Barfx Obd2 refers to a potential tool or device related to On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD2), a system used in vehicles to monitor and diagnose issues. OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN can help you understand how to use this tool effectively for vehicle diagnostics and repairs. This comprehensive guide will delve into the world of OBD2 scanners, exploring their functionality, benefits, and how they can assist in troubleshooting car problems.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the Basics of OBD2
- 1.1 The History and Evolution of OBD2
- 1.2 Key Components of an OBD2 System
- 1.3 Benefits of Using OBD2
- 2. What is a Barfx OBD2 Scanner?
- 2.1 Types of OBD2 Scanners Available
- 2.2 Features to Look for in an OBD2 Scanner
- 2.3 How an OBD2 Scanner Works
- 3. Common OBD2 Codes and Their Meanings
- 3.1 Understanding the Structure of OBD2 Codes
- 3.2 Examples of Common OBD2 Codes
- 3.3 Troubleshooting Common OBD2 Codes
- 4. Step-by-Step Guide to Using an OBD2 Scanner
- 4.1 Preparing to Use the Scanner
- 4.2 Reading and Interpreting OBD2 Codes
- 4.3 Clearing OBD2 Codes
- 4.4 Reading Live Data with an OBD2 Scanner
- 5. Advanced OBD2 Scanner Functions
- 5.1 Bi-Directional Control
- 5.2 ABS and SRS Diagnostics
- 5.3 Programming and Key Fob Programming
- 6. Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner for Your Needs
- 6.1 Budget Considerations
- 6.2 DIY vs. Professional Use
- 6.3 Compatibility with Your Vehicle
- 6.4 User Reviews and Recommendations
- 7. Maintaining and Updating Your OBD2 Scanner
- 7.1 Software Updates
- 7.2 Proper Storage and Handling
- 8. Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using an OBD2 Scanner
- 8.1 Ignoring Freeze Frame Data
- 8.2 Clearing Codes Without Repairing the Problem
- 8.3 Misinterpreting OBD2 Codes
- 8.4 Neglecting Software Updates
- 9. The Future of OBD2 Technology
- 9.1 OBD3 and Beyond
- 9.2 Integration with Telematics Systems
- 9.3 Advancements in Diagnostic Capabilities
- 10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Barfx OBD2
- Take the Next Step: Contact OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN Today
1. Understanding the Basics of OBD2
What is OBD2, and why is it essential for modern vehicles?
On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD2) is a standardized system that monitors a vehicle’s engine, transmission, and other critical components. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), OBD2 was implemented in all cars and light trucks sold in the United States after 1996 to reduce emissions. This system provides valuable data for diagnosing problems and ensuring vehicles operate efficiently.
1.1 The History and Evolution of OBD2
How did OBD2 evolve from its predecessors?
The evolution of On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) systems began in the late 1960s due to increasing concerns about air pollution. The California Air Resources Board (CARB) was the first to mandate basic diagnostic capabilities in vehicles sold in California.
- OBD-I: The first generation, OBD-I, was manufacturer-specific and lacked standardization. Each automaker used different diagnostic connectors and protocols, making it difficult for technicians to access data.
- OBD-1.5: This was an interim step towards standardization, used by some manufacturers before OBD2 was fully implemented. It included some OBD2 features but was not fully compliant.
- OBD2: In 1996, OBD2 became mandatory in the United States, standardizing diagnostic connectors (SAE J1962), communication protocols (SAE J1850, ISO 9141-2, CAN), and diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
1.2 Key Components of an OBD2 System
What are the main parts of an OBD2 system?
The OBD2 system consists of several key components working together:
- Sensors: These monitor various parameters like engine temperature, oxygen levels, and airflow.
- Engine Control Unit (ECU): This is the “brain” of the system, processing data from sensors and making adjustments to optimize performance and emissions.
- Diagnostic Connector (DLC): This standardized 16-pin connector allows access to the vehicle’s diagnostic data.
- Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): These standardized codes indicate specific problems detected by the system.
- Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL): Also known as the “check engine light,” it illuminates when the ECU detects a problem.
1.3 Benefits of Using OBD2
What advantages does OBD2 offer to vehicle owners and technicians?
OBD2 provides numerous benefits:
- Early Problem Detection: Allows for early identification of potential issues before they become major problems.
- Reduced Emissions: Helps maintain optimal engine performance, reducing harmful emissions.
- Standardized Diagnostics: Provides a standardized approach to diagnosing vehicle problems, making it easier for technicians.
