The 2013 Mazda Obd2 Protocol is the standardized system your car uses to communicate diagnostic information, which you can access through a scan tool; you can retrieve valuable insights into your vehicle’s performance and health. At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we are committed to offering expertise and support for your automotive diagnostic needs. This guide provides a comprehensive understanding of the OBD2 protocol for 2013 Mazda vehicles, helping you to use this information effectively and optimize your vehicle’s functionality.
Contents
- 1. Understanding OBD2 Protocols
- 1.1. Key Functions of OBD2
- 1.2. OBD2 Communication Protocols
- 1.3. How to Determine the Protocol
- 2. 2013 Mazda OBD2 Protocol Details
- 2.1. Understanding the CAN Protocol
- 2.2. Locating the DLC in a 2013 Mazda
- 2.3. Required Pins for CAN Protocol in 2013 Mazda
- 3. Using an OBD2 Scanner with a 2013 Mazda
- 3.1. Step-by-Step Guide to Using an OBD2 Scanner
- 3.2. Common OBD2 Codes for Mazda Vehicles
- 3.3. Tips for Effective Scanning
- 4. Advanced Diagnostic Procedures
- 4.1. Interpreting Live Data
- 4.2. Performing Component Tests
- 4.3. When to Seek Professional Help
- 5. Benefits of Understanding Your Mazda’s OBD2 Protocol
- 5.1. Reducing Repair Costs
- 5.2. Improving Fuel Efficiency
- 5.3. Extending Vehicle Lifespan
- 6. Common Misconceptions About OBD2 Protocols
- 6.1. Debunking the Myths
- 6.2. Best Practices for Using OBD2
- 7. Future Trends in OBD Technology
- 7.1. OBD III and Beyond
- 7.2. Staying Updated with OBD Innovations
- 8. Troubleshooting Common OBD2 Scanner Issues
- 8.1. Common Fixes and Solutions
- 8.2. When to Contact Support
- 9. Maximizing the Value of OBD2 Information
- 9.1. Integrating OBD2 with Routine Maintenance
- 9.2. Using OBD2 for Preventative Care
- 10. Leveraging OBD2 Data for Vehicle Optimization
- 10.1. Fine-Tuning for Fuel Economy
- 10.2. Enhancing Performance Through OBD2 Insights
1. Understanding OBD2 Protocols
OBD2 (On-Board Diagnostics II) is a standardized system used in vehicles to monitor and diagnose various systems, and it is crucial for understanding how your 2013 Mazda communicates diagnostic information.
- What is OBD2? OBD2 is a standardized system implemented in vehicles to monitor engine performance, emissions, and other critical systems. It provides a way for technicians and vehicle owners to access diagnostic information.
- Why is it important? It is important because it enables early detection of problems, reduces emissions, and helps maintain optimal vehicle performance. According to the EPA, OBD2 systems have significantly contributed to cleaner air by ensuring vehicles meet emission standards.
- OBD2 Compliance: Since 1996, all cars and light trucks sold in the United States are required to be OBD-II compliant. The European Union OBD legislation is somewhat more complicated.
1.1. Key Functions of OBD2
The OBD2 system continuously monitors various vehicle parameters to ensure they are within acceptable ranges. When a problem is detected, the system stores a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) that can be accessed using an OBD2 scanner.
- Monitoring Engine Performance: OBD2 monitors engine components such as oxygen sensors, fuel injectors, and the catalytic converter to ensure they are functioning correctly.
- Emission Control: OBD2 monitors the vehicle’s emissions to ensure they meet regulatory standards, helping to reduce air pollution. A study by the California Air Resources Board (CARB) showed that effective OBD2 systems significantly reduce vehicle emissions.
- Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): OBD2 stores DTCs when a fault is detected, providing valuable information for diagnosing and repairing vehicle problems.
- Data Accessibility: OBD2 provides a standardized way to access vehicle data, making it easier for technicians and vehicle owners to diagnose and repair issues.
