Car drop down idle, often accompanied by misfires and rough running, can be a frustrating issue. An OBD2 scanner from OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN can help you diagnose the problem, potentially saving you time and money on repairs. By understanding the common causes, diagnostic procedures, and the benefits of using an OBD2 scanner, you can effectively address car drop down idle issues and maintain your vehicle’s performance, and proper idle speed. Learn about car diagnostic tools, and engine performance issues.
Contents
- 1. Understanding Car Drop Down Idle
- 1.1. What is Car Drop Down Idle?
- 1.2. Common Symptoms of Car Drop Down Idle
- 1.3. Potential Causes of Car Drop Down Idle
- 2. The Role of OBD2 Scanners in Diagnosing Car Drop Down Idle
- 2.1. What is an OBD2 Scanner?
- 2.2. How OBD2 Scanners Help Diagnose Car Drop Down Idle
- 2.3. Types of OBD2 Scanners
- 2.4. Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner
- 3. Step-by-Step Guide to Diagnosing Car Drop Down Idle with an OBD2 Scanner
- 3.1. Connecting the OBD2 Scanner
- 3.2. Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 3.3. Interpreting Common DTCs Related to Car Drop Down Idle
- 3.4. Monitoring Live Engine Data
- 3.5. Performing Component Tests (If Available)
- 4. Common Causes of Car Drop Down Idle and How to Fix Them
- 4.1. Vacuum Leaks
- 4.2. Faulty Idle Air Control (IAC) Valve
- 4.3. Dirty or Failing Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor
- 4.4. Clogged Fuel Injectors
- 4.5. Faulty Oxygen (O2) Sensors
- 4.6. Spark Plug Issues
- 4.7. Faulty Coils
- 4.8. Low Fuel Pressure
- 4.9. Engine Control Unit (ECU) Problems
- 4.10. Carbon Buildup
- 5. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques
- 5.1. Using a Scan Tool for Advanced Diagnostics
- 5.2. Performing a Compression Test
- 5.3. Checking for Intake Manifold Leaks
- 5.4. Evaluating Fuel Trim Data
- 6. Preventive Maintenance to Avoid Car Drop Down Idle
- 6.1. Regular Spark Plug Replacement
- 6.2. Fuel System Cleaning
- 6.3. Air Filter Replacement
- 6.4. Throttle Body Cleaning
- 6.5. Regular Vehicle Inspections
- 7. The Benefits of Choosing OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
- 7.1. Wide Range of OBD2 Scanners
- 7.2. Expert Advice and Support
- 7.3. High-Quality Products
- 7.4. Customer Satisfaction Guarantee
- 8. Real-World Examples and Case Studies
- 8.1. Case Study 1: Diagnosing a Vacuum Leak with an OBD2 Scanner
- 8.2. Case Study 2: Identifying a Faulty IAC Valve
- 9. FAQ About Car Drop Down Idle and OBD2 Scanners
- 9.1. What is the normal idle speed for my car?
- 9.2. Can a bad battery cause car drop down idle?
- 9.3. How often should I clean my MAF sensor?
- 9.4. Can I use any OBD2 scanner on my car?
- 9.5. What does it mean when my car idles high?
- 9.6. How do I reset the Check Engine Light after fixing the problem?
- 9.7. Is it safe to drive with car drop down idle?
- 9.8. How much does it cost to fix car drop down idle?
- 9.9. Where can I find reliable information about OBD2 codes?
- 9.10. What should I do if I can’t diagnose the problem myself?
- 10. Conclusion: Take Control of Your Vehicle’s Performance with OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
1. Understanding Car Drop Down Idle
1.1. What is Car Drop Down Idle?
Car drop down idle refers to a situation where the engine’s idle speed drops below the normal range, causing the engine to run roughly or even stall. According to a study by the University of Michigan Transportation Research Institute, unstable idling can often be attributed to issues within the engine’s air-fuel management system.
