Chevy Obd2 Port Wire Connection is crucial for vehicle diagnostics and security. This comprehensive guide, brought to you by OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, will help you understand the wiring of your Chevy’s OBD2 port and provide effective strategies to protect it from unauthorized access, including hiding the port or using a dummy connector. By understanding the OBD2 port and its wiring, you will be able to protect your car and perform your own automotive repairs.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the Chevy OBD2 Port
- 1.1. What is an OBD2 Port?
- 1.2. Location of the OBD2 Port in Chevy Vehicles
- 1.3. Why is the OBD2 Port Important?
- 2. Chevy OBD2 Port Wire Connection: Pinout and Functionality
- 2.1. Standard OBD2 Pinout Configuration
- 2.2. Identifying Wires in a Chevy OBD2 Port
- 2.3. Common Wire Issues and How to Diagnose Them
- 3. Security Risks Associated with the OBD2 Port
- 3.1. Vulnerabilities to Theft and Hacking
- 3.2. Real-World Examples of OBD2 Port Exploitation
- 3.3. Why Chevy Vehicles are Targeted
- 4. Strategies to Secure the Chevy OBD2 Port Wire Connection
- 4.1. Physical Security Measures
- 4.1.1. OBD2 Port Locks and Covers
- 4.1.2. Relocating the OBD2 Port
- 4.1.3. Installing a Dummy OBD2 Port
- 4.2. Electronic Security Measures
- 4.2.1. OBD2 Port Immobilizers
- 4.2.2. Data Interruption Switches
- 4.2.3. Software-Based Security
- 4.3. DIY Solutions for Securing the OBD2 Port
- 4.3.1. Hiding the Existing Port
- 4.3.2. Creating a False Wiring Configuration
- 5. Step-by-Step Guide: Relocating the Chevy OBD2 Port
- 5.1. Tools and Materials Needed
- 5.2. Disconnecting the Battery
- 5.3. Removing the OBD2 Port from its Original Location
- 5.4. Extending the Wiring Harness
- 5.5. Choosing a New Location
- 5.6. Mounting the Relocated Port
- 5.7. Reconnecting the Battery and Testing
- 6. Creating a Dummy OBD2 Port for Your Chevy
- 6.1. Purchasing a Replacement OBD2 Port
- 6.2. Wiring the Dummy Port with Basic Functionality
- 6.3. Installing the Dummy Port in the Original Location
- 7. Understanding OBD2 Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 7.1. Common OBD2 Codes in Chevy Vehicles
- 7.2. How to Read and Interpret DTCs
- 7.3. Resources for Decoding OBD2 Codes
- 8. Maintaining Your Chevy’s OBD2 Port Wire Connection
- 8.1. Regular Inspections for Damage and Corrosion
- 8.2. Cleaning and Protecting the Connector
- 8.3. Ensuring Secure Wire Connections
- 9. Advanced Security Systems and OBD2 Port Protection
- 9.1. Aftermarket Security Systems with OBD2 Protection
- 9.2. Integrating Security Systems with Your Chevy’s Electronics
- 9.3. Professional Installation vs. DIY: What’s Right for You?
- 10. Legal and Ethical Considerations
- 10.1. Tampering with the OBD2 Port: Potential Legal Issues
- 10.2. Ethical Considerations When Modifying Vehicle Electronics
- 10.3. Disclosing Modifications to Technicians and Future Owners
- 11. Troubleshooting Common OBD2 Port Problems
- 11.1. Scanner Not Connecting
- 11.2. Intermittent Connection Issues
- 11.3. Error Messages and How to Resolve Them
- 12. The Future of OBD2 and Vehicle Security
- 12.1. Emerging Technologies in Vehicle Diagnostics
- 12.2. Advancements in OBD2 Port Security
- 12.3. How These Changes Will Affect Chevy Owners
- 13. Expert Tips for Chevy OBD2 Port Wire Connection Security
- 13.1. Recommendations from Automotive Security Professionals
- 13.2. Best Practices for Maintaining a Secure OBD2 Port
- 13.3. Resources for Staying Informed About OBD2 Security
- 14. Case Studies: Successful OBD2 Port Security Measures
- 14.1. Real-Life Examples of Theft Prevention
- 14.2. Lessons Learned from Failed Security Attempts
- 14.3. How to Adapt Security Measures to Your Specific Needs
- 15. Conclusion: Protecting Your Chevy Through OBD2 Port Security
- FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions About Chevy OBD2 Port Wire Connection
- 1. What is the Chevy OBD2 port wire connection?