1.2. OBD2 Communication Protocols
OBD2 uses several communication protocols to transmit data between the vehicle and the diagnostic tool. These protocols ensure that different vehicles and scan tools can communicate effectively.
- J1850 PWM (Pulse Width Modulation): Used primarily by Ford vehicles. It communicates data by varying the width of a pulse signal.
- J1850 VPW (Variable Pulse Width): Used primarily by General Motors vehicles. It communicates data by varying the width of a pulse signal, similar to PWM but with different voltage levels.
- ISO9141-2: Commonly used in European and Asian vehicles. It uses an asynchronous serial communication protocol.
- ISO14230-4 (Keyword Protocol 2000): An updated version of ISO9141-2, also used in European and Asian vehicles. It includes additional features for faster communication and more detailed diagnostics.
- ISO15765-4/SAE J2480 (CAN – Controller Area Network): The most modern protocol, used in all vehicles sold in the US since 2008. CAN is a robust and efficient communication protocol that allows multiple ECUs (Electronic Control Units) to communicate with each other.
1.3. How to Determine the Protocol
You can usually determine the protocol your vehicle uses by examining the Diagnostic Link Connector (DLC) pinout.
- Location of DLC: The DLC is typically located in the passenger or driver’s compartment, within easy reach of the driver’s seat. According to SAE J1962, it should be easily accessible.
- Pinout Examination: By examining the pins present in the DLC, you can identify the protocol used by your vehicle.
- Connector Pin Configuration:The connector should have pins 4 (Chassis Ground), 5 (Signal Ground), and 16 (Battery Positive), along with specific pins for each protocol.
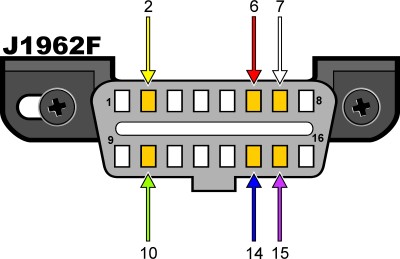 J1962F OBDII connector pinout
J1962F OBDII connector pinout
- PWM: The connector must have pins 2, 4, 5, 10, and 16.
- VPW: The connector must have pins 2, 4, 5, and 16, but not 10.
- ISO: The connector must have pins 4, 5, 7, and 16. Pin 15 may or may not be present.
- CAN: The connector must have pins 4, 5, 6, 14, and 16.
2. 2013 Mazda OBD2 Protocol Details
For 2013 Mazda vehicles, the OBD2 protocol primarily used is ISO15765-4/SAE J2480 (CAN).
- Why CAN? CAN protocol is chosen for its robustness, speed, and ability to handle a large amount of data, which is essential for modern vehicle diagnostics.
- Benefits of CAN: The CAN protocol allows for faster communication between the vehicle’s ECUs and the diagnostic tool, providing more detailed and accurate diagnostic information.
- Backward Compatibility: While 2013 Mazdas primarily use CAN, they are also designed to be backward compatible with older protocols to support older diagnostic tools.
2.1. Understanding the CAN Protocol
The CAN protocol is a sophisticated communication system that allows various electronic control units (ECUs) in the vehicle to communicate with each other without a host computer.
- How CAN Works: CAN uses a two-wire system where data is transmitted in messages or frames. Each message has an identifier that indicates the content’s priority.
- Key Features of CAN:
- High-Speed Communication: CAN allows for high-speed data transmission, enabling real-time monitoring and diagnostics.
- Error Detection: CAN includes robust error detection mechanisms, ensuring data integrity. According to Bosch, the CAN protocol’s error detection capabilities significantly reduce the risk of data corruption.
- Priority-Based Communication: CAN messages are prioritized, ensuring critical data is transmitted first.
2.2. Locating the DLC in a 2013 Mazda
The DLC is typically located inside the cabin, making it easy to access for diagnostic purposes.
- Typical Locations: The DLC is usually found under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Specific Locations: In 2013 Mazda vehicles, the DLC is often located to the left of the steering column or in the center console area.
