Introduction to 4R44E Transmission OBD2 Testing
4r44e Transmission Obd2 Test is crucial for diagnosing and addressing issues in your vehicle’s automatic transmission system. The On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD2) system allows automotive technicians and car owners to retrieve valuable data, error codes, and performance metrics from a vehicle’s computer. Understanding the intricacies of the 4R44E transmission and how to leverage OBD2 testing can save time and money while ensuring optimal vehicle performance. By using the services provided by OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, you can improve your diagnostic skills, access reliable repair information, and make informed decisions regarding your vehicle’s maintenance. Explore further solutions with transmission diagnostic tools, identify possible causes of transmission failure, and understand transmission control module programming.
Contents
- Introduction to 4R44E Transmission OBD2 Testing
- 1. Understanding the 4R44E Transmission
- 1.1 Key Features and Specifications
- 1.2 Common Issues with the 4R44E Transmission
- 1.3 Preventative Maintenance for the 4R44E Transmission
- 2. Introduction to OBD2 Testing
- 2.1 Understanding OBD2 Codes
- 2.2 Essential Tools for OBD2 Testing
- 2.3 Step-by-Step Guide to Performing an OBD2 Test
- 3. Diagnosing Common 4R44E Transmission Problems with OBD2
- 3.1 Slipping Gears
- 3.2 Rough Shifting
- 3.3 Overdrive Issues
- 3.4 Torque Converter Problems
- 3.5 Electrical Issues
- 4. Advanced OBD2 Testing Techniques
- 4.1 Live Data Streaming
- 4.2 Graphing and Data Logging
- 4.3 Using Bi-Directional Control
- 5. Case Studies: Real-World 4R44E Transmission Diagnostics
- 5.1 Case Study 1: Diagnosing a P0741 Code
- 5.2 Case Study 2: Resolving Rough Shifting
- 5.3 Case Study 3: Addressing Overdrive Issues
- 6. Optimizing 4R44E Transmission Performance
- 6.1 Performance Upgrades
- 6.2 Driving Techniques
- 6.3 Fluid Management
- 7. When to Seek Professional Help
- 7.1 Complex Diagnostic Issues
- 7.2 Major Repairs
- 7.3 Safety Concerns
- 8. The Future of OBD2 Testing
- 8.1 Enhanced Diagnostic Capabilities
- 8.2 Integration with Mobile Devices
- 8.3 Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
- 9. Resources for Further Learning
- 9.1 Online Forums and Communities
- 9.2 Technical Manuals and Guides
- 9.3 Training Programs and Certifications
- 10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- 10.1 What is the 4R44E transmission?
- 10.2 How does OBD2 testing help diagnose transmission problems?
- 10.3 What are common issues with the 4R44E transmission?
- 10.4 What maintenance can prevent these issues?
- 10.5 How do I interpret OBD2 codes?
- 10.6 What tools are needed for OBD2 testing?
- 10.7 What is live data streaming and how does it help?
- 10.8 When should I seek professional help for transmission problems?
- 10.9 How is OBD2 technology evolving?
- 10.10 What are some performance upgrades for the 4R44E transmission?
- Conclusion:
1. Understanding the 4R44E Transmission
What is the 4R44E transmission and why is it important to understand its workings?
The 4R44E transmission is an electronically controlled four-speed automatic transmission used primarily in Ford vehicles, such as the Ranger and Explorer, during the late 1990s and early 2000s. This transmission is known for its durability and reliability, but like any mechanical system, it can experience issues over time. Understanding the 4R44E transmission is vital because it allows vehicle owners and technicians to diagnose problems accurately and efficiently.
1.1 Key Features and Specifications
What are the main features and technical specifications of the 4R44E transmission?
The 4R44E transmission has specific features and specifications that make it essential to the vehicles it supports. These features ensure smooth operation and efficient power delivery.
-
Four-Speed Automatic: The transmission offers four forward gears and one reverse gear, providing a suitable range of ratios for varying driving conditions.
-
Electronic Control: Electronically controlled shifting improves shift quality and allows the vehicle’s computer to adapt to driving conditions.
-
Torque Converter: The torque converter multiplies engine torque, providing enhanced low-speed acceleration.
-
Gear Ratios:
- First Gear: 2.47:1
- Second Gear: 1.47:1
- Third Gear: 1.00:1
- Fourth Gear: 0.75:1
- Reverse Gear: 2.09:1
-
Vehicle Applications: Ford Ranger, Ford Explorer, Mazda B-Series Trucks.