1.2. Common Symptoms of Car Drop Down Idle
- Rough idling, especially when the engine is cold
- Engine misfires
- Stalling at idle
- Hesitation upon acceleration
- Check Engine Light (CEL) illumination
1.3. Potential Causes of Car Drop Down Idle
Several factors can contribute to car drop down idle. Here’s a breakdown of the most common culprits:
- Vacuum Leaks: Leaks in vacuum lines can disrupt the air-fuel mixture, leading to unstable idling.
- Faulty Idle Air Control (IAC) Valve: The IAC valve regulates airflow to maintain a stable idle speed. If it’s malfunctioning, the idle may drop.
- Dirty or Failing Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor: The MAF sensor measures the amount of air entering the engine. A dirty or failing sensor can provide incorrect data, affecting the air-fuel mixture and causing idle issues.
- Clogged Fuel Injectors: Clogged injectors can restrict fuel flow, leading to a lean mixture and rough idling.
- Faulty Oxygen (O2) Sensors: O2 sensors monitor the oxygen content in the exhaust. If they’re providing inaccurate readings, the engine’s computer may misadjust the air-fuel mixture.
- Spark Plug Issues: Worn or fouled spark plugs can cause misfires, leading to a drop in idle speed.
- Faulty Coils: Ignition coils are responsible for providing the spark needed for combustion. A failing coil can cause misfires and rough idling.
- Low Fuel Pressure: Insufficient fuel pressure can result in a lean mixture and unstable idle.
- Engine Control Unit (ECU) Problems: Although less common, issues with the ECU can also cause car drop down idle.
- Carbon Buildup: Carbon deposits in the intake manifold and throttle body can disrupt airflow, affecting idle speed.
2. The Role of OBD2 Scanners in Diagnosing Car Drop Down Idle
2.1. What is an OBD2 Scanner?
An OBD2 (On-Board Diagnostics II) scanner is a diagnostic tool that can access and interpret data from a vehicle’s computer system. It reads diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and provides insights into various engine parameters.
2.2. How OBD2 Scanners Help Diagnose Car Drop Down Idle
An OBD2 scanner is invaluable for diagnosing car drop down idle because it can:
- Retrieve Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): DTCs provide specific information about the issue causing the problem.
- Monitor Live Engine Data: Observing real-time data such as MAF sensor readings, O2 sensor values, and engine temperature can help pinpoint the cause of the drop down idle.
- Perform Component Tests: Some OBD2 scanners can activate certain components (like the IAC valve) to test their functionality.
- Clear Codes: After addressing the issue, the scanner can clear the DTCs and reset the Check Engine Light.
2.3. Types of OBD2 Scanners
There are several types of OBD2 scanners available, ranging from basic code readers to advanced professional-grade tools:
- Basic Code Readers: These scanners can only read and clear DTCs.
- Mid-Range Scanners: These offer live data monitoring and some component testing capabilities.
- Professional-Grade Scanners: These advanced tools provide comprehensive diagnostics, including bidirectional control, advanced coding, and access to manufacturer-specific data.
2.4. Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner
When selecting an OBD2 scanner, consider the following factors:
- Compatibility: Ensure the scanner is compatible with your vehicle’s make and model.
- Features: Choose a scanner with the features you need for your diagnostic requirements.
- Ease of Use: Opt for a scanner with an intuitive interface.
- Price: Scanners range in price, so set a budget and choose one that offers the best value.
OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN offers a variety of OBD2 scanners to suit different needs and budgets. Contact us at +1 (641) 206-8880 for personalized recommendations.
3. Step-by-Step Guide to Diagnosing Car Drop Down Idle with an OBD2 Scanner
3.1. Connecting the OBD2 Scanner
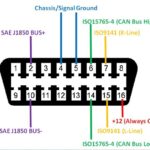
- Locate the OBD2 port in your vehicle (usually under the dashboard on the driver’s side).
- Plug the OBD2 scanner into the port.
- Turn the ignition key to the “ON” position (do not start the engine).
3.2. Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- Power on the OBD2 scanner.
- Navigate to the “Read Codes” or “Diagnostic Codes” option in the scanner’s menu.
- The scanner will display any stored DTCs. Record these codes for further research.