- Easy Access: The DLC is designed to be easily accessible, allowing for quick connection of diagnostic tools.
2.3. Required Pins for CAN Protocol in 2013 Mazda
To ensure proper communication with a 2013 Mazda using the CAN protocol, the DLC must have specific pins populated.
- Essential Pins: The required pins for CAN communication are 4 (Chassis Ground), 5 (Signal Ground), 6 (CAN High), 14 (CAN Low), and 16 (Battery Positive).
- Ensuring Proper Connection: Before connecting an OBD2 scanner, verify that these pins are present and in good condition to ensure a reliable connection.
3. Using an OBD2 Scanner with a 2013 Mazda
Using an OBD2 scanner with your 2013 Mazda is a straightforward process that can provide valuable insights into your vehicle’s health.
- Selecting a Compatible Scanner: Ensure that the OBD2 scanner supports the CAN protocol, which is the primary protocol used by 2013 Mazda vehicles.
- Connecting the Scanner: Locate the DLC in your 2013 Mazda and plug the OBD2 scanner into the connector.
3.1. Step-by-Step Guide to Using an OBD2 Scanner
Follow these steps to effectively use an OBD2 scanner with your 2013 Mazda:
- Step 1: Ignition: Turn the ignition to the “ON” position without starting the engine. This provides power to the vehicle’s electrical systems without running the engine.
- Step 2: Connect Scanner: Plug the OBD2 scanner into the DLC. Ensure it is securely connected.
- Step 3: Power On: Turn on the OBD2 scanner. Most scanners will power on automatically once connected.
- Step 4: Read Codes: Follow the scanner’s instructions to read the Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) stored in the vehicle’s computer.
- Step 5: Interpret Codes: Consult the scanner’s manual or an online database to interpret the meaning of the DTCs. Websites like OBD-Codes.com offer detailed information on OBD2 codes.
- Step 6: Clear Codes (Optional): After addressing the issue, you can clear the DTCs using the scanner. Be cautious when clearing codes, as it may erase valuable diagnostic data.
 OBD2 scanner
OBD2 scanner
3.2. Common OBD2 Codes for Mazda Vehicles
Certain OBD2 codes are more commonly encountered in Mazda vehicles. Understanding these codes can help you diagnose and address issues more efficiently.
| Code | Description | Possible Causes |
|---|---|---|
| P0171 | System Too Lean (Bank 1) | Vacuum leak, faulty oxygen sensor, fuel injector issue |
| P0300 | Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected | Faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, fuel injectors |
| P0401 | Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Flow Insufficient Detected | Clogged EGR valve, faulty EGR sensor, vacuum leaks |
| P0420 | Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1) | Faulty catalytic converter, exhaust leaks, oxygen sensor issues |
| P0507 | Idle Air Control (IAC) System RPM Higher Than Expected | Vacuum leak, faulty IAC valve, throttle body issues |
| B1000 | ECU Malfunction | ECU needs to be reprogrammed or replaced |
| U0100 | Lost Communication with ECM/PCM | Wiring problems, damaged computer |
3.3. Tips for Effective Scanning
To ensure you get the most accurate and useful information from your OBD2 scanner, keep these tips in mind:
- Read the Manual: Familiarize yourself with your scanner’s features and functions by reading the manual.
- Ensure Proper Connection: Make sure the scanner is securely connected to the DLC to avoid communication errors.
- Record Codes: Write down any DTCs you retrieve, along with the order they appear.
- Research Codes: Use reliable sources to research the meaning of the DTCs and potential causes.
- Address Issues Promptly: Address any identified issues as soon as possible to prevent further damage to your vehicle.
- Regular Checks: Perform regular OBD2 scans to monitor your vehicle’s health and catch potential problems early.
4. Advanced Diagnostic Procedures
For more complex issues, advanced diagnostic procedures may be necessary. These procedures often require specialized tools and expertise.
- Live Data Monitoring: Many OBD2 scanners can display live data from the vehicle’s sensors. This can be useful for identifying intermittent problems or monitoring sensor performance.