Knowing these specifications helps in diagnosing issues, as deviations from these norms can indicate potential problems within the transmission.
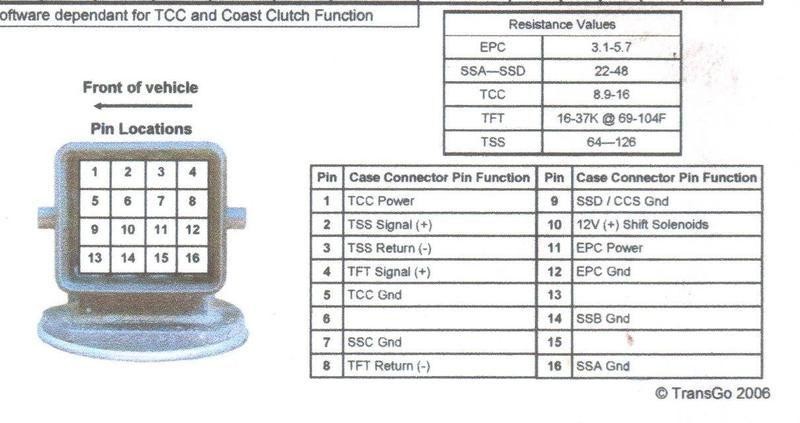 4r44e transmission 16 pin plug
4r44e transmission 16 pin plug
1.2 Common Issues with the 4R44E Transmission
What are the common problems that can occur with the 4R44E transmission?
Several common issues can plague the 4R44E transmission. Recognizing these problems early can prevent more extensive damage and costly repairs.
- Slipping Gears: This occurs when the transmission fails to maintain the correct gear, leading to a loss of power and erratic shifting.
- Rough Shifting: Harsh or jerky gear changes can indicate problems with the solenoids or valve body.
- Overdrive Issues: Problems with engaging or disengaging overdrive can lead to poor fuel economy and reduced performance.
- Torque Converter Problems: Issues with the torque converter can cause stalling, vibrations, or complete loss of drive.
- Fluid Leaks: Transmission fluid leaks can lead to low fluid levels, causing overheating and transmission damage.
- Complete Failure: In severe cases, the transmission may fail completely, requiring a rebuild or replacement.
1.3 Preventative Maintenance for the 4R44E Transmission
What maintenance steps can prevent common issues with the 4R44E transmission?
Preventive maintenance is key to prolonging the life and performance of the 4R44E transmission. Regular maintenance can help identify and address minor issues before they escalate into major problems.
- Regular Fluid Checks: Check the transmission fluid level and condition regularly. Low or dirty fluid can cause significant damage.
- Fluid and Filter Changes: Change the transmission fluid and filter every 30,000 to 50,000 miles, depending on driving conditions.
- Inspect for Leaks: Regularly inspect the transmission for any signs of leaks. Address leaks promptly to prevent fluid loss.
- Proper Driving Habits: Avoid harsh acceleration and frequent heavy loads, which can strain the transmission.
- Professional Inspections: Have the transmission professionally inspected during routine vehicle maintenance to identify potential issues.
2. Introduction to OBD2 Testing
What is OBD2 testing and how does it help in diagnosing transmission problems?
OBD2 testing is a standardized system used in modern vehicles to monitor and diagnose various components, including the transmission. The OBD2 system provides valuable data and diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) that can help pinpoint the source of transmission problems. By connecting an OBD2 scanner to the vehicle’s diagnostic port, technicians and vehicle owners can access this information and make informed decisions about repairs. The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) standardized OBD2 in the mid-1990s to ensure consistent diagnostic practices across different vehicle manufacturers.
2.1 Understanding OBD2 Codes
How can you interpret OBD2 codes related to the 4R44E transmission?
OBD2 codes are alphanumeric identifiers that indicate specific problems within the vehicle’s systems. Understanding how to interpret these codes is crucial for diagnosing transmission issues accurately.
- P0700 – Transmission Control System Malfunction: This is a general code indicating a problem within the transmission control system.
- P0715 – Input/Turbine Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction: This code indicates a problem with the input speed sensor, which monitors the transmission’s input speed.
- P0720 – Output Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction: This code indicates a problem with the output speed sensor, which monitors the transmission’s output speed.