- 2. Where is the OBD2 port located in my Chevy?
- 3. Why is it important to secure the Chevy OBD2 port?
- 4. What are common security measures for the OBD2 port?
- 5. How can I diagnose wiring issues in my Chevy OBD2 port?
- 6. What tools are needed to relocate the OBD2 port?
- 7. What are common OBD2 diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) in Chevy vehicles?
- 8. Can I tamper with the OBD2 port without legal consequences?
- 9. How can I stay informed about OBD2 security updates?
- 10. What should I do if my OBD2 scanner is not connecting to my Chevy?
1. Understanding the Chevy OBD2 Port
1.1. What is an OBD2 Port?
The On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD2) port is a standardized interface in most modern vehicles that allows access to the vehicle’s computer for diagnostics and monitoring. According to the EPA, OBD2 was standardized in 1996 to monitor emissions-related components.
1.2. Location of the OBD2 Port in Chevy Vehicles
The OBD2 port in Chevy vehicles is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side. Common locations include near the steering column or inside the glove compartment. Always consult your vehicle’s manual for the exact location.
1.3. Why is the OBD2 Port Important?
The OBD2 port is critical for several reasons:
- Diagnostics: It allows technicians and car owners to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) to identify issues.
- Monitoring: It provides real-time data on vehicle performance, such as engine temperature, speed, and sensor readings.
- Programming: It can be used to reprogram or update the vehicle’s computer.
According to a study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), proper use of the OBD2 port can significantly reduce diagnostic time and improve repair accuracy.
2. Chevy OBD2 Port Wire Connection: Pinout and Functionality
2.1. Standard OBD2 Pinout Configuration
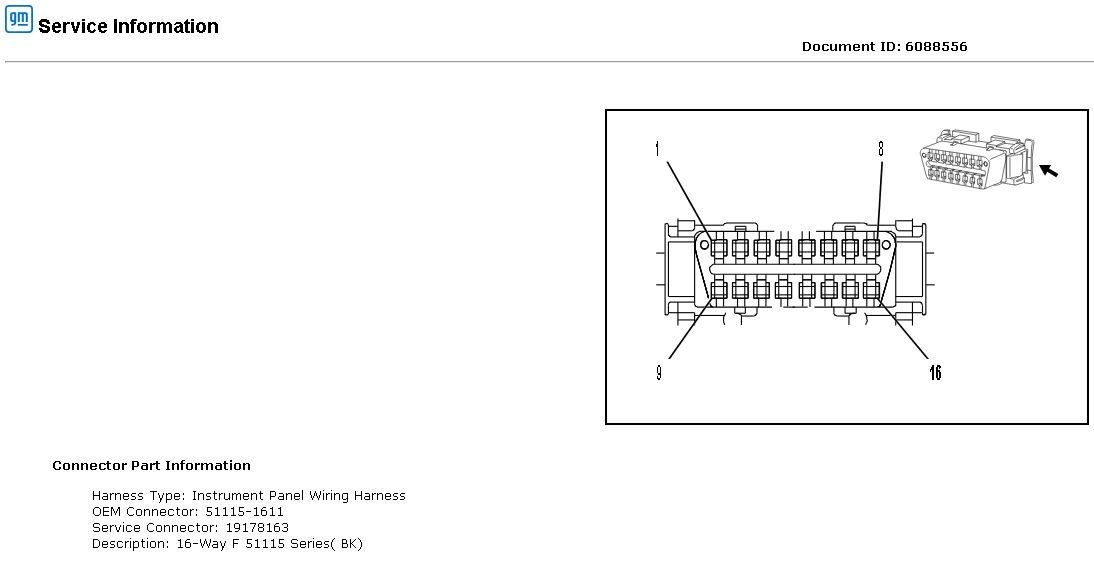
The OBD2 port has 16 pins, each with a specific function. Here’s a table outlining the standard OBD2 pinout configuration:
| Pin | Function | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | J1850 Bus+ | Used for SAE J1850 VPW and PWM communication protocols. |
| 4 | Chassis Ground | Provides a ground connection for the vehicle’s chassis. |
| 5 | Signal Ground | Provides a ground reference for the OBD2 system. |
| 6 | CAN High (J-2284) | High signal line for the Controller Area Network (CAN) bus. |
| 7 | K-Line ISO 9141-2 & ISO 14230-4 | Used for ISO 9141-2 and ISO 14230-4 communication protocols. |
| 10 | J1850 Bus- | Used for SAE J1850 VPW and PWM communication protocols. |