- Component Testing: Some OBD2 scanners have the ability to perform component testing, such as activating fuel injectors or testing the EGR valve.
- Software Updates: Ensure your OBD2 scanner has the latest software updates to support the latest vehicle models and diagnostic capabilities.
4.1. Interpreting Live Data
Live data monitoring can provide valuable insights into your vehicle’s performance.
- What is Live Data? Live data refers to real-time information from the vehicle’s sensors, such as engine RPM, coolant temperature, and oxygen sensor readings.
- How to Use Live Data: By monitoring live data, you can identify anomalies or deviations from normal operating parameters. For example, an unusually high coolant temperature may indicate a cooling system problem.
- Key Parameters to Monitor: Important parameters to monitor include:
- Engine RPM: Indicates the speed at which the engine is running.
- Coolant Temperature: Indicates the engine’s operating temperature.
- Oxygen Sensor Readings: Indicates the performance of the oxygen sensors and the air-fuel mixture.
- Fuel Trim: Indicates the adjustments the engine control unit (ECU) is making to the fuel mixture.
- Vehicle Speed: Measures how fast your car is traveling at any given moment
4.2. Performing Component Tests
Component tests allow you to directly test the functionality of specific components.
- What are Component Tests? Component tests involve using the OBD2 scanner to activate or monitor specific components, such as fuel injectors, EGR valves, or oxygen sensors.
- How to Perform Component Tests: Follow the scanner’s instructions to initiate the component test. The scanner will typically provide feedback on the component’s performance.
- Benefits of Component Tests: Component tests can help you isolate problems to specific components, reducing the time and effort required for diagnosis.
4.3. When to Seek Professional Help
While OBD2 scanners can be a valuable tool for diagnosing vehicle problems, there are times when it is best to seek professional help.
- Complex Issues: If you are unable to diagnose the problem or if the problem is complex, it is best to consult a qualified technician.
- Lack of Experience: If you lack experience in automotive repair, attempting to fix complex issues yourself may lead to further damage.
- Specialized Tools: Some repairs require specialized tools or equipment that are not available to the average vehicle owner.
- Safety Concerns: Certain repairs, such as those involving the fuel system or airbags, can be dangerous and should only be performed by trained professionals.
5. Benefits of Understanding Your Mazda’s OBD2 Protocol
Understanding your 2013 Mazda’s OBD2 protocol offers numerous benefits, helping you maintain your vehicle and save money.
- Early Problem Detection: By regularly scanning your vehicle, you can detect problems early, before they become more severe and costly to repair.
- Informed Decision Making: Knowing the DTCs and their meanings allows you to make informed decisions about repairs, avoiding unnecessary services.
- Cost Savings: Diagnosing and addressing issues yourself can save you money on diagnostic fees at a repair shop.
- Improved Vehicle Performance: Addressing issues promptly can help maintain optimal vehicle performance and fuel efficiency.
- Increased Vehicle Lifespan: Regular maintenance and timely repairs can extend the lifespan of your vehicle.
5.1. Reducing Repair Costs
One of the most significant benefits of understanding your Mazda’s OBD2 protocol is the ability to reduce repair costs.
- Accurate Diagnosis: By accurately diagnosing the problem yourself, you can avoid unnecessary repairs or replacements.
- DIY Repairs: Many simple repairs can be performed yourself with the help of online resources and tutorials.
- Negotiating with Mechanics: Armed with diagnostic information, you can negotiate with mechanics and ensure you are only paying for necessary repairs.
5.2. Improving Fuel Efficiency
Addressing issues identified by the OBD2 system can also improve your vehicle’s fuel efficiency.
- Optimal Engine Performance: A well-maintained engine operates more efficiently, resulting in better fuel economy.
- Emission Control: Addressing emission-related issues can help your vehicle meet emission standards and improve fuel efficiency.
- Regular Maintenance: Regular maintenance, such as replacing spark plugs and air filters, can also improve fuel efficiency. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, keeping your tires properly inflated can improve gas mileage by up to 3%.
