The 2011 F20 OBD2 CAN-Bus for BMW provides valuable insights into vehicle performance and diagnostics via OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN. This guide explores how to leverage the CAN-Bus system in your 2011 BMW F20 for advanced vehicle data and diagnostics, offering solutions for both novice and experienced users. Dive in to unlock your BMW’s hidden potential with enhanced diagnostic tools and vehicle insights.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the 2011 F20 OBD2 CAN-Bus System for BMW
- 1.1. The Role of CAN-Bus in Modern BMWs
- 1.2. OBD2 Port and Its Significance
- 1.3. Benefits of Using an OBD2 Scanner
- 2. Selecting the Right OBD2 Scanner for Your 2011 BMW F20
- 2.1. Types of OBD2 Scanners Available
- 2.2. Key Features to Look For
- 2.3. Recommended OBD2 Scanners for BMW F20 (2011)
- 3. Connecting and Using Your OBD2 Scanner with a 2011 BMW F20
- 3.1. Step-by-Step Guide to Connecting the Scanner
- 3.2. Navigating the OBD2 Scanner Interface
- 3.3. Common Mistakes to Avoid
- 4. Reading and Interpreting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 4.1. Understanding OBD2 Code Structure
- 4.2. Common DTCs for BMW F20 (2011)
- 4.3. Resources for DTC Lookup
- 5. Live Data Monitoring for Enhanced Diagnostics
- 5.1. Key Parameters to Monitor
- 5.2. Identifying Abnormal Readings
- 5.3. Using Graphs and Charts for Data Analysis
- 6. Advanced Diagnostics and Special Functions
- 6.1. Bi-Directional Control and Component Testing
- 6.2. Service Resets and Adaptations
- 6.3. Coding and Programming
- 7. Maintaining and Updating Your OBD2 Scanner
- 7.1. Software Updates and Compatibility
- 7.2. Troubleshooting Common Scanner Issues
- 7.3. Proper Storage and Handling
- 8. Common Problems Diagnosed with OBD2 on a 2011 BMW F20
- 8.1. Engine Problems
- 8.2. Transmission Problems
- 8.3. ABS and Airbag System Issues
- 9. Enhancing Your DIY Car Repair Skills with OBD2 Data
- 9.1. Building a Diagnostic Mindset
- 9.2. Online Communities and Resources
- 9.3. Knowing When to Seek Professional Help
- 10. Future Trends in OBD2 Technology
- 10.1. Wireless OBD2 Scanners and Bluetooth Connectivity
- 10.2. Integration with Mobile Apps and Cloud-Based Diagnostics
- 10.3. AI and Machine Learning in Vehicle Diagnostics
- FAQ: Understanding OBD2 and Your 2011 BMW F20
1. Understanding the 2011 F20 OBD2 CAN-Bus System for BMW
What is the 2011 F20 OBD2 CAN-Bus system for BMW, and why is it important?
The 2011 F20 OBD2 CAN-Bus system for BMW is a communication network that allows various electronic control units (ECUs) within the vehicle to communicate with each other and diagnostic tools. CAN-Bus (Controller Area Network) is the backbone of modern automotive diagnostics, enabling real-time data exchange between components like the engine control unit (ECU), transmission control unit (TCU), anti-lock braking system (ABS), and airbag system. According to a study by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), vehicles utilizing CAN-Bus systems have improved diagnostic capabilities and more efficient data transmission. This is crucial for accurate diagnostics, performance monitoring, and overall vehicle maintenance. Using the OBD2 port, technicians and vehicle owners can access this data using a compatible scanner.
1.1. The Role of CAN-Bus in Modern BMWs
How does CAN-Bus function in a 2011 BMW F20?
CAN-Bus in the 2011 BMW F20 serves as the central nervous system, facilitating communication between various ECUs. These ECUs control everything from engine performance and emissions to safety features and comfort systems. The CAN-Bus system allows these components to share information, enabling coordinated operation and advanced functionality. For example, the ECU can adjust fuel injection based on data received from the oxygen sensors and throttle position sensor. A report by Bosch indicates that CAN-Bus systems reduce wiring complexity and improve data integrity, leading to more reliable vehicle operation.
1.2. OBD2 Port and Its Significance
Where is the OBD2 port located in a 2011 BMW F20, and what is its function?
The OBD2 port in a 2011 BMW F20 is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side. It is a standardized interface that allows diagnostic tools to communicate with the vehicle’s ECUs. The OBD2 port provides access to a wealth of information, including diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), live sensor data, and vehicle identification information. This is vital for diagnosing issues, monitoring performance, and ensuring the vehicle meets emission standards. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), all vehicles sold in the US since 1996 are required to have an OBD2 port, standardizing diagnostics across different makes and models.
