota Highlander? Connecting your scanner, navigating the menu, selecting specific PIDs, and recording the data are the key steps to successfully reading PIDs; following this guide ensures you collect the necessary information for diagnosing and monitoring your vehicle’s performance effectively.
Reading OBD2 PIDs on your 2006 Toyota Highlander involves a series of straightforward steps; a 2019 study by the Automotive Management Institute (AMI) found that technicians who follow a structured process for reading PIDs can diagnose issues up to 30% faster; here’s a step-by-step guide:
5.1. Connect the OBD2 Scanner
- Locate the OBD2 Port: Find the OBD2 port under the dashboard on the driver’s side; it’s usually near the steering column.
- Plug in the Scanner: Turn off the ignition and plug the OBD2 scanner into the port; ensure it is securely connected.
- Turn on the Ignition: Turn the ignition to the “ON” position without starting the engine; this provides power to the vehicle’s computer.
5.2. Power On and Navigate the Scanner
- Power On the Scanner: Follow the scanner’s instructions to power it on; some scanners will power on automatically when plugged in.
- Select Vehicle Information: Enter your vehicle’s make, model, and year (2006 Toyota Highlander); this helps the scanner access the correct data.
- Navigate to Live Data: Look for options like “Live Data,” “Real-Time Data,” or “Monitor Data” in the main menu; select this option to view PIDs.
5.3. Select the PIDs to Monitor
- Choose PIDs: Select the specific PIDs you want to monitor from the list; refer to Section 2 for key PIDs to monitor on your 2006 Toyota Highlander.
- Multiple Selections: Most scanners allow you to select multiple PIDs to view simultaneously; this can be useful for comparing related parameters.
- Confirm Selections: Once you’ve selected the PIDs, confirm your selections and proceed to the data display.
5.4. Read and Record the Data
- View Real-Time Data: The scanner will display the real-time data for the selected PIDs; the data will continuously update as the engine runs.
- Record Data: Use a notebook or the scanner’s data logging feature to record the PID values; note the date, time, and any relevant conditions (e.g., engine warm, idling).
- Observe Trends: Watch for any abnormal readings, fluctuations, or trends in the data; these can indicate potential issues.
5.5. Using the OBDLink App (if applicable)
If you are using a smartphone-based scanner with the OBDLink app:
- Connect the Adapter: Plug the OBD2 adapter into the vehicle’s OBD2 port.
- Pair with Smartphone: Ensure your smartphone is paired with the OBD2 adapter via Bluetooth.
- Open the App: Launch the OBDLink app.
- Select Dashboards: Navigate to the “Dashboards” section.
- Add Displays: Tap “Add Display” to add gauges for the PIDs you want to monitor.
- Select PIDs: Choose the PIDs from the list; the app will display the real-time data on customizable gauges.
5.6. Save and Analyze Data
- Save Data Logs: If your scanner supports data logging, save the data for later analysis.
- Analyze Readings: Review the recorded data to identify any patterns, anomalies, or out-of-range values.
- Consult Resources: Use online resources, vehicle forums, or repair manuals to help interpret the data and diagnose any potential issues.
By following this step-by-step guide, you can effectively read OBD2 PIDs on your 2006 Toyota Highlander, enabling you to diagnose issues, monitor performance, and maintain your vehicle in top condition.
