Are you wondering if OBD2 scanner codes can help you fix your car? Absolutely, OBD2 scanner codes are instrumental in diagnosing and resolving vehicle issues, and at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we provide the insights and tools necessary to interpret these codes effectively. Utilizing an OBD II scan tool to read and understand these codes is the first step toward efficient automotive diagnostics, enabling informed repair decisions and cost savings. For comprehensive vehicle diagnostics, consider exploring resources on car diagnostic tools and automotive diagnostic services.
Contents
- 1. Understanding OBD2 Scanner Codes
- 1.1. How OBD2 Codes Work
- 1.2. Accessing OBD2 Codes
- 1.3. Why OBD2 Codes Matter
- 2. Types of OBD2 Scanner Codes
- 2.1. Powertrain Codes (P-Codes)
- Example: P0101 – Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor Issue
- 2.2. Body Codes (B-Codes)
- Example: B0020 – Driver’s Side Airbag Deployment Circuit Issue
- 2.3. Chassis Codes (C-Codes)
- Example: C1234 – Right Front Wheel Speed Sensor Issue
- 2.4. Network Communication Codes (U-Codes)
- Example: U0100 – Loss of Communication with Engine Control Module (ECM)
- 3. Decoding OBD2 Scanner Codes
- 3.1. Trouble Code System – The First Character
- 3.2. Code Type – The Second Character
- Example: Standardized vs. Manufacturer-Specific Codes
- 3.3. Affected System – The Third Character
- 3.4. Specific Code – The Fourth and Fifth Characters
- Example: P0420 Explained
- 4. Clearing OBD2 Scanner Codes
- 4.1. Using an OBD II Scanner
- Benefits of Using OBD2 Scanners
- 4.2. Drive Cycle
- Limitations of Drive Cycles
- 4.3. Consulting a Mechanic
- Advantages of Professional Diagnosis
- 5. Preventing OBD2 Scanner Codes
- 5.1. Regular Vehicle Maintenance
- Essential Maintenance Tasks
- Following the Maintenance Schedule
- Professional Maintenance Services
- 5.2. Using Quality Fuel and Fluids
- Impact of Low-Quality Fluids and Fuel
- Best Practices for Fuel and Fluids
- 6. Managing OBD2 Codes for Your Fleet
- 6.1. Centralized Code Tracking
- Benefits of Centralization
- 6.2. Ongoing Fleet Monitoring
- Advantages of Continuous Monitoring
- 6.3. Prioritizing Repairs Based on Severity
- Severity-Based Approach
- 7. Common OBD2 Codes and Their Meanings
- 8. The Role of OBD2 Scanners in Modern Car Repair
- 8.1. Enhanced Diagnostic Accuracy
- 8.2. Cost Savings
- 8.3. Preventive Maintenance
- 8.4. Real-Time Data Monitoring
- 9. Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner
- 9.1. Compatibility
- 9.2. Features
- 9.3. Ease of Use
- 9.4. Price
- 10. Staying Updated with OBD2 Technology
- 10.1. Professional Training and Certifications
- 10.2. Online Resources and Forums
- 10.3. Industry Publications and Trade Shows
- 10.4. Networking with Professionals
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- What is an OBD2 scanner?
- How do I read OBD2 scanner codes?
- What do the different types of OBD2 codes mean?
- Can I clear OBD2 codes myself?
- What are some common OBD2 codes and their meanings?
- How can I prevent OBD2 codes from appearing?
- When should I consult a mechanic for OBD2 codes?
- What are the benefits of using an OBD2 scanner?
- How do I choose the right OBD2 scanner?
- How can OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN help me with OBD2 codes?
- Closing Thoughts
1. Understanding OBD2 Scanner Codes
What exactly are OBD2 scanner codes, and how can they help you? On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD2) scanner codes are alphanumeric codes that a vehicle’s onboard computer system generates to indicate detected issues within the vehicle’s systems. According to a 2017 report by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), OBD2 systems have been mandatory on all cars and light trucks sold in the U.S. since 1996, making them a universal tool for vehicle diagnostics. These codes serve as a crucial communication method, helping car owners and technicians identify problems ranging from minor discrepancies to major malfunctions.