- P0740 – Torque Converter Clutch Circuit Malfunction: This code suggests a problem with the torque converter clutch, which can affect fuel economy and performance.
- P0741 – Torque Converter Clutch Circuit Performance or Stuck Off: Indicates the torque converter clutch is not engaging or performing as expected.
- P0743 – Torque Converter Clutch Circuit Electrical: This code suggests an electrical issue within the torque converter clutch circuit.
- P0750 – Shift Solenoid A Malfunction: This code indicates a problem with shift solenoid A, which controls the shifting of gears.
- P0755 – Shift Solenoid B Malfunction: This code indicates a problem with shift solenoid B, which controls the shifting of gears.
- P0760 – Shift Solenoid C Malfunction: This code indicates a problem with shift solenoid C, which controls the shifting of gears.
- P0765 – Shift Solenoid D Malfunction: This code indicates a problem with shift solenoid D, which controls the shifting of gears.
- P1747 – Pressure Control Solenoid A Short Circuit: Indicates a short circuit in the pressure control solenoid A.
- P1748 – EPC Solenoid Failure: Indicates a failure in the Electronic Pressure Control (EPC) solenoid.
These codes provide a starting point for diagnosing transmission problems. Further testing and inspection may be necessary to pinpoint the exact cause.
2.2 Essential Tools for OBD2 Testing
What tools are needed to perform OBD2 testing on the 4R44E transmission?
Having the right tools is essential for performing effective OBD2 testing. These tools allow you to retrieve and interpret diagnostic codes, monitor transmission performance, and perform necessary tests.
- OBD2 Scanner: A quality OBD2 scanner is the primary tool for retrieving diagnostic codes from the vehicle’s computer.
- Multimeter: A multimeter is used to test electrical circuits, such as solenoids and sensors, for continuity and voltage.
- Service Manual: A service manual provides detailed information about the 4R44E transmission, including wiring diagrams and diagnostic procedures.
- Scan Tool Software: Some advanced scan tools come with software that provides additional diagnostic information and testing capabilities.
- Laptop or Tablet: A laptop or tablet can be used to interface with the OBD2 scanner and display diagnostic data.
- OBD2 Adapter Cables: These cables are required to connect the scan tool to the OBD2 port if not connecting wirelessly.
2.3 Step-by-Step Guide to Performing an OBD2 Test
What are the steps involved in performing an OBD2 test on the 4R44E transmission?
Performing an OBD2 test involves several steps to ensure accurate and reliable results. Following these steps will help you identify and diagnose transmission problems effectively.
- Locate the OBD2 Port: The OBD2 port is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Connect the OBD2 Scanner: Plug the OBD2 scanner into the port.
- Turn On the Ignition: Turn the ignition key to the “on” position, but do not start the engine.
- Power On the Scanner: Turn on the OBD2 scanner and allow it to connect to the vehicle’s computer.
- Retrieve Diagnostic Codes: Use the scanner to retrieve any stored diagnostic codes. Record these codes for further analysis.
- Clear Diagnostic Codes (Optional): After recording the codes, you can clear them to see if they reappear after a test drive.
- Perform a Test Drive: Drive the vehicle under various conditions to see if any new codes appear or if the transmission problems persist.
- Analyze the Data: Use the service manual and online resources to interpret the diagnostic codes and identify potential causes.
- Perform Further Testing: Based on the diagnostic codes, perform additional tests, such as checking wiring, solenoids, and sensors, to pinpoint the exact cause of the problem.
- Consult a Professional: If you are unsure about the diagnostic results or repair procedures, consult a professional technician.
3. Diagnosing Common 4R44E Transmission Problems with OBD2
How can OBD2 testing help diagnose specific problems with the 4R44E transmission?
OBD2 testing is invaluable for diagnosing a wide range of problems with the 4R44E transmission. By understanding how to interpret diagnostic codes and perform additional tests, you can pinpoint the source of the problem and implement effective repairs.
3.1 Slipping Gears
What OBD2 codes are associated with slipping gears, and how should you diagnose this issue?
Slipping gears can manifest through several OBD2 codes, each indicating a different aspect of the problem. Common codes include P0731 (Gear 1 Incorrect Ratio), P0732 (Gear 2 Incorrect Ratio), P0733 (Gear 3 Incorrect Ratio), and P0734 (Gear 4 Incorrect Ratio).
