All Data Obd2 refers to the comprehensive diagnostic information available through your vehicle’s On-Board Diagnostics II system. With the help of OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, accessing and interpreting this data becomes straightforward, enabling you to diagnose and resolve car issues effectively. This capability empowers you with detailed insights into your vehicle’s health and performance.
Contents
- 1. Understanding All Data OBD2: What is It?
- 1.1 What Does All Data OBD2 Include?
- 1.2 Why Is Accessing All Data OBD2 Important?
- 1.3 How Does OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN Help?
- 2. Key Components of All Data OBD2
- 2.1 The OBD2 Connector
- 2.2 Communication Protocols
- 2.3 Types of Data Available
- 3. How to Access All Data OBD2
- 3.1 Required Tools and Equipment
- 3.2 Step-by-Step Guide to Accessing OBD2 Data
- 3.3 Using OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for Assistance
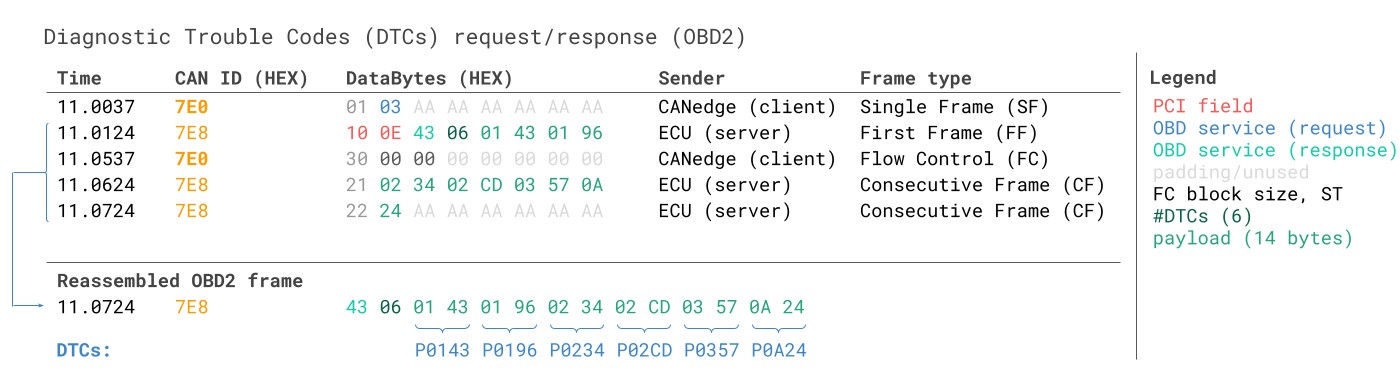
- 4. Interpreting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 4.1 Understanding the Structure of DTCs
- 4.2 Common DTC Categories and Their Meanings
- 4.3 Using Online Resources for DTC Lookup
- 4.4 OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN’s Expert Assistance
- 5. Reading and Understanding Live Data
- 5.1 Key Parameters to Monitor
- 5.2 Interpreting Common Live Data Readings
- 5.3 Using Graphs and Charts for Data Analysis
- 5.4 OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN’s Real-Time Data Monitoring Services
- 6. Advanced OBD2 Functions: Freeze Frame Data
- 6.1 What Is Freeze Frame Data?
- 6.2 How Freeze Frame Data Aids Diagnostics
- 6.3 Accessing and Interpreting Freeze Frame Data
- 6.4 Real-World Examples
- 6.5 Expert Diagnostic Assistance at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
- 7. Performing Active Tests with OBD2 Scanners
- 7.1 What Are Active Tests?
- 7.2 Benefits of Using Active Tests
- 7.3 Common Active Tests and Their Applications
- 7.4 How to Perform Active Tests Safely
- 7.5 OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN: Your Partner in Advanced Diagnostics
- 8. OBD2 Data Logging for Performance Analysis
- 8.1 What is OBD2 Data Logging?
- 8.2 Benefits of OBD2 Data Logging
- 8.3 Equipment Needed for OBD2 Data Logging
- 8.4 How to Set Up and Perform OBD2 Data Logging
- 8.5 Analyzing Logged Data for Performance and Issues
- 8.6 OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN: Expert Assistance for Data Logging Analysis
- 9. Resetting the Check Engine Light (CEL)
- 9.1 Understanding the Check Engine Light
- 9.2 When Is It Appropriate to Reset the CEL?
