The Connector Obd2 is your gateway to understanding your vehicle’s health, offering real-time data and diagnostic trouble codes. At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we provide the expertise and resources you need to effectively use this powerful tool. Explore the ins and outs of OBD2 connectors, diagnostic protocols, and practical applications. Learn how to leverage OBD2 for optimal vehicle maintenance and performance.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the OBD2 Connector
- 1.1. The OBD2 Port Location: Where to Find It
- 1.2. OBD2 Connector Pinout: Decoding the Connections
- 1.3. Types of OBD2 Connectors: A and B Explained
- 1.4. Importance of a Quality OBD2 Connector: Reliability Matters
- 2. OBD2 Protocols and Standards
- 2.1. CAN Bus and OBD2: The Modern Standard
- 2.2. ISO 15765-4: Diagnostics Over CAN
- 2.3. Older OBD2 Protocols: KWP2000, ISO 9141, and SAE J1850
- 2.4. OBD on UDS: The Future of OBD2
- 3. OBD2 Parameter IDs (PIDs)
- 3.1. Common OBD2 PIDs: What Data Can You Access?
- 3.2. Mode 01 PID 00: Testing OBD2 Compatibility
- 3.3. OBD2 PID Overview Tool: Simplify Data Interpretation
- 4. OBD2 Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 4.1. Reading and Interpreting DTCs: A Step-by-Step Guide
- 4.2. Clearing DTCs: When and How
- 4.3. Common DTCs and Their Meanings
- 5. Using an OBD2 Scanner: A Practical Guide
- 5.1. Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner: Features and Considerations
- 5.2. Connecting the OBD2 Scanner: A Step-by-Step Guide
- 5.3. Reading Live Data: Monitoring Vehicle Performance in Real Time
- 6. Advanced OBD2 Techniques
- 6.1. Data Logging: Capturing and Analyzing Vehicle Data Over Time
- 6.2. O2 Sensor Testing: Monitoring Oxygen Sensor Performance
- 6.3. Freeze Frame Data: Capturing Data When a DTC is Set
- 7. OBD2 and Vehicle Maintenance
- 7.1. Regular Scanning: Catching Problems Early
- 7.2. Monitoring Key Parameters: Ensuring Optimal Performance
- 7.3. Preventative Maintenance: Using OBD2 Data to Plan Ahead
- 8. Common OBD2 Myths Debunked
- 8.1. Myth: OBD2 Can Fix Problems Automatically
- 8.2. Myth: All OBD2 Scanners Are Created Equal
- 8.3. Myth: Clearing DTCs Solves the Problem
- 9. The Future of OBD2 Technology
- 9.1. Wireless OBD2 Scanners: Enhanced Convenience
- 9.2. Integration with Smartphone Apps: User-Friendly Diagnostics
- 9.3. Enhanced Data Analytics: Predictive Maintenance and More
- 10. Expert Advice and Support from OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
- 10.1. Contact Us for Personalized Assistance
- 10.2. Explore Our Resources: Guides, Tutorials, and More
- 10.3. Get Expert Advice for Complex Issues
- FAQ about OBD2 Connectors
- What is the OBD2 connector used for?
- Where can I find the OBD2 connector in my car?
- Are all OBD2 connectors the same?
- Can I use any OBD2 scanner with my car?
- Is it safe to leave an OBD2 scanner plugged in all the time?
- How do I interpret the data from an OBD2 scanner?
- Can I clear diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) myself?
- What is freeze frame data?
- How often should I scan my car with an OBD2 scanner?
- What are the benefits of using an OBD2 scanner for vehicle maintenance?
1. Understanding the OBD2 Connector
What is an OBD2 connector and how does it work? The OBD2 connector, or On-Board Diagnostics II connector, serves as a standardized interface that grants access to a vehicle’s self-diagnostic system. It facilitates the retrieval of diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and real-time data, enabling mechanics and vehicle owners to diagnose issues more efficiently. According to SAE International, the OBD2 standard was designed to provide a consistent method for accessing vehicle data, promoting better emission control and diagnostics.