- Cost Savings: Enables more accurate and efficient repairs, saving time and money.
- Improved Fuel Efficiency: Ensures the engine runs efficiently, improving fuel economy.
- Enhanced Vehicle Performance: Helps maintain peak performance by addressing issues promptly.
2. What is a Barfx OBD2 Scanner?
Is Barfx OBD2 a specific brand or type of scanner, and what does it do?
“Barfx OBD2” likely refers to a specific brand or model of OBD2 scanner, but without more context, it’s hard to confirm. An OBD2 scanner, in general, is a tool used to read and interpret data from a vehicle’s OBD2 system, helping diagnose issues. It connects to the diagnostic connector (DLC) and retrieves diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and other information.
2.1 Types of OBD2 Scanners Available
What different kinds of OBD2 scanners can I choose from?
There are various types of OBD2 scanners available, each with different features and capabilities:
- Basic Code Readers: These are the simplest and most affordable scanners. They can read and clear DTCs but offer limited additional features.
- Enhanced OBD2 Scanners: These provide more advanced features like live data streaming, freeze frame data, and the ability to perform some basic tests.
- Professional-Grade Scanners: Used by automotive technicians, these scanners offer comprehensive diagnostics, bi-directional control, and advanced programming capabilities.
- Smartphone-Based Scanners: These consist of a Bluetooth or Wi-Fi adapter that connects to the OBD2 port and an app on your smartphone or tablet. They offer a range of features and convenience.
2.2 Features to Look for in an OBD2 Scanner
What should I consider when choosing an OBD2 scanner?
When selecting an OBD2 scanner, consider the following features:
- Code Reading and Clearing: The ability to read and clear DTCs.
- Live Data Streaming: Displays real-time data from various sensors.
- Freeze Frame Data: Captures data when a DTC is triggered, providing a snapshot of conditions.
- Bi-Directional Control: Allows you to control certain vehicle functions for testing purposes.
- Compatibility: Ensure the scanner is compatible with your vehicle’s make and model.
- Ease of Use: Look for a scanner with an intuitive interface and clear instructions.
- Updateability: Choose a scanner that can be updated with the latest vehicle information and software.
- Additional Features: Some scanners offer features like ABS, SRS, and transmission diagnostics.
2.3 How an OBD2 Scanner Works
How does an OBD2 scanner connect to my car and retrieve data?
An OBD2 scanner connects to your vehicle’s diagnostic connector (DLC), usually located under the dashboard. Once connected, the scanner communicates with the vehicle’s ECU using standardized protocols. The scanner requests data, and the ECU responds with information such as DTCs, sensor readings, and other diagnostic data.
This information is then displayed on the scanner’s screen, allowing you to interpret the data and diagnose problems.
3. Common OBD2 Codes and Their Meanings
What are some typical OBD2 codes, and what do they indicate about my vehicle’s health?
OBD2 codes are standardized alphanumeric codes that indicate specific problems detected by the vehicle’s diagnostic system. These codes start with a letter (P, C, B, or U) followed by four numbers and sometimes additional characters.
3.1 Understanding the Structure of OBD2 Codes
How are OBD2 codes organized, and what do the different parts signify?
The structure of OBD2 codes is as follows:
- First Character:
- P: Powertrain (engine, transmission)
- C: Chassis (brakes, suspension)
- B: Body (airbags, lights)
- U: Network (communication)
- Second Character:
- 0: Generic (SAE) code
- 1: Manufacturer-specific code
- Third Character: Indicates the specific system:
- 1: Fuel and air metering
- 2: Fuel and air metering (injector circuit)
- 3: Ignition system or misfire
- 4: Auxiliary emission controls
- 5: Vehicle speed control and idle control system
- 6: Computer output circuit
- 7: Transmission
- 8: Transmission
- Last Two Characters: Indicate the specific fault within the system.
3.2 Examples of Common OBD2 Codes
What are some frequent OBD2 codes and their meanings?
Here are some common OBD2 codes and their meanings:
| Code | Description | Possible Causes |
|---|---|---|
| P0171 | System Too Lean (Bank 1) | Vacuum leak, faulty oxygen sensor, MAF sensor issue, fuel pump problem |
| P0300 | Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected | Faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, fuel injectors, vacuum leaks, low compression |
| P0420 | Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold | Faulty catalytic converter, oxygen sensor issue, exhaust leak |
| P0401 | Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Flow Insufficient Detected | Clogged EGR valve or tube, faulty EGR valve, vacuum leak |
| P0113 | Intake Air Temperature Sensor Circuit High Input | Faulty IAT sensor, wiring issue |
3.3 Troubleshooting Common OBD2 Codes
How can I diagnose and fix problems indicated by common OBD2 codes?