3.3. Interpreting Common DTCs Related to Car Drop Down Idle
Here are some common DTCs related to car drop down idle and their possible causes:
| DTC Code | Description | Possible Causes |
|---|---|---|
| P0171 | System Too Lean (Bank 1) | Vacuum leak, faulty MAF sensor, clogged fuel injectors, low fuel pressure, faulty O2 sensor |
| P0174 | System Too Lean (Bank 2) | Vacuum leak, faulty MAF sensor, clogged fuel injectors, low fuel pressure, faulty O2 sensor |
| P0300 | Random Misfire Detected | Worn spark plugs, faulty ignition coils, vacuum leak, clogged fuel injectors, low fuel pressure, engine mechanical issues |
| P0505 | Idle Air Control System Malfunction | Faulty IAC valve, carbon buildup in the throttle body |
| P0102 | Mass Air Flow (MAF) Circuit Low Input | Faulty MAF sensor, wiring issues |
| P0113 | Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor High Input | Faulty IAT sensor, wiring issues |
3.4. Monitoring Live Engine Data
-
Select the “Live Data” or “Data Stream” option on the OBD2 scanner.
-
Choose the parameters relevant to idle control, such as:
- MAF sensor reading
- O2 sensor values
- Engine RPM
- Intake air temperature
- Throttle position
-
Observe the data while the engine is idling. Look for any abnormal readings. For example, a low MAF sensor reading could indicate a vacuum leak.
3.5. Performing Component Tests (If Available)
Some OBD2 scanners have the capability to perform component tests. For example, you might be able to activate the IAC valve to see if it’s responding correctly. Follow the scanner’s instructions for performing these tests.
4. Common Causes of Car Drop Down Idle and How to Fix Them
4.1. Vacuum Leaks
Vacuum leaks are a frequent cause of car drop down idle. They allow unmetered air to enter the engine, disrupting the air-fuel mixture.
How to Identify Vacuum Leaks:
- Visual Inspection: Check all vacuum lines and hoses for cracks, damage, or loose connections.
- Smoke Test: A smoke test introduces smoke into the intake system, revealing leaks as smoke escapes.
- Carburetor Cleaner Test: Spray carburetor cleaner around vacuum lines and intake manifold gaskets. If the engine RPM changes, there’s likely a leak in that area.
How to Fix Vacuum Leaks:
- Replace any damaged or cracked vacuum lines.
- Tighten loose connections.
- Replace intake manifold gaskets if necessary.
4.2. Faulty Idle Air Control (IAC) Valve
The IAC valve regulates airflow to maintain a stable idle speed. If it’s not working correctly, the idle can drop or surge.
How to Test the IAC Valve:
- Visual Inspection: Check for carbon buildup or damage.
- OBD2 Scanner Test: Some scanners can activate the IAC valve to test its functionality.
- Multimeter Test: Use a multimeter to check the IAC valve’s resistance according to the manufacturer’s specifications.
How to Fix a Faulty IAC Valve:
- Clean the IAC valve with throttle body cleaner.
- If cleaning doesn’t help, replace the IAC valve.
4.3. Dirty or Failing Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor
The MAF sensor measures the amount of air entering the engine. A dirty or failing sensor can provide inaccurate readings, affecting the air-fuel mixture and causing idle problems. According to the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), maintaining a clean MAF sensor is crucial for optimal engine performance.
How to Test the MAF Sensor:
- Visual Inspection: Check for dirt or debris on the sensor.
- OBD2 Scanner: Monitor the MAF sensor reading with an OBD2 scanner while the engine is idling. Compare the reading to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Multimeter Test: Use a multimeter to check the MAF sensor’s voltage output.
How to Fix a Dirty or Failing MAF Sensor:
- Clean the MAF sensor with MAF sensor cleaner.
- If cleaning doesn’t help, replace the MAF sensor.
4.4. Clogged Fuel Injectors
Clogged fuel injectors can restrict fuel flow, leading to a lean mixture and rough idling.
How to Test Fuel Injectors:
- Listen: Use a stethoscope to listen to each injector. You should hear a clicking sound as they open and close.