1.1. How OBD2 Codes Work
How do these codes actually work inside your vehicle? Various components within your vehicle, such as the engine, transmission, and emissions systems, continuously exchange information with the onboard computer. As stated in a SAE International study, when an irregularity is detected, the computer generates a corresponding code. For instance, if the “Check Engine” light comes on, it signifies that a specific system or part in the engine is not performing as expected.
 OBD2 code meaning explained
OBD2 code meaning explained
1.2. Accessing OBD2 Codes
So how do you access these codes? By using an OBD II code reader or scan tool, you can connect to your vehicle’s OBD2 port, typically located beneath the dashboard. This scan tool retrieves the numerical trouble code, which pinpoints the underlying problem. It acts as a guide, helping you or your mechanic determine the exact source of the issue.
1.3. Why OBD2 Codes Matter
Why should you even care about OBD2 codes? These codes are a valuable resource for troubleshooting and making informed decisions about vehicle maintenance and repairs. According to a study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), understanding OBD2 codes can lead to quicker and more accurate diagnoses, reducing repair time and costs. For fleet managers, in particular, knowing these codes can significantly improve vehicle uptime and operational efficiency.
2. Types of OBD2 Scanner Codes
What are the different types of OBD2 scanner codes you might encounter? When one of your vehicles displays an OBD2 code, identifying the specific type is crucial for finding the general problem. These codes are categorized into four main types, each relating to different vehicle systems.
2.1. Powertrain Codes (P-Codes)
What do powertrain codes indicate? Powertrain codes (P-codes) highlight problems within your vehicle’s engine, transmission, and drivetrain components. These codes offer essential information about issues affecting your vehicle’s power and performance aspects.
Example: P0101 – Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor Issue
Let’s say you encounter the powertrain code P0101. According to research from the University of Michigan’s Automotive Research Center, this code indicates a potential problem with the Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor. The MAF sensor measures the air entering the engine, helping the vehicle’s computer determine the correct fuel-air mixture for optimal performance. If the MAF sensor isn’t functioning correctly, it could lead to issues like poor fuel efficiency and reduced engine performance.
2.2. Body Codes (B-Codes)
What do body codes signify? Body codes (B-codes) identify potential problems within various vehicle body systems, such as lighting, airbags, and climate control.
Example: B0020 – Driver’s Side Airbag Deployment Circuit Issue
Consider the body code B0020. This code indicates an issue with the driver’s side airbag deployment circuit. If this circuit isn’t functioning correctly, the driver’s side airbag may not deploy as intended during a collision. This poses a significant safety risk, as airbags play a crucial role in protecting occupants during accidents, as noted by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA).
2.3. Chassis Codes (C-Codes)
What do chassis codes reveal? Chassis codes (C-codes) identify potential issues within the vehicle’s chassis and related systems, including suspension, steering, and brakes.
Example: C1234 – Right Front Wheel Speed Sensor Issue
For instance, the chassis code C1234 indicates a problem with the right front wheel speed sensor. According to a study by Bosch Automotive Electronics, when this sensor doesn’t function correctly, it can compromise the vehicle’s stability and handling, making it unsafe to drive, especially in challenging road conditions. Additionally, a malfunctioning speed sensor can trigger problems with the vehicle’s anti-lock brake system (ABS), leading to reduced braking effectiveness.
2.4. Network Communication Codes (U-Codes)
What do network communication codes imply? Network communication codes (U-codes) identify potential problems within the vehicle’s communication systems, including modules and sensors that exchange information.
Example: U0100 – Loss of Communication with Engine Control Module (ECM)
Take the network communication code U0100, which signals a breakdown in communication with the Engine Control Module (ECM). This issue often stems from a faulty battery or wiring. The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) explains that if the U0100 code appears, you might notice symptoms such as diminished engine power, slow acceleration, and decreased fuel efficiency. In rare occurrences, this breakdown could even lead to the engine stalling while driving, posing a significant safety risk.