5.3. Extending Vehicle Lifespan
Regularly monitoring your vehicle’s health with an OBD2 scanner can help extend its lifespan.
- Preventative Maintenance: By identifying and addressing issues early, you can prevent more significant problems from developing.
- Timely Repairs: Timely repairs can prevent further damage to your vehicle’s components, extending its lifespan.
- Consistent Performance: Consistent maintenance ensures your vehicle performs reliably for years to come.
6. Common Misconceptions About OBD2 Protocols
There are several common misconceptions about OBD2 protocols that can lead to confusion and incorrect diagnostic practices.
- Misconception 1: All OBD2 Scanners Are Created Equal: While all OBD2 scanners can read basic DTCs, they vary widely in terms of features, compatibility, and accuracy.
- Misconception 2: Clearing DTCs Fixes the Problem: Clearing DTCs only erases the code from the vehicle’s computer. It does not fix the underlying issue.
- Misconception 3: OBD2 Scanners Can Fix Problems: OBD2 scanners are diagnostic tools, not repair tools. They can identify problems but cannot fix them.
- Misconception 4: OBD2 Covers All Vehicle Systems: While OBD2 covers many critical systems, it does not monitor every aspect of the vehicle.
- Misconception 5: OBD2 is Only for Professionals: While professionals use OBD2 scanners, they are also accessible and beneficial for vehicle owners.
6.1. Debunking the Myths
Let’s address these misconceptions to provide a clearer understanding of OBD2 protocols.
- OBD2 Scanner Quality: Invest in a quality OBD2 scanner that is compatible with your vehicle and offers the features you need.
- DTCs and Repairs: Always address the underlying issue that caused the DTC, rather than just clearing the code.
- OBD2 Scanner Limitations: Understand the limitations of OBD2 scanners and when to seek professional help.
- Comprehensive Vehicle Monitoring: Be aware that OBD2 is just one aspect of vehicle maintenance and does not cover all systems.
- OBD2 for Vehicle Owners: Vehicle owners can benefit from using OBD2 scanners for basic diagnostics and preventative maintenance.
6.2. Best Practices for Using OBD2
To ensure you are using OBD2 effectively, follow these best practices:
- Read the Manual: Familiarize yourself with your OBD2 scanner’s features and functions by reading the manual.
- Use Reliable Resources: Consult reliable sources, such as manufacturer’s websites or trusted online databases, for information on DTCs and repair procedures.
- Document Findings: Keep a record of DTCs, live data readings, and any repairs you perform.
- Regularly Scan Your Vehicle: Perform regular OBD2 scans to monitor your vehicle’s health and catch potential problems early.
- Seek Professional Help When Needed: Don’t hesitate to seek professional help when you encounter complex issues or lack the experience to perform repairs.
7. Future Trends in OBD Technology
OBD technology is continuously evolving to meet the demands of modern vehicles.
- Advanced Diagnostics: Future OBD systems will offer more advanced diagnostic capabilities, including predictive maintenance and remote diagnostics.
- Integration with Mobile Devices: OBD systems will increasingly integrate with mobile devices, allowing vehicle owners to access diagnostic information and perform basic functions from their smartphones.
- Enhanced Cybersecurity: As vehicles become more connected, cybersecurity will be a growing concern. Future OBD systems will incorporate enhanced security measures to protect against hacking and data breaches.
7.1. OBD III and Beyond
The future of OBD technology includes more sophisticated systems and features.
- OBD III: OBD III is a proposed standard that would require vehicles to automatically report emission-related problems to regulatory agencies.
- Remote Diagnostics: Remote diagnostics will allow technicians to diagnose and repair vehicles remotely, reducing the need for physical visits to a repair shop.
- Predictive Maintenance: Predictive maintenance will use data from the OBD system to predict when components are likely to fail, allowing for proactive maintenance and preventing breakdowns.
7.2. Staying Updated with OBD Innovations
To stay informed about the latest innovations in OBD technology, follow these tips:
- Industry Publications: Read industry publications and websites that cover OBD technology and automotive diagnostics.