-
Diagnostic Steps:
- Retrieve and Record Codes: Use an OBD2 scanner to retrieve and record any stored diagnostic codes.
- Check Fluid Level and Condition: Inspect the transmission fluid level and condition. Low or dirty fluid can cause slipping gears.
- Test Shift Solenoids: Use a multimeter to test the shift solenoids for proper resistance and function.
- Inspect Wiring and Connectors: Check the wiring and connectors for any signs of damage or corrosion.
- Monitor Transmission Performance: Use the OBD2 scanner to monitor transmission performance during a test drive, looking for anomalies in gear ratios.
- Band Adjustment: Ensure the intermediate and overdrive bands are correctly adjusted to specification.
-
Potential Causes:
- Low or Dirty Transmission Fluid
- Faulty Shift Solenoids
- Worn Clutch Packs
- Damaged Valve Body
- Incorrect Band Adjustments
3.2 Rough Shifting
Which OBD2 codes indicate rough shifting, and how can you troubleshoot this problem?
Rough shifting can be indicated by codes such as P0750 (Shift Solenoid A Malfunction), P0755 (Shift Solenoid B Malfunction), P0760 (Shift Solenoid C Malfunction), and P0765 (Shift Solenoid D Malfunction).
-
Diagnostic Steps:
- Retrieve and Record Codes: Use an OBD2 scanner to retrieve and record any stored diagnostic codes.
- Inspect Fluid Condition: Check the transmission fluid for contamination or debris, indicating internal damage.
- Test Shift Solenoids: Use a multimeter to test the shift solenoids for proper resistance and function.
- Check Valve Body: Inspect the valve body for any signs of damage or sticking valves.
- Monitor Transmission Performance: Use the OBD2 scanner to monitor transmission performance during a test drive, paying attention to shift times and quality.
-
Potential Causes:
- Faulty Shift Solenoids
- Sticking Valves in the Valve Body
- Contaminated Transmission Fluid
- Internal Transmission Damage
3.3 Overdrive Issues
What OBD2 codes are associated with overdrive problems, and how can you resolve them?
Overdrive issues can be indicated by codes such as P0750 (Shift Solenoid A Malfunction), P0755 (Shift Solenoid B Malfunction), or general transmission malfunction codes like P0700.
-
Diagnostic Steps:
- Retrieve and Record Codes: Use an OBD2 scanner to retrieve and record any stored diagnostic codes.
- Check Overdrive Solenoid: Test the overdrive solenoid for proper function using a multimeter.
- Inspect Wiring and Connectors: Check the wiring and connectors for any signs of damage or corrosion.
- Monitor Transmission Performance: Use the OBD2 scanner to monitor transmission performance during a test drive, specifically when the transmission attempts to shift into overdrive.
-
Potential Causes:
- Faulty Overdrive Solenoid
- Damaged Wiring or Connectors
- Internal Transmission Damage
- Incorrect Band Adjustments
3.4 Torque Converter Problems
Which OBD2 codes suggest issues with the torque converter, and how should you address them?
Torque converter problems are often indicated by codes such as P0740 (Torque Converter Clutch Circuit Malfunction), P0741 (Torque Converter Clutch Circuit Performance or Stuck Off), and P0743 (Torque Converter Clutch Circuit Electrical).
-
Diagnostic Steps:
- Retrieve and Record Codes: Use an OBD2 scanner to retrieve and record any stored diagnostic codes.
- Test Torque Converter Clutch Solenoid: Use a multimeter to test the torque converter clutch solenoid for proper resistance and function.
- Inspect Wiring and Connectors: Check the wiring and connectors for any signs of damage or corrosion.
- Monitor Torque Converter Performance: Use the OBD2 scanner to monitor torque converter performance during a test drive, paying attention to lock-up and release.
-
Potential Causes:
- Faulty Torque Converter Clutch Solenoid
- Damaged Wiring or Connectors
- Internal Torque Converter Damage
3.5 Electrical Issues
How can OBD2 testing help diagnose electrical problems within the 4R44E transmission?
Electrical issues can cause a variety of problems with the 4R44E transmission. OBD2 testing can help pinpoint these issues by providing specific diagnostic codes related to electrical circuits and components.
-
Diagnostic Steps:
- Retrieve and Record Codes: Use an OBD2 scanner to retrieve and record any stored diagnostic codes.