- 9.3 Steps to Reset the Check Engine Light
- 9.4 Using an OBD2 Scanner to Reset the CEL
- 9.5 Potential Risks of Resetting the CEL Too Soon
- 9.6 OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN: Expert Guidance for Resetting the CEL
- 10. Maximizing the Benefits of All Data OBD2 with OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
- 10.1 Comprehensive Solutions for Vehicle Diagnostics and Maintenance
- 10.2 Expert Support and Assistance from Certified Technicians
1. Understanding All Data OBD2: What is It?
All Data OBD2 encompasses the complete range of diagnostic information accessible via a vehicle’s On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD2) system. This includes diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), real-time sensor data, and other parameters that provide a comprehensive overview of the vehicle’s health. According to the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), the OBD2 standard was designed to offer standardized access to vehicle data for emissions control and diagnostics. Let’s dive deeper into what makes up All Data OBD2.
1.1 What Does All Data OBD2 Include?
All Data OBD2 includes a wide array of information, such as:
- Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): These codes indicate specific issues the vehicle has detected.
- Live Sensor Data: Real-time readings from various sensors, such as engine temperature, O2 sensor readings, and vehicle speed.
- Freeze Frame Data: A snapshot of sensor data recorded when a DTC is triggered.
- Vehicle Identification Number (VIN): Unique identifier for the vehicle.
- Emission Readiness Tests: Indicators of whether the vehicle has completed the necessary tests for emissions compliance.
1.2 Why Is Accessing All Data OBD2 Important?
Accessing All Data OBD2 is crucial for several reasons:
- Accurate Diagnostics: Provides detailed information to pinpoint the exact cause of vehicle issues.
- Preventive Maintenance: Allows for early detection of potential problems before they become major repairs.
- Performance Monitoring: Enables monitoring of vehicle performance metrics for efficiency and optimization.
- Cost Savings: Helps avoid unnecessary repairs by providing accurate diagnostic information.
According to a study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), accurate diagnostics can reduce repair costs by up to 40%.
1.3 How Does OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN Help?
OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN simplifies the process of accessing and interpreting All Data OBD2. We provide:
- User-Friendly Interfaces: Easy-to-navigate platforms for retrieving and viewing OBD2 data.
- Detailed Guides: Comprehensive guides and tutorials on understanding and using OBD2 information.
- Expert Support: Access to expert advice and assistance for diagnosing and resolving vehicle issues.
An OBD2 scanner displaying real-time diagnostic information, highlighting its importance for accurate vehicle diagnostics and preventive maintenance.
2. Key Components of All Data OBD2
To fully grasp All Data OBD2, understanding its key components is essential. This includes the OBD2 connector, various communication protocols, and the types of data available.
2.1 The OBD2 Connector
The OBD2 connector, standardized as SAE J1962, is a 16-pin port located inside the vehicle, typically under the dashboard. This connector serves as the physical interface for accessing the vehicle’s diagnostic data.
- Pin Layout: The connector includes pins for power, ground, and various communication protocols.
- Location: Usually found within easy reach of the driver, but can sometimes be hidden.
- Function: Allows OBD2 scanners and other diagnostic tools to interface with the vehicle’s computer.
2.2 Communication Protocols
OBD2 utilizes several communication protocols to transmit data. These protocols ensure that different vehicles and diagnostic tools can communicate effectively.
- CAN (Controller Area Network): The most common protocol, used in most modern vehicles since 2008. It uses pins 6 and 14 on the OBD2 connector.
- ISO 9141-2: Used in older European and Asian vehicles.
- KWP2000 (Keyword Protocol 2000): Another protocol used in many vehicles before the widespread adoption of CAN.
- SAE J1850 VPW and PWM: Used primarily in older General Motors and Ford vehicles, respectively.
According to the EPA (Environmental Protection Agency), standardization of these protocols was crucial for ensuring consistent access to emissions-related data across different vehicle manufacturers.
2.3 Types of Data Available
The data available through OBD2 can be categorized into several types, each providing unique insights into the vehicle’s operation.
- Real-Time Data: Dynamic data that changes as the vehicle operates, including:
- Engine RPM
- Vehicle Speed
- Coolant Temperature
- O2 Sensor Readings
- Fuel Trim
- Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Codes that indicate specific faults detected by the vehicle’s computer. These are categorized as:
- Powertrain (P-codes): Related to the engine and transmission.
- Chassis (C-codes): Related to braking, suspension, and steering.
- Body (B-codes): Related to interior and exterior body components.
- Network (U-codes): Related to the vehicle’s communication network.
- Freeze Frame Data: A snapshot of real-time data captured when a DTC is set, providing context for the fault.
- Vehicle Information: Includes the VIN and calibration identification numbers.
- Emission Readiness Status: Indicates whether the vehicle has completed the necessary tests for emissions compliance.
With OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, accessing this data is straightforward, allowing you to make informed decisions about your vehicle’s maintenance and repair. For example, you can quickly identify why your check engine light is on and take steps to resolve the issue.