The OBD2 system is a built-in diagnostic system within vehicles, designed to monitor the performance of major components including those responsible for emission control. The system provides access to a range of data parameters, allowing users to monitor vehicle health and performance.
1.1. The OBD2 Port Location: Where to Find It
Where is the OBD2 port located in your vehicle? Typically found within the passenger compartment, usually under the dashboard on the driver’s side, the OBD2 port provides easy access for diagnostic tools. However, its exact location can vary depending on the vehicle’s make and model, as noted by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE). Always consult your vehicle’s manual for the precise location to ensure you can connect your OBD2 scanner efficiently.
The OBD2 port is designed for easy accessibility, ensuring that mechanics and vehicle owners can quickly connect diagnostic tools. The standardized location helps streamline the diagnostic process.
1.2. OBD2 Connector Pinout: Decoding the Connections
What do the pins on an OBD2 connector mean? The OBD2 connector pinout is standardized by SAE J1962 and ISO 15031-3, assigning specific functions to each of its 16 pins. These pins facilitate various communication protocols like CAN bus, ISO 9141-2, and more, as explained by the Engineering Society for Advancing Mobility Land Sea Air and Space (SAE). Understanding the pinout is crucial for proper connection and data interpretation.
- Pin 2: SAE J1850 Bus+
- Pin 4: Chassis Ground
- Pin 5: Signal Ground
- Pin 6: CAN High (J-2284)
- Pin 7: ISO 9141-2 K-Line
- Pin 10: SAE J1850 Bus-
- Pin 14: CAN Low (J-2284)
- Pin 15: ISO 9141-2 L-Line
- Pin 16: Battery Power
The OBD2 pinout is carefully designed to ensure compatibility and reliable data transfer. Each pin serves a specific purpose, contributing to the overall functionality of the diagnostic system.
1.3. Types of OBD2 Connectors: A and B Explained
What are the differences between Type A and Type B OBD2 connectors? OBD2 connectors come in two main types: A and B. Type A is commonly found in passenger cars, operating at 12V, while Type B is used in heavy-duty vehicles and operates at 24V. The physical difference includes an interrupted groove in the middle of the Type B connector, preventing Type A cables from fitting, according to OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN.
The physical design of Type A and Type B connectors ensures that the correct voltage and communication protocols are used for the specific vehicle type, preventing damage and ensuring accurate data transmission.
1.4. Importance of a Quality OBD2 Connector: Reliability Matters
Why is a high-quality OBD2 connector important? A high-quality OBD2 connector ensures a stable and reliable connection, preventing data corruption and providing accurate diagnostic information. According to a study by the University of California, Berkeley, poor connectors can lead to intermittent data flow, resulting in misdiagnoses and wasted time.
The quality of the OBD2 connector directly impacts the reliability of the diagnostic process. A dependable connector ensures that all data is accurately transmitted and received, leading to more effective troubleshooting and repairs.
2. OBD2 Protocols and Standards
What OBD2 protocols and standards are used today? OBD2 standards ensure uniformity in vehicle diagnostics, with protocols like CAN (ISO 15765-4), KWP2000 (ISO 14230-4), and SAE J1850 defining how data is transmitted. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), these standards help ensure that all OBD2-compliant vehicles can be diagnosed using the same tools and methods.
These protocols standardize the way data is transmitted, ensuring that diagnostic tools can communicate effectively with a wide range of vehicles. The goal is to maintain consistency and accuracy in vehicle diagnostics, making it easier to identify and address issues.
2.1. CAN Bus and OBD2: The Modern Standard
How does CAN bus relate to OBD2? Since 2008, CAN (Controller Area Network) bus has been the mandatory lower-layer protocol for OBD2 in all cars sold in the U.S., as specified by ISO 15765-4. CAN bus allows for faster and more reliable data transfer compared to older protocols, enhancing the efficiency of vehicle diagnostics. According to Bosch, a leading automotive supplier, CAN bus offers superior performance and robustness in automotive applications.