3. Decoding OBD2 Scanner Codes
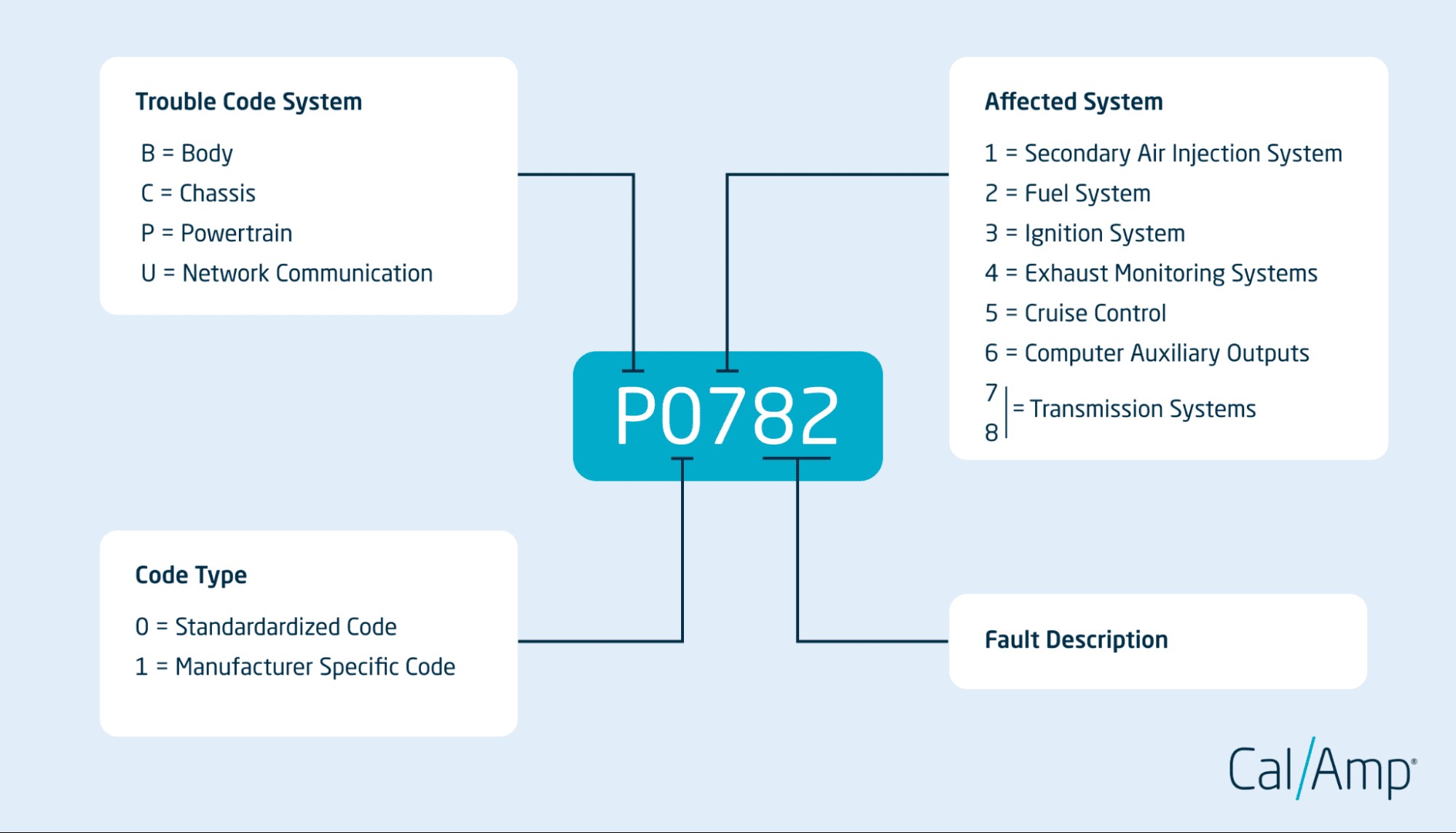
How do you interpret OBD2 scanner codes? OBD2 codes consist of five letters and digits, each conveying a distinct meaning. Understanding the trouble code system, code type, affected system, and specific code is valuable for pinpointing the exact problem.
3.1. Trouble Code System – The First Character
What does the first character of an OBD2 code indicate? The first character indicates the area of concern:
- P stands for Powertrain (engine, transmission, etc.)
- B stands for Body (airbags, lighting, etc.)
- C stands for Chassis (brakes, steering, suspension, etc.)
- U stands for Network Communication
3.2. Code Type – The Second Character
What does the second character of an OBD2 code signify? The second character indicates whether the code is standardized or manufacturer-specific:
- 0 indicates a standardized (or generic) code, which is the same across all vehicles.
