The best Bluetooth OBD2 protocol for a 2007 Dodge Grand Caravan is ISO15765-4/SAE J2480 (CAN). Using the right protocol ensures accurate data and efficient diagnostics for your vehicle, and at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we’re committed to providing the knowledge and tools you need for optimal car care. This protocol is vital for effective car diagnostics, enhancing your ability to monitor vehicle health, troubleshoot problems, and maintain peak performance, all while keeping you informed and in control. Embrace the ease of modern vehicle diagnostics, improve your troubleshooting abilities, and ensure your car’s lasting performance with the right protocol.
Contents
- 1. Understanding OBD2 Protocols
- 1.1. What Are OBD2 Protocols?
- 1.2. Key OBD2 Protocols
- 1.3. Why Protocol Compatibility Matters
- 1.4. Evolution of OBD2 Protocols
- 1.5. Identifying the Correct Protocol
- 1.6. Resources for Further Learning
- 2. CAN Protocol: The Modern Standard
- 2.1. Advantages of CAN Protocol
- 2.2. Why CAN Became the Standard
- 2.3. CAN Protocol Pinout
- 2.4. Identifying CAN Protocol on Your Vehicle
- 2.5. Using CAN Protocol with Bluetooth OBD2 Scanners
- 2.6. Resources for Further Learning
- 3. Setting Up Your Bluetooth OBD2 Scanner
- 3.1. Step 1: Purchase a Compatible Scanner
- 3.2. Step 2: Download the Scanner App
- 3.3. Step 3: Plug the Scanner into the DLC
- 3.4. Step 4: Pair the Scanner with Your Device
- 3.5. Step 5: Configure the App
- 3.6. Step 6: Start Scanning
- 3.7. Troubleshooting Connection Issues
- 3.8. Resources for Further Assistance
- 4. Reading and Interpreting OBD2 Trouble Codes
- 4.1. What Are OBD2 Trouble Codes?
- 4.2. Structure of OBD2 Trouble Codes
- 4.3. Common OBD2 Trouble Codes
- 4.4. Reading Trouble Codes with a Bluetooth OBD2 Scanner
- 4.5. Interpreting Trouble Codes
- 4.6. Clearing Trouble Codes
- 4.7. Resources for Further Learning
- 5. Real-Time Data Monitoring
- 5.1. What Is Real-Time Data Monitoring?
- 5.2. Key Parameters to Monitor
- 5.3. Using a Bluetooth OBD2 Scanner for Real-Time Data Monitoring
- 5.4. Interpreting Real-Time Data
- 5.5. Resources for Further Learning
- 6. Performing Diagnostic Tests
- 6.1. Types of Diagnostic Tests
- 6.2. How to Perform Diagnostic Tests
- 6.3. Interpreting Test Results
- 6.4. Resources for Further Learning
- 7. Common Issues and Solutions for 2007 Dodge Grand Caravan
- 7.1. Transmission Problems
- 7.2. Engine Misfires
- 7.3. Oxygen Sensor Problems
- 7.4. Catalytic Converter Failure
- 7.5. Evaporative Emission Control System (EVAP) Leaks
- 7.6. Resources for Further Assistance
- 8. Advanced Diagnostics with OBD2 Scanners
- 8.1. Enhanced Code Reading
- 8.2. Bi-Directional Control
- 8.3. Freeze Frame Data
- 8.4. I/M Readiness Monitors
- 8.5. On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) Monitoring
- 8.6. Accessing Advanced Diagnostics
- 8.7. Resources for Further Learning
- 9. Maintaining Your 2007 Dodge Grand Caravan
- 9.1. Regular Oil Changes
- 9.2. Tire Maintenance
- 9.3. Brake Service
- 9.4. Fluid Checks
- 9.5. Air Filter Replacement
- 9.6. Spark Plug Replacement
- 9.7. Belt and Hose Inspection
- 9.8. OBD2 Scanning
- 9.9. Resources for Further Assistance
- 10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- 10.1. What is an OBD2 scanner?
- 10.2. How do I read OBD2 codes?
- 10.3. What does the P0300 code mean?