| 14 | CAN Low (J-2284) | Low signal line for the Controller Area Network (CAN) bus. |
| 15 | L-Line ISO 9141-2 & ISO 14230-4 | Used for ISO 9141-2 and ISO 14230-4 communication protocols. |
| 16 | Battery Voltage (12V+) | Provides power to the OBD2 scanner. |
2.2. Identifying Wires in a Chevy OBD2 Port
Identifying the wires in your Chevy OBD2 port is crucial for any modifications or security measures. Typically, the wires are color-coded, but it’s essential to refer to your vehicle’s specific wiring diagram.
2.3. Common Wire Issues and How to Diagnose Them
Common issues include:
- Corrosion: Corrosion can cause poor connections and intermittent issues. Clean the contacts with a contact cleaner.
- Loose Connections: Loose wires can cause communication errors. Ensure all connections are tight and secure.
- Damaged Wires: Damaged wires can lead to shorts or open circuits. Inspect the wires for any signs of damage and repair or replace as necessary.
Using a multimeter, you can check for continuity and voltage at each pin to diagnose wiring issues effectively.
3. Security Risks Associated with the OBD2 Port
3.1. Vulnerabilities to Theft and Hacking
The OBD2 port can be a point of vulnerability for theft and hacking. Thieves can use it to:
- Disable Immobilizers: Bypass the vehicle’s immobilizer system.
- Reprogram Keys: Program new keys to steal the vehicle.
- Access Vehicle Systems: Gain access to other electronic control units (ECUs) to manipulate vehicle functions.
A report by the National Insurance Crime Bureau (NICB) indicates a rise in thefts involving OBD2 port exploitation.
3.2. Real-World Examples of OBD2 Port Exploitation
There have been several documented cases of thieves using the OBD2 port to steal vehicles. In one instance, a group of thieves used a readily available OBD2 programming tool to disable the immobilizer of a high-end vehicle, allowing them to drive away in minutes.
3.3. Why Chevy Vehicles are Targeted
Chevy vehicles, like many modern cars, rely heavily on electronic systems, making them potential targets. The standardization of the OBD2 port means that tools and techniques used on one vehicle can often be applied to others, increasing the risk.
4. Strategies to Secure the Chevy OBD2 Port Wire Connection
4.1. Physical Security Measures
4.1.1. OBD2 Port Locks and Covers
OBD2 port locks and covers are physical barriers that prevent unauthorized access. These devices typically require a key or special tool for removal.
4.1.2. Relocating the OBD2 Port
Relocating the OBD2 port involves moving it to a less obvious location, making it harder for thieves to find and access. This requires extending the wiring harness, which can be a deterrent in itself.