When troubleshooting OBD2 codes, follow these steps:
- Record the Code: Write down the code and any freeze frame data.
- Research the Code: Use reliable sources like OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN to understand the code’s meaning and possible causes.
- Inspect the Vehicle: Check for obvious issues like loose gas caps, vacuum leaks, or damaged wiring.
- Test Components: Use a multimeter or other diagnostic tools to test sensors and components.
- Repair or Replace: Fix any identified problems or replace faulty parts.
- Clear the Code: After completing repairs, clear the code and monitor the vehicle to ensure the problem is resolved.
4. Step-by-Step Guide to Using an OBD2 Scanner
How do I use an OBD2 scanner to diagnose my car’s problems?
Using an OBD2 scanner is a straightforward process. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
4.1 Preparing to Use the Scanner
What do I need to do before connecting the OBD2 scanner?
- Locate the OBD2 Port: The OBD2 port is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Turn Off the Ignition: Ensure the vehicle’s ignition is turned off before connecting the scanner.
- Plug in the Scanner: Connect the OBD2 scanner to the diagnostic port.
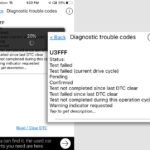
4.2 Reading and Interpreting OBD2 Codes
How do I retrieve and understand the codes from my car?
- Turn On the Ignition: Turn the ignition to the “on” position without starting the engine.
- Power On the Scanner: The scanner should power on automatically. If not, follow the scanner’s instructions.
- Select “Read Codes”: Navigate the scanner’s menu to find the “Read Codes” or “Diagnostic Codes” option.
- View the Codes: The scanner will display any stored DTCs. Record these codes.
- Interpret the Codes: Use the scanner’s manual or online resources like OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN to understand the meaning of each code.
4.3 Clearing OBD2 Codes
When and how should I clear the codes from my car’s computer?
- Repair the Problem: Ensure the underlying issue causing the code has been resolved.
- Select “Clear Codes”: Navigate the scanner’s menu to find the “Clear Codes” or “Erase Codes” option.
- Confirm the Action: The scanner may ask you to confirm that you want to clear the codes.
- Turn Off the Ignition: Turn off the ignition for a few minutes.
- Restart the Vehicle: Start the vehicle and check if the check engine light remains off.
- Monitor the Vehicle: Drive the vehicle and monitor for any recurring codes.
Note: Clearing codes without addressing the underlying problem will only temporarily turn off the check engine light. The light will likely return if the issue persists.
4.4 Reading Live Data with an OBD2 Scanner
What is live data, and how can it help with diagnostics?
Live data, also known as real-time data, is a stream of information from various sensors in the vehicle. It can provide valuable insights into how the engine and other components are performing.
- Select “Live Data”: Navigate the scanner’s menu to find the “Live Data” or “Data Stream” option.
- Select Parameters: Choose the parameters you want to monitor, such as engine RPM, coolant temperature, oxygen sensor readings, and fuel trim.
- View the Data: The scanner will display the real-time data. Monitor the values and look for any abnormalities.
- Analyze the Data: Compare the data to specifications to identify potential issues.
For example, if you suspect a faulty oxygen sensor, you can monitor its voltage readings in real-time. A healthy oxygen sensor should fluctuate between 0.1 and 0.9 volts.
5. Advanced OBD2 Scanner Functions
What additional capabilities do advanced OBD2 scanners offer?
Advanced OBD2 scanners provide more sophisticated functions that can aid in complex diagnostics and repairs.
5.1 Bi-Directional Control
What is bi-directional control, and how is it used?
Bi-directional control allows the scanner to send commands to the vehicle’s ECU to activate certain components. This can be useful for testing purposes.
- Activating Solenoids: Test solenoids for proper function.
- Cycling Relays: Check relays for correct operation.
- Running Tests: Perform tests like cylinder balance tests or EGR valve tests.
5.2 ABS and SRS Diagnostics
Can an OBD2 scanner diagnose ABS and airbag system problems?
Some advanced OBD2 scanners can diagnose problems with the Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) and Supplemental Restraint System (SRS). These scanners can read and clear ABS and SRS codes, as well as provide live data from these systems.