- Check Wiring and Connectors: Inspect the wiring and connectors for any signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections.
- Test Solenoids and Sensors: Use a multimeter to test solenoids and sensors for proper resistance and voltage.
- Inspect the Transmission Control Module (TCM): Check the TCM for any signs of damage or corrosion.
- Verify Power and Ground: Ensure the TCM has proper power and ground connections.
-
Potential Causes:
- Damaged Wiring or Connectors
- Faulty Solenoids or Sensors
- Damaged Transmission Control Module (TCM)
- Poor Power or Ground Connections
4. Advanced OBD2 Testing Techniques
What advanced techniques can enhance the accuracy of OBD2 testing?
Advanced OBD2 testing techniques can provide more in-depth diagnostic information, helping you pinpoint elusive transmission problems.
4.1 Live Data Streaming
How can live data streaming assist in diagnosing 4R44E transmission issues?
Live data streaming involves monitoring real-time data from the transmission while the vehicle is running. This can provide valuable insights into transmission performance and help identify problems that may not trigger diagnostic codes.
-
Key Parameters to Monitor:
- Transmission Fluid Temperature
- Input Speed Sensor (ISS) Readings
- Output Speed Sensor (OSS) Readings
- Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) Engagement
- Shift Solenoid States
- Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) Readings
- Engine RPM
By monitoring these parameters, you can identify anomalies and patterns that indicate potential problems within the transmission.
4.2 Graphing and Data Logging
How can graphing and data logging improve your diagnostic capabilities?
Graphing and data logging involve recording live data over a period of time and then analyzing it graphically. This can help identify intermittent problems and subtle performance issues.
-
Benefits of Graphing and Data Logging:
- Identify Intermittent Problems
- Analyze Performance Trends
- Compare Data to Specifications
- Create a Diagnostic Record
4.3 Using Bi-Directional Control
What is bi-directional control, and how can it be used in OBD2 testing?
Bi-directional control allows you to send commands to the vehicle’s computer and control specific components. This can be useful for testing solenoids, actuators, and other devices.
-
Examples of Bi-Directional Control in Transmission Testing:
- Activating Shift Solenoids
- Engaging the Torque Converter Clutch
- Adjusting Electronic Pressure Control (EPC)
By using bi-directional control, you can verify the functionality of individual components and isolate problems within the transmission.
5. Case Studies: Real-World 4R44E Transmission Diagnostics
Can you provide examples of how OBD2 testing has been used to solve real-world transmission problems?
Real-world case studies can illustrate how OBD2 testing can be used to diagnose and resolve complex transmission problems.
5.1 Case Study 1: Diagnosing a P0741 Code
How was a P0741 code (Torque Converter Clutch Circuit Performance or Stuck Off) diagnosed using OBD2 testing?
A vehicle exhibited a P0741 code, indicating a problem with the torque converter clutch. The technician performed the following steps:
- Retrieved the Code: Used an OBD2 scanner to retrieve the P0741 code.
- Checked Fluid Condition: Inspected the transmission fluid and found it to be clean and at the proper level.
- Monitored Live Data: Monitored live data while driving and observed that the torque converter clutch was not engaging as expected.
- Tested the TCC Solenoid: Used a multimeter to test the torque converter clutch solenoid and found it to be faulty.
- Replaced the Solenoid: Replaced the torque converter clutch solenoid and cleared the code.
- Verified Repair: Performed a test drive and confirmed that the torque converter clutch was now engaging properly, and the code did not return.
5.2 Case Study 2: Resolving Rough Shifting
How was rough shifting resolved using OBD2 testing and diagnostics?
A vehicle exhibited rough shifting between gears. The technician performed the following steps:
- Retrieved Codes: Used an OBD2 scanner to retrieve codes P0750 and P0755, indicating issues with shift solenoids A and B.
- Inspected Fluid: Checked the transmission fluid and found it to be contaminated with debris.
- Tested Solenoids: Tested shift solenoids A and B with a multimeter and found them to be out of specification.
- Replaced Solenoids and Fluid: Replaced shift solenoids A and B, and performed a transmission fluid and filter change.
- Cleared Codes and Tested: Cleared the codes and performed a test drive. The rough shifting issue was resolved, and the codes did not return.
5.3 Case Study 3: Addressing Overdrive Issues
How were overdrive issues diagnosed and fixed using OBD2 testing techniques?