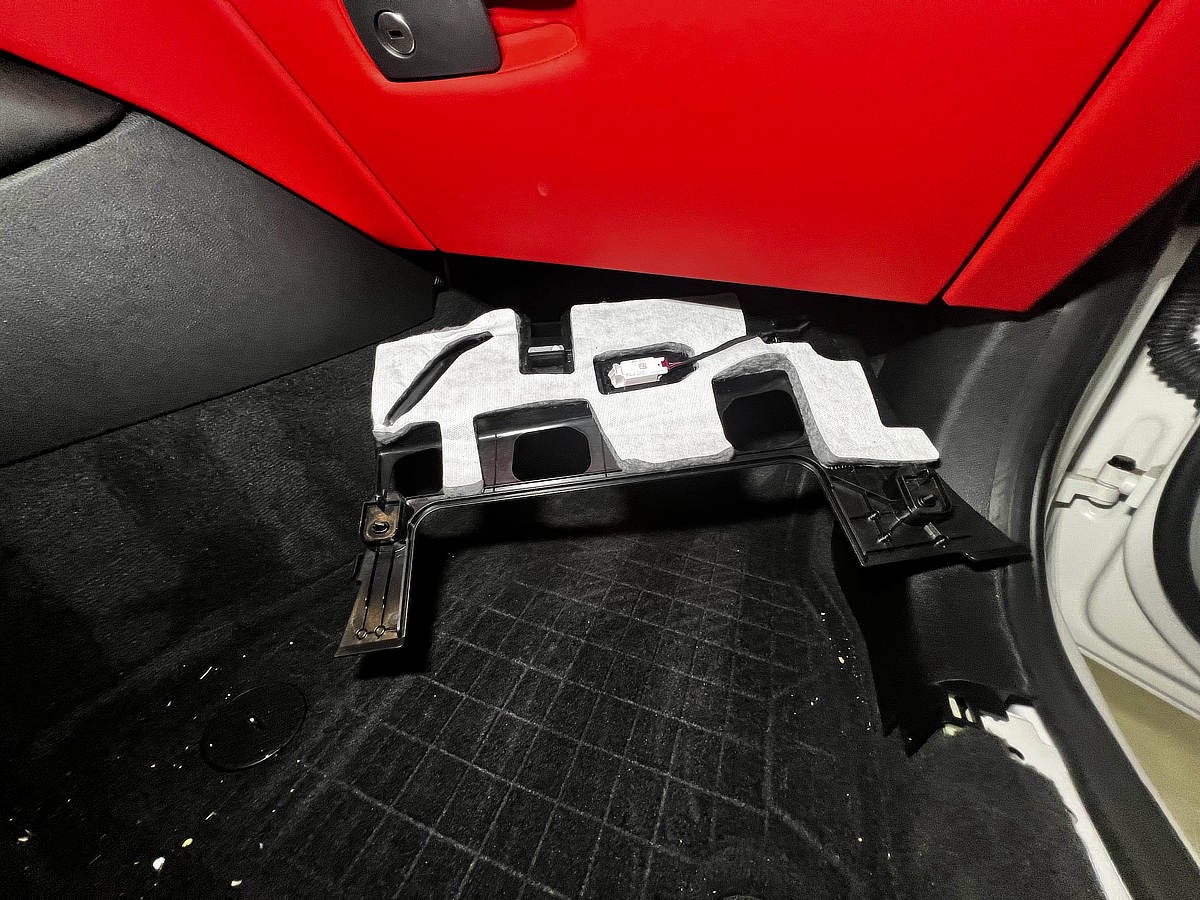 OBD2 Port Location in BMW F20
OBD2 Port Location in BMW F20
Alt: OBD2 port location in the passenger footwell of a 2011 BMW F20, showing the connection interface.
1.3. Benefits of Using an OBD2 Scanner
What are the primary advantages of using an OBD2 scanner with a 2011 BMW F20?
Using an OBD2 scanner with a 2011 BMW F20 provides numerous benefits. It allows you to read and clear diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), monitor live sensor data, perform vehicle diagnostics, and gain insights into your vehicle’s performance. By identifying and addressing issues early, you can prevent costly repairs and ensure your BMW operates efficiently. A study by AAA found that using diagnostic tools like OBD2 scanners can significantly reduce vehicle repair costs by identifying problems before they escalate. Additionally, understanding your vehicle’s data can help you optimize fuel efficiency and extend its lifespan.
2. Selecting the Right OBD2 Scanner for Your 2011 BMW F20
How do you choose the best OBD2 scanner for a 2011 BMW F20?