- 10.4. Can I use any OBD2 scanner with my 2007 Dodge Grand Caravan?
- 10.5. How do I clear OBD2 codes?
- 10.6. What is real-time data monitoring?
- 10.7. How often should I scan my car for trouble codes?
- 10.8. Can an OBD2 scanner fix my car?
- 10.9. What is the DLC location in a 2007 Dodge Grand Caravan?
- 10.10. Where can I get help with my OBD2 scanner?
1. Understanding OBD2 Protocols
OBD2 (On-Board Diagnostics version 2) protocols are standardized communication interfaces used to access diagnostic data from a vehicle’s engine control unit (ECU). These protocols enable diagnostic tools, like Bluetooth OBD2 scanners, to read trouble codes, monitor real-time data, and perform various diagnostic tests. Understanding these protocols is essential for anyone involved in vehicle diagnostics and repair.
1.1. What Are OBD2 Protocols?
OBD2 protocols are sets of rules and standards that govern how diagnostic tools communicate with a vehicle’s computer. These protocols ensure that different tools can effectively retrieve data from a wide range of vehicles. According to the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), the primary goal of OBD2 is to standardize vehicle diagnostics, making it easier for technicians to identify and address issues across different makes and models.
1.2. Key OBD2 Protocols
Several OBD2 protocols have been used over the years, each with its own specifications and applications. The main protocols include:
- J1850 PWM (Pulse Width Modulation): Used primarily by Ford.
- J1850 VPW (Variable Pulse Width): Used primarily by General Motors.
- ISO9141-2: Used by Chrysler, European, and Asian vehicles.
- ISO14230-4 (KWP2000): Also used by Chrysler, European, and Asian vehicles.
- ISO15765-4/SAE J2480 (CAN – Controller Area Network): The modern standard used by all vehicles sold in the US after 2008.
1.3. Why Protocol Compatibility Matters
Selecting the correct OBD2 protocol is crucial for establishing a reliable connection between the diagnostic tool and the vehicle’s ECU. Using an incompatible protocol can result in a failure to communicate, inaccurate data readings, or even potential damage to the vehicle’s electronic systems. Therefore, it’s vital to verify the appropriate protocol for your specific vehicle model and year.
1.4. Evolution of OBD2 Protocols
The transition from older protocols to CAN was driven by the need for faster communication speeds, increased data capacity, and improved error detection. According to a study by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), CAN offers significant advantages in terms of diagnostic capabilities and real-time data monitoring, leading to more accurate and efficient vehicle maintenance.
1.5. Identifying the Correct Protocol
There are several ways to identify the correct OBD2 protocol for your vehicle:
- Check the Vehicle’s Manual: The owner’s manual often specifies the OBD2 protocol used by the vehicle.
- Inspect the DLC Connector: The Diagnostic Link Connector (DLC) pinout can indicate the protocol (more details on this below).
- Use a Protocol Detection Tool: Some OBD2 scanners can automatically detect the vehicle’s protocol.
1.6. Resources for Further Learning
For more in-depth information on OBD2 protocols, consider exploring these resources:
- SAE International: Provides detailed technical specifications and standards for OBD2 protocols.
- EPA (Environmental Protection Agency): Offers regulatory information and studies related to vehicle emissions and diagnostics.
- OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN: Your go-to source for expert advice, detailed guides, and the latest tools in OBD2 technology.
2. CAN Protocol: The Modern Standard
The CAN (Controller Area Network) protocol represents a significant advancement in vehicle communication technology. It is the standard protocol for all vehicles manufactured and sold in the United States since 2008, including the 2007 Dodge Grand Caravan.
2.1. Advantages of CAN Protocol
CAN offers several advantages over older OBD2 protocols:
- Faster Communication Speed: CAN allows for quicker data transfer, enabling real-time monitoring of various vehicle parameters.
- Increased Data Capacity: CAN can handle a larger volume of data, providing more comprehensive diagnostic information.
- Improved Error Detection: CAN incorporates robust error detection mechanisms, ensuring the accuracy and reliability of the data transmitted.