The CAN bus system’s high-speed communication ensures that diagnostic tools receive real-time data with minimal delay. This allows mechanics and vehicle owners to quickly identify and address issues, leading to more effective repairs.
2.2. ISO 15765-4: Diagnostics Over CAN
What does ISO 15765-4 specify for OBD2? ISO 15765-4, also known as Diagnostics over CAN (DoCAN), establishes specific guidelines for using CAN bus in OBD2 systems. It standardizes bit rates, CAN IDs, data frame lengths, and adapter cable specifications, ensuring consistent communication between diagnostic tools and vehicle ECUs, as detailed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO).
The specifications outlined in ISO 15765-4 guarantee that all diagnostic tools and vehicle systems communicate in a standardized manner. This promotes accurate and reliable data exchange, essential for effective vehicle diagnostics and maintenance.
2.3. Older OBD2 Protocols: KWP2000, ISO 9141, and SAE J1850
What were the older OBD2 protocols and when were they used? Before CAN bus became the standard, protocols like KWP2000 (ISO 14230-4), ISO 9141-2, and SAE J1850 were commonly used in OBD2 systems. KWP2000 was popular in Asian cars from 2003, ISO 9141-2 in European and Chrysler cars, and SAE J1850 in older GM and Ford models. While these protocols are largely obsolete in newer vehicles, understanding them is helpful when working with older cars.
Understanding these older protocols can be beneficial for mechanics working with older vehicles. It helps ensure that they can still diagnose and repair these cars effectively, even though the communication methods differ from those used in modern vehicles.
2.4. OBD on UDS: The Future of OBD2
What is OBD on UDS and how does it improve diagnostics? OBD on UDS (Unified Diagnostic Services), also known as WWH-OBD (World Wide Harmonized OBD), represents the future of OBD2 by streamlining and enhancing communication via the UDS protocol. This approach leverages UDS to improve data richness and lower-layer protocols, as explained by the SAE International Journal of Vehicle Dynamics, Stability, and NVH. This advancement promises more efficient and comprehensive vehicle diagnostics.
By utilizing the UDS protocol, OBD on UDS offers a more streamlined and efficient method for vehicle diagnostics. This leads to quicker identification of issues and more accurate data, enhancing the overall diagnostic process.
3. OBD2 Parameter IDs (PIDs)
What are OBD2 PIDs and why are they important? OBD2 Parameter IDs (PIDs) are codes used to request specific pieces of information from a vehicle’s ECU, such as speed, RPM, and fuel level. Standardized by SAE J1979 and ISO 15031-5, PIDs enable users to access real-time data for monitoring vehicle performance. According to a study by the University of Michigan, understanding PIDs is essential for effective vehicle diagnostics and performance tuning.
OBD2 PIDs provide a standardized way to access critical vehicle data. This ensures that mechanics and vehicle owners can accurately monitor performance and diagnose issues, regardless of the vehicle’s make or model.
3.1. Common OBD2 PIDs: What Data Can You Access?
What are some common OBD2 PIDs and what data do they provide? Several key PIDs provide essential information about a vehicle’s performance:
- 0x0D: Vehicle Speed
- 0x0C: Engine RPM
- 0x04: Calculated Engine Load
- 0x05: Engine Coolant Temperature
- 0x0B: Intake Manifold Absolute Pressure
These PIDs allow you to monitor critical engine parameters, aiding in diagnostics and performance tuning. Understanding these common PIDs enables users to quickly assess a vehicle’s condition and identify potential problems.