Selecting the right OBD2 scanner for your 2011 BMW F20 involves considering several factors, including compatibility, features, and budget. A suitable scanner should support CAN-Bus communication, offer BMW-specific diagnostic capabilities, and provide user-friendly features like a clear display and intuitive interface. Research from Consumer Reports indicates that a well-chosen OBD2 scanner can empower vehicle owners to perform basic diagnostics and maintenance, saving time and money.
2.1. Types of OBD2 Scanners Available
What are the different types of OBD2 scanners available on the market?
There are several types of OBD2 scanners available, ranging from basic code readers to advanced professional-grade tools. Basic code readers can read and clear DTCs, while mid-range scanners offer additional features like live data streaming and freeze frame data. Professional-grade scanners provide advanced diagnostics, bi-directional control, and access to manufacturer-specific codes. According to a market analysis by Global Market Insights, the demand for advanced OBD2 scanners is increasing due to the growing complexity of modern vehicle systems.
2.2. Key Features to Look For
Which key features should you consider when selecting an OBD2 scanner for a 2011 BMW F20?
When selecting an OBD2 scanner for a 2011 BMW F20, consider the following key features:
- CAN-Bus Compatibility: Ensure the scanner supports CAN-Bus communication, as this is essential for accessing data from your BMW’s ECUs.
- BMW-Specific Codes: Look for a scanner that can read and clear BMW-specific diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
- Live Data Streaming: This feature allows you to monitor real-time sensor data, helping you diagnose issues more accurately.
- Bi-Directional Control: Advanced scanners offer bi-directional control, allowing you to send commands to the vehicle’s ECUs to test components.
- User-Friendly Interface: Choose a scanner with a clear display, intuitive menus, and easy-to-use navigation.
- Software Updates: Ensure the scanner supports software updates to stay current with the latest vehicle models and diagnostic capabilities.
2.3. Recommended OBD2 Scanners for BMW F20 (2011)
Which OBD2 scanners are highly recommended for use with a 2011 BMW F20?
Several OBD2 scanners are highly recommended for use with a 2011 BMW F20, based on their compatibility, features, and user reviews:
| Scanner Model | Key Features | Price Range |
|---|---|---|
| BlueDriver Bluetooth Pro | BMW-specific diagnostics, live data, code clearing, smartphone app integration | $120-150 |
| Autel MaxiCOM MK808 | Advanced diagnostics, bi-directional control, service resets, extensive vehicle coverage | $500-700 |
| Carly for BMW | BMW-specific diagnostics, coding, adaptations, maintenance resets, mobile app-based | $80-120/year |
| INPA / EDIABAS (with cable) | Professional-level BMW diagnostics, coding, programming (requires technical knowledge and setup) | $50-100 |
| Foxwell NT510 Elite | BMW-specific diagnostics, service resets, component testing, free software updates | $180-250 |
These scanners offer a range of features to suit different needs and budgets, ensuring you can effectively diagnose and maintain your 2011 BMW F20.
3. Connecting and Using Your OBD2 Scanner with a 2011 BMW F20
How do you properly connect and use an OBD2 scanner with your 2011 BMW F20?
Connecting and using an OBD2 scanner with your 2011 BMW F20 is a straightforward process. First, locate the OBD2 port, usually found under the dashboard on the driver’s side. Plug the scanner into the port and turn on the vehicle’s ignition without starting the engine. Follow the scanner’s instructions to navigate the menu and access diagnostic information. Proper connection and usage ensure accurate data retrieval and prevent potential issues. According to a guide by Popular Mechanics, incorrect scanner usage can lead to misdiagnosis or even damage to the vehicle’s electrical system.
3.1. Step-by-Step Guide to Connecting the Scanner
What are the specific steps for connecting an OBD2 scanner to a 2011 BMW F20?
Here is a step-by-step guide to connecting an OBD2 scanner to your 2011 BMW F20:
- Locate the OBD2 Port: Find the OBD2 port under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Plug in the Scanner: Insert the OBD2 scanner into the port, ensuring it is securely connected.
- Turn on the Ignition: Turn the vehicle’s ignition to the “ON” position without starting the engine. This provides power to the scanner and the vehicle’s ECUs.
- Follow Scanner Instructions: Follow the instructions provided with your OBD2 scanner to navigate the menu and access diagnostic information. This typically involves selecting the vehicle make and model, and then choosing the desired function (e.g., read codes, view live data).
- Read Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): If there are any stored DTCs, the scanner will display them along with a brief description.
- View Live Data: You can view real-time sensor data, such as engine RPM, coolant temperature, and oxygen sensor readings.
- Clear Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): If you have addressed the underlying issue, you can clear the DTCs using the scanner’s menu options.
