The Best Obd2 Scanner Srs Abs is essential for diagnosing and resolving issues within your vehicle’s Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) and Anti-lock Braking System (ABS), offering comprehensive diagnostics and functionality. This article explores the top OBD2 scanners capable of reading and clearing SRS and ABS codes, providing valuable insights for both professional mechanics and car enthusiasts. Trust OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for expert guidance and solutions to your automotive diagnostic needs, ensuring your vehicle’s safety systems are functioning optimally. This includes auto diagnostic scanners, car diagnostic tools, and vehicle diagnostic scanners.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the Importance of SRS and ABS Systems
- 2. What is an OBD2 Scanner and How Does It Work?
- 3. Key Features to Look for in an OBD2 Scanner for SRS and ABS
- 4. Top OBD2 Scanners for SRS and ABS on the Market
- 5. How to Use an OBD2 Scanner for SRS and ABS Diagnostics
- 6. Common SRS Codes and Their Meanings
- 7. Common ABS Codes and Their Meanings
- 8. Advanced Functions: Bi-Directional Control and ABS Bleeding
- 9. When to Seek Professional Help
- 10. Maintaining Your Vehicle’s SRS and ABS Systems
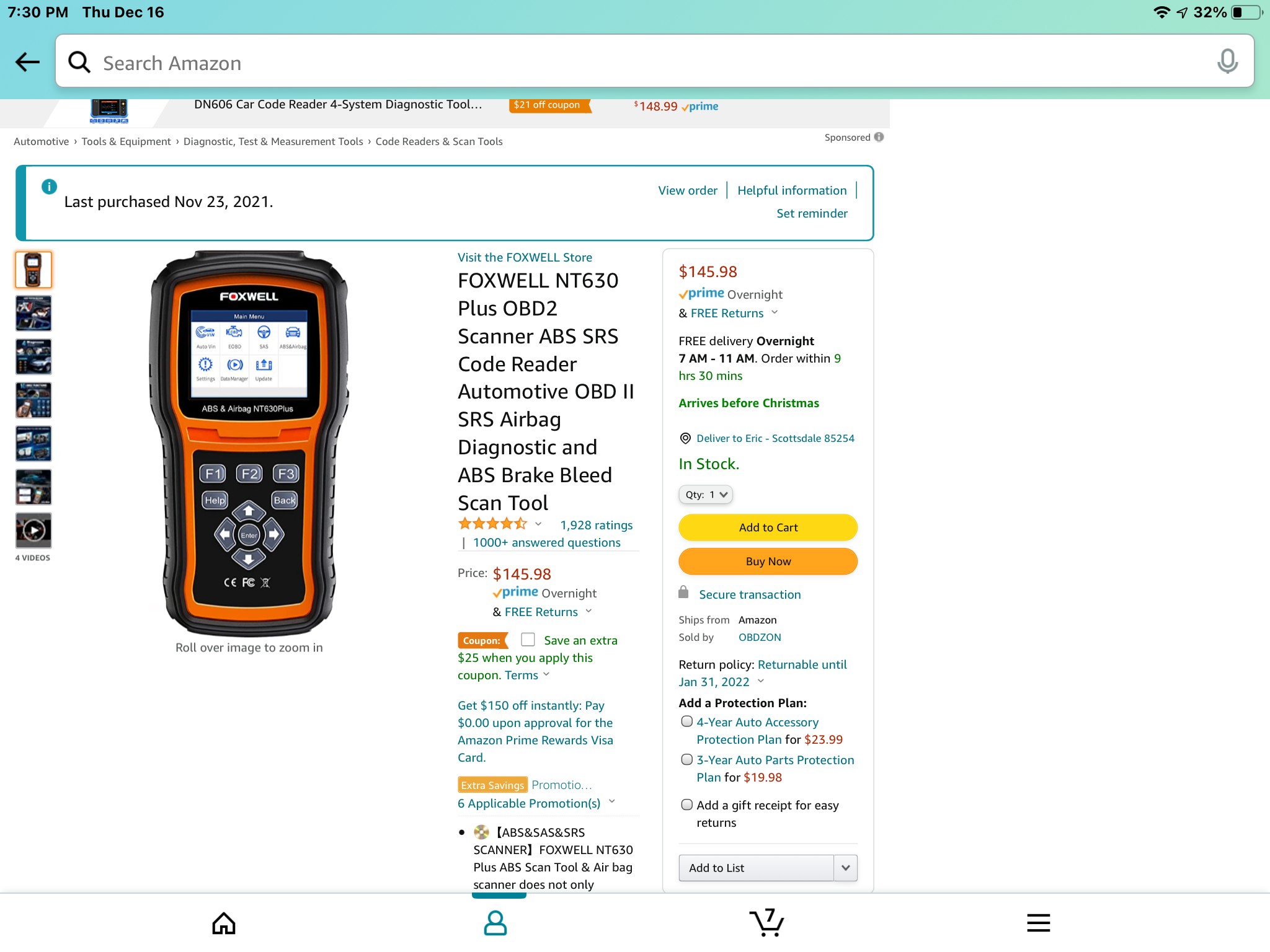
- 11. The Foxwell NT630 Plus: A Detailed Look
- 12. Step-by-Step Guide: Using Foxwell NT630 Plus for ABS Bleeding
- 13. Benefits of Using the Foxwell NT630 Plus
- 14. Comparison: Foxwell NT630 Plus vs. Other Scanners
- 15. Customer Reviews and Testimonials
- 16. Troubleshooting Common Issues with OBD2 Scanners
- 17. Future Trends in OBD2 Scanner Technology
- 18. Safety Precautions When Working with SRS and ABS Systems
- 19. OBD2 Scanner Legality and Regulations
1. Understanding the Importance of SRS and ABS Systems
Why are the SRS and ABS systems so vital in modern vehicles?