3. How to Access All Data OBD2
Accessing All Data OBD2 involves using the right tools and following a systematic process. This section outlines the necessary equipment and steps to retrieve valuable information from your vehicle’s OBD2 system.
3.1 Required Tools and Equipment
To access All Data OBD2, you will need:
- OBD2 Scanner: A device that plugs into the OBD2 port and communicates with the vehicle’s computer. There are various types of scanners available:
- Basic Code Readers: Display DTCs and their descriptions.
- Advanced Scanners: Provide live data, freeze frame data, and enhanced diagnostic capabilities.
- Smartphone-Based Scanners: Use a Bluetooth or Wi-Fi adapter to connect to a smartphone app.
- OBD2 Adapter (if needed): Some vehicles may require an adapter to ensure compatibility with the scanner.
- Vehicle’s User Manual: Provides information on the location of the OBD2 port and specific vehicle information.
- Reliable Internet Connection: Needed to look up DTC definitions and access online resources.
3.2 Step-by-Step Guide to Accessing OBD2 Data
Follow these steps to access OBD2 data:
- Locate the OBD2 Port: The OBD2 port is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side. Consult your vehicle’s user manual if you cannot find it.
- Plug in the OBD2 Scanner: Connect the scanner to the OBD2 port. Ensure it is securely plugged in.
- Turn on the Ignition: Turn the ignition to the “ON” position without starting the engine. This provides power to the OBD2 system.
- Power on the Scanner: Turn on the OBD2 scanner and wait for it to initialize.
- Select Vehicle Information: Enter the vehicle’s make, model, and year if prompted.
- Read Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Select the option to read DTCs. The scanner will display any stored codes along with brief descriptions.
- View Live Data: Choose the option to view live data. Select the specific parameters you want to monitor, such as engine RPM, vehicle speed, and coolant temperature.
- Access Freeze Frame Data: If DTCs are present, access the freeze frame data to see the conditions when the code was set.
- Clear Codes (Optional): If you have addressed the issues and want to clear the codes, select the option to clear DTCs. Note that this will also reset the emission readiness monitors.
- Disconnect the Scanner: Once you have retrieved the necessary data, disconnect the scanner from the OBD2 port.
According to research from the University of California, using a systematic approach to accessing and interpreting OBD2 data can significantly improve diagnostic accuracy.
3.3 Using OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for Assistance
OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN offers resources to assist you in this process:
- Detailed Tutorials: Step-by-step guides on using various OBD2 scanners and accessing different types of data.
- Troubleshooting Tips: Solutions to common issues encountered while accessing OBD2 data.
- Code Lookup Tools: Databases for looking up DTC definitions and potential causes.
By using these resources, you can confidently access and interpret All Data OBD2 to maintain your vehicle’s health. And remember, if you run into any difficulties, our expert support team at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN is just a phone call or WhatsApp message away at +1 (641) 206-8880.
A visual representation of the vehicle diagnostic process, showing the OBD2 scanner connected to a car, highlighting the ease of accessing vehicle data.
4. Interpreting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
Interpreting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) is a crucial step in diagnosing vehicle issues. DTCs provide specific information about the faults detected by the vehicle’s computer, enabling targeted repairs.
4.1 Understanding the Structure of DTCs
DTCs are five-character codes that follow a standardized format. Understanding this format can help you quickly identify the area of the vehicle affected and the nature of the problem.
- First Character: Indicates the system affected:
- P: Powertrain (engine and transmission)
- C: Chassis (braking, suspension, and steering)
- B: Body (interior and exterior body components)
- U: Network (communication systems)
- Second Character: Indicates whether the code is generic or manufacturer-specific:
- 0: Generic (SAE-defined) code
- 1: Manufacturer-specific code
- Third Character: Indicates the specific subsystem:
- 0: Fuel and air metering and auxiliary emission controls
- 1: Fuel and air metering
- 2: Fuel and air injection circuit
- 3: Ignition system or misfire
- 4: Auxiliary emission controls
- 5: Vehicle speed and idle control system
- 6: Computer output circuit
- 7: Transmission
- 8: Transmission
- 9: Transmission
- Fourth and Fifth Characters: Indicate the specific fault within the subsystem.
4.2 Common DTC Categories and Their Meanings
Here are some common DTC categories and their typical meanings:
- P0XXX: Generic powertrain codes related to fuel and air metering.
- P0171: System Too Lean (Bank 1)
- P0300: Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected
- P04XX: Generic powertrain codes related to auxiliary emission controls.
- P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
- P0442: Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (Small Leak)
- P07XX: Generic powertrain codes related to the transmission.
- P0700: Transmission Control System Malfunction
- P0741: Torque Converter Clutch Circuit Performance or Stuck Off
- B1XXX: Body codes related to interior and exterior components.