- Flexibility and Scalability: CAN supports a wide range of electronic control units (ECUs) within the vehicle, allowing for seamless integration and expansion of diagnostic capabilities.
2.2. Why CAN Became the Standard
The transition to CAN was driven by the increasing complexity of modern vehicles and the need for more efficient and reliable diagnostic capabilities. As vehicles incorporated more electronic systems, the older OBD2 protocols struggled to keep up with the data demands. According to Bosch, a leading supplier of automotive technology, CAN provides the necessary bandwidth and robustness to handle the data-intensive tasks required by modern vehicle systems.
2.3. CAN Protocol Pinout
The CAN protocol uses specific pins on the DLC connector for communication:
- Pin 4: Chassis Ground
- Pin 5: Signal Ground
- Pin 6: CAN High (CAN+)
- Pin 14: CAN Low (CAN-)
- Pin 16: Battery Positive
2.4. Identifying CAN Protocol on Your Vehicle
To verify that your vehicle uses the CAN protocol, inspect the DLC connector for the presence of pins 6 and 14. If these pins are populated, your vehicle is CAN-compliant.
2.5. Using CAN Protocol with Bluetooth OBD2 Scanners
Bluetooth OBD2 scanners that support the CAN protocol can communicate with your vehicle’s ECU wirelessly, allowing you to read trouble codes, monitor real-time data, and perform diagnostic tests using your smartphone or tablet. These scanners offer convenience and portability, making them ideal for both professional technicians and DIY enthusiasts.
2.6. Resources for Further Learning
For more detailed information on the CAN protocol, consider exploring these resources:
- Controller Area Network (CAN) Specification: Provides the technical details of the CAN protocol.
- SAE J1939 Standards: Defines the use of CAN in heavy-duty vehicles.
- OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN: Your trusted resource for expert guidance, detailed tutorials, and the latest advancements in OBD2 technology.
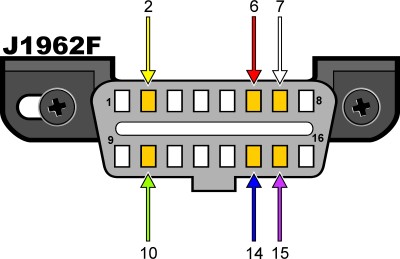 OBDII connector pinout
OBDII connector pinout
3. Setting Up Your Bluetooth OBD2 Scanner
Setting up a Bluetooth OBD2 scanner for your 2007 Dodge Grand Caravan is a straightforward process. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you get started:
3.1. Step 1: Purchase a Compatible Scanner
Ensure that the Bluetooth OBD2 scanner you purchase supports the CAN protocol, as this is the standard for your 2007 Dodge Grand Caravan. Look for scanners that specifically mention CAN or ISO15765-4 compatibility.
3.2. Step 2: Download the Scanner App
Most Bluetooth OBD2 scanners require a companion app to function. Download the app recommended by the scanner manufacturer from the App Store (iOS) or Google Play Store (Android). Popular apps include Torque Pro, OBD Fusion, and Car Scanner ELM OBD2.
3.3. Step 3: Plug the Scanner into the DLC
Locate the DLC connector in your 2007 Dodge Grand Caravan. It is typically found under the dashboard on the driver’s side. Plug the Bluetooth OBD2 scanner into the DLC connector.
3.4. Step 4: Pair the Scanner with Your Device
Turn on your vehicle’s ignition (but don’t start the engine). Enable Bluetooth on your smartphone or tablet and search for available devices. Select the Bluetooth OBD2 scanner from the list of available devices. You may be prompted to enter a pairing code (usually “1234” or “0000”).
3.5. Step 5: Configure the App
Open the scanner app and configure the connection settings. Select the appropriate OBD2 protocol (usually set to “Automatic” or “CAN”). Follow the app’s instructions to establish a connection with the scanner.
3.6. Step 6: Start Scanning
Once the connection is established, you can start scanning your vehicle for trouble codes, monitor real-time data, and perform diagnostic tests using the app’s features.
3.7. Troubleshooting Connection Issues
If you encounter connection issues, try the following:
- Verify that the scanner is securely plugged into the DLC connector.