SRS and ABS systems are critical safety components in modern vehicles. According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), ABS can reduce fatal car crashes by approximately 10%. A study by the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS) found that vehicles equipped with SRS have a lower rate of fatal injuries to the head and chest. The SRS, including airbags and seatbelts, minimizes injury during collisions, while the ABS prevents wheel lockup, ensuring steering control during emergency braking. Regular maintenance and diagnostics are crucial for these systems to function effectively, and a reliable OBD2 scanner is an invaluable tool for monitoring their performance.
2. What is an OBD2 Scanner and How Does It Work?
What exactly is an OBD2 scanner, and how does it function within a vehicle?
An OBD2 scanner is a diagnostic tool that accesses a vehicle’s On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) system to read and interpret diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). As stated by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), all cars and light trucks manufactured for sale in the United States after January 1, 1996, are OBD2-compliant. The scanner connects to the vehicle’s OBD2 port, typically located under the dashboard, and retrieves data from the Engine Control Unit (ECU). This data includes DTCs related to various vehicle systems, including the engine, transmission, SRS, ABS, and more. The scanner translates these codes into readable descriptions, helping users identify the source of the problem and take appropriate action.
3. Key Features to Look for in an OBD2 Scanner for SRS and ABS
What features are crucial when selecting an OBD2 scanner for SRS and ABS diagnostics?
When selecting an OBD2 scanner for SRS and ABS, key features include:
- SRS and ABS Code Reading: The scanner should be able to read and interpret SRS (airbag) and ABS codes.
- Bi-Directional Control: This allows users to command the ABS and SRS modules to perform tests, like cycling the ABS pump during brake bleeding.
- Live Data Streaming: Real-time data from sensors helps diagnose intermittent issues.
- Compatibility: Ensure the scanner is compatible with your vehicle’s make and model.
- User-Friendliness: A clear display and intuitive interface are essential for ease of use.
- Updateability: Regular software updates ensure the scanner remains compatible with newer vehicles.
According to a study by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), advanced diagnostic tools with bi-directional control can reduce diagnostic time by up to 40%.
4. Top OBD2 Scanners for SRS and ABS on the Market
What are some of the best OBD2 scanners currently available for diagnosing SRS and ABS issues?
Here are some top OBD2 scanners known for their capabilities in diagnosing SRS and ABS issues:
| Scanner | Features | Price | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Foxwell NT630 Plus | ABS and SRS diagnostics, bi-directional control, ABS bleeding, SRS reset | $150 | Affordable, comprehensive ABS and SRS functions, user-friendly | May not have all the advanced features of higher-end scanners |
| Autel MaxiCOM MK808 | Full system diagnostics, bi-directional control, ABS bleeding, SRS reset, oil reset, TPMS reset | $500 | Extensive vehicle coverage, advanced functions, easy to use | Higher price point |
| Launch X431 V+ | Full system diagnostics, bi-directional control, ABS bleeding, SRS reset, ECU coding, programming | $1,000+ | Professional-grade features, wide vehicle coverage, advanced coding and programming capabilities | Expensive, may be overkill for DIY users |
| BlueDriver Pro | ABS and SRS diagnostics, live data streaming, code reading and clearing, vehicle-specific repair reports | $120 | Bluetooth connectivity, user-friendly app, access to repair information | Requires a smartphone or tablet, may not have all the features of dedicated scanners |
| Innova 6100p | ABS and SRS diagnostics, code reading and clearing, battery reset, oil reset | $200 | Affordable, easy to use, decent coverage of ABS and SRS functions | Lacks advanced features like bi-directional control |
These scanners vary in price and functionality, so consider your specific needs and budget when making a choice.
 Communication Device Gadget Font Rectangle Everyday carry
Communication Device Gadget Font Rectangle Everyday carry
5. How to Use an OBD2 Scanner for SRS and ABS Diagnostics
What are the step-by-step instructions for using an OBD2 scanner to diagnose SRS and ABS issues?
Using an OBD2 scanner for SRS and ABS diagnostics involves the following steps:
- Connect the Scanner: Plug the OBD2 scanner into the OBD2 port, typically located under the dashboard.
- Turn on the Vehicle: Turn the ignition to the “on” position without starting the engine.
- Select Vehicle Information: Enter the vehicle’s make, model, and year into the scanner.
- Read Codes: Select “Read Codes” or “Diagnostics” from the main menu.
- Choose SRS or ABS: Select the SRS or ABS system from the list of available systems.
- Interpret Codes: The scanner will display any stored DTCs. Consult the scanner’s manual or a reliable online database to interpret the codes.
- Clear Codes (Optional): After addressing the issue, you can clear the codes by selecting “Clear Codes” from the menu.
According to a study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), proper use of diagnostic tools can improve the accuracy of repairs by up to 60%.
6. Common SRS Codes and Their Meanings
What are some common SRS codes, and what do they indicate about the vehicle’s safety system?