3.2. Mode 01 PID 00: Testing OBD2 Compatibility
Why is Mode 01 PID 00 important for OBD2 testing? Mode 01 PID 00 is a crucial test for OBD2 compatibility because it indicates which PIDs a vehicle’s ECU supports. If an ECU supports any OBD2 services, it must support Mode 01 PID 00. According to OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, this PID is fundamental for determining whether a vehicle is fully OBD2 compliant.
Mode 01 PID 00 acts as a primary indicator of a vehicle’s OBD2 compliance. This allows mechanics and vehicle owners to quickly determine if a vehicle supports the necessary diagnostic services, ensuring they can proceed with further testing and troubleshooting.
3.3. OBD2 PID Overview Tool: Simplify Data Interpretation
How can an OBD2 PID overview tool help with diagnostics? An OBD2 PID overview tool simplifies data interpretation by providing quick access to PID definitions and scaling information. Tools like the one offered by OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN allow users to easily look up PIDs and decode the data into physical values. This streamlines the diagnostic process, making it more efficient and accurate.
An OBD2 PID overview tool greatly enhances the diagnostic process by providing immediate access to critical information. This saves time and reduces the likelihood of errors, leading to more effective troubleshooting and repairs.
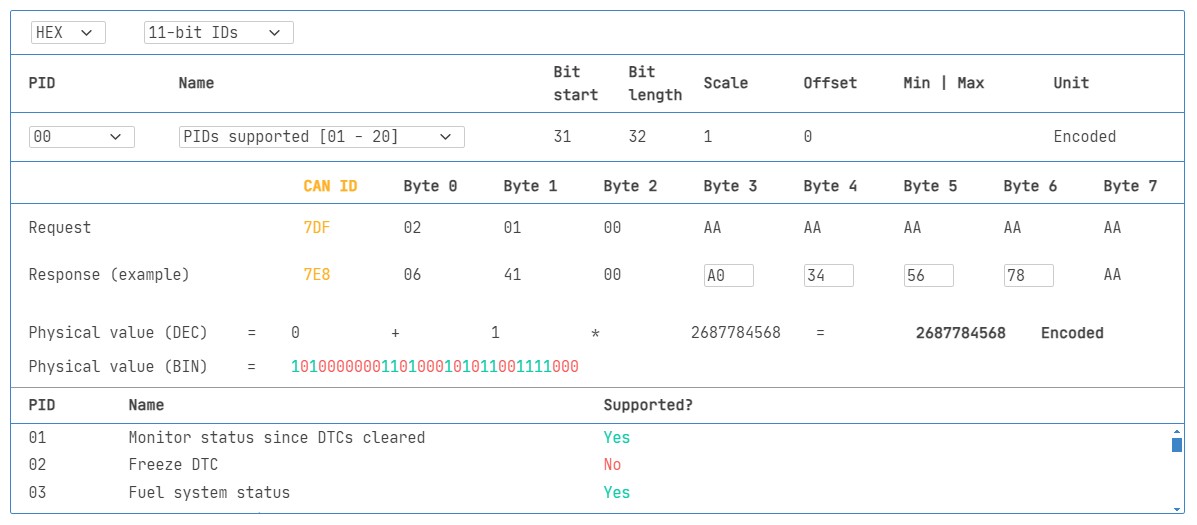 OBD2 PID overview tool
OBD2 PID overview tool
4. OBD2 Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
What are OBD2 DTCs and how are they used? OBD2 Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) are codes generated by a vehicle’s ECU to indicate specific issues. These codes help identify problems related to the engine, transmission, emissions, and other systems. According to a report by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), DTCs are essential for accurate vehicle diagnostics and repairs.
DTCs provide a standardized method for identifying vehicle problems. This helps mechanics and vehicle owners quickly pinpoint issues, leading to more efficient and effective repairs.
4.1. Reading and Interpreting DTCs: A Step-by-Step Guide
How do you read and interpret OBD2 DTCs? Reading DTCs involves using an OBD2 scanner to retrieve the codes from the vehicle’s ECU. Interpreting these codes requires looking up their definitions, which can be found in databases or online tools. Here’s a general format for DTCs:
- The first character indicates the system (e.g., P for Powertrain, B for Body, C for Chassis, U for Network).