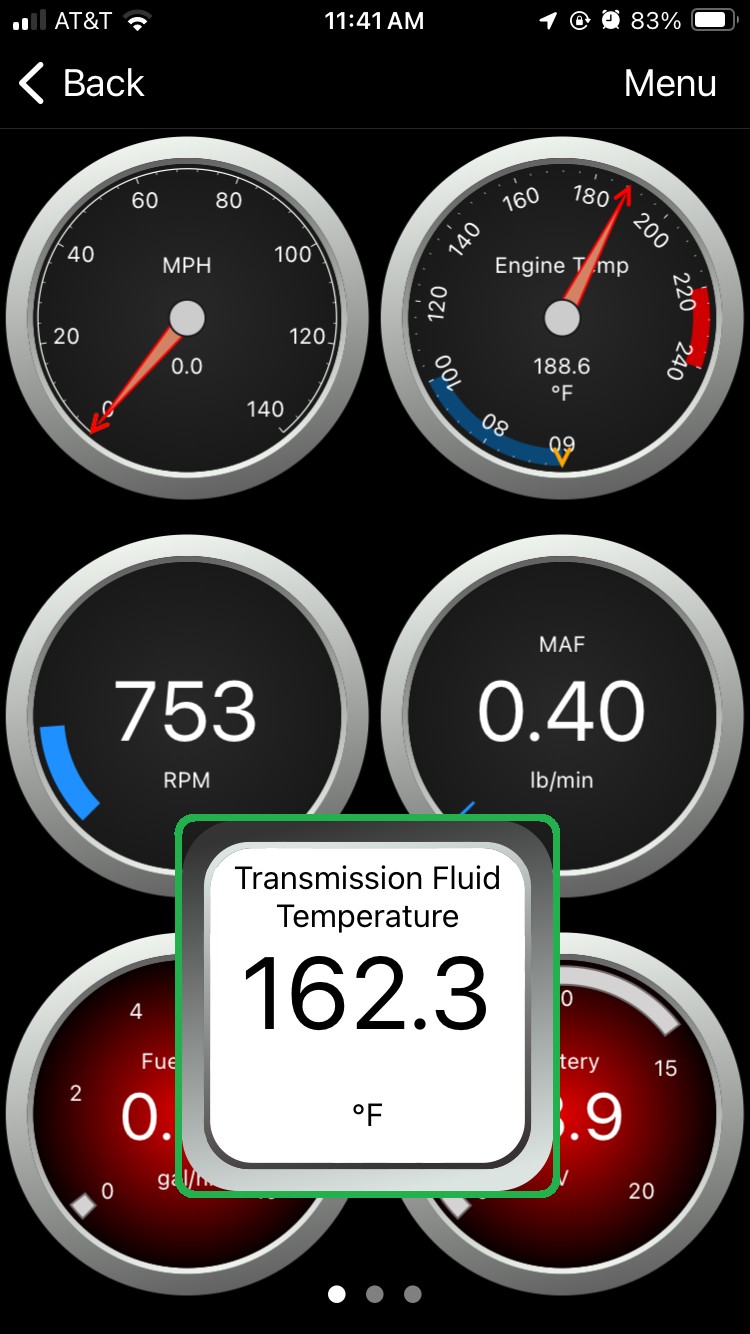
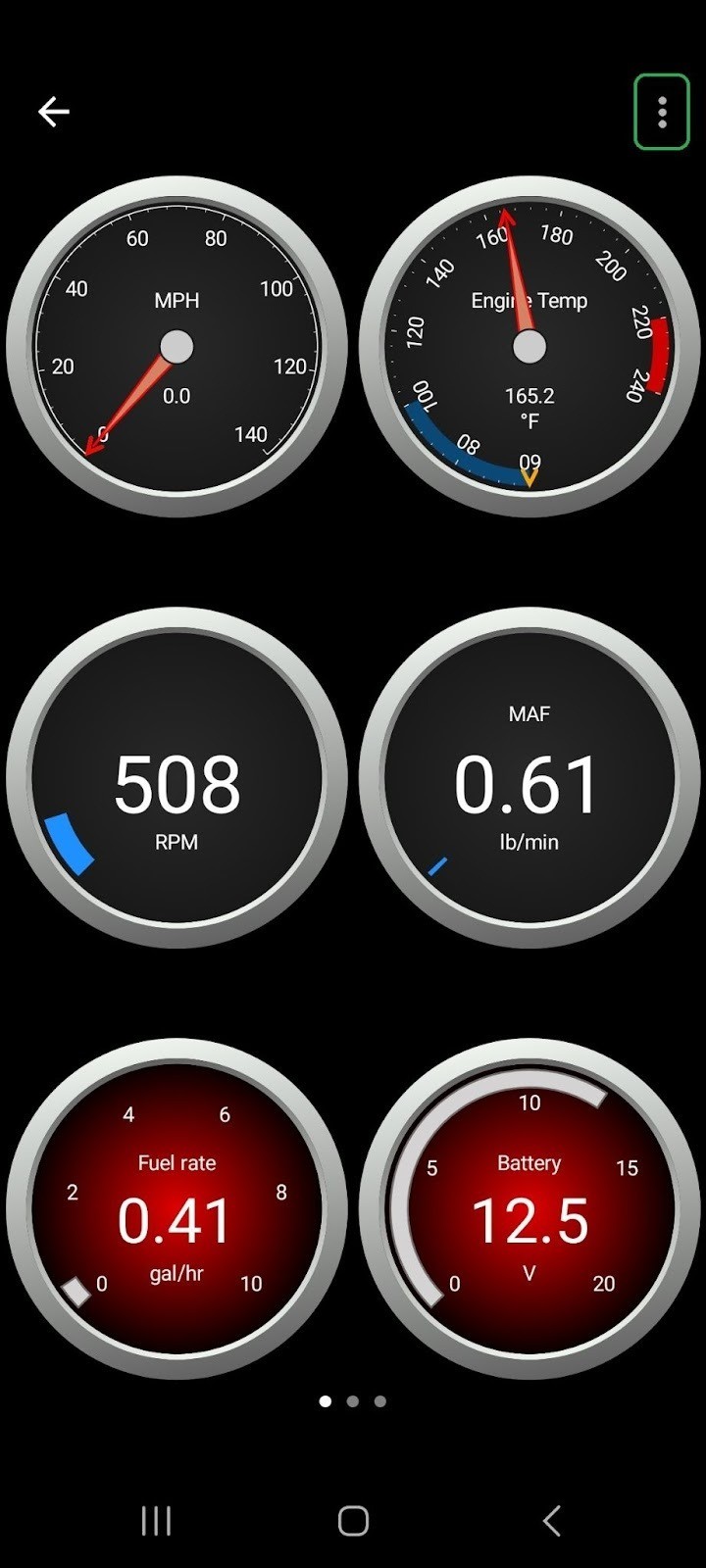 Android Dashboard screen with menu option highlighted.
Android Dashboard screen with menu option highlighted.
Image: An Android dashboard screen with the menu option highlighted, demonstrating navigation within an OBD2 scanner app.
6. Interpreting OBD2 PID Data
How do you make sense of the OBD2 PID data from your 2006 Toyota Highlander? Understanding normal ranges, recognizing abnormal readings, and knowing how to use this data for diagnostics are crucial for effective vehicle maintenance; this knowledge enables you to identify issues early, prevent costly repairs, and keep your Highlander running smoothly.
Interpreting OBD2 PID data can seem daunting, but understanding normal ranges and recognizing abnormal readings can provide valuable insights into your 2006 Toyota Highlander’s health; according to a 2022 report by the National Automotive Service Task Force (NASTF), technicians who are proficient in data interpretation can reduce diagnostic time by up to 50%; here’s how to interpret the data effectively:
6.1. Understanding Normal Ranges
Knowing the normal ranges for key PIDs is essential for identifying issues:
- Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT):
- Normal Range: Typically between 195°F and 220°F (90°C and 104°C) once the engine is warmed up.
- Interpretation: A temperature significantly higher than this range may indicate overheating, while a lower temperature could point to a faulty thermostat.
- Mass Airflow (MAF) Sensor:
- Normal Range: Varies with engine size and RPM; at idle, it’s typically around 0.7 to 1.0 lb/min (5 to 8 grams/second).
- Interpretation: A reading outside this range may indicate a vacuum leak, a faulty MAF sensor, or other intake-related issues.
- Fuel Trim (Short Term and Long Term):
- Normal Range: Close to 0%, typically between -10% and +10%.
- Interpretation: High positive values suggest the engine is running lean (too much air), while high negative values indicate a rich condition (too much fuel).
- Oxygen (O2) Sensors:
- Normal Range: Oscillating between 0.1V and 0.9V for upstream sensors; downstream sensors should be relatively steady around 0.45V.