- 1 indicates a manufacturer-specific code, which offers more detailed insights unique to each carmaker.
Example: Standardized vs. Manufacturer-Specific Codes
- P0420 is a generic code that often points to a problem with the catalytic converter.
- P1101 could be a manufacturer-specific code indicating a particular issue with the air intake system.
3.3. Affected System – The Third Character
What does the third character of an OBD2 code refer to? The third character refers to the specific part of your vehicle that’s experiencing an issue:
- 1: Secondary Air Injection System
- 2: Fuel System
- 3: Ignition System
- 4: Exhaust Monitoring Systems
- 5: Cruise Control
- 6: Computer Auxiliary Outputs
- 7, 8: Transmission System
3.4. Specific Code – The Fourth and Fifth Characters
What do the fourth and fifth characters specify? These characters provide a detailed identifier that precisely describes the particular issue within the affected system.
Example: P0420 Explained
In the code “P0420,” the ’20’ indicates a potential problem with the catalytic converter in the powertrain system.
4. Clearing OBD2 Scanner Codes
How do you clear OBD2 codes, and when should you do it? Although it’s generally not advisable to clear OBD2 codes without addressing the underlying issues, there are instances where you might need to clear them.
4.1. Using an OBD II Scanner
How can an OBD2 scanner help clear codes? OBD2 scanners not only identify issues within a vehicle’s systems by retrieving Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) but also allow you to clear these codes after addressing the problem.
Benefits of Using OBD2 Scanners
According to a study by the Automotive Aftermarket Industry Association (AAIA), using OBD2 scanners enables vehicle owners and fleet managers to perform preliminary diagnostics, potentially resolving minor issues without costly visits to mechanics. By addressing problems early, you prevent them from escalating into more significant, expensive repairs. OBD2 scanners are particularly useful for monitoring and clearing codes related to the fuel system and emissions. This proactive approach can enhance fuel efficiency, resulting in cost savings, reduced emissions, and positive environmental impacts.
4.2. Drive Cycle
What is a drive cycle, and how does it help? Some codes may clear on their own after a series of successful drive cycles. This typically involves driving your vehicle under certain conditions (e.g., at a specific speed and temperature range) to allow the system to retest and potentially clear the code.
Limitations of Drive Cycles
While drive cycles can assist in clearing some codes, they may not work for all issues. Complex problems might require professional intervention.
4.3. Consulting a Mechanic
When should you seek professional help? If you’re unsure how to clear codes or suspect a deeper issue, consulting a mechanic is always a wise decision.
Advantages of Professional Diagnosis
Mechanics have the training, experience, and diagnostic tools to accurately identify the root cause of the OBD2 codes. They can pinpoint the problem, ensuring it’s not just temporarily cleared but properly fixed. This approach helps prevent further damage to your vehicle, ultimately saving you money and hassle. Moreover, professional mechanics often conduct thorough inspections, checking related components and systems to ensure the issue won’t resurface.
5. Preventing OBD2 Scanner Codes
What steps can you take to prevent OBD2 codes from appearing? Preventing the occurrence of OBD2 codes is essential to avoid costly repairs and keep your vehicles running smoothly.
5.1. Regular Vehicle Maintenance
Why is regular maintenance important? Regularly maintaining your vehicles, including routine inspections, fluid changes, and timely repairs, can prevent OBD2 codes from occurring.
Essential Maintenance Tasks
According to the Car Care Council, routine maintenance tasks include:
- Regular oil changes
- Air filter replacements
- Spark plug inspections
- Brake system checks
- Tire rotations
 OBD2 code meaning explained
OBD2 code meaning explained
Following the Maintenance Schedule
Adhering to the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule, as outlined in your vehicle’s owner’s manual, is crucial. This schedule considers factors such as mileage and time to determine when specific maintenance tasks are due.
Professional Maintenance Services
For comprehensive maintenance, consider using a mechanic who can conduct thorough inspections and address issues before they escalate into problems that trigger OBD2 codes.
5.2. Using Quality Fuel and Fluids
Why does the quality of fuel and fluids matter? Using high-quality fuel and fluids is vital to prevent OBD2 codes.