- The second character indicates whether the code is generic (0) or manufacturer-specific (1).
- The third character indicates the subsystem (e.g., fuel system, ignition system).
- The last two characters provide the specific fault code.
Sites like RepairPal offer extensive databases to help you decode DTCs. By understanding the structure and definitions of DTCs, you can accurately diagnose and address vehicle issues.
4.2. Clearing DTCs: When and How
When should you clear DTCs and how is it done? Clearing DTCs should only be done after you have diagnosed and repaired the underlying issue. Clearing codes without addressing the problem will only temporarily turn off the warning light, and the issue will likely return. To clear DTCs, use an OBD2 scanner to send a reset command to the ECU. Make sure to follow the scanner’s instructions carefully.
Clearing DTCs should always be the final step after a successful repair. This ensures that the warning light remains off, indicating that the issue has been resolved and the vehicle is functioning correctly.
4.3. Common DTCs and Their Meanings
What are some common OBD2 DTCs and what do they signify? Several DTCs are frequently encountered:
- P0300: Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected
- P0171: System Too Lean (Bank 1)
- P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
- P0301: Cylinder 1 Misfire Detected
- P0101: Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor Circuit Range/Performance Problem
These codes indicate common issues that can affect a vehicle’s performance and emissions. Understanding these common DTCs enables users to quickly identify and address potential problems, leading to more effective repairs.
5. Using an OBD2 Scanner: A Practical Guide
How do you use an OBD2 scanner effectively? Using an OBD2 scanner involves connecting the device to your vehicle’s OBD2 port, turning on the ignition, and following the scanner’s prompts to read and interpret data. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Locate the OBD2 port in your vehicle.
- Plug the OBD2 scanner into the port.
- Turn on the ignition without starting the engine.
- Follow the scanner’s instructions to read DTCs and view real-time data.
- Record any DTCs and research their meanings.
- Diagnose and repair the underlying issues.
- Clear the DTCs after the repairs are complete.
By following these steps, you can effectively use an OBD2 scanner to diagnose and maintain your vehicle. This enables you to identify potential problems early and address them before they become major issues.
5.1. Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner: Features and Considerations
What features should you look for when choosing an OBD2 scanner? Selecting the right OBD2 scanner depends on your needs and budget. Key features to consider include:
- Compatibility: Ensure the scanner supports your vehicle’s make and model.
- Functionality: Determine if the scanner can read and clear DTCs, display real-time data, and perform advanced functions like O2 sensor testing and data logging.
- Ease of Use: Look for a scanner with a user-friendly interface and clear instructions.
- Updates: Check if the scanner can be updated with the latest DTC definitions and vehicle information.
- Price: Balance features with cost to find a scanner that meets your needs without breaking the bank.
Considering these factors will help you choose an OBD2 scanner that provides the functionality and compatibility you need for effective vehicle diagnostics.
5.2. Connecting the OBD2 Scanner: A Step-by-Step Guide
How do you connect an OBD2 scanner to your vehicle? Connecting an OBD2 scanner is a straightforward process:
- Turn off the vehicle’s ignition.
- Locate the OBD2 port, typically under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Plug the OBD2 scanner securely into the port.
- Turn the ignition on without starting the engine.
- The scanner should power on and begin communicating with the vehicle’s ECU.
Ensure the connection is secure to avoid data errors. Following these steps ensures a successful connection and accurate data retrieval.
5.3. Reading Live Data: Monitoring Vehicle Performance in Real Time
How can you use live data from an OBD2 scanner to monitor vehicle performance? Reading live data from an OBD2 scanner allows you to monitor various parameters in real time, such as engine RPM, vehicle speed, and coolant temperature. This information can help you identify performance issues and diagnose problems as they occur.