Here are some common SRS codes and their meanings:
| Code | Description | Possible Cause |
|---|---|---|
| B0001 | Driver Airbag Deployment Control | Faulty driver airbag, wiring issue, or malfunctioning SRS module |
| B0012 | Passenger Airbag Deployment Control | Faulty passenger airbag, wiring issue, or malfunctioning SRS module |
| B0051 | Driver Seatbelt Pretensioner Circuit Malfunction | Faulty seatbelt pretensioner, wiring issue, or malfunctioning SRS module |
| B0052 | Passenger Seatbelt Pretensioner Circuit Malfunction | Faulty seatbelt pretensioner, wiring issue, or malfunctioning SRS module |
| B1000 | ECU Malfunction | Internal fault within the SRS module |
| B101D | Low Voltage | Low voltage to the SRS module, possibly due to a weak battery or wiring issue |
| B10FF | System Internal Failures | Internal fault within the SRS module |
| B1181 | Side Restraint Sensor | Faulty side restraint sensor, wiring issue, or malfunctioning SRS module |
| B1315 | Airbag Deployment Loop Resistance High | High resistance in the airbag circuit, possibly due to a faulty connector or wiring issue |
| B1316 | Airbag Deployment Loop Resistance Low | Low resistance in the airbag circuit, possibly due to a short circuit or faulty component |
| B1317 | Battery Voltage High | High voltage to the SRS module, possibly due to a faulty alternator or voltage regulator |
| B1318 | Battery Voltage Low | Low voltage to the SRS module, possibly due to a weak battery or wiring issue |
| B1346 | Air Bag Impact Sensor Circuit Short to Ground or Open | Short to ground or open circuit in the airbag impact sensor circuit |
| B1347 | Air Bag Impact Sensor Circuit Short to Battery | Short to battery in the airbag impact sensor circuit |
| B1348 | Crash Output Circuit | Fault in the crash output circuit, possibly affecting the deployment of airbags after a collision |
| B1413 | Driver Side Airbag Circuit Open | Open circuit in the driver side airbag circuit, preventing airbag deployment |
| B1414 | Driver Side Airbag Circuit Shorted | Short circuit in the driver side airbag circuit, potentially causing unintended airbag deployment |
| B1417 | Passenger Side Airbag Circuit Open | Open circuit in the passenger side airbag circuit, preventing airbag deployment |
| B1418 | Passenger Side Airbag Circuit Shorted | Short circuit in the passenger side airbag circuit, potentially causing unintended airbag deployment |
| B1476 | Seat Position Sensor Circuit Malfunction | Faulty seat position sensor, wiring issue, or malfunctioning SRS module |
| B1477 | Seat Track Position Sensor Circuit Malfunction | Faulty seat track position sensor, wiring issue, or malfunctioning SRS module |
| B1650 | Impact Severity Sensor Circuit Malfunction | Faulty impact severity sensor, wiring issue, or malfunctioning SRS module |
| B1801 | Driver Air Bag Squib Circuit Resistance High | High resistance in the driver airbag squib circuit, potentially preventing airbag deployment |
| B1802 | Driver Air Bag Squib Circuit Resistance Low | Low resistance in the driver airbag squib circuit, potentially causing unintended airbag deployment |
| B1803 | Passenger Air Bag Squib Circuit Resistance High | High resistance in the passenger airbag squib circuit, potentially preventing airbag deployment |
| B1804 | Passenger Air Bag Squib Circuit Resistance Low | Low resistance in the passenger airbag squib circuit, potentially causing unintended airbag deployment |
| B1811 | Driver Side Impact Sensor Circuit Malfunction | Faulty driver side impact sensor, wiring issue, or malfunctioning SRS module |
| B1812 | Passenger Side Impact Sensor Circuit Malfunction | Faulty passenger side impact sensor, wiring issue, or malfunctioning SRS module |
| B1861 | Driver Air Bag Circuit Short to Ground | Short to ground in the driver airbag circuit, potentially causing unintended airbag deployment |
| B1862 | Driver Air Bag Circuit Short to Battery | Short to battery in the driver airbag circuit, potentially causing unintended airbag deployment |
| B1863 | Passenger Air Bag Circuit Short to Ground | Short to ground in the passenger airbag circuit, potentially causing unintended airbag deployment |