- Conferences and Trade Shows: Attend conferences and trade shows to learn about new products and technologies.
- Online Forums: Participate in online forums and communities to share information and learn from other professionals and enthusiasts.
- Training Programs: Attend training programs and workshops to enhance your knowledge and skills in OBD diagnostics.
8. Troubleshooting Common OBD2 Scanner Issues
Even with the best equipment and knowledge, you may encounter issues when using an OBD2 scanner. Here are some common problems and how to troubleshoot them:
- Problem 1: Scanner Won’t Connect:
- Possible Causes: Loose connection, faulty DLC, scanner incompatibility.
- Troubleshooting Steps: Ensure the scanner is securely connected to the DLC, check the DLC for damage or corrosion, verify that the scanner is compatible with your vehicle.
- Problem 2: Unable to Read Codes:
- Possible Causes: Ignition not in the “ON” position, scanner malfunction, vehicle communication problem.
- Troubleshooting Steps: Ensure the ignition is in the “ON” position without starting the engine, restart the scanner, check for communication errors in the scanner’s settings.
- Problem 3: Incorrect Codes:
- Possible Causes: Scanner malfunction, incorrect vehicle selection, data corruption.
- Troubleshooting Steps: Verify that the scanner is set to the correct vehicle model, update the scanner’s software, try a different scanner.
- Problem 4: Live Data Not Displaying:
- Possible Causes: Scanner incompatibility, sensor malfunction, communication problem.
- Troubleshooting Steps: Check the scanner’s compatibility with live data features, verify that the sensors are functioning correctly, check for communication errors.
8.1. Common Fixes and Solutions
Here are some quick fixes for common OBD2 scanner issues:
- Check the Connection: Ensure the scanner is securely connected to the DLC and that the DLC is in good condition.
- Restart the Scanner: Restarting the scanner can often resolve communication errors and other issues.
- Update the Software: Ensure the scanner has the latest software updates to support the latest vehicle models and diagnostic capabilities.
- Try a Different Scanner: If you continue to experience problems, try using a different scanner to rule out a hardware issue.
- Consult the Manual: Refer to the scanner’s manual for troubleshooting tips and specific instructions.
8.2. When to Contact Support
If you are unable to resolve the issue on your own, it may be necessary to contact the scanner manufacturer’s support team.
- Hardware Issues: If you suspect a hardware problem with the scanner, contact the manufacturer for assistance.
- Software Bugs: If you encounter software bugs or errors, report them to the manufacturer for resolution.
- Compatibility Issues: If you are unsure whether the scanner is compatible with your vehicle, contact the manufacturer for clarification.
9. Maximizing the Value of OBD2 Information
To truly maximize the value of the information you gain from your OBD2 scanner, it’s essential to integrate this data into a comprehensive vehicle maintenance plan. This involves not only identifying problems but also proactively addressing them to prevent future issues.
- Creating a Maintenance Schedule: Develop a maintenance schedule based on the diagnostic insights from your OBD2 scans. This schedule should include regular checks for common issues, such as those related to emissions, engine performance, and sensor functionality.
- Prioritizing Repairs: Learn to prioritize repairs based on the severity and potential impact of each issue. Address critical problems immediately to avoid further damage, and schedule less urgent repairs for a later date.
- Keeping Detailed Records: Maintain detailed records of all OBD2 scans, diagnostic codes, and repair work performed. This information can be invaluable for tracking your vehicle’s history and identifying recurring problems.
9.1. Integrating OBD2 with Routine Maintenance
Integrating OBD2 information into your routine maintenance practices can significantly enhance your ability to keep your vehicle in top condition.
- Regular Scanning: Incorporate regular OBD2 scans into your maintenance routine, performing scans at least once a month or whenever you notice unusual behavior in your vehicle.
- Cross-Referencing with Maintenance Tasks: Use OBD2 data to inform and enhance your regular maintenance tasks. For example, if an OBD2 scan reveals an issue with the oxygen sensor, address it during your next scheduled tune-up.