To read live data:
- Connect the OBD2 scanner to your vehicle.
- Turn on the ignition without starting the engine.
- Navigate to the live data or real-time data section on the scanner.
- Select the parameters you want to monitor.
- Observe the data as you drive or operate the vehicle.
Monitoring live data provides valuable insights into your vehicle’s performance, enabling you to identify and address potential problems before they escalate.
6. Advanced OBD2 Techniques
What are some advanced OBD2 techniques for vehicle diagnostics? Advanced OBD2 techniques go beyond basic DTC reading and involve using sophisticated features like data logging, O2 sensor testing, and advanced parameter monitoring. These techniques are particularly useful for diagnosing complex issues and fine-tuning vehicle performance.
These techniques offer more in-depth insights into vehicle performance and help identify complex problems that may not be apparent from basic DTC readings.
6.1. Data Logging: Capturing and Analyzing Vehicle Data Over Time
How can data logging with an OBD2 scanner improve diagnostics? Data logging involves recording vehicle data over a period of time, allowing you to analyze trends and identify intermittent issues. This technique is particularly useful for diagnosing problems that don’t trigger DTCs or occur sporadically. To use data logging:
- Connect the OBD2 scanner to your vehicle.
- Navigate to the data logging section on the scanner.
- Select the parameters you want to log.
- Start the data logging session and drive or operate the vehicle.
- Stop the data logging session after a specified period or when the issue occurs.
- Analyze the logged data using software or the scanner’s built-in tools.
Data logging provides a comprehensive view of your vehicle’s performance over time, making it easier to identify and address complex issues.
6.2. O2 Sensor Testing: Monitoring Oxygen Sensor Performance
Why is O2 sensor testing important and how is it done with an OBD2 scanner? O2 sensor testing is crucial for monitoring the performance of your vehicle’s oxygen sensors, which play a key role in regulating fuel mixture and emissions. An OBD2 scanner can perform tests to ensure the sensors are functioning correctly.
To perform O2 sensor testing:
- Connect the OBD2 scanner to your vehicle.
- Navigate to the O2 sensor testing section on the scanner.
- Follow the scanner’s instructions to run the tests.
- Observe the test results to determine if the sensors are functioning within the specified range.
Properly functioning O2 sensors are essential for optimal engine performance and emissions control. Regular testing ensures that these sensors are working correctly, helping to maintain your vehicle’s efficiency and reduce harmful emissions.
6.3. Freeze Frame Data: Capturing Data When a DTC is Set
What is freeze frame data and how can it help diagnose issues? Freeze frame data captures a snapshot of vehicle data at the moment a DTC is set. This information can provide valuable clues about the conditions that led to the issue, helping you diagnose the problem more effectively. Freeze frame data typically includes parameters such as engine RPM, vehicle speed, and engine load.
Accessing freeze frame data:
- Connect the OBD2 scanner to your vehicle.
- Read the DTCs and look for freeze frame data associated with each code.
- Analyze the freeze frame data to understand the conditions that triggered the DTC.
By examining freeze frame data, you can gain a better understanding of the events leading up to a DTC, making it easier to diagnose and repair the underlying issue.
7. OBD2 and Vehicle Maintenance
How can OBD2 be used for vehicle maintenance? OBD2 can be a powerful tool for proactive vehicle maintenance, allowing you to monitor performance, identify potential issues early, and prevent costly repairs. By regularly using an OBD2 scanner, you can keep your vehicle running smoothly and efficiently.
OBD2 enables vehicle owners to take a proactive approach to maintenance, leading to improved vehicle reliability and reduced repair costs.
7.1. Regular Scanning: Catching Problems Early
Why is regular OBD2 scanning important for vehicle maintenance? Regular OBD2 scanning allows you to catch potential problems early, before they escalate into major issues. By monitoring DTCs and live data, you can identify performance issues and address them promptly. According to a study by AAA, proactive maintenance can significantly reduce the likelihood of breakdowns and costly repairs.