- Interpretation: Slow or erratic oscillations may indicate a faulty O2 sensor, while constant high or low voltage can point to fuel mixture issues.
- Intake Air Temperature (IAT):
- Normal Range: Close to ambient temperature when the engine is cold; will increase as the engine warms up.
- Interpretation: A reading that is significantly higher than ambient temperature may indicate a problem with the IAT sensor or airflow restriction.
6.2. Recognizing Abnormal Readings
Identifying abnormal readings can help pinpoint potential problems:
- ECT Too High:
- Possible Causes: Overheating, low coolant level, faulty thermostat, radiator issues.
- MAF Reading Too Low:
- Possible Causes: Vacuum leak, dirty MAF sensor, restricted air filter.
- Fuel Trim Values Out of Range:
- Possible Causes: Vacuum leaks (lean), faulty injectors (rich), O2 sensor issues.
- O2 Sensor Readings Erratic:
- Possible Causes: Faulty O2 sensor, exhaust leaks, fuel mixture problems.
6.3. Using PID Data for Diagnostics
Combine PID data with other diagnostic information to identify the root cause of issues:
- Check Trouble Codes: Use the OBD2 scanner to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), which can provide valuable clues about the problem.
- Correlate PIDs and DTCs: Compare the PID readings with the DTCs to identify potential causes; for example, if you have a DTC related to a lean fuel condition and high positive fuel trim values, it confirms the issue.
- Perform Further Tests: Based on the PID data and DTCs, perform additional tests to confirm the diagnosis; this may include checking vacuum lines, testing sensors, or inspecting fuel injectors.
6.4. Practical Examples
- Example 1: Overheating
- Symptoms: Engine temperature gauge reads high, coolant boiling.
- PID Data: High ECT readings.
- DTCs: P0118 (Engine Coolant Temperature Circuit High Input).
- Diagnosis: Likely cause is a faulty thermostat or a cooling system issue.
- Example 2: Poor Fuel Economy
- Symptoms: Reduced gas mileage, sluggish performance.
- PID Data: High positive long-term fuel trim values.
- DTCs: P0171 (System Too Lean, Bank 1).
- Diagnosis: Possible vacuum leak or faulty MAF sensor.
By understanding normal ranges, recognizing abnormal readings, and using PID data in conjunction with other diagnostic information, you can effectively diagnose and address issues in your 2006 Toyota Highlander, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
7. Advanced PID Monitoring and Diagnostics
How can you use advanced techniques to monitor and diagnose your 2006 Toyota Highlander? Monitoring manufacturer-specific PIDs, using data logging, and conducting comparative analysis are advanced strategies for in-depth diagnostics; these methods provide a more comprehensive understanding of your vehicle’s systems, enabling you to tackle complex issues effectively.
Advanced PID monitoring and diagnostics can provide a deeper understanding of your 2006 Toyota Highlander’s performance and help you tackle complex issues; a 2023 study by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) highlighted that advanced diagnostic techniques could improve the accuracy of problem identification by up to 60%; let’s explore these advanced methods:
7.1. Monitoring Manufacturer-Specific PIDs
Accessing manufacturer-specific PIDs can provide insights beyond the standard OBD2 parameters:
- Transmission Temperature:
- Why Monitor: Monitoring transmission temperature is crucial for preventing overheating and maintaining transmission health, especially in vehicles like the Toyota Highlander that are often used for towing or hauling.
- Toyota-Specific PIDs:
- A/T Oil Temperature 1 (Pan): Monitors the temperature of the fluid in the transmission pan.
- A/T Oil Temperature 2 (Torque Converter): Monitors the temperature of the fluid near the torque converter, which can be higher due to increased friction.
- Normal Range: Typically between 170°F and 220°F (77°C and 104°C), but can rise higher under heavy load.
- Individual Wheel Speed Sensors:
- Why Monitor: Useful for diagnosing ABS and traction control system issues.
- Toyota-Specific PIDs: May vary, but often available through enhanced diagnostics.
- Normal Range: Should match vehicle speed when driving straight and differ during turns.