- Adjusting Maintenance Intervals: Adjust your maintenance intervals based on the insights you gain from OBD2 scans. If you frequently encounter certain issues, you may need to increase the frequency of related maintenance tasks.
9.2. Using OBD2 for Preventative Care
OBD2 data can be a powerful tool for preventative care, allowing you to identify and address potential problems before they escalate.
- Monitoring Key Parameters: Use live data monitoring to keep an eye on key vehicle parameters, such as engine temperature, fuel trim, and oxygen sensor readings. Deviations from normal values can indicate underlying problems that need attention.
- Addressing Minor Issues Promptly: Don’t ignore minor issues identified by your OBD2 scanner. Addressing them promptly can prevent them from turning into major problems down the road.
- Staying Ahead of Potential Failures: Use OBD2 data to anticipate potential failures and take proactive steps to prevent them. For example, if you notice signs of wear on a particular component, consider replacing it before it fails completely.
10. Leveraging OBD2 Data for Vehicle Optimization
Beyond diagnostics and maintenance, OBD2 data can also be used to optimize your vehicle’s performance and efficiency. By carefully analyzing and interpreting this data, you can make informed decisions about how to fine-tune your vehicle for maximum results.
- Improving Fuel Efficiency: Use OBD2 data to identify and address issues that may be affecting your vehicle’s fuel efficiency. This includes monitoring oxygen sensor readings, fuel trim, and other parameters related to fuel consumption.
- Enhancing Engine Performance: Use OBD2 data to fine-tune your engine for optimal performance. This may involve adjusting the air-fuel mixture, ignition timing, and other settings to maximize power and responsiveness.
- Optimizing Driving Habits: Analyze OBD2 data to identify and correct inefficient driving habits, such as excessive idling, hard acceleration, and aggressive braking.
10.1. Fine-Tuning for Fuel Economy
Improving your vehicle’s fuel economy is not only good for your wallet but also beneficial for the environment. OBD2 data can help you identify specific areas where you can make improvements.
- Monitoring Oxygen Sensor Readings: Keep an eye on your oxygen sensor readings to ensure that your engine is running at the optimal air-fuel mixture. Adjustments may be necessary if the readings are consistently too high or too low.
- Adjusting Fuel Trim: Use fuel trim data to fine-tune the amount of fuel being injected into your engine. Minor adjustments can often result in significant improvements in fuel economy.
- Checking for Vacuum Leaks: Vacuum leaks can disrupt your engine’s air-fuel mixture and reduce fuel efficiency. Use OBD2 data to check for vacuum leaks and address them promptly.
10.2. Enhancing Performance Through OBD2 Insights
OBD2 data can also be used to enhance your vehicle’s performance, allowing you to unlock its full potential.
- Optimizing Air-Fuel Mixture: Fine-tuning your engine’s air-fuel mixture can result in significant improvements in power and responsiveness. Use OBD2 data to monitor the mixture and make adjustments as needed.
- Adjusting Ignition Timing: Adjusting your ignition timing can also enhance your engine’s performance. Experiment with different timing settings to find the optimal balance between power and fuel efficiency.
- Monitoring Engine Temperature: Keeping your engine at the optimal temperature is essential for peak performance. Use OBD2 data to monitor your engine temperature and address any cooling issues promptly.
Understanding the 2013 Mazda OBD2 protocol empowers you to take control of your vehicle’s diagnostics and maintenance. By using an OBD2 scanner, interpreting the data, and following best practices, you can ensure your Mazda runs smoothly and efficiently for years to come. Regular OBD2 scans are essential for maintaining your 2013 Mazda, helping you detect and address issues early, reduce repair costs, and improve vehicle performance.
For further assistance or to explore our range of OBD2 scanners and diagnostic services, visit us at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN or contact us at +1 (641) 206-8880. Our address is 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States. Don’t wait until a small issue becomes a big problem – reach out today for expert guidance on using OBD2 technology to keep your 2013 Mazda running at its best.