A vehicle was unable to shift into overdrive. The technician performed the following steps:
- Retrieved Codes: Used an OBD2 scanner to retrieve a general transmission malfunction code P0700.
- Checked Wiring: Inspected the wiring and connectors to the overdrive solenoid and found a damaged wire.
- Repaired Wiring: Repaired the damaged wire and cleared the code.
- Tested Functionality: Performed a test drive and confirmed that the transmission was now shifting into overdrive properly.
6. Optimizing 4R44E Transmission Performance
What steps can be taken to optimize the performance and longevity of the 4R44E transmission?
Optimizing the performance of the 4R44E transmission involves a combination of regular maintenance, proper driving habits, and performance upgrades.
6.1 Performance Upgrades
What performance upgrades can enhance the 4R44E transmission?
Performance upgrades can improve the 4R44E transmission’s durability, shift quality, and overall performance.
- Shift Kits: Shift kits modify the valve body to provide firmer and quicker shifts.
- High-Performance Torque Converters: High-performance torque converters can improve low-end acceleration and overall power delivery.
- Upgraded Clutch Packs: Upgraded clutch packs can handle more power and provide improved durability.
- Transmission Coolers: Transmission coolers can help keep the transmission fluid temperature down, reducing the risk of overheating and damage.
6.2 Driving Techniques
How do driving techniques affect the 4R44E transmission, and what should be avoided?
Driving techniques can significantly impact the longevity and performance of the 4R44E transmission.
- Avoid Harsh Acceleration: Avoid harsh acceleration and frequent heavy loads, which can strain the transmission.
- Smooth Shifting: Practice smooth and controlled shifting to reduce wear and tear on the transmission components.
- Regular Maintenance: Adhere to a regular maintenance schedule, including fluid and filter changes, to keep the transmission in good condition.
6.3 Fluid Management
Why is proper fluid management crucial for maintaining the 4R44E transmission?
Proper fluid management is essential for maintaining the 4R44E transmission’s performance and longevity.
- Regular Fluid Checks: Check the transmission fluid level and condition regularly. Low or dirty fluid can cause significant damage.
- Fluid and Filter Changes: Change the transmission fluid and filter every 30,000 to 50,000 miles, depending on driving conditions.
- Use the Correct Fluid Type: Use the correct type of transmission fluid as specified by the vehicle manufacturer.
7. When to Seek Professional Help
When should you consult a professional technician for 4R44E transmission problems?
While OBD2 testing can help diagnose many transmission problems, there are situations where it is best to seek professional help.
7.1 Complex Diagnostic Issues
When should a complex diagnostic issue be handled by a professional?
Complex diagnostic issues may require specialized tools, knowledge, and experience. If you are unable to pinpoint the cause of the problem using OBD2 testing, it is best to consult a professional technician.
7.2 Major Repairs
When is professional intervention necessary for major transmission repairs?
Major transmission repairs, such as rebuilding or replacing the transmission, should always be performed by a qualified technician. These repairs require specialized tools and expertise to ensure proper operation.
7.3 Safety Concerns
When should safety concerns prompt a visit to a professional mechanic?
If you have any safety concerns related to the transmission, such as unusual noises, vibrations, or shifting problems, it is best to consult a professional technician. These issues could indicate a serious problem that could affect the safety of the vehicle.
8. The Future of OBD2 Testing
How is OBD2 technology evolving, and what advancements can be expected in the future?
OBD2 technology is constantly evolving to meet the demands of modern vehicles. Future advancements are expected to improve diagnostic capabilities and provide more detailed information about transmission performance.
8.1 Enhanced Diagnostic Capabilities
What enhancements are expected in future OBD2 systems?
Future OBD2 systems are expected to offer enhanced diagnostic capabilities, including:
- More Detailed Diagnostic Codes: More specific diagnostic codes will provide more information about the nature and location of the problem.
- Improved Live Data Streaming: Enhanced live data streaming will provide more real-time information about transmission performance.
- Advanced Bi-Directional Control: More advanced bi-directional control will allow technicians to perform more comprehensive tests and calibrations.
8.2 Integration with Mobile Devices
How will OBD2 testing integrate with mobile devices in the future?
Future OBD2 systems are expected to integrate more seamlessly with mobile devices, allowing vehicle owners to monitor their vehicle’s performance and diagnose problems using their smartphones or tablets.
8.3 Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
How will AI and machine learning impact OBD2 testing?