4.1.3. Installing a Dummy OBD2 Port
A dummy OBD2 port looks like the real thing but is not connected to the vehicle’s systems. This can deter thieves who may move on to an easier target. You can even wire the dummy port with a 12V and ground connection to power up their tools, giving the illusion of functionality.
4.2. Electronic Security Measures
4.2.1. OBD2 Port Immobilizers
These devices prevent communication through the OBD2 port unless a specific code or key is entered.
4.2.2. Data Interruption Switches
Installing a switch to interrupt the data lines can prevent unauthorized access. This can be a simple toggle switch that disables communication when activated.
4.2.3. Software-Based Security
Some aftermarket security systems offer software-based protection that monitors OBD2 port activity and alerts the owner of suspicious access.
4.3. DIY Solutions for Securing the OBD2 Port
4.3.1. Hiding the Existing Port
Hiding the existing port involves removing it from its original location and concealing it elsewhere. This is a simple and free method that can deter thieves looking for an easy target.
4.3.2. Creating a False Wiring Configuration
Re-wiring the port with a false configuration can damage any tool connected to it. However, this is not recommended as it can also damage legitimate diagnostic tools and may lead to liability issues.
 OBD2 Connector
OBD2 Connector
5. Step-by-Step Guide: Relocating the Chevy OBD2 Port
5.1. Tools and Materials Needed
- OBD2 Extension Cable
- Wire Strippers
- Crimping Tool
- Butt Connectors
- Electrical Tape
- Screwdrivers
- Drill (if needed for mounting)
5.2. Disconnecting the Battery
Before starting any electrical work, disconnect the negative terminal of the battery to prevent shorts and electrical damage.
5.3. Removing the OBD2 Port from its Original Location
The OBD2 port is typically held in place by clips. Depress these clips from the cabin side to remove the port from its housing.
5.4. Extending the Wiring Harness
- Cut the Wires: Cut the wires of the OBD2 port harness, leaving enough length to work with.
- Strip the Wires: Strip the ends of each wire on both the vehicle side and the OBD2 port side.
- Connect the Extension Cable: Use butt connectors to connect the extension cable wires to the corresponding wires on the vehicle and the OBD2 port. Ensure each connection is secure.
- Secure the Connections: Wrap each connection with electrical tape to prevent shorts and corrosion.
5.5. Choosing a New Location
Select a hidden but accessible location for the relocated OBD2 port. Consider areas such as behind the glove box, under the seat, or inside the center console.
5.6. Mounting the Relocated Port
Use screws or adhesive to mount the relocated OBD2 port securely. Ensure it is easily accessible for diagnostics but not easily visible to potential thieves.
5.7. Reconnecting the Battery and Testing
Reconnect the negative terminal of the battery. Use an OBD2 scanner to test the relocated port and ensure it is functioning correctly.
6. Creating a Dummy OBD2 Port for Your Chevy
6.1. Purchasing a Replacement OBD2 Port
You can purchase a replacement OBD2 port from automotive parts suppliers like Mouser Electronics.
6.2. Wiring the Dummy Port with Basic Functionality
Wire the dummy port with a 12V and ground connection to power up any tool connected to it, giving the illusion of functionality. You can also add 10k ohm resistors between the data pins to simulate activity.
6.3. Installing the Dummy Port in the Original Location
Install the dummy port in the original location to deter thieves. Ensure it looks identical to the real port to avoid suspicion.
7. Understanding OBD2 Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
7.1. Common OBD2 Codes in Chevy Vehicles
Common OBD2 codes in Chevy vehicles include:
- P0171: System Too Lean (Bank 1)
- P0300: Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected
- P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
- P0442: Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (Small Leak)
- P0507: Idle Control System RPM Higher Than Expected
7.2. How to Read and Interpret DTCs
To read DTCs, you will need an OBD2 scanner. Connect the scanner to the OBD2 port and follow the scanner’s instructions to retrieve the codes. Each code has a specific meaning, which can be found in the vehicle’s service manual or online databases.