- Ensure that Bluetooth is enabled on your device and that the scanner is properly paired.
- Check the app settings to ensure that the correct OBD2 protocol is selected.
- Restart your vehicle and try again.
3.8. Resources for Further Assistance
For additional help with setting up your Bluetooth OBD2 scanner, consider these resources:
- Scanner Manufacturer’s Website: Provides detailed instructions and troubleshooting tips for your specific scanner model.
- Online Forums and Communities: Offers valuable insights and solutions from other users.
- OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN: Your dedicated partner for expert guidance, step-by-step tutorials, and the latest innovations in OBD2 technology.
4. Reading and Interpreting OBD2 Trouble Codes
Reading and interpreting OBD2 trouble codes is a critical skill for diagnosing and repairing vehicle issues. Here’s a comprehensive guide to help you understand the process:
4.1. What Are OBD2 Trouble Codes?
OBD2 trouble codes are standardized codes that indicate specific issues or malfunctions detected by the vehicle’s ECU. These codes are designed to help technicians quickly identify the source of a problem and perform the necessary repairs. According to the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), understanding these codes is essential for effective vehicle diagnostics.
4.2. Structure of OBD2 Trouble Codes
OBD2 trouble codes consist of five characters: one letter followed by four numbers. Each character provides specific information about the nature and location of the problem:
- First Character (Letter):
- P: Powertrain (engine, transmission, fuel system)
- B: Body (interior, exterior, safety systems)
- C: Chassis (brakes, suspension, steering)
- U: Network (communication systems)
- Second Character (Number):
- 0: Generic (SAE standard)
- 1: Manufacturer-specific
- Third Character (Number): Indicates the system or subsystem affected:
- 0: Fuel and air metering and auxiliary emission controls
- 1: Fuel and air metering
- 2: Fuel and air metering (injector circuit)
- 3: Ignition system or misfires
- 4: Auxiliary emission controls
- 5: Vehicle speed controls and idle control system
- 6: Computer output circuit
- 7: Transmission
- 8: Transmission
- Fourth and Fifth Characters (Numbers): Specify the exact fault within the identified system.
4.3. Common OBD2 Trouble Codes
Here are some common OBD2 trouble codes and their meanings:
| Code | Description | Possible Causes |
|---|---|---|
| P0300 | Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected | Faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, fuel injectors, vacuum leaks |
| P0171 | System Too Lean (Bank 1) | Vacuum leaks, faulty O2 sensor, low fuel pressure, MAF sensor issues |
| P0420 | Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1) | Faulty catalytic converter, O2 sensor issues, exhaust leaks |
| P0101 | Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor Circuit Range/Performance Problem | Dirty or faulty MAF sensor, vacuum leaks |
| P0301 | Cylinder 1 Misfire Detected | Faulty spark plug, ignition coil, fuel injector, low compression in cylinder 1 |
4.4. Reading Trouble Codes with a Bluetooth OBD2 Scanner
To read trouble codes using a Bluetooth OBD2 scanner, follow these steps:
- Connect the scanner to the DLC connector.
- Turn on the vehicle’s ignition (but don’t start the engine).
- Pair the scanner with your smartphone or tablet via Bluetooth.
- Open the scanner app and select the “Read Codes” or “Diagnostic Codes” option.
- The app will display any stored trouble codes, along with their descriptions.
4.5. Interpreting Trouble Codes
Once you have read the trouble codes, use online resources or repair manuals to understand their meanings and potential causes. Remember to address the most likely causes first, and always follow proper diagnostic procedures.
4.6. Clearing Trouble Codes
After addressing the underlying issue, you can clear the trouble codes using the scanner app. Select the “Clear Codes” or “Erase Codes” option. Keep in mind that clearing codes does not fix the problem; it only removes the symptom. If the underlying issue persists, the trouble code will reappear.
4.7. Resources for Further Learning
For more in-depth information on reading and interpreting OBD2 trouble codes, consider these resources:
- OBD-II Trouble Code Database: Provides detailed information on thousands of OBD2 trouble codes.
- Vehicle Repair Manuals: Offers specific diagnostic and repair procedures for your vehicle make and model.
- OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN: Your ultimate destination for expert advice, detailed guides, and the latest innovations in OBD2 technology.
5. Real-Time Data Monitoring
Real-time data monitoring is a powerful feature of Bluetooth OBD2 scanners that allows you to observe various vehicle parameters as they change over time. This can be invaluable for diagnosing intermittent issues, monitoring engine performance, and identifying potential problems before they lead to breakdowns.
5.1. What Is Real-Time Data Monitoring?
Real-time data monitoring involves accessing and displaying live data streams from the vehicle’s ECU. This data can include engine speed (RPM), vehicle speed, coolant temperature, intake air temperature, oxygen sensor readings, fuel trim values, and many other parameters. According to a study by the American Automobile Association (AAA), real-time data monitoring can significantly improve diagnostic accuracy and reduce repair times.
5.2. Key Parameters to Monitor
Some of the most useful parameters to monitor in real-time include:
- Engine RPM: Indicates the speed at which the engine is running.
- Vehicle Speed: Shows the current speed of the vehicle.
- Coolant Temperature: Monitors the temperature of the engine coolant, helping to identify overheating issues.
- Intake Air Temperature (IAT): Measures the temperature of the air entering the engine, which can affect performance and fuel efficiency.
- Oxygen Sensor Readings: Provides insights into the performance of the oxygen sensors, which are crucial for proper fuel mixture control.
- Fuel Trim Values: Indicates how the ECU is adjusting the fuel mixture to compensate for lean or rich conditions.
- Mass Air Flow (MAF): Measures the amount of air entering the engine, which is essential for calculating the correct fuel mixture.
- Throttle Position: Shows the position of the throttle, which affects engine power and acceleration.
5.3. Using a Bluetooth OBD2 Scanner for Real-Time Data Monitoring
To monitor real-time data using a Bluetooth OBD2 scanner, follow these steps:
- Connect the scanner to the DLC connector.
- Turn on the vehicle’s ignition (but don’t start the engine).
- Pair the scanner with your smartphone or tablet via Bluetooth.
- Open the scanner app and select the “Real-Time Data” or “Live Data” option.
- The app will display a list of available parameters. Select the ones you want to monitor.
- The app will then display the real-time values of the selected parameters, often in the form of graphs or gauges.
5.4. Interpreting Real-Time Data
Interpreting real-time data requires a good understanding of how each parameter relates to the overall performance of the vehicle. Here are some tips:
- Compare Data to Specifications: Consult your vehicle’s repair manual or online resources to find the expected range of values for each parameter.
- Look for Abnormal Readings: Pay attention to any values that are outside the expected range, as this may indicate a problem.
- Monitor Trends: Observe how the values change over time, looking for any unusual patterns or fluctuations.
- Correlate Data with Symptoms: Relate the data to any symptoms you are experiencing with the vehicle, such as poor performance, rough idling, or unusual noises.
5.5. Resources for Further Learning
For more in-depth information on real-time data monitoring, consider these resources:
- Vehicle Repair Manuals: Provides detailed specifications and diagnostic procedures for your vehicle make and model.
- Online Forums and Communities: Offers valuable insights and tips from other users.
- OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN: Your trusted partner for expert guidance, comprehensive tutorials, and the latest advancements in OBD2 technology.
6. Performing Diagnostic Tests
In addition to reading trouble codes and monitoring real-time data, Bluetooth OBD2 scanners can also perform various diagnostic tests. These tests can help you further pinpoint the source of a problem and verify the effectiveness of repairs.
6.1. Types of Diagnostic Tests
Some common diagnostic tests that can be performed with a Bluetooth OBD2 scanner include:
- Oxygen Sensor Test: Evaluates the performance of the oxygen sensors, ensuring they are providing accurate readings.
- Catalyst Monitor Test: Checks the efficiency of the catalytic converter, verifying that it is properly reducing emissions.
- Evaporative System Test: Tests the integrity of the evaporative emissions control system, ensuring that it is not leaking fuel vapors into the atmosphere.
- Misfire Monitor Test: Monitors the engine for misfires, which can indicate problems with the ignition system, fuel injectors, or compression.