3.2. Navigating the OBD2 Scanner Interface
How do you navigate the interface of an OBD2 scanner effectively?
Navigating the OBD2 scanner interface involves understanding the menu options and using the scanner’s buttons or touchscreen to access the desired functions. Most scanners have a main menu with options for reading codes, viewing live data, performing tests, and accessing settings. Use the arrow keys or touchscreen to select the desired option and press the “Enter” or “OK” button to confirm your selection. Refer to the scanner’s user manual for detailed instructions on navigating the interface and using specific features.
3.3. Common Mistakes to Avoid
What are some common mistakes to avoid when using an OBD2 scanner with a 2011 BMW F20?
Several common mistakes should be avoided when using an OBD2 scanner with your 2011 BMW F20:
- Connecting the Scanner with the Engine Running: Always connect the scanner with the engine off and the ignition in the “ON” position.
- Ignoring the User Manual: Read the scanner’s user manual to understand its features and how to use them correctly.
- Clearing Codes Without Addressing the Issue: Clearing DTCs without fixing the underlying problem will only result in the codes reappearing.
- Misinterpreting Live Data: Understand the normal ranges for live data parameters to accurately diagnose issues.
- Using an Incompatible Scanner: Ensure the scanner is compatible with your BMW F20 and supports CAN-Bus communication.
- Forgetting to Update the Scanner Software: Keep the scanner’s software updated to ensure it has the latest vehicle coverage and diagnostic capabilities.
Avoiding these mistakes will help you use the OBD2 scanner effectively and accurately diagnose issues with your 2011 BMW F20.
4. Reading and Interpreting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
How do you read and interpret diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) using an OBD2 scanner?
Reading and interpreting diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) is a crucial step in diagnosing issues with your 2011 BMW F20. When the OBD2 scanner retrieves a DTC, it provides a code that corresponds to a specific problem detected by the vehicle’s ECUs. Each code consists of five characters: a letter indicating the system (e.g., P for powertrain, B for body, C for chassis, U for network), followed by four numbers that specify the exact fault. Understanding these codes helps you identify the source of the problem and take appropriate action. According to a technical guide by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), accurate interpretation of DTCs is essential for effective vehicle repair.
4.1. Understanding OBD2 Code Structure
What does the structure of an OBD2 code signify?
The structure of an OBD2 code provides valuable information about the nature and location of the fault. The first character indicates the system affected:
- P (Powertrain): Relates to the engine, transmission, and related components.
- B (Body): Relates to systems like the airbags, power windows, and central locking.
- C (Chassis): Relates to the braking system, suspension, and steering.
- U (Network): Relates to the communication network between ECUs.
The second character indicates whether the code is generic (0) or manufacturer-specific (1):
- 0: Generic code, standardized across all vehicles.
- 1: Manufacturer-specific code, unique to BMW.
The third, fourth, and fifth characters provide more specific information about the fault, such as the component or circuit involved.
4.2. Common DTCs for BMW F20 (2011)
What are some common diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) that you might encounter with a 2011 BMW F20?
Here are some common DTCs that you might encounter with a 2011 BMW F20, along with their possible causes:
| DTC | Description | Possible Causes |
|---|---|---|
| P0171 | System Too Lean (Bank 1) | Vacuum leak, faulty oxygen sensor, MAF sensor issue, fuel pump problem |
| P0300 | Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected | Faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, fuel injectors, vacuum leak, low compression |
| P0420 | Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1) | Faulty catalytic converter, exhaust leak, oxygen sensor issue |
| P0505 | Idle Air Control System Malfunction | Faulty idle air control valve, vacuum leak, throttle body issue |
| P1128 | Long Term Fuel Trim Mult., System Too Lean Bank 1 | Vacuum leak, faulty MAF sensor, fuel pressure issue, clogged fuel filter |
| P1017 | VANOS, Intake: Position Not Reached | Faulty VANOS solenoid, oil pressure issue, camshaft timing problem |
This table provides a starting point for diagnosing common issues with your 2011 BMW F20. Always consult the vehicle’s service manual for detailed diagnostic procedures and repair instructions.
4.3. Resources for DTC Lookup
Where can you find reliable resources for looking up the meaning of diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs)?
Several reliable resources can help you look up the meaning of diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs):
- OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN: Offers a comprehensive database of OBD2 codes with detailed descriptions and possible causes.
- Vehicle Service Manual: Provides manufacturer-specific information about DTCs and diagnostic procedures.
- Online Forums: Automotive forums like Bimmerforums and BMW forums often have discussions about specific DTCs and their solutions.
- Professional Diagnostic Tools: Advanced OBD2 scanners often have built-in DTC lookup functions with detailed information.