- B1000: ECU Malfunction
- B1318: Battery Voltage Low
- C0XXX: Chassis codes related to braking, suspension, and steering.
- C0035: Right Front Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit
- C0265: ABS/EBCM Relay Circuit Malfunction
4.3 Using Online Resources for DTC Lookup
Several online resources can help you look up DTC definitions and potential causes:
- OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN: Offers a comprehensive DTC lookup tool with detailed descriptions and troubleshooting tips.
- RepairPal: Provides detailed information on DTCs, including symptoms, causes, and potential solutions.
- AutoCodes: Offers a database of DTCs with explanations, technical service bulletins (TSBs), and repair information.
For example, if you encounter a P0300 code, you can use these resources to determine that it indicates a random or multiple cylinder misfire. From there, you can investigate potential causes such as faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, or fuel injectors.
4.4 OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN’s Expert Assistance
At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we provide expert assistance to help you interpret DTCs accurately. Our services include:
- Personalized Diagnostic Support: Expert technicians available via phone and WhatsApp to help you understand DTCs and their implications.
- Detailed Diagnostic Reports: Comprehensive reports that provide in-depth analysis of DTCs and recommended actions.
- Troubleshooting Guides: Step-by-step guides to help you diagnose and resolve common issues indicated by DTCs.
Don’t let complex codes intimidate you. Reach out to us at +1 (641) 206-8880 for personalized support and expert guidance. Let OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN be your trusted partner in vehicle diagnostics.
A screenshot of an OBD2 PID lookup tool, demonstrating how to find specific information and definitions for diagnostic trouble codes, aiding in accurate vehicle diagnostics.
5. Reading and Understanding Live Data
Reading and understanding live data is essential for diagnosing intermittent issues and monitoring vehicle performance in real-time. Live data provides a dynamic view of various parameters as the vehicle operates, offering valuable insights into its overall health.
5.1 Key Parameters to Monitor
Several key parameters can provide valuable information about your vehicle’s condition. Some of the most important ones include:
- Engine RPM (Revolutions Per Minute): Indicates the speed at which the engine is running.
- Vehicle Speed: The current speed of the vehicle.
- Coolant Temperature: The temperature of the engine coolant, which is critical for preventing overheating.
- Intake Air Temperature (IAT): The temperature of the air entering the engine, affecting combustion efficiency.
- Mass Air Flow (MAF): The amount of air entering the engine, used to calculate fuel delivery.
- O2 Sensor Readings: The voltage output of the oxygen sensors, indicating the air-fuel mixture.
- Fuel Trim (Short Term and Long Term): Adjustments made by the engine control unit (ECU) to maintain the correct air-fuel mixture.
- Throttle Position: The position of the throttle valve, indicating how much power is being requested.
- Ignition Timing Advance: The amount of advance in the ignition timing, affecting engine performance.
5.2 Interpreting Common Live Data Readings
Interpreting these live data readings can help you diagnose various issues:
- High Engine RPM: Could indicate issues with the idle control system or vacuum leaks.
- Abnormal Coolant Temperature: Could indicate a faulty thermostat, radiator issues, or a failing water pump.
- Incorrect MAF Readings: Could indicate a faulty MAF sensor or vacuum leaks.
- Out-of-Range O2 Sensor Readings: Could indicate a faulty O2 sensor, exhaust leaks, or issues with the catalytic converter.
- Excessive Fuel Trim: Could indicate vacuum leaks, faulty fuel injectors, or issues with the fuel pump.
For example, if you notice that your vehicle’s short-term fuel trim is consistently high (e.g., +20%), it suggests that the engine is running lean. This could be due to a vacuum leak, a dirty mass airflow sensor, or a failing fuel pump. Monitoring these parameters in real-time allows you to identify and address such issues promptly.