5.3 Programming and Key Fob Programming
Can OBD2 scanners be used for programming or key fob programming?
Certain professional-grade OBD2 scanners offer programming capabilities, allowing you to reprogram the ECU or program new key fobs. This typically requires specialized software and knowledge.
- ECU Reprogramming: Update the ECU with the latest software.
- Key Fob Programming: Program new key fobs or remotes.
Note: Programming functions should be performed by qualified technicians due to the risk of damaging the ECU.
6. Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner for Your Needs
How do I select the best OBD2 scanner for my specific requirements?
Selecting the right OBD2 scanner depends on your needs and budget. Consider the following factors:
6.1 Budget Considerations
How much should I expect to spend on an OBD2 scanner?
OBD2 scanners range in price from around $20 for basic code readers to several thousand dollars for professional-grade scanners.
- Basic Code Readers: $20 – $50
- Enhanced OBD2 Scanners: $50 – $200
- Professional-Grade Scanners: $200 – $5000+
6.2 DIY vs. Professional Use
Should I buy a basic scanner or a more advanced model?
If you’re a DIY enthusiast who only needs to read and clear codes occasionally, a basic or enhanced OBD2 scanner may be sufficient. If you’re a professional technician, you’ll need a professional-grade scanner with advanced features.
6.3 Compatibility with Your Vehicle
How do I ensure the scanner will work with my car’s make and model?
Check the scanner’s compatibility list to ensure it supports your vehicle’s make, model, and year. Most OBD2 scanners are compatible with all vehicles sold in the United States after 1996, but it’s always best to verify.
6.4 User Reviews and Recommendations
What do other users say about specific OBD2 scanners?
Read user reviews and seek recommendations from other vehicle owners or technicians. This can provide valuable insights into the scanner’s performance and reliability.
7. Maintaining and Updating Your OBD2 Scanner
How do I keep my OBD2 scanner in good working condition?
Proper maintenance and updates are essential for keeping your OBD2 scanner in good working condition.
7.1 Software Updates
Why are software updates important for OBD2 scanners?
Software updates ensure your scanner has the latest vehicle information and diagnostic capabilities. They also fix bugs and improve performance.
- Regular Updates: Check for updates regularly and install them as needed.
- Improved Performance: Updates can improve the scanner’s speed and accuracy.
- New Vehicle Support: Updates add support for newer vehicle models.
7.2 Proper Storage and Handling
How should I store and handle my OBD2 scanner to prevent damage?
- Store in a Safe Place: Store the scanner in a clean, dry place away from extreme temperatures and humidity.
- Avoid Dropping: Handle the scanner carefully to avoid dropping it, which can damage the internal components.
- Protect the Connector: Keep the connector clean and protected to ensure a good connection with the vehicle’s diagnostic port.
8. Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using an OBD2 Scanner
What are some frequent errors people make when using OBD2 scanners?
To ensure accurate diagnostics, avoid these common mistakes:
8.1 Ignoring Freeze Frame Data
Why is freeze frame data important, and how should I use it?
Freeze frame data captures a snapshot of the vehicle’s operating conditions when a DTC is triggered. This data can provide valuable clues about the cause of the problem.
- Analyze the Data: Review the freeze frame data to understand the conditions under which the code was set.
- Identify Patterns: Look for patterns or abnormalities in the data that may indicate the cause of the problem.
8.2 Clearing Codes Without Repairing the Problem
Why is it important to fix the underlying issue before clearing codes?
Clearing codes without addressing the underlying problem will only temporarily turn off the check engine light. The light will likely return if the issue persists.
- Address the Root Cause: Always diagnose and repair the underlying problem before clearing codes.
- Prevent Recurring Issues: Repairing the problem ensures it doesn’t recur, saving you time and money in the long run.
8.3 Misinterpreting OBD2 Codes
How can I avoid misinterpreting OBD2 codes and making incorrect repairs?
- Use Reliable Resources: Use reliable sources like OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN to understand the meaning of OBD2 codes.
- Consult a Technician: If you’re unsure about a code’s meaning or how to diagnose the problem, consult a qualified technician.
- Consider All Possible Causes: Don’t jump to conclusions based on the code alone. Consider all possible causes and test components to confirm the diagnosis.
8.4 Neglecting Software Updates
What are the consequences of not updating my OBD2 scanner’s software?
Neglecting software updates can result in inaccurate diagnostics and reduced functionality.