Impact of Low-Quality Fluids and Fuel
Low-quality fluids lack proper lubrication, leading to increased wear and potentially triggering engine or transmission codes. Inferior fuel can cause incomplete combustion, leading to efficiency issues and emissions-related codes.
Best Practices for Fuel and Fluids
- Fuel: Choose reputable gas stations and use high-quality fuel that meets or exceeds recommended octane ratings.
- Fluids: Use manufacturer-recommended fluids, such as engine oil, transmission fluid, coolant, and brake fluid.
- Regular Checks: Periodically check and top up fluids, including engine oil, to ensure they remain at the correct levels and maintain their effectiveness.
6. Managing OBD2 Codes for Your Fleet
How can you efficiently manage OBD2 codes for an entire fleet of vehicles? Streamlining the management of OBD2 codes through standardization and automation can save you from individually inspecting each vehicle.
6.1. Centralized Code Tracking
What does centralized code tracking involve? Centralizing code tracking means gathering OBD2 code data from all fleet vehicles into one system, simplifying data management and access.
Benefits of Centralization
This centralized system provides real-time insights, keeping fleet managers informed about ongoing issues. It also enables the analysis of historical code data, helping managers identify patterns and trends in specific vehicles or systems.
6.2. Ongoing Fleet Monitoring
How does ongoing monitoring help? Ongoing monitoring employs telematics systems to collect real-time data from fleet vehicles. This data includes vehicle location, performance metrics, and OBD2 code occurrences.
Advantages of Continuous Monitoring
With monitoring, fleet managers can detect OBD2 codes and associated issues as they occur, facilitating swift responses to minimize vehicle downtime. Proactive monitoring contributes to cost reduction by preventing major breakdowns, reducing repair expenses, and optimizing vehicle performance and fuel efficiency.
6.3. Prioritizing Repairs Based on Severity
Why is prioritization important? Fleet managers should categorize OBD2 codes based on their severity and potential impact on vehicle operation. Prioritizing repairs ensures efficient resource allocation.
Severity-Based Approach
High-severity codes should be addressed promptly to minimize vehicle downtime and maintain uninterrupted fleet operations. Low-severity codes can be scheduled for repair during planned maintenance intervals.
7. Common OBD2 Codes and Their Meanings
What are some of the most common OBD2 codes and their typical causes? Knowing the common codes can help you quickly identify and address frequent issues.
| Code | Description | Possible Causes |
|---|---|---|
| P0171 | System Too Lean (Bank 1) | Vacuum leak, faulty MAF sensor, clogged fuel filter, low fuel pressure |
| P0300 | Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected | Faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, fuel injectors, vacuum leaks, low compression |
| P0420 | Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold Bank 1 | Faulty catalytic converter, exhaust leaks, faulty oxygen sensors |
| P0442 | Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected | Loose or faulty gas cap, cracked or damaged vapor lines, faulty purge valve, faulty vent valve |
| P0455 | Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected | Loose or faulty gas cap, cracked or damaged vapor lines, faulty purge valve, faulty vent valve |
| P0101 | Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor Circuit Range/Performance | Dirty or faulty MAF sensor, vacuum leaks, faulty wiring or connections |
| P0113 | Intake Air Temperature Circuit High Input | Faulty intake air temperature sensor, open circuit in wiring, poor connection |
| P0301 | Cylinder 1 Misfire Detected | Faulty spark plug, ignition coil, fuel injector, low compression in cylinder 1 |
| P0304 | Cylinder 4 Misfire Detected | Faulty spark plug, ignition coil, fuel injector, low compression in cylinder 4 |
| P0135 | O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1, Sensor 1) | Faulty oxygen sensor, open or short circuit in heater wiring, faulty ECM |
| P0133 | O2 Sensor Slow Response (Bank 1, Sensor 1) | Faulty oxygen sensor, exhaust leaks, contaminated sensor |
| P0118 | Engine Coolant Temperature Circuit High Input | Faulty coolant temperature sensor, open circuit in wiring, poor connection |
| P0128 | Coolant Thermostat (Coolant Temperature Below Thermostat Regulating Temperature) | Faulty thermostat, low coolant level, faulty coolant temperature sensor |
| P0116 | Engine Coolant Temperature Circuit Range/Performance | Faulty coolant temperature sensor, low coolant level, wiring issues |
| P0401 | Exhaust Gas Recirculation Flow Insufficient Detected | Clogged EGR valve or passages, faulty EGR valve solenoid, vacuum leaks |
| P0403 | Exhaust Gas Recirculation Circuit Malfunction | Faulty EGR valve solenoid, wiring issues, faulty ECM |
| P0102 | Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor Circuit Low Input | Dirty or faulty MAF sensor, wiring issues, vacuum leaks |
| P0103 | Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor Circuit High Input | Faulty MAF sensor, wiring issues, vacuum leaks |
| P0174 | System Too Lean (Bank 2) | Vacuum leak, faulty MAF sensor, clogged fuel filter, low fuel pressure |
| P0155 | O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Malfunction (Bank 2, Sensor 1) | Faulty oxygen sensor, wiring issues, faulty ECM |
8. The Role of OBD2 Scanners in Modern Car Repair
How essential are OBD2 scanners in today’s automotive repair landscape? As vehicles become increasingly complex with advanced computer systems, the role of OBD2 scanners in modern car repair has become indispensable. According to a report by Grand View Research, the global automotive diagnostics market is expected to reach $46.9 billion by 2027, highlighting the growing reliance on diagnostic tools like OBD2 scanners.