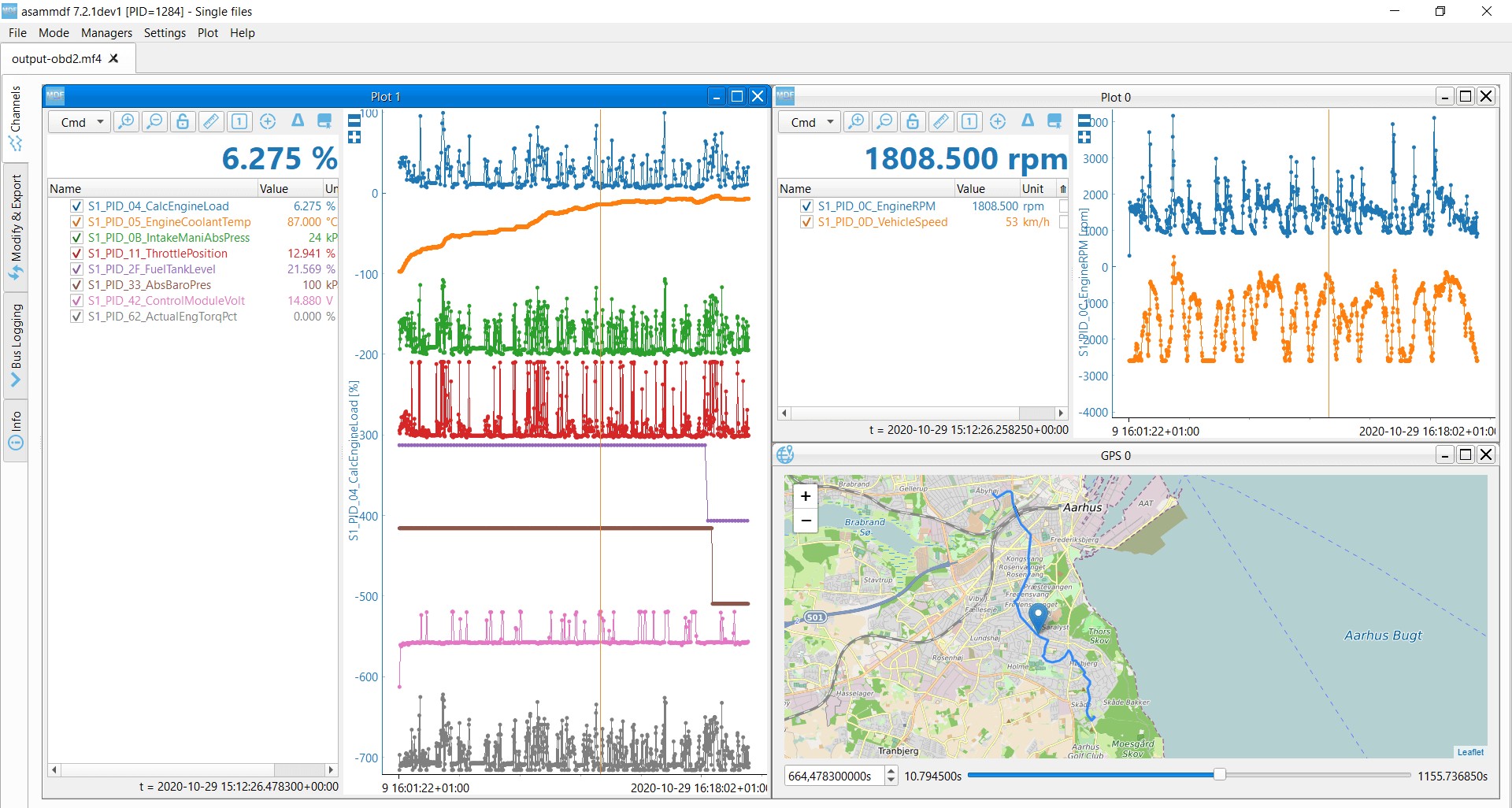
5.3 Using Graphs and Charts for Data Analysis
Many advanced OBD2 scanners and software applications offer the ability to display live data in graphs and charts. This can be particularly useful for identifying trends and intermittent issues.
- Graphs: Provide a visual representation of data over time, making it easier to spot fluctuations and anomalies.
- Charts: Allow you to compare multiple parameters simultaneously, helping you identify correlations and dependencies.
By plotting live data on a graph, you can easily see how various parameters change over time and identify any unusual patterns. For instance, you can monitor O2 sensor readings while driving to see if they are fluctuating correctly, indicating proper catalytic converter function.
5.4 OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN’s Real-Time Data Monitoring Services
At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we offer real-time data monitoring services to help you get the most out of your OBD2 system:
- Remote Diagnostics: Our experts can remotely monitor your vehicle’s live data to help you diagnose issues and optimize performance.
- Customized Monitoring Plans: We can create customized monitoring plans based on your vehicle’s specific needs and your driving habits.
- Detailed Diagnostic Reports: We provide detailed diagnostic reports that include analysis of live data and recommended actions.
Let us help you unlock the full potential of your vehicle’s OBD2 system. Contact us today at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN or call +1 (641) 206-8880 to learn more about our real-time data monitoring services.
 Live Data Display on OBD2 Scanner
Live Data Display on OBD2 Scanner
6. Advanced OBD2 Functions: Freeze Frame Data
Freeze frame data is a snapshot of your vehicle’s operating conditions at the moment a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) is set. It’s a valuable tool for diagnosing the root cause of problems, especially intermittent issues.