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are expected to play a significant role in the future of OBD2 testing. AI and ML algorithms can analyze diagnostic data to identify patterns and predict potential problems before they occur.
9. Resources for Further Learning
Where can you find additional resources for learning more about OBD2 testing and the 4R44E transmission?
Several resources are available for those who want to learn more about OBD2 testing and the 4R44E transmission.
9.1 Online Forums and Communities
What online forums and communities offer valuable information and support?
Online forums and communities can provide valuable information, support, and advice from experienced technicians and vehicle owners.
- Ford Ranger Forums: These forums offer discussions about the Ford Ranger, including the 4R44E transmission.
- Automotive Diagnostic Forums: These forums focus on automotive diagnostics and provide a platform for sharing knowledge and experience.
9.2 Technical Manuals and Guides
What technical manuals and guides can provide detailed information about the 4R44E transmission?
Technical manuals and guides can provide detailed information about the 4R44E transmission, including specifications, wiring diagrams, and diagnostic procedures.
- Haynes Repair Manuals: These manuals offer step-by-step instructions for repairing and maintaining the 4R44E transmission.
- Factory Service Manuals: These manuals provide comprehensive information about the 4R44E transmission, including detailed diagnostic procedures and repair instructions.
9.3 Training Programs and Certifications
What training programs and certifications are available for automotive technicians?
Training programs and certifications can help automotive technicians develop the skills and knowledge necessary to diagnose and repair complex transmission problems.
- ASE Certifications: The National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE) offers certifications in various areas of automotive repair, including transmissions.
- Technical Training Schools: Technical training schools offer courses in automotive diagnostics and repair, including specific training on transmissions.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
10.1 What is the 4R44E transmission?
The 4R44E is an electronically controlled four-speed automatic transmission commonly used in Ford vehicles like the Ranger and Explorer. It’s known for its reliability, but can face issues over time. Understanding it helps with accurate diagnosis and efficient repairs.
10.2 How does OBD2 testing help diagnose transmission problems?
OBD2 testing uses a standardized system to monitor vehicle components, including the transmission. It provides data and diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) that pinpoint problem sources. An OBD2 scanner connects to the vehicle’s diagnostic port to access this information.
10.3 What are common issues with the 4R44E transmission?
Common issues include slipping gears, rough shifting, overdrive problems, torque converter issues, fluid leaks, and complete failure. Early recognition prevents extensive damage.
10.4 What maintenance can prevent these issues?
Regular fluid checks, fluid and filter changes every 30,000 to 50,000 miles, leak inspections, proper driving habits, and professional inspections are essential.
10.5 How do I interpret OBD2 codes?
OBD2 codes are alphanumeric identifiers for specific vehicle problems. For example, P0700 indicates a transmission control system malfunction, while P0715 signals an input/turbine speed sensor circuit issue. These codes offer a starting point for diagnostics.
10.6 What tools are needed for OBD2 testing?
Essential tools include an OBD2 scanner, multimeter, service manual, scan tool software, laptop or tablet, and OBD2 adapter cables.
10.7 What is live data streaming and how does it help?
Live data streaming monitors real-time data from the transmission while the vehicle is running, offering insights into performance and helping identify issues that may not trigger codes.
10.8 When should I seek professional help for transmission problems?
Consult a professional for complex diagnostic issues, major repairs like rebuilding or replacing the transmission, and any safety concerns such as unusual noises or vibrations.
10.9 How is OBD2 technology evolving?
OBD2 technology is evolving with enhanced diagnostic capabilities, improved live data streaming, advanced bi-directional control, seamless integration with mobile devices, and the incorporation of artificial intelligence and machine learning.
10.10 What are some performance upgrades for the 4R44E transmission?
Performance upgrades include shift kits, high-performance torque converters, upgraded clutch packs, and transmission coolers to improve durability and performance.
Conclusion:
Mastering the 4R44E transmission OBD2 test is essential for maintaining your vehicle’s performance and longevity. By understanding the transmission’s features, interpreting OBD2 codes, and performing regular maintenance, you can address issues early and prevent costly repairs. For expert guidance and reliable solutions, trust OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN.
Are you experiencing transmission issues or need help interpreting OBD2 codes? Contact us today for expert assistance and comprehensive diagnostic services.
- Address: 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
- Website: OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
Let OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN help you keep your vehicle running smoothly and efficiently.