8.1. Enhanced Diagnostic Accuracy
How do OBD2 scanners improve diagnostic accuracy? OBD2 scanners provide precise diagnostic information, enabling mechanics and car owners to pinpoint issues quickly and accurately. By retrieving specific trouble codes, these tools eliminate guesswork and reduce the time needed to diagnose problems, leading to more efficient and effective repairs.
8.2. Cost Savings
How can using OBD2 scanners lead to cost savings? By facilitating accurate diagnoses and preventing unnecessary repairs, OBD2 scanners help save money. Car owners can avoid costly trips to the mechanic for issues they can resolve themselves with the help of a scanner, and mechanics can focus on fixing the actual problem rather than spending time on trial-and-error troubleshooting.
8.3. Preventive Maintenance
Can OBD2 scanners support preventive maintenance? OBD2 scanners support preventive maintenance by allowing users to monitor their vehicle’s performance and identify potential problems before they escalate. Regular scanning can reveal minor issues that, if left unaddressed, could lead to major repairs. This proactive approach helps extend the lifespan of the vehicle and ensures its reliability.
8.4. Real-Time Data Monitoring
What real-time data can OBD2 scanners provide? Many advanced OBD2 scanners offer real-time data monitoring, providing insights into various vehicle parameters such as engine temperature, RPM, and fuel efficiency. This information can be invaluable for diagnosing performance issues and optimizing vehicle operation.
9. Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner
What factors should you consider when selecting an OBD2 scanner? With a wide range of OBD2 scanners available on the market, choosing the right one can be overwhelming. Here are some key factors to consider:
9.1. Compatibility
Is the scanner compatible with your vehicle? Ensure that the OBD2 scanner is compatible with your vehicle’s make, model, and year. While most scanners support standard OBD2 protocols, some may not work with older or non-standard vehicles.
9.2. Features
What features do you need? Consider the features that are important to you. Basic scanners can read and clear trouble codes, while more advanced models offer features such as real-time data monitoring, graphing, and access to repair databases.
9.3. Ease of Use
How user-friendly is the scanner? Choose a scanner that is easy to use, with a clear display and intuitive interface. Some scanners also come with mobile apps that make it easy to view and interpret data on your smartphone or tablet.
9.4. Price
What is your budget? OBD2 scanners range in price from affordable basic models to expensive professional-grade tools. Determine your budget and choose a scanner that offers the best value for your money.
10. Staying Updated with OBD2 Technology
How can you stay informed about the latest advancements in OBD2 technology? The field of automotive diagnostics is constantly evolving, with new technologies and standards emerging regularly. Staying updated with the latest advancements in OBD2 technology is essential for mechanics and car owners alike.
10.1. Professional Training and Certifications
How can professional training help? Consider pursuing professional training and certifications in automotive diagnostics. Organizations such as the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE) offer certifications that demonstrate your knowledge and expertise in the field.