- EGR System Test: Evaluates the performance of the exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) system, which helps to reduce emissions.
6.2. How to Perform Diagnostic Tests
The specific steps for performing diagnostic tests vary depending on the scanner app and the test being performed. However, the general process is as follows:
- Connect the scanner to the DLC connector.
- Turn on the vehicle’s ignition (but don’t start the engine).
- Pair the scanner with your smartphone or tablet via Bluetooth.
- Open the scanner app and select the “Diagnostic Tests” or “On-Board Monitoring” option.
- Choose the test you want to perform from the list of available tests.
- Follow the app’s instructions to initiate and complete the test.
- The app will display the results of the test, indicating whether the system passed or failed.
6.3. Interpreting Test Results
Interpreting the results of diagnostic tests requires a good understanding of the system being tested and the expected outcome. Consult your vehicle’s repair manual or online resources for guidance. If a test fails, it indicates that there is a problem with the system that needs to be addressed.
6.4. Resources for Further Learning
For more in-depth information on performing diagnostic tests, consider these resources:
- Vehicle Repair Manuals: Provides detailed diagnostic procedures and specifications for your vehicle make and model.
- Online Forums and Communities: Offers valuable insights and tips from other users.
- OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN: Your dedicated partner for expert guidance, comprehensive tutorials, and the latest innovations in OBD2 technology.
7. Common Issues and Solutions for 2007 Dodge Grand Caravan
The 2007 Dodge Grand Caravan is a reliable vehicle, but like all cars, it can experience certain common issues. Here are some of the most frequent problems and potential solutions, which can be diagnosed using a Bluetooth OBD2 scanner:
7.1. Transmission Problems
Issue: The 2007 Dodge Grand Caravan is known for transmission problems, including rough shifting, slipping gears, and complete transmission failure.
Possible Causes: Low transmission fluid, worn-out clutches, faulty solenoids, or a defective torque converter.
Solutions:
- Check Transmission Fluid: Use the dipstick to check the transmission fluid level and condition. If the fluid is low or dirty, add or replace it as needed.
- OBD2 Scan: Use a Bluetooth OBD2 scanner to check for transmission-related trouble codes, such as P0700 (Transmission Control System Malfunction) or P0740 (Torque Converter Clutch Circuit Malfunction).
- Professional Inspection: If the problem persists, take the vehicle to a qualified mechanic for a thorough inspection and repair.
7.2. Engine Misfires
Issue: Engine misfires can cause rough idling, poor acceleration, and reduced fuel economy.
Possible Causes: Faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, fuel injectors, or vacuum leaks.
Solutions:
- Check Spark Plugs: Inspect the spark plugs for wear, damage, or carbon buildup. Replace them as needed.
- Inspect Ignition Coils: Use a multimeter to test the ignition coils for proper resistance. Replace any faulty coils.
- Check Fuel Injectors: Use a fuel injector cleaner to clean the fuel injectors. If the problem persists, have them professionally tested and replaced if necessary.
- Check for Vacuum Leaks: Inspect vacuum hoses for cracks, leaks, or loose connections. Replace any damaged hoses.
- OBD2 Scan: Use a Bluetooth OBD2 scanner to check for misfire-related trouble codes, such as P0300 (Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected) or P0301 (Cylinder 1 Misfire Detected).
7.3. Oxygen Sensor Problems
Issue: Faulty oxygen sensors can cause poor fuel economy, increased emissions, and engine performance issues.
Possible Causes: Worn-out sensors, contamination, or wiring problems.
Solutions:
- Inspect Oxygen Sensors: Visually inspect the oxygen sensors for damage or contamination.
- Test Oxygen Sensors: Use a multimeter to test the oxygen sensors for proper voltage and resistance. Replace any faulty sensors.
- OBD2 Scan: Use a Bluetooth OBD2 scanner to check for oxygen sensor-related trouble codes, such as P0131 (O2 Sensor Circuit Low Voltage – Bank 1 Sensor 1) or P0171 (System Too Lean – Bank 1).