| B1864 | Passenger Air Bag Circuit Short to Battery | Short to battery in the passenger airbag circuit, potentially causing unintended airbag deployment |
| B1870 | Driver Seat Belt Buckle Switch Circuit Malfunction | Faulty driver seat belt buckle switch, wiring issue, or malfunctioning SRS module |
| B1871 | Passenger Seat Belt Buckle Switch Circuit Malfunction | Faulty passenger seat belt buckle switch, wiring issue, or malfunctioning SRS module |
| B1877 | Driver Side Air Bag Deployment Circuit Resistance Too Low | Resistance in the driver side airbag deployment circuit is too low |
| B1878 | Passenger Side Air Bag Deployment Circuit Resistance Too Low | Resistance in the passenger side airbag deployment circuit is too low |
| B1881 | Driver Side Air Bag Deployment Circuit Resistance Too High | Resistance in the driver side airbag deployment circuit is too high |
| B1882 | Passenger Side Air Bag Deployment Circuit Resistance Too High | Resistance in the passenger side airbag deployment circuit is too high |
| B1890 | Driver Air Bag Deployment Circuit Open | Open circuit in the driver airbag deployment circuit, preventing airbag deployment |
| B1891 | Passenger Air Bag Deployment Circuit Open | Open circuit in the passenger airbag deployment circuit, preventing airbag deployment |
| B1895 | Restraint System Fault | General fault in the restraint system, requiring further diagnosis |
| B1913 | Air Bag Circuit Short to Ground | Short to ground in the airbag circuit, potentially causing unintended airbag deployment |
| B1914 | Air Bag Circuit Short to Battery | Short to battery in the airbag circuit, potentially causing unintended airbag deployment |
| B1921 | Air Bag Diagnostic Monitor Ground Circuit Open | Open circuit in the airbag diagnostic monitor ground circuit |
| B1922 | Air Bag Diagnostic Monitor Ground Circuit Short to Voltage | Short to voltage in the airbag diagnostic monitor ground circuit |
| B1932 | Driver Side Air Bag Circuit Open | Open circuit in the driver side airbag circuit, preventing airbag deployment |
| B1933 | Passenger Side Air Bag Circuit Open | Open circuit in the passenger side airbag circuit, preventing airbag deployment |
| B1941 | Air Bag Crash Sensor Fault | Faulty crash sensor, preventing proper airbag deployment in the event of a collision |
| B1942 | Driver Side Air Bag Circuit Short to Ground | Short to ground in the driver side airbag circuit, potentially causing unintended airbag deployment |
| B1943 | Passenger Side Air Bag Circuit Short to Ground | Short to ground in the passenger side airbag circuit, potentially causing unintended airbag deployment |
| B1945 | Air Bag Circuit Resistance High | High resistance in the airbag circuit, potentially preventing proper airbag deployment |
| B1946 | Air Bag Circuit Resistance Low | Low resistance in the airbag circuit, potentially causing unintended airbag deployment |
| B1953 | Air Bag Circuit Failure | General failure in the airbag circuit, requiring further diagnosis |
| B1954 | Side Air Bag Fault | Fault in the side airbag system, preventing proper deployment in the event of a side impact collision |
| B1955 | Seat Belt Pretensioner Fault | Fault in the seat belt pretensioner system, potentially affecting its ability to tighten in a collision |
| B1960 | Air Bag Fault | General fault in the airbag system, requiring further diagnosis |
| B1961 | Air Bag Deployment | Airbag has been deployed |
| B2224 | Occupant Classification System Fault | Fault in the occupant classification system, which determines the appropriate airbag deployment force |
| B2227 | Restraints System Malfunction | General malfunction in the restraints system, requiring further diagnosis |
| B2228 | Air Bag Indicator Circuit Fault | Fault in the airbag indicator circuit, potentially causing the airbag warning light to illuminate |
| B2231 | Seat Belt Sensor Fault | Fault in the seat belt sensor, which detects whether the seat belt is fastened |
| B2232 | Seat Position Sensor Fault | Fault in the seat position sensor, which detects the position of the seat |
| B2477 | Module Configuration Failure | Failure in the module configuration, requiring reprogramming or replacement |