- OBD2 Scanner: Some scanners can perform an injector balance test.
- Fuel Pressure Test: Check the fuel pressure to ensure it’s within the specified range.
How to Fix Clogged Fuel Injectors:
- Use a fuel injector cleaner additive in the fuel tank.
- Have the injectors professionally cleaned.
- Replace the injectors if cleaning doesn’t help.
4.5. Faulty Oxygen (O2) Sensors
O2 sensors monitor the oxygen content in the exhaust. If they’re providing inaccurate readings, the engine’s computer may misadjust the air-fuel mixture.
How to Test O2 Sensors:
- OBD2 Scanner: Monitor the O2 sensor readings with an OBD2 scanner. The voltage should fluctuate between 0.1 and 0.9 volts.
- Visual Inspection: Check for damage or contamination.
How to Fix Faulty O2 Sensors:
- Replace the faulty O2 sensor.
4.6. Spark Plug Issues
Worn or fouled spark plugs can cause misfires, leading to a drop in idle speed.
How to Inspect Spark Plugs:
- Remove the spark plugs and inspect them for wear, damage, or fouling.
- Check the spark plug gap.
How to Fix Spark Plug Issues:
- Replace worn or fouled spark plugs.
- Adjust the spark plug gap to the manufacturer’s specifications.
4.7. Faulty Coils
Ignition coils are responsible for providing the spark needed for combustion. A failing coil can cause misfires and rough idling.
How to Test Ignition Coils:
- Spark Test: Use a spark tester to check if each coil is producing a strong spark.
- OBD2 Scanner: Check for misfire codes (e.g., P0301, P0302).
- Resistance Test: Use a multimeter to check the coil’s resistance.
How to Fix Faulty Coils:
- Replace the faulty ignition coil.
4.8. Low Fuel Pressure
Insufficient fuel pressure can result in a lean mixture and unstable idle.
How to Test Fuel Pressure:
- Use a fuel pressure gauge to measure the fuel pressure at the fuel rail.
How to Fix Low Fuel Pressure:
- Check the fuel filter and replace it if necessary.
- Inspect the fuel pump and replace it if it’s failing.
- Check the fuel pressure regulator.
4.9. Engine Control Unit (ECU) Problems
Although less common, issues with the ECU can also cause car drop down idle.
How to Diagnose ECU Problems:
- Check for any DTCs related to the ECU.
- Inspect the ECU for damage or corrosion.
How to Fix ECU Problems:
- Consult a qualified technician for ECU diagnostics and repair.
- In some cases, the ECU may need to be replaced or reprogrammed.
4.10. Carbon Buildup
Carbon deposits in the intake manifold and throttle body can disrupt airflow, affecting idle speed.
How to Identify Carbon Buildup:
- Visual Inspection: Check the throttle body and intake manifold for carbon deposits.
How to Fix Carbon Buildup:
- Clean the throttle body with throttle body cleaner.
- Use a fuel system cleaner to remove carbon deposits from the intake manifold.
5. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques
5.1. Using a Scan Tool for Advanced Diagnostics
Advanced scan tools offer features like bidirectional control, which allows you to activate and test various engine components.
5.2. Performing a Compression Test
A compression test can help identify engine mechanical issues that may be contributing to car drop down idle.
5.3. Checking for Intake Manifold Leaks
Intake manifold leaks can cause vacuum leaks that affect idle speed.
5.4. Evaluating Fuel Trim Data
Fuel trim data provides insights into how the engine’s computer is adjusting the air-fuel mixture. Positive fuel trim values indicate a lean condition, while negative values indicate a rich condition.
6. Preventive Maintenance to Avoid Car Drop Down Idle
6.1. Regular Spark Plug Replacement
Replace spark plugs according to the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule.
6.2. Fuel System Cleaning
Use a fuel system cleaner periodically to keep fuel injectors clean.
6.3. Air Filter Replacement
Replace the air filter regularly to ensure proper airflow to the engine.
6.4. Throttle Body Cleaning
Clean the throttle body periodically to prevent carbon buildup.