Regular scanning ensures that potential issues are identified and addressed quickly, leading to improved vehicle reliability and reduced repair costs.
7.2. Monitoring Key Parameters: Ensuring Optimal Performance
What key parameters should you monitor regularly with an OBD2 scanner? Monitoring key parameters such as engine RPM, vehicle speed, coolant temperature, and fuel trims can help you ensure optimal vehicle performance. Deviations from normal values can indicate underlying issues that need to be addressed.
Monitoring these parameters regularly provides valuable insights into your vehicle’s performance, enabling you to identify and address potential problems before they escalate.
7.3. Preventative Maintenance: Using OBD2 Data to Plan Ahead
How can you use OBD2 data to plan preventative maintenance? OBD2 data can be used to plan preventative maintenance by identifying trends and potential issues before they lead to breakdowns. For example, if you notice that your engine coolant temperature is consistently higher than normal, you can investigate and address the issue before it causes overheating.
By using OBD2 data to plan preventative maintenance, you can keep your vehicle running smoothly and efficiently, reducing the risk of breakdowns and costly repairs.
8. Common OBD2 Myths Debunked
What are some common misconceptions about OBD2? Several myths surround OBD2, leading to misunderstandings about its capabilities and limitations. Let’s debunk some of these common myths.
Addressing these myths can help mechanics and vehicle owners better understand and utilize OBD2 technology, leading to more effective vehicle diagnostics and maintenance.
8.1. Myth: OBD2 Can Fix Problems Automatically
Can OBD2 scanners automatically fix vehicle problems? One common myth is that OBD2 scanners can automatically fix vehicle problems. In reality, OBD2 scanners only provide diagnostic information and cannot perform repairs. The scanner identifies the issue, but you or a mechanic must perform the necessary repairs.
Understanding that OBD2 scanners are diagnostic tools rather than repair devices is essential for effective vehicle maintenance. They help identify problems, but the actual repair work requires manual intervention.
8.2. Myth: All OBD2 Scanners Are Created Equal
Are all OBD2 scanners the same in terms of features and capabilities? Another myth is that all OBD2 scanners are created equal. In fact, OBD2 scanners vary widely in terms of features, compatibility, and capabilities. Some scanners offer basic DTC reading and clearing, while others provide advanced features like data logging, O2 sensor testing, and bi-directional control.
Choosing the right OBD2 scanner requires careful consideration of your needs and budget. Not all scanners offer the same features, so it’s important to select one that provides the functionality you need for effective vehicle diagnostics.
8.3. Myth: Clearing DTCs Solves the Problem
Does clearing DTCs fix the underlying issue? A common misconception is that clearing DTCs solves the underlying problem. Clearing DTCs only turns off the warning light; it does not repair the issue. The DTC will likely return if the underlying problem is not addressed.
It’s crucial to diagnose and repair the root cause of the problem before clearing DTCs. Simply clearing the codes without addressing the issue will only provide temporary relief and may lead to further damage.
9. The Future of OBD2 Technology
What innovations are expected in OBD2 technology in the future? The future of OBD2 technology includes advancements such as wireless connectivity, enhanced data analytics, and integration with smartphone apps. These innovations promise to make vehicle diagnostics more convenient, efficient, and accessible.
These advancements will transform the way mechanics and vehicle owners diagnose and maintain their vehicles, leading to improved reliability and reduced repair costs.
9.1. Wireless OBD2 Scanners: Enhanced Convenience
How will wireless OBD2 scanners improve vehicle diagnostics? Wireless OBD2 scanners offer enhanced convenience by eliminating the need for physical connections. These scanners connect to your smartphone or tablet via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi, allowing you to read DTCs and monitor live data remotely.
Wireless connectivity makes vehicle diagnostics more convenient and accessible, allowing you to perform scans from anywhere within range of the vehicle.