7.4. Catalytic Converter Failure
Issue: A failing catalytic converter can cause reduced engine performance, increased emissions, and a rotten egg smell.
Possible Causes: Contamination, overheating, or physical damage.
Solutions:
- Inspect Catalytic Converter: Visually inspect the catalytic converter for damage or corrosion.
- Test Catalytic Converter Efficiency: Use a Bluetooth OBD2 scanner to perform a catalyst monitor test. If the test fails, the catalytic converter may need to be replaced.
- OBD2 Scan: Use a Bluetooth OBD2 scanner to check for catalytic converter-related trouble codes, such as P0420 (Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold – Bank 1).
7.5. Evaporative Emission Control System (EVAP) Leaks
Issue: EVAP leaks can cause fuel odors, poor fuel economy, and increased emissions.
Possible Causes: Leaky gas cap, damaged fuel tank, or faulty EVAP system components.
Solutions:
- Check Gas Cap: Ensure that the gas cap is properly tightened and in good condition.
- Inspect EVAP System Components: Visually inspect the EVAP system components for damage or leaks.
- Perform EVAP System Test: Use a Bluetooth OBD2 scanner to perform an EVAP system test. If the test fails, further diagnosis is needed to pinpoint the source of the leak.
- OBD2 Scan: Use a Bluetooth OBD2 scanner to check for EVAP system-related trouble codes, such as P0440 (Evaporative Emission Control System Malfunction).
7.6. Resources for Further Assistance
For additional help with diagnosing and repairing common issues in your 2007 Dodge Grand Caravan, consider these resources:
- Vehicle Repair Manuals: Provides detailed diagnostic and repair procedures for your vehicle make and model.
- Online Forums and Communities: Offers valuable insights and tips from other owners.
- OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN: Your trusted resource for expert guidance, comprehensive tutorials, and the latest advancements in OBD2 technology.
8. Advanced Diagnostics with OBD2 Scanners
Advanced diagnostics with OBD2 scanners go beyond basic code reading and real-time data monitoring, offering sophisticated tools for in-depth vehicle analysis. These features are particularly useful for diagnosing complex issues and optimizing vehicle performance.
8.1. Enhanced Code Reading
Enhanced code reading allows you to access manufacturer-specific trouble codes that are not part of the standard OBD2 protocol. These codes can provide more detailed information about the nature and location of a problem.
8.2. Bi-Directional Control
Bi-directional control enables you to send commands to the vehicle’s ECU to activate specific components or systems. This can be useful for testing actuators, solenoids, and other devices.
8.3. Freeze Frame Data
Freeze frame data captures a snapshot of the vehicle’s operating conditions at the moment a trouble code was triggered. This information can help you understand the circumstances that led to the problem.
8.4. I/M Readiness Monitors
I/M readiness monitors indicate whether the vehicle’s emission control systems have been tested and are ready for an emissions inspection.
8.5. On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) Monitoring
On-board diagnostics monitoring provides detailed information about the performance of various vehicle systems, including the engine, transmission, and emissions controls.
8.6. Accessing Advanced Diagnostics
To access advanced diagnostics, you will need a Bluetooth OBD2 scanner that supports these features. Some scanner apps may require a subscription or additional purchase to unlock advanced functionality.
8.7. Resources for Further Learning
For more in-depth information on advanced diagnostics, consider these resources:
- Vehicle Repair Manuals: Provides detailed diagnostic procedures and specifications for your vehicle make and model.
- Online Forums and Communities: Offers valuable insights and tips from other users.
- OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN: Your dedicated partner for expert guidance, comprehensive tutorials, and the latest innovations in OBD2 technology.
9. Maintaining Your 2007 Dodge Grand Caravan
Proper maintenance is essential for keeping your 2007 Dodge Grand Caravan running smoothly and reliably. Here are some key maintenance tasks that you should perform regularly:
9.1. Regular Oil Changes
Change the engine oil and filter according to the manufacturer’s recommended intervals. This will help to keep the engine clean and properly lubricated.
9.2. Tire Maintenance
Check the tire pressure regularly and rotate the tires every 6,000 to 8,000 miles. This will help to ensure even wear and prolong the life of the tires.