6.5. Regular Vehicle Inspections
Have your vehicle inspected regularly by a qualified technician.
7. The Benefits of Choosing OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
7.1. Wide Range of OBD2 Scanners
OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN offers a wide range of OBD2 scanners to suit different needs and budgets.
7.2. Expert Advice and Support
Our team of experts can provide advice and support to help you choose the right OBD2 scanner and diagnose car drop down idle issues.
7.3. High-Quality Products
We offer only high-quality OBD2 scanners from trusted brands.
7.4. Customer Satisfaction Guarantee
We are committed to customer satisfaction and offer a guarantee on our products.
8. Real-World Examples and Case Studies
8.1. Case Study 1: Diagnosing a Vacuum Leak with an OBD2 Scanner
A customer reported car drop down idle and a Check Engine Light. Using an OBD2 scanner from OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, the technician found a P0171 code (System Too Lean, Bank 1). Live data monitoring revealed a high MAF sensor reading at idle. A smoke test confirmed a vacuum leak in the intake manifold. After replacing the intake manifold gasket, the idle returned to normal, and the code was cleared.
8.2. Case Study 2: Identifying a Faulty IAC Valve
Another customer experienced car drop down idle without any DTCs. The technician used an OBD2 scanner to monitor the IAC valve’s operation. The scanner showed that the IAC valve was not responding correctly. After replacing the IAC valve, the idle stabilized.
9. FAQ About Car Drop Down Idle and OBD2 Scanners
9.1. What is the normal idle speed for my car?
The normal idle speed varies depending on the vehicle’s make and model. Consult your owner’s manual or a repair manual for the correct specifications.
9.2. Can a bad battery cause car drop down idle?
Yes, a weak battery can contribute to car drop down idle, especially during cold starts.
9.3. How often should I clean my MAF sensor?
It’s generally recommended to clean your MAF sensor every 12,000 to 15,000 miles or when you replace your air filter.
9.4. Can I use any OBD2 scanner on my car?
Most OBD2 scanners are compatible with all vehicles manufactured after 1996. However, it’s essential to check the scanner’s compatibility with your specific make and model.
9.5. What does it mean when my car idles high?
High idle can be caused by several factors, including a faulty IAC valve, vacuum leaks, or a malfunctioning throttle position sensor.
9.6. How do I reset the Check Engine Light after fixing the problem?
Use an OBD2 scanner to clear the DTCs. This will reset the Check Engine Light.
9.7. Is it safe to drive with car drop down idle?
Driving with car drop down idle can be risky, as the engine may stall unexpectedly. It’s best to address the issue as soon as possible.
9.8. How much does it cost to fix car drop down idle?
The cost to fix car drop down idle varies depending on the cause and the cost of parts and labor. Diagnosing the issue with an OBD2 scanner from OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN can help reduce repair costs.
9.9. Where can I find reliable information about OBD2 codes?
OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN provides a comprehensive database of OBD2 codes and their meanings.
9.10. What should I do if I can’t diagnose the problem myself?
If you’re unable to diagnose the problem yourself, consult a qualified technician.
10. Conclusion: Take Control of Your Vehicle’s Performance with OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
Car drop down idle can be a challenging issue, but with the right tools and knowledge, you can effectively diagnose and resolve it. An OBD2 scanner from OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN is an invaluable tool for identifying the root cause of the problem and saving time and money on repairs.
By understanding the common causes of car drop down idle, following the diagnostic steps outlined in this guide, and performing regular maintenance, you can ensure your vehicle runs smoothly and efficiently.
Ready to take control of your vehicle’s performance? Contact OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN today!
Address: 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States
WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
Website: OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
Our team is ready to assist you with expert advice, high-quality products, and unparalleled support. Don’t let car drop down idle keep you off the road – contact us now and experience the difference! Let OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN empower you to maintain your vehicle’s peak performance and ensure a smooth driving experience. Remember, proactive maintenance and accurate diagnostics are key to a long-lasting and reliable vehicle. Trust OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN to provide the tools and knowledge you need to keep your car running at its best.