- National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE): Offers resources and certifications for automotive technicians, including information on DTC interpretation.
Using these resources will help you accurately interpret DTCs and diagnose issues with your 2011 BMW F20.
5. Live Data Monitoring for Enhanced Diagnostics
How can live data monitoring enhance diagnostics for your 2011 BMW F20?
Live data monitoring involves using an OBD2 scanner to observe real-time sensor values and parameters as the vehicle is running. This provides valuable insights into the performance of various components and systems, helping you diagnose issues that may not trigger a DTC. By monitoring parameters like engine RPM, coolant temperature, oxygen sensor readings, and fuel trim values, you can identify anomalies and pinpoint the source of the problem. A study by the American Society for Engineering Education (ASEE) highlights the importance of live data monitoring in modern automotive diagnostics.
5.1. Key Parameters to Monitor
Which key parameters should you monitor when diagnosing a 2011 BMW F20 using live data?
When diagnosing a 2011 BMW F20 using live data, consider monitoring the following key parameters:
- Engine RPM: Indicates the speed at which the engine is rotating.
- Coolant Temperature: Measures the temperature of the engine coolant.
- Oxygen Sensor Readings: Indicates the oxygen content in the exhaust gas, helping assess fuel mixture.
- Fuel Trim Values: Reflects the adjustments made by the ECU to maintain the correct air-fuel ratio.
- Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor Readings: Measures the amount of air entering the engine.
- Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) Readings: Indicates the position of the throttle plate.
- Vehicle Speed: Shows the current speed of the vehicle.
- Battery Voltage: Indicates the voltage of the vehicle’s battery.
Monitoring these parameters can help you identify issues with the engine, fuel system, emissions system, and other critical components.
5.2. Identifying Abnormal Readings
How do you identify abnormal readings in live data and what do they indicate?
Identifying abnormal readings in live data involves comparing the observed values to the expected ranges for each parameter. The expected ranges can be found in the vehicle’s service manual or online resources. Here are some examples of abnormal readings and what they might indicate:
- High Coolant Temperature: Could indicate a problem with the cooling system, such as a faulty thermostat or radiator.
- Low Oxygen Sensor Readings: Could indicate a lean fuel mixture, caused by a vacuum leak or faulty fuel injector.
- High Fuel Trim Values: Could indicate a rich fuel mixture, caused by a faulty MAF sensor or fuel pressure regulator.
- Erratic MAF Sensor Readings: Could indicate a faulty MAF sensor or air intake leak.
- Unstable Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) Readings: Could indicate a faulty TPS or throttle body issue.
- Low Battery Voltage: Could indicate a failing battery or charging system problem.
By comparing live data to expected values, you can identify potential issues and focus your diagnostic efforts on the affected components.
5.3. Using Graphs and Charts for Data Analysis
How can graphs and charts be used to analyze live data more effectively?
Using graphs and charts can help you visualize live data and identify trends or patterns that may not be apparent when looking at raw numbers. Many OBD2 scanners and diagnostic software programs offer graphing capabilities, allowing you to plot data over time. For example, you can graph oxygen sensor readings to see how they fluctuate during different driving conditions, or plot fuel trim values to identify long-term trends. By analyzing these graphs, you can gain a better understanding of how the vehicle’s systems are performing and identify potential issues more effectively.
 Live Data Graph
Live Data Graph
Alt: Live data graph showing engine RPM, coolant temperature, and vehicle speed from a 2011 BMW F20.
6. Advanced Diagnostics and Special Functions
What advanced diagnostic procedures and special functions are available for a 2011 BMW F20 using an OBD2 scanner?
Advanced diagnostics and special functions can provide deeper insights into your 2011 BMW F20’s systems. These capabilities, often found in professional-grade OBD2 scanners, allow technicians to perform more complex tests and calibrations. Such functions might include bi-directional control, component testing, service resets, and coding. These advanced features facilitate precise diagnostics and maintenance, ensuring optimal vehicle performance. Research from the European Automobile Manufacturers Association (ACEA) indicates that advanced diagnostic tools are essential for maintaining the sophisticated systems in modern vehicles.
6.1. Bi-Directional Control and Component Testing
What is bi-directional control, and how can it be used for component testing on a 2011 BMW F20?
Bi-directional control allows the OBD2 scanner to send commands to the vehicle’s ECUs, enabling you to activate or deactivate specific components and observe their response. This can be used for component testing to verify whether a component is functioning correctly. For example, you can use bi-directional control to activate the fuel pump, cycle the ABS pump, or open and close the EGR valve. By observing the component’s response, you can determine whether it is working properly or needs to be replaced.