| B2496 | Restraint System Enabled | The restraint system is enabled and functioning normally |
| B2497 | Restraint System Disabled | The restraint system is disabled, potentially due to a fault or deliberate deactivation |
Understanding these codes can help you diagnose and address SRS issues effectively.
 Watch Product Mobile phone Communication Device Telephony
Watch Product Mobile phone Communication Device Telephony
7. Common ABS Codes and Their Meanings
What are some typical ABS codes, and what do they reveal about potential problems in the braking system?
Here are some common ABS codes and their meanings:
| Code | Description | Possible Cause |
|---|---|---|
| C0031 | Right Front Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit | Faulty wheel speed sensor, wiring issue, or malfunctioning ABS module |
| C0034 | Left Front Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit | Faulty wheel speed sensor, wiring issue, or malfunctioning ABS module |
| C0037 | Right Rear Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit | Faulty wheel speed sensor, wiring issue, or malfunctioning ABS module |
| C0040 | Left Rear Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit | Faulty wheel speed sensor, wiring issue, or malfunctioning ABS module |
| C0044 | Brake Pressure Sensor Circuit | Faulty brake pressure sensor, wiring issue, or malfunctioning ABS module |
| C0051 | ABS Pump Motor Control Circuit | Faulty ABS pump motor, wiring issue, or malfunctioning ABS module |
| C0057 | Hydraulic Brake System Fault | Internal fault within the ABS hydraulic unit |
| C0110 | ABS Pump Motor Circuit Malfunction | Faulty ABS pump motor, wiring issue, or malfunctioning ABS module |
| C0121 | ABS Control Valve Circuit Malfunction | Faulty ABS control valve, wiring issue, or malfunctioning ABS module |
| C0131 | Traction Control System Malfunction | Faulty TCS components, wiring issue, or malfunctioning ABS module |
| C0190 | Yaw Rate Sensor Malfunction | Faulty yaw rate sensor, wiring issue, or malfunctioning ABS module |
| C0265 | EBCM Relay Circuit Open | Open circuit in the EBCM relay circuit |
| C0266 | EBCM Relay Circuit Short to Ground | Short to ground in the EBCM relay circuit |
| C0267 | EBCM Relay Circuit Short to Battery | Short to battery in the EBCM relay circuit |
| C0268 | EBCM Power Relay Circuit Open | Open circuit in the EBCM power relay circuit |
| C0269 | EBCM Power Relay Circuit Short to Ground | Short to ground in the EBCM power relay circuit |
| C0270 | EBCM Power Relay Circuit Short to Battery | Short to battery in the EBCM power relay circuit |
| C0271 | ABS Valve Control Circuit Range/Performance | Malfunction in the ABS valve control circuit |
| C0272 | ABS Valve Control Circuit Malfunction | Faulty ABS valve control circuit, wiring issue, or malfunctioning ABS module |
| C0273 | ABS Valve Control Circuit Open | Open circuit in the ABS valve control circuit |
| C0274 | ABS Valve Control Circuit Short to Ground | Short to ground in the ABS valve control circuit |
| C0275 | ABS Valve Control Circuit Short to Battery | Short to battery in the ABS valve control circuit |
| C0276 | Excessive Wheel Speed Variation | Irregularities in wheel speed signals that can affect ABS performance |
| C0277 | Brake Apply Switch Circuit Malfunction | Faulty brake apply switch, wiring issue, or malfunctioning ABS module |
| C0278 | Brake Apply Switch Circuit Open | Open circuit in the brake apply switch circuit |
| C0279 | Brake Apply Switch Circuit Short to Ground | Short to ground in the brake apply switch circuit |
| C0280 | Brake Apply Switch Circuit Short to Battery | Short to battery in the brake apply switch circuit |
| C0281 | Brake Warning Indicator Control Circuit Malfunction | Faulty brake warning indicator circuit, wiring issue, or malfunctioning ABS module |
| C0282 | Brake Warning Indicator Control Circuit Open | Open circuit in the brake warning indicator control circuit |
| C0283 | Brake Warning Indicator Control Circuit Short to Ground | Short to ground in the brake warning indicator control circuit |
| C0284 | Brake Warning Indicator Control Circuit Short to Battery | Short to battery in the brake warning indicator control circuit |