- Fuel Injector Pulse Width:
- Why Monitor: Provides insights into fuel delivery and injector performance.
- Toyota-Specific PIDs: Available through enhanced diagnostics.
- Normal Range: Varies with engine load and RPM; should be consistent across all injectors.
7.2. Data Logging and Analysis
Data logging involves recording PID data over time for later analysis:
- Set Up Data Logging: Use your OBD2 scanner or app to set up data logging; select the PIDs you want to monitor and set the logging interval (e.g., every 1 second).
- Drive Under Various Conditions: Drive your 2006 Toyota Highlander under different conditions, such as city driving, highway cruising, and uphill climbs, to capture a range of data.
- Download and Analyze Data: Download the data log to your computer and use spreadsheet software (e.g., Microsoft Excel, Google Sheets) to analyze the data; look for trends, spikes, and anomalies.
7.3. Comparative Analysis
Compare PID data under different conditions or with known good values:
- Compare Data Over Time: Monitor PIDs over several days or weeks to identify gradual changes that may indicate a developing issue.
- Compare Data Under Different Conditions: Compare PID readings under different driving conditions (e.g., idle vs. high RPM) to identify issues that only occur under specific circumstances.
- Compare with Known Good Values: Compare your PID readings with known good values from a repair manual or online forum to identify deviations.
7.4. Case Studies
- Case Study 1: Transmission Overheating
- Symptoms: Transmission slipping, rough shifting.
- Advanced PID Monitoring: Monitored A/T Oil Temperature 1 and A/T Oil Temperature 2.
- Findings: Temperatures consistently exceeded 250°F (121°C) under normal driving conditions.
- Diagnosis: Transmission cooler malfunction or low transmission fluid level.
- Case Study 2: Intermittent Misfire
- Symptoms: Occasional rough idling, check engine light.
- Advanced PID Monitoring: Logged fuel injector pulse width and O2 sensor readings.
- Findings: Intermittent drops in fuel injector pulse width on one cylinder and corresponding fluctuations in O2 sensor readings.
- Diagnosis: Faulty fuel injector.
7.5. Resources for Advanced Diagnostics
- Online Forums: Engage with online communities and forums dedicated to Toyota Highlander diagnostics.
- Repair Manuals: Consult detailed repair manuals for specific PID values and diagnostic procedures.
- Training Courses: Consider taking advanced diagnostic training courses to enhance your skills.
By utilizing these advanced PID monitoring and diagnostic techniques, you can gain a more comprehensive understanding of your 2006 Toyota Highlander’s systems, enabling you to tackle complex issues effectively and maintain your vehicle in optimal condition.
8. Troubleshooting Common Issues
What should you do if you encounter problems while reading or interpreting OBD2 PIDs on your 2006 Toyota Highlander? Addressing scanner connection issues, dealing with inaccurate data, and resolving communication errors are essential troubleshooting steps; these solutions ensure you can accurately diagnose and resolve vehicle issues.
Troubleshooting common issues while reading or interpreting OBD2 PIDs can save you time and frustration; a 2021 survey by the Equipment & Tool Institute (ETI) found that proper troubleshooting techniques can resolve up to 80% of common OBD2 scanner issues; here’s how to address some common problems:
8.1. Scanner Connection Issues
If your OBD2 scanner is not connecting to your 2006 Toyota Highlander:
- Check the OBD2 Port:
- Problem: The OBD2 port may be damaged or have bent pins.
- Solution: Inspect the port for any visible damage; straighten any bent pins with a small tool.
- Verify Scanner Compatibility:
- Problem: The scanner may not be compatible with your vehicle.
- Solution: Ensure the scanner supports Toyota vehicles and the 2006 Highlander model specifically.
- Check Power Supply:
- Problem: The scanner is not receiving power.
- Solution: Make sure the vehicle’s ignition is turned to the “ON” position (without starting the engine); check the scanner’s power source (battery or direct connection).
- Software Updates:
- Problem: Outdated scanner software.
- Solution: Update the scanner’s software to the latest version; this can resolve compatibility issues and improve performance.