6.1 What Is Freeze Frame Data?
Freeze frame data includes critical parameters like:
- Engine Speed (RPM)
- Vehicle Speed
- Engine Load
- Coolant Temperature
- Fuel Trim
- Intake Air Temperature (IAT)
- Mass Air Flow (MAF)
- O2 Sensor Readings
This information provides a context for the DTC, helping you understand what was happening when the fault occurred. For instance, if a misfire code (P0300) is accompanied by freeze frame data showing high engine load and low RPM, it suggests the misfire occurred during heavy acceleration.
6.2 How Freeze Frame Data Aids Diagnostics
Freeze frame data is particularly helpful for:
- Diagnosing Intermittent Issues: Captures the conditions under which a problem occurs, even if the problem is not currently present.
- Verifying Repairs: Confirming that the conditions leading to a DTC have been resolved.
- Identifying Root Causes: Provides clues about the underlying causes of a fault, such as vacuum leaks, sensor failures, or fuel delivery problems.
For example, consider a scenario where the check engine light comes on intermittently, and the code is P0171 (System Too Lean, Bank 1). The freeze frame data reveals that the code was set at high speed with an elevated engine load. This information directs the technician to inspect components like the fuel pump, fuel filter, and injectors, as these are often stressed during high-demand conditions.
6.3 Accessing and Interpreting Freeze Frame Data
To access freeze frame data:
- Connect an OBD2 scanner: Plug the scanner into the vehicle’s OBD2 port.
- Read DTCs: Identify the DTC that triggered the freeze frame.
- Access Freeze Frame Data: Select the option to view freeze frame data associated with the DTC.
- Record the Data: Note the values of the key parameters.
- Analyze the Data: Compare the freeze frame data to normal operating conditions to identify anomalies.
OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN simplifies this process by providing tools and resources to help you:
- Retrieve Freeze Frame Data: Step-by-step instructions for accessing freeze frame data with various OBD2 scanners.
- Interpret Freeze Frame Data: Guides on understanding the meaning of different freeze frame parameters.
- Troubleshoot Issues: Tips for using freeze frame data to diagnose and resolve common vehicle problems.
6.4 Real-World Examples
- Example 1: P0420 – Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1):
- Freeze Frame Data: High engine load, elevated exhaust gas temperature.
- Possible Cause: Failing catalytic converter due to prolonged exposure to high temperatures.
- Example 2: P0301 – Cylinder 1 Misfire Detected:
- Freeze Frame Data: Low engine speed, cold engine temperature.
- Possible Cause: Faulty spark plug or ignition coil in cylinder 1, exacerbated by cold start conditions.
6.5 Expert Diagnostic Assistance at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
We understand that interpreting freeze frame data can be challenging. That’s why OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN offers expert diagnostic assistance:
- Consult with Certified Technicians: Contact our certified technicians via phone or WhatsApp for personalized guidance.
- Detailed Diagnostic Reports: Receive comprehensive reports analyzing your freeze frame data and recommending diagnostic steps.
- Access Online Resources: Utilize our extensive library of articles and tutorials to enhance your diagnostic skills.
Don’t let complex diagnostic data overwhelm you. Contact OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN at +1 (641) 206-8880 and let our experts guide you to accurate and effective solutions.
 Freeze Frame Data on OBD2 Scanner
Freeze Frame Data on OBD2 Scanner
7. Performing Active Tests with OBD2 Scanners
Performing active tests with OBD2 scanners can greatly enhance diagnostic capabilities by allowing you to directly control and monitor specific vehicle components.
7.1 What Are Active Tests?
Active tests, also known as bi-directional controls, are diagnostic procedures that allow you to send commands to the vehicle’s computer (ECU) to activate or adjust certain components. Unlike simply reading data, active tests enable you to interact with the vehicle’s systems in real-time.
- Purpose: To verify the functionality of specific components, diagnose intermittent issues, and confirm repairs.
- Examples: Activating fuel injectors, turning on/off the cooling fan, adjusting idle speed, cycling the ABS pump, and testing EGR valves.
7.2 Benefits of Using Active Tests
- Enhanced Diagnostics: Direct control over components allows for more accurate and efficient troubleshooting.
- Time Savings: Can quickly identify faulty components without extensive manual testing.
- Verification of Repairs: Confirms that a replaced or repaired component is functioning correctly.
- Diagnosis of Intermittent Issues: Activating components under specific conditions can help reproduce and diagnose intermittent problems.
7.3 Common Active Tests and Their Applications
- Fuel Injector Activation:
- Application: Verifies that each fuel injector is firing correctly.
- Diagnostic Use: Identifies faulty or clogged injectors causing misfires or lean conditions.
- Cooling Fan Control:
- Application: Tests the operation of the cooling fan at different speeds.