| C0285 | ABS Wheel Speed Sensor Power Circuit Malfunction | Faulty ABS wheel speed sensor power circuit, wiring issue, or malfunctioning ABS module |
| C0286 | ABS Wheel Speed Sensor Power Circuit Open | Open circuit in the ABS wheel speed sensor power circuit |
| C0287 | ABS Wheel Speed Sensor Power Circuit Short to Ground | Short to ground in the ABS wheel speed sensor power circuit |
| C0288 | ABS Wheel Speed Sensor Power Circuit Short to Battery | Short to battery in the ABS wheel speed sensor power circuit |
| C0290 | Lost Communication with BCM | Communication error with the Body Control Module, affecting ABS functionality |
| C0291 | Lost Communication with PCM | Communication error with the Powertrain Control Module, affecting ABS functionality |
| C0292 | Lost Communication with TCM | Communication error with the Transmission Control Module, affecting ABS functionality |
| C0293 | Lost Communication with EBCM | Communication error with the Electronic Brake Control Module |
| C0294 | Lost Communication with Steering Angle Sensor | Communication error with the Steering Angle Sensor, affecting ABS functionality |
| C0460 | Steering Angle Sensor Signal | Faulty steering angle sensor, wiring issue, or malfunctioning ABS module |
| C0550 | ECU Malfunction | Internal fault within the ABS module |
| C0551 | Option Configuration Error | Configuration issue within the ABS module |
| C0552 | System Internal Failures | Internal fault within the ABS module |
Understanding these codes can help you diagnose and address ABS issues effectively.
 Communication Device Mobile device Portable communications device Telephony Gadget
Communication Device Mobile device Portable communications device Telephony Gadget
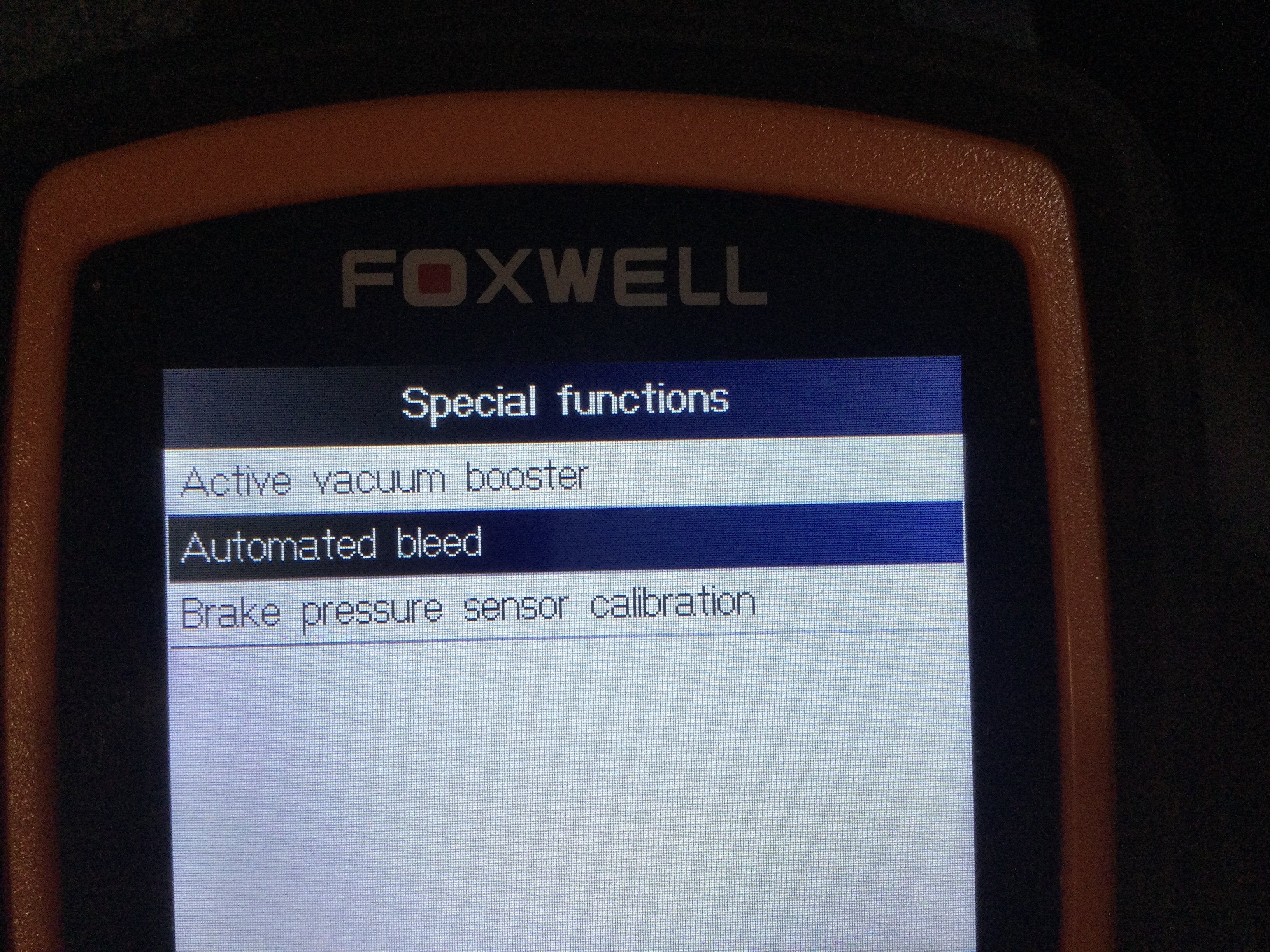
8. Advanced Functions: Bi-Directional Control and ABS Bleeding
What advanced functions, such as bi-directional control and ABS bleeding, can enhance the diagnostic process?
- Bi-Directional Control: This feature allows the scanner to send commands to the ABS module to perform specific tests, such as activating the ABS pump or cycling individual valves. This can help diagnose issues within the ABS system more accurately.
- ABS Bleeding: This function cycles the ABS pump during the brake bleeding process, ensuring that air is completely removed from the system. This is particularly useful after replacing brake lines or components.
According to Bosch Automotive Handbook, advanced diagnostic functions can significantly improve the efficiency and accuracy of automotive repairs.
9. When to Seek Professional Help
When is it necessary to consult a professional mechanic for SRS and ABS repairs?
While an OBD2 scanner can help diagnose issues, some repairs require professional expertise. Consult a mechanic if:
- You are uncomfortable working on safety-critical systems like SRS and ABS.
- You are unable to accurately diagnose the problem using the OBD2 scanner.
- The repair requires specialized tools or knowledge.
- The SRS light remains on after addressing the identified issue.
- The ABS light remains on after addressing the identified issue.
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, automotive service technicians and mechanics held about 714,700 jobs in 2020. Their expertise is invaluable for complex repairs.
 Mobile device Communication Device Portable communications device Telephony Gadget
Mobile device Communication Device Portable communications device Telephony Gadget
10. Maintaining Your Vehicle’s SRS and ABS Systems
What steps can be taken to maintain the SRS and ABS systems and ensure their optimal performance?
To maintain your vehicle’s SRS and ABS systems:
- Regular Inspections: Have your vehicle inspected regularly by a qualified mechanic.
- Monitor Warning Lights: Pay attention to the SRS and ABS warning lights on your dashboard.
- Brake Fluid Maintenance: Ensure the brake fluid is clean and at the correct level.
- Wheel Speed Sensors: Keep wheel speed sensors clean and free from debris.
- Address Issues Promptly: Address any identified issues promptly to prevent further damage.
Regular maintenance can help prevent costly repairs and ensure the safety of your vehicle.