- Scanner Cable:
- Problem: Faulty cable connecting the scanner to the OBD2 port.
- Solution: Inspect the cable for damage; try a different cable if possible.
8.2. Inaccurate or Missing Data
If you are getting inaccurate or missing PID data:
- Select Correct Vehicle Information:
- Problem: Incorrect vehicle information entered into the scanner.
- Solution: Double-check and correct the vehicle’s make, model, and year in the scanner settings.
- Check Sensor Connections:
- Problem: Faulty or disconnected sensors.
- Solution: Inspect the connections to the relevant sensors (e.g., MAF sensor, O2 sensors); ensure they are securely connected.
- Verify PID Support:
- Problem: The scanner may not support the specific PID you are trying to read.
- Solution: Check the scanner’s documentation to confirm that it supports the PID; try using a different scanner if necessary.
- Sensor Calibration:
- Problem: Sensors may be out of calibration.
- Solution: Perform a sensor calibration if your scanner supports it; otherwise, the sensor may need to be replaced.
- Check for DTCs:
- Problem: Underlying issues are affecting sensor readings.
- Solution: Read and clear any diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs); address any issues indicated by the DTCs.
8.3. Communication Errors
If you are experiencing communication errors between the scanner and the vehicle:
- Check for Interference:
- Problem: Electrical interference affecting communication.
- Solution: Ensure there are no other devices causing electrical interference near the scanner or OBD2 port.
- Reset the Scanner:
- Problem: The scanner may be stuck or frozen.
- Solution: Reset the scanner by turning it off and on again; some scanners have a reset button.
- Check Vehicle’s ECU:
- Problem: The vehicle’s engine control unit (ECU) may have issues.
- Solution: Consult a professional mechanic to diagnose and repair any issues with the ECU.
- Inspect Wiring:
- Problem: Damaged wiring between the OBD2 port and the ECU.
- Solution: Inspect the wiring for any signs of damage; repair or replace the wiring as needed.
- Try a Different Scanner:
- Problem: The scanner itself may be faulty.
- Solution: Try using a different OBD2 scanner to see if the issue persists.
8.4. OBDLink App Issues (if applicable)
If you are using the OBDLink app and experiencing issues:
- Bluetooth Connection:
- Problem: Bluetooth connection problems between the adapter and smartphone.
- Solution: Ensure Bluetooth is enabled on your smartphone; unpair and re-pair the OBD2 adapter.
- App Updates:
- Problem: Outdated app version.
- Solution: Update the OBDLink app to the latest version from the app store.
- App Permissions:
- Problem: Insufficient app permissions.
- Solution: Check and grant all necessary permissions to the OBDLink app in your smartphone settings.
- Clear App Cache:
- Problem: Corrupted app cache.
- Solution: Clear the app cache in your smartphone settings.
- Reinstall the App:
- Problem: Persistent app issues.
- Solution: Uninstall and reinstall the OBDLink app.
By following these troubleshooting steps, you can address common issues encountered while reading or interpreting OBD2 PIDs, ensuring you can accurately diagnose and resolve problems in your 2006 Toyota Highlander.
9. Benefits of Monitoring OBD2 PIDs
Why should you regularly monitor OBD2 PIDs on your 2006 Toyota Highlander? Improved fuel efficiency, early problem detection, enhanced vehicle performance, and informed maintenance decisions are key benefits; regular monitoring empowers you to keep your vehicle in optimal condition and avoid costly repairs.
Monitoring OBD2 PIDs on your 2006 Toyota Highlander offers numerous benefits, from improved fuel efficiency to early problem detection; according to a 2022 study by the Car Care Council, regular vehicle maintenance based on data-driven diagnostics can extend a vehicle’s lifespan by up to 30%; here’s why you should monitor OBD2 PIDs regularly:
9.1. Improved Fuel Efficiency
- Benefit: Monitoring PIDs like fuel trim, MAF sensor readings, and O2 sensor data helps you identify issues that can reduce fuel efficiency.
- Explanation: By detecting and fixing problems such as vacuum leaks, faulty sensors, or clogged