9.3. Brake Service
Inspect the brake pads, rotors, and calipers regularly. Replace any worn or damaged components.
9.4. Fluid Checks
Check the levels and condition of all essential fluids, including engine oil, coolant, transmission fluid, brake fluid, and power steering fluid. Add or replace fluids as needed.
9.5. Air Filter Replacement
Replace the engine air filter and cabin air filter according to the manufacturer’s recommended intervals. This will help to ensure proper engine performance and air quality inside the vehicle.
9.6. Spark Plug Replacement
Replace the spark plugs according to the manufacturer’s recommended intervals. This will help to maintain proper ignition and engine performance.
9.7. Belt and Hose Inspection
Inspect the belts and hoses for cracks, wear, or leaks. Replace any damaged components.
9.8. OBD2 Scanning
Regularly scan your vehicle for trouble codes using a Bluetooth OBD2 scanner. This will help you identify potential problems early on and prevent them from escalating into more serious issues.
9.9. Resources for Further Assistance
For more detailed information on maintaining your 2007 Dodge Grand Caravan, consider these resources:
- Vehicle Owner’s Manual: Provides detailed maintenance schedules and recommendations.
- Vehicle Repair Manuals: Offers step-by-step instructions for performing various maintenance tasks.
- OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN: Your trusted resource for expert guidance, comprehensive tutorials, and the latest advancements in OBD2 technology.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Here are some frequently asked questions about Bluetooth OBD2 scanners and the 2007 Dodge Grand Caravan:
10.1. What is an OBD2 scanner?
An OBD2 scanner is a diagnostic tool used to read trouble codes, monitor real-time data, and perform diagnostic tests on vehicles. It connects to the vehicle’s diagnostic link connector (DLC) and communicates with the engine control unit (ECU).
10.2. How do I read OBD2 codes?
To read OBD2 codes, connect the scanner to the DLC, turn on the vehicle’s ignition, pair the scanner with your smartphone or tablet via Bluetooth, and use the scanner app to select the “Read Codes” or “Diagnostic Codes” option.
10.3. What does the P0300 code mean?
The P0300 code indicates a random/multiple cylinder misfire detected. It means that the engine is experiencing misfires in one or more cylinders.
10.4. Can I use any OBD2 scanner with my 2007 Dodge Grand Caravan?
Yes, as long as the scanner supports the CAN protocol, which is the standard for all vehicles sold in the US after 2008.
10.5. How do I clear OBD2 codes?
To clear OBD2 codes, connect the scanner to the DLC, turn on the vehicle’s ignition, pair the scanner with your smartphone or tablet via Bluetooth, and use the scanner app to select the “Clear Codes” or “Erase Codes” option.
10.6. What is real-time data monitoring?
Real-time data monitoring involves accessing and displaying live data streams from the vehicle’s ECU, such as engine speed, vehicle speed, coolant temperature, and oxygen sensor readings.
10.7. How often should I scan my car for trouble codes?
You should scan your car for trouble codes whenever you experience a warning light or unusual symptoms, such as poor performance, rough idling, or unusual noises. Regular scanning can also help you identify potential problems early on.
10.8. Can an OBD2 scanner fix my car?
No, an OBD2 scanner cannot fix your car. It is a diagnostic tool that helps you identify the source of a problem. You will need to perform the necessary repairs to fix the underlying issue.
10.9. What is the DLC location in a 2007 Dodge Grand Caravan?
The DLC connector is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
10.10. Where can I get help with my OBD2 scanner?
You can get help with your OBD2 scanner from the scanner manufacturer’s website, online forums and communities, or OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN.
Understanding the correct Bluetooth OBD2 protocol for your 2007 Dodge Grand Caravan, combined with regular maintenance and timely diagnostics, will keep your vehicle running smoothly and reliably for years to come.
Are you ready to take control of your vehicle’s diagnostics? Contact us at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN today. Our experts are available to guide you through selecting the right OBD2 scanner and interpreting your vehicle’s data for optimal performance. Call us at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit us at 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States. Let us help you keep your 2007 Dodge Grand Caravan in top condition.