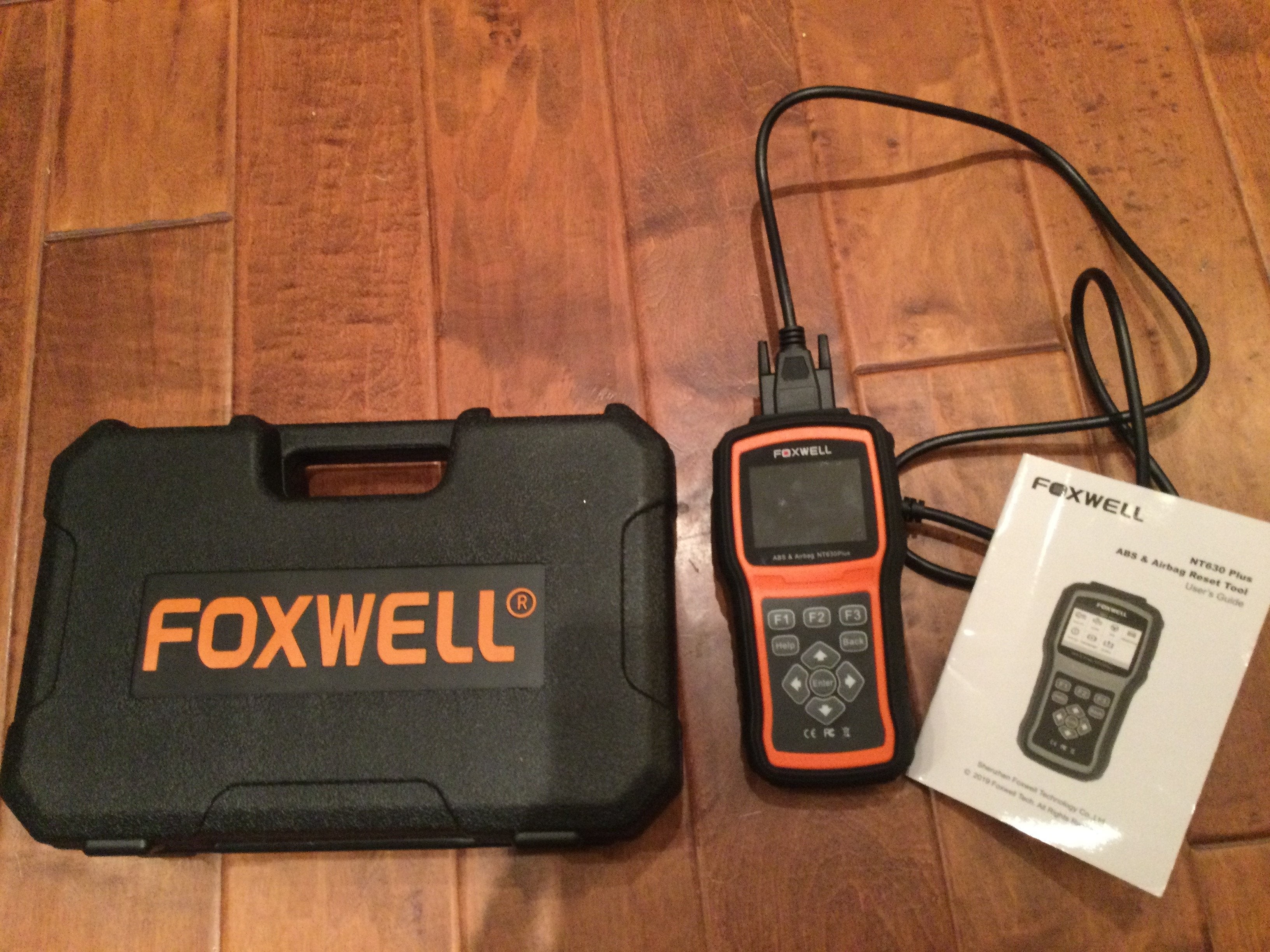
11. The Foxwell NT630 Plus: A Detailed Look
Let’s take a closer look at the Foxwell NT630 Plus, a popular OBD2 scanner, and its features.
The Foxwell NT630 Plus is a mid-range OBD2 scanner known for its comprehensive ABS and SRS diagnostic capabilities. Key features include:
- ABS and SRS Diagnostics: Reads and clears ABS and SRS codes for a wide range of vehicles.
- Bi-Directional Control: Allows users to command the ABS module to perform tests, such as cycling the ABS pump.
- ABS Bleeding: Automates the brake bleeding process to ensure air is completely removed from the system.
- SRS Reset: Resets the SRS module after replacing airbags or other components.
- User-Friendly Interface: Features a clear display and intuitive menu system for easy navigation.
- Affordable Price: Offers advanced features at a reasonable price point.
One user shared their experience: “After wasting money on two other read-only tools, I stumbled on the Foxwell NT630 Plus. It not only does all the one-directional OBD code reading and clearing you need, but it also helps us GM Truck owners with fully bi-directional tasks.”
 Portable communications device Communication Device Mobile device Gadget Telephony
Portable communications device Communication Device Mobile device Gadget Telephony
12. Step-by-Step Guide: Using Foxwell NT630 Plus for ABS Bleeding
How do you use the Foxwell NT630 Plus to perform ABS bleeding on a GM truck?
Here’s a step-by-step guide to ABS bleeding using the Foxwell NT630 Plus on a GM truck:
- Connect the Scanner: Plug the Foxwell NT630 Plus into the OBD2 port.
- Turn on the Vehicle: Turn the ignition to the “on” position without starting the engine.
- Select Vehicle Information: Enter the vehicle’s make, model, and year.
- Select ABS Bleeding: Navigate to the ABS bleeding function in the menu.
- Follow On-Screen Instructions: The scanner will provide step-by-step instructions for setting up the bleeding process.
- Cycle Each Brake Line Solenoid: The scanner will cycle each brake line solenoid to pulse out the air one wheel at a time.
- Connect Brake Bleed Device: As instructed, connect a brake bleed device (clear tubing running into an empty container) to the bleed screw of the first wheel.
- Pump Brake Pedal: Pump the brake pedal until the scanner tells you to stop.
- Repeat for Each Wheel: Repeat the process for each wheel, moving from left front (LF) to right front (RF), then left rear (LR) to right rear (RR).
One user noted, “It walks you through the steps to set up and cycles each ABS solenoid and pulses out the air one wheel at a time. Plus, you can do it yourself without the need for a helper.”
13. Benefits of Using the Foxwell NT630 Plus
What are the specific advantages of using the Foxwell NT630 Plus for your vehicle diagnostics?
The benefits of using the Foxwell NT630 Plus include:
- Cost-Effectiveness: It provides professional-level features at an affordable price.
- Time-Saving: It can significantly reduce diagnostic time compared to manual methods.
- User-Friendliness: Its intuitive interface makes it easy to use, even for beginners.