10.2. Online Resources and Forums
Where can you find information online? Take advantage of online resources and forums to stay informed about the latest OBD2 technologies and best practices. Websites, blogs, and online communities dedicated to automotive diagnostics can provide valuable insights and tips.
10.3. Industry Publications and Trade Shows
What industry publications should you follow? Follow industry publications and attend trade shows to learn about new products and technologies. Automotive magazines, journals, and trade events are excellent sources of information.
10.4. Networking with Professionals
Why is networking important? Network with other professionals in the automotive industry to exchange knowledge and experiences. Attending industry events and joining professional organizations can help you connect with experts and stay up-to-date on the latest trends.
OBD2 scanner codes are invaluable for diagnosing and resolving vehicle issues, and at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we are dedicated to providing you with the knowledge and resources you need to effectively use these tools. From understanding the basics of OBD2 codes to managing them for an entire fleet, our comprehensive guides and expert advice will empower you to keep your vehicles running smoothly and efficiently.
Contact us today at:
- Address: 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
- Website: OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
Let OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN be your trusted partner in automotive diagnostics and maintenance, ensuring your vehicles are always in top condition.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is an OBD2 scanner?
An OBD2 scanner is a diagnostic tool used to read and interpret diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) from a vehicle’s onboard computer system. These codes indicate potential issues within the vehicle’s systems, such as the engine, transmission, and emissions systems. According to the EPA, all cars and light trucks sold in the U.S. since 1996 are equipped with OBD2 systems.
How do I read OBD2 scanner codes?
To read OBD2 scanner codes, you need an OBD2 scanner or scan tool. Plug the scanner into the OBD2 port, typically located beneath the dashboard. Turn on the vehicle’s ignition and follow the scanner’s instructions to retrieve the DTCs. The scanner will display the codes, which you can then research to understand the potential issues.
What do the different types of OBD2 codes mean?
OBD2 codes are categorized into four main types: Powertrain (P-codes), Body (B-codes), Chassis (C-codes), and Network Communication (U-codes). Each type indicates a problem within a specific area of the vehicle. For example, P-codes relate to the engine and transmission, while B-codes relate to body systems like airbags and lighting.
Can I clear OBD2 codes myself?
Yes, you can clear OBD2 codes using an OBD2 scanner after addressing the underlying issue. However, it’s generally not advisable to clear codes without fixing the problem, as the issue may return. Clearing the code simply resets the check engine light, but it doesn’t resolve the problem.
What are some common OBD2 codes and their meanings?
Some common OBD2 codes include P0171 (System Too Lean), P0300 (Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire), and P0420 (Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold). Each code indicates a specific issue, and understanding these codes can help you diagnose and resolve common vehicle problems.
How can I prevent OBD2 codes from appearing?
Preventing OBD2 codes involves regular vehicle maintenance, using high-quality fuel and fluids, and addressing small issues before they escalate. Routine tasks such as oil changes, air filter replacements, and spark plug inspections can help prevent codes from appearing.
When should I consult a mechanic for OBD2 codes?
Consult a mechanic if you’re unsure how to clear codes or suspect a deeper issue. Mechanics have the training, experience, and diagnostic tools to accurately identify the root cause of the OBD2 codes and ensure they are properly fixed.
What are the benefits of using an OBD2 scanner?
The benefits of using an OBD2 scanner include enhanced diagnostic accuracy, cost savings, support for preventive maintenance, and real-time data monitoring. These tools help you identify and address vehicle issues quickly and effectively.
How do I choose the right OBD2 scanner?
Consider compatibility, features, ease of use, and price when choosing an OBD2 scanner. Ensure that the scanner is compatible with your vehicle, offers the features you need, is easy to use, and fits within your budget.
How can OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN help me with OBD2 codes?
OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN provides comprehensive guides, expert advice, and resources to help you understand and use OBD2 scanner codes effectively. We offer insights into the basics of OBD2 codes, managing them for an entire fleet, and staying updated with the latest advancements in OBD2 technology. Contact us for assistance with your automotive diagnostic needs.
Closing Thoughts
In conclusion, OBD2 scanner codes are essential tools for diagnosing and maintaining modern vehicles. Understanding how to read, interpret, and address these codes can save you time and money while ensuring your vehicle operates efficiently and reliably. With the right knowledge and resources, you can take control of your vehicle’s health and keep it running smoothly for years to come.