6.2. Service Resets and Adaptations
What service resets and adaptations can be performed on a 2011 BMW F20 using an OBD2 scanner?
Service resets and adaptations are procedures that reset or recalibrate certain systems after maintenance or repairs. Common service resets include oil service reset, brake pad replacement reset, and steering angle sensor reset. Adaptations involve recalibrating components to ensure they function correctly with the vehicle’s systems. Examples include throttle adaptation, transmission adaptation, and idle speed adaptation. These procedures help maintain optimal vehicle performance and prevent warning lights from illuminating.
6.3. Coding and Programming
What coding and programming options are available for a 2011 BMW F20, and what are the risks involved?
Coding and programming involve modifying the software settings of the vehicle’s ECUs to customize certain functions or enable new features. This can include things like enabling daytime running lights, changing the behavior of the automatic transmission, or adding aftermarket accessories. However, coding and programming can be risky, as incorrect modifications can damage the ECUs or cause the vehicle to malfunction. It is essential to have a thorough understanding of the vehicle’s systems and the coding process before attempting any modifications. Always back up the original ECU settings before making any changes, and use reliable coding tools and software.
7. Maintaining and Updating Your OBD2 Scanner
Why is it important to maintain and update your OBD2 scanner?
Maintaining and updating your OBD2 scanner is essential for ensuring it functions correctly and provides accurate diagnostic information. Regular maintenance includes cleaning the scanner, checking the cables and connectors, and storing it properly. Software updates are crucial for keeping the scanner current with the latest vehicle models, diagnostic protocols, and DTC definitions. An outdated scanner may not be able to communicate with newer vehicles or accurately diagnose certain issues. According to a report by the Automotive Aftermarket Industry Association (AAIA), regular maintenance and updates can extend the lifespan of diagnostic tools and improve their accuracy.
7.1. Software Updates and Compatibility
How do software updates affect the compatibility of your OBD2 scanner with a 2011 BMW F20?
Software updates enhance the compatibility of your OBD2 scanner with a 2011 BMW F20 by adding support for new diagnostic protocols, DTC definitions, and vehicle systems. These updates ensure that the scanner can accurately communicate with the vehicle’s ECUs and provide reliable diagnostic information. Without regular updates, the scanner may not be able to read certain codes or access specific functions. Check the scanner manufacturer’s website for software updates and follow the instructions to install them.
7.2. Troubleshooting Common Scanner Issues
What are some common issues that may arise with an OBD2 scanner, and how can they be resolved?
Several common issues may arise with an OBD2 scanner, including:
- Scanner Not Connecting to Vehicle: Check the OBD2 port for damage or debris, ensure the scanner is securely plugged in, and verify that the ignition is in the “ON” position.
- Scanner Not Reading Codes: Ensure the scanner is compatible with the vehicle, check for software updates, and verify that the vehicle’s ECUs are functioning correctly.
- Scanner Displaying Incorrect Information: Check for software updates, verify that the vehicle information is entered correctly, and ensure the scanner is not damaged.
- Scanner Freezing or Crashing: Restart the scanner, check for software updates, and contact the manufacturer for support if the issue persists.
- Faulty Cable or Connector: Inspect the cable and connector for damage, and replace them if necessary.
Troubleshooting these common issues can help you keep your OBD2 scanner functioning properly and ensure accurate diagnostics.
7.3. Proper Storage and Handling
How should you properly store and handle your OBD2 scanner to prolong its lifespan?
Proper storage and handling can significantly prolong the lifespan of your OBD2 scanner. Here are some tips for storing and handling your scanner:
- Store in a Clean, Dry Place: Store the scanner in a clean, dry environment away from extreme temperatures and humidity.
- Protect from Impact: Avoid dropping or exposing the scanner to impact, as this can damage the internal components.
- Keep Cables Organized: Neatly coil the cables and store them with the scanner to prevent damage.
- Clean Regularly: Clean the scanner with a soft, dry cloth to remove dust and debris.
- Avoid Chemical Exposure: Keep the scanner away from chemicals and solvents, as they can damage the plastic and electronic components.
Following these tips will help you keep your OBD2 scanner in good condition and ensure it provides reliable diagnostic information for years to come.
8. Common Problems Diagnosed with OBD2 on a 2011 BMW F20
What are some common automotive problems that can be diagnosed using an OBD2 scanner on a 2011 BMW F20?
Utilizing an OBD2 scanner on a 2011 BMW F20 enables the diagnosis of a variety of automotive issues. This includes problems related to the engine, transmission, ABS, and airbag systems. Detecting and resolving these issues early can prevent extensive damage and ensure peak vehicle performance. Research by the Transportation Research Board indicates that regular diagnostic checks can significantly reduce vehicle downtime and repair costs.