7.3. Resources for Decoding OBD2 Codes
Several online resources and mobile apps can help you decode OBD2 codes. Reputable sources include OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), and automotive forums.
8. Maintaining Your Chevy’s OBD2 Port Wire Connection
8.1. Regular Inspections for Damage and Corrosion
Regularly inspect the OBD2 port and its wiring for any signs of damage or corrosion. Clean the contacts with a contact cleaner to ensure good connectivity.
8.2. Cleaning and Protecting the Connector
Use a contact cleaner to remove any dirt or debris from the connector. Apply a dielectric grease to protect the contacts from moisture and corrosion.
8.3. Ensuring Secure Wire Connections
Check the wire connections regularly to ensure they are tight and secure. Loose connections can cause intermittent issues and communication errors.
9. Advanced Security Systems and OBD2 Port Protection
9.1. Aftermarket Security Systems with OBD2 Protection
Many aftermarket security systems offer advanced features such as OBD2 port monitoring, immobilizers, and GPS tracking. These systems can provide comprehensive protection against theft and unauthorized access.
9.2. Integrating Security Systems with Your Chevy’s Electronics
When integrating a security system with your Chevy’s electronics, it is crucial to follow the manufacturer’s instructions and consult with a professional installer. Incorrect installation can damage the vehicle’s systems.
9.3. Professional Installation vs. DIY: What’s Right for You?
Professional installation is recommended for complex security systems to ensure proper functionality and avoid damaging the vehicle. DIY installation may be suitable for simpler measures such as installing an OBD2 port lock or hiding the existing port.
10. Legal and Ethical Considerations
10.1. Tampering with the OBD2 Port: Potential Legal Issues
Tampering with the OBD2 port can have legal implications, especially if it affects the vehicle’s emissions control systems. According to the EPA, it is illegal to tamper with or disable any emissions control device.
10.2. Ethical Considerations When Modifying Vehicle Electronics
When modifying vehicle electronics, it is essential to consider the ethical implications. Avoid modifications that could compromise safety or violate regulations.
10.3. Disclosing Modifications to Technicians and Future Owners
Always disclose any modifications to the OBD2 port or vehicle electronics to technicians and future owners. This ensures they are aware of any potential issues and can properly diagnose and repair the vehicle.
11. Troubleshooting Common OBD2 Port Problems
11.1. Scanner Not Connecting
If your scanner is not connecting, check the following:
- Ensure the scanner is compatible with your vehicle.
- Verify the OBD2 port has power.
- Check for damaged or corroded pins.
- Try a different scanner to rule out a faulty device.
11.2. Intermittent Connection Issues
Intermittent connection issues can be caused by loose wires or corrosion. Inspect the wiring and clean the contacts with a contact cleaner.
11.3. Error Messages and How to Resolve Them
Error messages can indicate a variety of issues, from communication errors to faulty sensors. Refer to the scanner’s manual or online resources for troubleshooting steps.
12. The Future of OBD2 and Vehicle Security
12.1. Emerging Technologies in Vehicle Diagnostics
Emerging technologies in vehicle diagnostics include wireless OBD2 scanners, cloud-based diagnostics, and artificial intelligence-powered diagnostic tools.
12.2. Advancements in OBD2 Port Security
Advancements in OBD2 port security include enhanced encryption, biometric authentication, and real-time monitoring systems.
12.3. How These Changes Will Affect Chevy Owners
These changes will provide Chevy owners with more advanced diagnostic capabilities and enhanced security features, making it easier to maintain and protect their vehicles.
13. Expert Tips for Chevy OBD2 Port Wire Connection Security
13.1. Recommendations from Automotive Security Professionals
Automotive security professionals recommend a layered approach to OBD2 port security, combining physical and electronic measures. This includes using OBD2 port locks, relocating the port, and installing an aftermarket security system.