- Outdated Information: The scanner may not have the latest vehicle information or diagnostic capabilities.
- Reduced Performance: Updates improve the scanner’s speed and accuracy.
- Missed Bugs: Updates fix bugs that can cause errors or malfunctions.
9. The Future of OBD2 Technology
How is OBD2 technology evolving, and what new features can we expect in the future?
OBD2 technology is continuously evolving to meet the demands of modern vehicles.
9.1 OBD3 and Beyond
What is OBD3, and what improvements will it offer?
OBD3 is a proposed future standard that would enhance the capabilities of OBD2. While not yet implemented, it’s expected to include features like:
- Real-Time Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of vehicle emissions and performance.
- Remote Reporting: Automatic reporting of emissions violations to regulatory agencies.
- Enhanced Security: Improved security to prevent tampering with the diagnostic system.
9.2 Integration with Telematics Systems
How are OBD2 systems being integrated with telematics and connected car technologies?
OBD2 data is increasingly being integrated with telematics systems and connected car technologies. This allows for:
- Remote Diagnostics: Remote monitoring of vehicle health and performance.
- Predictive Maintenance: Predictive maintenance alerts based on OBD2 data.
- Usage-Based Insurance: Insurance rates based on driving behavior and vehicle usage.
- Fleet Management: Monitoring and management of vehicle fleets.
9.3 Advancements in Diagnostic Capabilities
What new diagnostic capabilities are being added to OBD2 scanners?
Advancements in diagnostic capabilities include:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI-powered diagnostics that can analyze data and suggest potential solutions.
- Cloud-Based Diagnostics: Cloud-based diagnostic platforms that provide access to a vast database of information and resources.
- Augmented Reality (AR): AR-enhanced diagnostics that provide visual guidance for repairs.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Barfx OBD2
Need quick answers? Check out these common questions about OBD2 scanners and diagnostics.
Q1: What is an OBD2 scanner?
An OBD2 scanner is a diagnostic tool used to read and interpret data from a vehicle’s On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD2) system. It helps diagnose issues by retrieving diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and other information.
Q2: How do I connect an OBD2 scanner to my car?
Locate the OBD2 port, typically under the dashboard on the driver’s side, and plug the scanner into the port.
Q3: What do OBD2 codes mean?
OBD2 codes are standardized alphanumeric codes that indicate specific problems detected by the vehicle’s diagnostic system.
Q4: Can I clear OBD2 codes myself?
Yes, you can clear OBD2 codes using a scanner, but ensure the underlying issue has been resolved first.
Q5: What is live data, and how is it useful?
Live data is a stream of real-time information from various sensors in the vehicle. It provides valuable insights into how the engine and other components are performing.
Q6: What are the benefits of using an OBD2 scanner?
Benefits include early problem detection, reduced emissions, standardized diagnostics, cost savings, improved fuel efficiency, and enhanced vehicle performance.
Q7: How often should I update my OBD2 scanner’s software?
Check for updates regularly and install them as needed to ensure the scanner has the latest vehicle information and diagnostic capabilities.
Q8: Can an OBD2 scanner diagnose ABS and SRS problems?
Some advanced OBD2 scanners can diagnose problems with the Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) and Supplemental Restraint System (SRS).
Q9: What is bi-directional control?
Bi-directional control allows the scanner to send commands to the vehicle’s ECU to activate certain components for testing purposes.
Q10: How do I choose the right OBD2 scanner for my needs?
Consider your budget, whether you need it for DIY or professional use, compatibility with your vehicle, and user reviews.
By understanding the basics of OBD2 systems, the functionality of OBD2 scanners, and common troubleshooting techniques, you can effectively diagnose and address vehicle problems. For more in-depth information and assistance, visit OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN.
Don’t let car troubles keep you guessing. With the right knowledge and tools, you can take control of your vehicle’s health and keep it running smoothly.
Take the Next Step: Contact OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN Today
Facing car troubles and unsure where to start? Let OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN help you diagnose and fix your vehicle issues quickly and efficiently.
- Expert Guidance: Get personalized advice on using OBD2 scanners effectively.
- Comprehensive Diagnostics: Understand what your car’s trouble codes really mean.
- Reliable Repairs: Find trusted repair solutions tailored to your vehicle’s needs.
Contact us now for a consultation:
- Address: 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
- Website: OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
Let OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN be your partner in vehicle diagnostics and repair. Reach out today and drive with confidence!