- Diagnostic Use: Checks for proper cooling system function and overheating issues.
- Idle Speed Adjustment:
- Application: Adjusts the engine’s idle speed to a specified RPM.
- Diagnostic Use: Diagnoses and corrects idle speed issues, such as stalling or rough idling.
- ABS Pump Cycling:
- Application: Cycles the ABS pump to test its functionality.
- Diagnostic Use: Verifies the proper operation of the ABS system.
- EGR Valve Testing:
- Application: Controls the EGR valve to test its opening and closing.
- Diagnostic Use: Checks for proper EGR valve function, which is essential for emissions control.
7.4 How to Perform Active Tests Safely
- Use a Compatible Scanner: Ensure your OBD2 scanner supports active tests for your vehicle’s make and model.
- Follow Instructions: Carefully follow the scanner’s instructions and the vehicle’s service manual.
- Ensure Safety: Perform active tests in a safe environment, away from moving parts and potential hazards.
- Monitor Results: Closely monitor the results of the tests and compare them to expected values.
7.5 OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN: Your Partner in Advanced Diagnostics
At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we are committed to providing the resources and support you need to perform advanced diagnostics effectively:
- Expert Guidance: Consult with our certified technicians for assistance in performing active tests.
- Detailed Tutorials: Access step-by-step tutorials on how to perform specific active tests.
- Troubleshooting Support: Get help with interpreting test results and troubleshooting any issues that arise.
Ready to take your diagnostic skills to the next level? Contact us at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN or call +1 (641) 206-8880 and let our experts guide you.
 Active Test Example on OBD2 Scanner
Active Test Example on OBD2 Scanner
8. OBD2 Data Logging for Performance Analysis
OBD2 data logging involves recording vehicle data over time, enabling detailed analysis of performance and identification of potential issues.
8.1 What is OBD2 Data Logging?
OBD2 data logging is the process of recording data from your vehicle’s OBD2 system over a period of time. This data can then be analyzed to identify trends, diagnose issues, and evaluate performance.
- Process: Connecting an OBD2 data logger or scanner to the vehicle’s OBD2 port and recording data while driving or during specific tests.
- Parameters Recorded: Engine RPM, vehicle speed, coolant temperature, fuel trim, O2 sensor readings, and other relevant parameters.
- Applications: Performance analysis, fuel efficiency monitoring, diagnosing intermittent issues, and tracking vehicle health.
8.2 Benefits of OBD2 Data Logging
- Detailed Performance Analysis: Provides insights into how the vehicle performs under different conditions.
- Early Issue Detection: Identifies subtle changes in data that may indicate developing problems.
- Intermittent Issue Diagnosis: Captures data during intermittent events, making diagnosis easier.
- Fuel Efficiency Monitoring: Tracks fuel consumption and identifies areas for improvement.
- Customized Vehicle Tuning: Helps optimize engine parameters for better performance and efficiency.
8.3 Equipment Needed for OBD2 Data Logging
- OBD2 Data Logger: A device that connects to the OBD2 port and records data to internal memory or an SD card.
- OBD2 Scanner with Data Logging Capability: Some advanced OBD2 scanners can also log data.
- Software for Data Analysis: Software applications that allow you to download, view, and analyze the logged data.
8.4 How to Set Up and Perform OBD2 Data Logging
- Connect the Data Logger: Plug the OBD2 data logger or scanner into the vehicle’s OBD2 port.
- Configure Logging Parameters: Select the parameters you want to record and set the logging frequency.
- Start Logging: Start the data logging process and drive the vehicle under the desired conditions.
- Stop Logging: Stop the data logging process after the desired period or when the event of interest has occurred.
- Download Data: Download the logged data to your computer.
- Analyze Data: Use data analysis software to view and analyze the recorded data.
8.5 Analyzing Logged Data for Performance and Issues
- Identify Trends: Look for trends in the data, such as increasing coolant temperature or decreasing fuel efficiency.
- Compare to Baseline: Compare the logged data to baseline values to identify deviations.
- Correlate Parameters: Look for correlations between different parameters to understand how they affect each other.
- Diagnose Issues: Use the data to diagnose potential issues, such as vacuum leaks, sensor failures, or fuel delivery problems.
8.6 OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN: Expert Assistance for Data Logging Analysis
At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we offer expert assistance to help you make the most of your OBD2 data logging efforts:
- Consultation with Technicians: Our certified technicians can help you set up data logging, interpret the data, and diagnose issues.
- Data Analysis Services: We offer data analysis services to help you extract valuable insights from your logged data.
- Detailed Reports: Receive detailed reports summarizing the data analysis and recommending actions.
Contact OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN today at +1 (641) 206-8880 to learn more about our OBD2 data logging services and how we can help you improve your vehicle’s performance and reliability.