13.2. Best Practices for Maintaining a Secure OBD2 Port
Best practices for maintaining a secure OBD2 port include regular inspections, cleaning the connector, and keeping the vehicle’s software up to date.
13.3. Resources for Staying Informed About OBD2 Security
Stay informed about OBD2 security by subscribing to automotive security newsletters, following industry blogs, and participating in online forums.
14. Case Studies: Successful OBD2 Port Security Measures
14.1. Real-Life Examples of Theft Prevention
Several case studies demonstrate the effectiveness of OBD2 port security measures in preventing theft. In one case, a vehicle equipped with an OBD2 port lock and a hidden port deterred a thief who moved on to an easier target.
14.2. Lessons Learned from Failed Security Attempts
Failed security attempts often highlight the importance of a comprehensive approach. Simply hiding the port may not be enough if the thief is determined and has the right tools.
14.3. How to Adapt Security Measures to Your Specific Needs
Adapt security measures to your specific needs by considering your vehicle’s make and model, your location, and your risk tolerance. A layered approach that combines physical and electronic measures is often the most effective.
 OBD Image
OBD Image
15. Conclusion: Protecting Your Chevy Through OBD2 Port Security
Securing your Chevy’s OBD2 port wire connection is essential for protecting your vehicle from theft and unauthorized access. By understanding the risks and implementing appropriate security measures, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of becoming a victim. Whether you choose physical barriers, electronic deterrents, or a combination of both, taking proactive steps will safeguard your investment and provide peace of mind.
For personalized advice and professional assistance with your Chevy OBD2 port security, contact us at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN. Our experts are ready to help you choose the best solutions tailored to your needs.
Address: 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States
WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
Website: OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
Don’t wait until it’s too late—secure your Chevy today with the expertise of OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN.
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions About Chevy OBD2 Port Wire Connection
1. What is the Chevy OBD2 port wire connection?
The Chevy OBD2 port wire connection refers to the wiring configuration of the 16-pin OBD2 port in Chevrolet vehicles, which allows for diagnostic scanning and vehicle monitoring. Understanding this connection is crucial for security and maintenance.
2. Where is the OBD2 port located in my Chevy?
The OBD2 port is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side. Consult your vehicle’s manual for the exact location, as it can vary by model and year.
3. Why is it important to secure the Chevy OBD2 port?
Securing the OBD2 port prevents unauthorized access to your vehicle’s computer, which can be exploited for theft or hacking. It protects your vehicle’s systems and personal information.
4. What are common security measures for the OBD2 port?
Common security measures include OBD2 port locks, relocating the port, installing a dummy port, and using electronic immobilizers or data interruption switches.
5. How can I diagnose wiring issues in my Chevy OBD2 port?
Use a multimeter to check for continuity and voltage at each pin. Inspect the wires for corrosion, loose connections, or damage.
6. What tools are needed to relocate the OBD2 port?
Tools needed include an OBD2 extension cable, wire strippers, a crimping tool, butt connectors, electrical tape, screwdrivers, and a drill (if needed for mounting).
7. What are common OBD2 diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) in Chevy vehicles?
Common DTCs include P0171 (System Too Lean), P0300 (Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire), and P0420 (Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold).
8. Can I tamper with the OBD2 port without legal consequences?
Tampering with the OBD2 port, especially if it affects emissions control systems, can have legal consequences. It is essential to comply with EPA regulations.
9. How can I stay informed about OBD2 security updates?
Stay informed by subscribing to automotive security newsletters, following industry blogs, and participating in online forums.
10. What should I do if my OBD2 scanner is not connecting to my Chevy?
Check the scanner’s compatibility, verify the OBD2 port has power, inspect for damaged pins, and try a different scanner.
Contact OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for expert advice and solutions to secure your Chevy OBD2 port. Our team is ready to assist you!