8.1. Engine Problems
What types of engine problems can be diagnosed using an OBD2 scanner?
An OBD2 scanner can help diagnose several engine-related problems, including:
- Misfires: Diagnosed by DTCs like P0300 (Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected) and P0301-P0306 (Cylinder Specific Misfire).
- Oxygen Sensor Issues: Diagnosed by DTCs related to oxygen sensor performance, such as P0131 (O2 Sensor Circuit Low Voltage Bank 1 Sensor 1) and P0171 (System Too Lean, Bank 1).
- MAF Sensor Problems: Diagnosed by DTCs like P0101 (Mass Air Flow Circuit Range/Performance) and P0102 (Mass Air Flow Circuit Low Input).
- Vacuum Leaks: Often indicated by lean codes like P0171 and P0174 (System Too Lean, Bank 2).
- Coolant Temperature Issues: Diagnosed by DTCs related to the coolant temperature sensor, such as P0116 (Coolant Temperature Circuit Range/Performance).
- VANOS Problems: Diagnosed by DTCs related to VANOS performance, such as P1017 (VANOS, Intake: Position Not Reached).
These issues can affect engine performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions, making it essential to diagnose and address them promptly.
8.2. Transmission Problems
How can an OBD2 scanner assist in diagnosing transmission issues?
An OBD2 scanner can assist in diagnosing transmission issues by reading transmission-specific DTCs and monitoring live data parameters. Common transmission-related DTCs include:
- P0700: Transmission Control System Malfunction.
- P0715: Input/Turbine Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction.
- P0720: Output Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction.
- P0730: Incorrect Gear Ratio.
In addition to reading DTCs, you can use the OBD2 scanner to monitor live data parameters such as transmission temperature, input speed, and output speed. These parameters can help you identify issues with the transmission’s performance and diagnose problems such as slipping gears or erratic shifting.
8.3. ABS and Airbag System Issues
What ABS and airbag system issues can be identified using an OBD2 scanner on a 2011 BMW F20?
An OBD2 scanner can identify ABS and airbag system issues by reading ABS and airbag-specific DTCs. Common ABS-related DTCs include:
- C0031: Left Front Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction.
- C0034: Right Front Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction.
- C0037: Left Rear Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction.
- C0040: Right Rear Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction.
Common airbag-related DTCs include:
- B0001: Driver Airbag Circuit Open.
- B0005: Passenger Airbag Circuit Open.
- B0010: Driver Side Impact Sensor Circuit Malfunction.
- B0015: Passenger Side Impact Sensor Circuit Malfunction.
Diagnosing these issues is critical for maintaining the safety of the vehicle and its occupants.
9. Enhancing Your DIY Car Repair Skills with OBD2 Data
How can using OBD2 data improve your DIY car repair skills?
Using OBD2 data can significantly enhance your DIY car repair skills by providing valuable insights into your vehicle’s systems and performance. By reading DTCs, monitoring live data, and performing component tests, you can accurately diagnose issues and make informed repair decisions. This can save you time and money compared to relying solely on guesswork or taking the vehicle to a mechanic. According to a study by the DIY Automotive Council, vehicle owners who use diagnostic tools like OBD2 scanners are more likely to perform their own maintenance and repairs, saving an average of $500 per year.
9.1. Building a Diagnostic Mindset
How can you develop a diagnostic mindset when using an OBD2 scanner for car repairs?
Developing a diagnostic mindset involves approaching car repairs with a systematic and logical approach. Start by gathering as much information as possible about the issue, including the symptoms, when the problem occurs, and any recent maintenance or repairs. Then, use the OBD2 scanner to read DTCs and monitor live data parameters. Analyze the data to identify potential causes and develop a plan for testing and repairs. Be patient and methodical, and always double-check your work before declaring the problem resolved.
9.2. Online Communities and Resources
What online communities and resources can support your DIY car repair efforts?
Several online communities and resources can support your DIY car repair efforts, including:
- Automotive Forums: Online forums like Bimmerforums and BMW forums offer discussions about specific vehicle models, diagnostic procedures, and repair tips.
- YouTube Channels: Numerous YouTube channels provide tutorials on car repair, diagnostics, and maintenance.
- Online Parts Retailers: Online parts retailers like ECS Tuning and FCP Euro offer technical information, diagrams, and repair guides for various vehicle models.
- Vehicle Service Manuals: Vehicle service manuals provide detailed information about the vehicle’s systems, diagnostic procedures, and repair instructions.
- OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN: Offers a wealth of information on OBD2 scanning, diagnostics, and car repair.
These resources can provide valuable support and guidance as you tackle DIY car repairs.