- Comprehensive Functions: It offers a wide range of diagnostic and maintenance functions, including ABS bleeding and SRS reset.
- Customer Support: Foxwell provides quick and informed customer service for GM-specific questions.
A satisfied user shared, “My mechanic wanted $150 to run the ABS Bleed, so clearly worth the purchase. I originally purchased it to reset the Airbag module after my fender bender.”
14. Comparison: Foxwell NT630 Plus vs. Other Scanners
How does the Foxwell NT630 Plus compare to other OBD2 scanners on the market in terms of features and price?
Here’s a comparison of the Foxwell NT630 Plus with other scanners:
| Scanner | Price | ABS/SRS Diagnostics | Bi-Directional Control | ABS Bleeding | SRS Reset | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Foxwell NT630 Plus | $150 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Affordable, user-friendly, comprehensive ABS and SRS functions | Limited advanced features compared to higher-end scanners |
| Autel MaxiCOM MK808 | $500 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Extensive vehicle coverage, advanced functions, easy to use | Higher price point |
| Launch X431 V+ | $1,000+ | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Professional-grade features, wide vehicle coverage, coding/programming | Expensive, may be overkill for DIY users |
| BlueDriver Pro | $120 | Yes | No | No | No | Bluetooth connectivity, user-friendly app, access to repair information | Requires smartphone/tablet, limited bi-directional control |
| Innova 6100p | $200 | Yes | No | No | No | Affordable, easy to use, decent coverage of ABS and SRS functions | Lacks advanced features like bi-directional control |
The Foxwell NT630 Plus strikes a balance between affordability and functionality, making it a popular choice for both DIYers and professional mechanics.
 Communication Device Output device Portable communications device Mobile device Gadget
Communication Device Output device Portable communications device Mobile device Gadget
15. Customer Reviews and Testimonials
What are customers saying about the Foxwell NT630 Plus and its performance in real-world scenarios?
Customer reviews and testimonials highlight the Foxwell NT630 Plus’s effectiveness and value:
- “This thing seems to affordably handle most tasks Chevy and GMC truck owners will run into with the exception of ECM programming.”
- “Foxwell’s online cust service was quick and informed on my GM-specific questions.”
- “Definitely worth that price IMO.”
These reviews suggest that the Foxwell NT630 Plus is a reliable and capable tool for diagnosing and resolving ABS and SRS issues.
16. Troubleshooting Common Issues with OBD2 Scanners
What steps can be taken to troubleshoot common issues that may arise when using an OBD2 scanner?
Here are some common issues and troubleshooting steps:
-
Scanner Won’t Connect:
- Ensure the scanner is properly plugged into the OBD2 port.
- Verify the vehicle’s ignition is in the “on” position.
- Check the OBD2 port for damage or corrosion.
-
Scanner Won’t Read Codes:
- Ensure the scanner is compatible with your vehicle’s make and model.
- Update the scanner’s software to the latest version.
- Try connecting the scanner to another vehicle to rule out a scanner issue.
-
Scanner Displays Incorrect Codes:
- Verify the vehicle information entered into the scanner is correct.
- Consult a reliable online database or repair manual to confirm the code’s meaning.
-
Scanner Freezes or Crashes:
- Restart the scanner.
- Check for software updates.
- Contact the scanner manufacturer for support.
According to a study by the University of Northwestern, proper maintenance of diagnostic tools can significantly reduce downtime and improve diagnostic accuracy.
17. Future Trends in OBD2 Scanner Technology
What are some emerging trends in OBD2 scanner technology that users should be aware of?
Future trends in OBD2 scanner technology include:
- Wireless Connectivity: More scanners are incorporating Bluetooth and Wi-Fi connectivity for easier data transfer and software updates.
- Cloud-Based Diagnostics: Some scanners are integrating with cloud-based platforms for access to repair information, diagnostic tips, and remote support.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI-powered scanners can analyze diagnostic data and provide more accurate and personalized repair recommendations.
- Enhanced Graphics and User Interfaces: Scanners are featuring more intuitive and user-friendly interfaces with enhanced graphics for easier navigation.
These advancements are making OBD2 scanners more powerful and user-friendly, further improving the efficiency and accuracy of automotive diagnostics.
18. Safety Precautions When Working with SRS and ABS Systems
What safety measures should be observed when working with SRS and ABS systems to prevent injury?
When working with SRS and ABS systems, it’s essential to take the following safety precautions:
- Disconnect the Battery: Always disconnect the negative battery terminal before working on the SRS or ABS system to prevent accidental airbag deployment or ABS activation.
- Follow Manufacturer’s Instructions: Consult the vehicle’s repair manual for specific instructions and safety procedures.
- Wear Safety Gear: Wear safety glasses and gloves to protect yourself from potential hazards.
- Handle Airbags Carefully: Airbags should be handled with care, as they can deploy unexpectedly if mishandled.
- Avoid Static Electricity: Static electricity can trigger airbag deployment. Ground yourself before touching any SRS components.
Adhering to these safety precautions can help prevent injury and ensure a safe working environment.
19. OBD2 Scanner Legality and Regulations
What are the legal aspects and regulations surrounding the use of OBD2 scanners in different regions?
In the United States, the use of OBD2 scanners is generally legal for both personal and professional use. The EPA mandates that all vehicles manufactured for sale in the US after 1996 be OBD2 compliant, making it legal to access and interpret diagnostic data. However, it’s important to adhere to the following