An OBD2 data logging device connected to a vehicle, illustrating how data is recorded over time for performance analysis and diagnostic purposes.
9. Resetting the Check Engine Light (CEL)
Resetting the Check Engine Light (CEL) is a common task for vehicle owners and technicians. However, it’s essential to understand when and how to do it properly to avoid potential issues.
9.1 Understanding the Check Engine Light
The Check Engine Light (CEL) is an indicator that signals a problem within your vehicle’s engine or related systems. It is designed to alert you to potential issues that may affect performance, fuel efficiency, or emissions.
- Reasons for Illumination: The CEL can be triggered by a wide range of issues, from minor problems like a loose gas cap to severe issues like engine misfires or catalytic converter failure.
- Severity of Issues: The CEL can indicate a problem that requires immediate attention or one that can be addressed at your convenience. It’s essential to diagnose the underlying cause before resetting the light.
9.2 When Is It Appropriate to Reset the CEL?
It is appropriate to reset the CEL only after you have properly diagnosed and resolved the underlying issue. Resetting the light without addressing the cause may lead to:
- Recurring Issues: The problem that triggered the CEL will likely return, potentially causing further damage.
- Emissions Failure: Resetting the light without fixing the issue may mask emissions problems, leading to failed emissions tests.
- Incorrect Diagnostic Data: Resetting the light clears the stored diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and freeze frame data, making it difficult to diagnose future problems.
9.3 Steps to Reset the Check Engine Light
- Diagnose the Issue: Use an OBD2 scanner to read the diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and identify the underlying problem.
- Repair the Issue: Perform the necessary repairs to address the problem identified by the DTCs.
- Verify the Repair: After completing the repairs, verify that the issue has been resolved and that the vehicle is functioning properly.
- Reset the CEL: Use the OBD2 scanner to clear the DTCs and reset the Check Engine Light.
- Test the Vehicle: Drive the vehicle for a period of time to ensure that the CEL does not reappear and that the vehicle is operating normally.
9.4 Using an OBD2 Scanner to Reset the CEL
- Connect the Scanner: Plug the OBD2 scanner into the vehicle’s OBD2 port.
- Turn on the Ignition: Turn the ignition to the “ON” position without starting the engine.
- Read DTCs: Select the option to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and confirm that you have addressed the underlying issue.
- Clear DTCs: Select the option to clear DTCs. The scanner will prompt you to confirm the action.
- Verify Reset: After clearing the DTCs, verify that the Check Engine Light has been turned off.
9.5 Potential Risks of Resetting the CEL Too Soon
- Masking Underlying Issues: Resetting the CEL without fixing the problem may mask severe issues that could lead to further damage.
- Recurring Problems: The issue will likely return, causing additional inconvenience and expense.
- Failed Emissions Tests: Resetting the CEL can clear the emissions readiness monitors, leading to failed emissions tests.
9.6 OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN: Expert Guidance for Resetting the CEL
At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we provide expert guidance to ensure that you reset the CEL safely and effectively:
- Consultation with Technicians: Consult with our certified technicians for assistance in diagnosing and repairing the underlying issue.
- Detailed Tutorials: Access step-by-step tutorials on how to reset the CEL using various OBD2 scanners.
- Troubleshooting Support: Get help with identifying and resolving any issues that may arise during the process.
Contact OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN today at +1 (641) 206-8880 to learn more about our services and how we can help you maintain your vehicle’s health.
An OBD2 scanner interface displaying the option to clear diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and reset the check engine light.
10. Maximizing the Benefits of All Data OBD2 with OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
To maximize the benefits of all data OBD2, partnering with OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN provides access to a wealth of resources, expert support, and comprehensive solutions for vehicle diagnostics and maintenance.
10.1 Comprehensive Solutions for Vehicle Diagnostics and Maintenance
OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN offers a range of comprehensive solutions designed to help you make the most of your vehicle’s OBD2 system:
- OBD2 Scanners: We provide a variety of high-quality OBD2 scanners to meet your specific needs.
- Diagnostic Software: Our diagnostic software applications enable you to download, view, and analyze OBD2 data.
- Expert Support: Our certified technicians are available to provide expert assistance in diagnosing and resolving vehicle issues.
- Tutorials and Guides: We offer a comprehensive library of tutorials and guides to help you understand and use OBD2 data.
10.2 Expert Support and Assistance from Certified Technicians
Our certified technicians are available to provide expert support and assistance with all aspects of OBD2 diagnostics and maintenance:
- Personalized Consultation: Consult with our technicians for assistance in diagnosing and resolving specific vehicle issues.
- Data Analysis: We can help you analyze OBD2 data to identify trends, diagnose problems