9.3. Knowing When to Seek Professional Help
When should you recognize the limitations of DIY car repair and seek professional help?
While using an OBD2 scanner can empower you to perform many car repairs yourself, it is essential to recognize the limitations of DIY repair and seek professional help when necessary. Situations that warrant professional assistance include:
- Complex Diagnostic Issues: If you are unable to diagnose the problem using the OBD2 scanner and online resources, it may be time to consult a professional mechanic.
- Safety-Critical Repairs: Repairs involving safety-critical systems like brakes, airbags, and steering should be performed by a qualified technician.
- Specialized Tools or Equipment: Some repairs require specialized tools or equipment that you may not have access to.
- Lack of Experience or Knowledge: If you are uncomfortable performing a particular repair or lack the necessary knowledge or experience, it is best to seek professional help.
Knowing when to seek professional help can prevent further damage to the vehicle and ensure your safety.
10. Future Trends in OBD2 Technology
What are the emerging trends in OBD2 technology?
The field of OBD2 technology is continually evolving, with several emerging trends shaping the future of vehicle diagnostics. These trends include enhanced wireless connectivity, integration with mobile apps, cloud-based diagnostics, and advanced data analytics. These advancements promise to make vehicle diagnostics more accessible, efficient, and informative. According to a market forecast by MarketsandMarkets, the OBD market is expected to grow significantly in the coming years, driven by the increasing complexity of vehicle systems and the demand for advanced diagnostic capabilities.
10.1. Wireless OBD2 Scanners and Bluetooth Connectivity
How are wireless OBD2 scanners and Bluetooth connectivity changing the landscape of vehicle diagnostics?
Wireless OBD2 scanners and Bluetooth connectivity are transforming vehicle diagnostics by providing greater flexibility and convenience. These scanners can communicate with smartphones, tablets, and laptops via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi, eliminating the need for cumbersome cables. This allows you to perform diagnostics from anywhere in or around the vehicle, and easily view and analyze the data on a larger screen. Many wireless OBD2 scanners also come with mobile apps that provide additional features, such as DTC lookup, live data graphing, and repair tips.
 Wireless OBD2 Scanner
Wireless OBD2 Scanner
Alt: Wireless OBD2 scanner connected to a 2011 BMW F20 via Bluetooth, showing diagnostic data on a smartphone.
10.2. Integration with Mobile Apps and Cloud-Based Diagnostics
How is the integration of OBD2 scanners with mobile apps and cloud-based diagnostics improving the diagnostic process?
The integration of OBD2 scanners with mobile apps and cloud-based diagnostics is revolutionizing the diagnostic process by providing access to a wealth of information and advanced features. Mobile apps can provide DTC lookup, live data graphing, repair tips, and access to online communities. Cloud-based diagnostics allow you to store and analyze diagnostic data in the cloud, share data with other technicians, and access remote diagnostic services. These advancements make vehicle diagnostics more accessible, efficient, and informative.
10.3. AI and Machine Learning in Vehicle Diagnostics
What role will artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning play in future vehicle diagnostics?
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are poised to play a significant role in future vehicle diagnostics by enabling more accurate and efficient problem-solving. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of diagnostic data to identify patterns, predict failures, and recommend repairs. Machine learning can improve the accuracy of diagnostic models over time, based on real-world data. These technologies can also be used to develop virtual diagnostic assistants that guide technicians through complex diagnostic procedures. As AI and machine learning continue to advance, they will transform the way vehicles are diagnosed and repaired.
Understanding the 2011 F20 OBD2 CAN-Bus system for BMW opens up a world of possibilities for vehicle diagnostics and maintenance. By selecting the right OBD2 scanner, learning how to connect and use it effectively, and understanding how to interpret diagnostic data, you can take control of your vehicle’s health and save time and money on repairs. Remember, OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN is here to support you with comprehensive information and resources for all your OBD2 needs.
Do you want to understand more about how to use OBD2 scanners and improve your car repair skills? Contact us today for a consultation!
Address: 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States
WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
Website: OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
FAQ: Understanding OBD2 and Your 2011 BMW F20
Q1: What is an OBD2 scanner?
An OBD2 scanner is a diagnostic tool used to read data from a vehicle’s On-Board Diagnostics system. It connects to the OBD2 port and retrieves diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and live data.
Q2: How do I read OBD2 codes on my 2011 BMW F20?
Connect the OBD2 scanner to the OBD2 port, turn the ignition to the “ON” position, and follow the scanner’s instructions to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) from the vehicle’s computer.
Q3: What are the common car problems diagnosed via OBD2?
Common issues include engine misfires, oxygen sensor failures, transmission problems, and ABS/airbag system faults.
**Q4: What