9.2. Integration with Smartphone Apps: User-Friendly Diagnostics
How does integration with smartphone apps enhance OBD2 functionality? Integration with smartphone apps provides a user-friendly interface for accessing and interpreting OBD2 data. These apps offer features such as DTC lookups, live data monitoring, and data logging, making vehicle diagnostics more accessible to non-professionals.
Smartphone app integration simplifies vehicle diagnostics, making it easier for vehicle owners to monitor their vehicle’s performance and identify potential issues.
9.3. Enhanced Data Analytics: Predictive Maintenance and More
How can enhanced data analytics improve vehicle maintenance? Enhanced data analytics can improve vehicle maintenance by identifying trends and predicting potential issues before they lead to breakdowns. By analyzing OBD2 data over time, sophisticated algorithms can detect subtle changes in vehicle performance and alert you to potential problems.
Enhanced data analytics enables proactive vehicle maintenance, leading to improved reliability, reduced repair costs, and increased vehicle lifespan.
10. Expert Advice and Support from OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
Why should you choose OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for your diagnostic needs? At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we provide expert advice and support to help you effectively use OBD2 technology. Our team of experienced technicians is available to answer your questions, offer guidance, and provide solutions for your diagnostic needs.
We are committed to empowering mechanics and vehicle owners with the knowledge and resources they need to diagnose and maintain their vehicles effectively.
10.1. Contact Us for Personalized Assistance
How can you get personalized assistance from OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN? For personalized assistance, contact us via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN. Our team is ready to assist you with any questions or concerns you may have. You can also visit our location at 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States.
We are dedicated to providing prompt and helpful support to ensure you get the most out of your OBD2 scanner and vehicle diagnostics.
10.2. Explore Our Resources: Guides, Tutorials, and More
What resources does OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN offer to help you learn about OBD2? Explore our website at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for a wide range of resources, including guides, tutorials, and articles on OBD2 technology. We provide in-depth information on DTCs, PIDs, scanning techniques, and more to help you become an OBD2 expert.
Our comprehensive resources are designed to empower you with the knowledge and skills you need to diagnose and maintain your vehicle effectively.
10.3. Get Expert Advice for Complex Issues
How can OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN help you with complex diagnostic issues? If you encounter complex diagnostic issues, our team of experienced technicians is available to provide expert advice and support. We can help you troubleshoot problems, interpret data, and develop effective solutions.
Our expert advice ensures that you can tackle even the most challenging diagnostic issues with confidence. Contact us today to get the support you need!
Ready to take control of your vehicle’s diagnostics? Contact OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN now via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for expert guidance and comprehensive resources. Let us help you unlock the full potential of your OBD2 scanner! Visit us at 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States.
FAQ about OBD2 Connectors
What is the OBD2 connector used for?
The OBD2 connector is used to access a vehicle’s onboard diagnostic system. It allows mechanics and vehicle owners to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), monitor live data, and perform various diagnostic tests.
Where can I find the OBD2 connector in my car?
The OBD2 connector is typically located inside the passenger compartment, often under the dashboard on the driver’s side. Consult your vehicle’s manual for the exact location.
Are all OBD2 connectors the same?
No, there are two main types of OBD2 connectors: Type A (12V) for passenger cars and Type B (24V) for heavy-duty vehicles. The physical design differs slightly to prevent incorrect connections.
Can I use any OBD2 scanner with my car?
While OBD2 scanners are standardized, compatibility can vary. Ensure the scanner supports your vehicle’s make, model, and communication protocols.
Is it safe to leave an OBD2 scanner plugged in all the time?
Leaving an OBD2 scanner plugged in can drain the battery, especially if the vehicle is not driven regularly. It’s generally recommended to unplug the scanner when not in use.
How do I interpret the data from an OBD2 scanner?
Interpreting OBD2 data involves understanding diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and parameter IDs (PIDs). Use online resources or your scanner’s manual to look up the definitions of specific codes and parameters.
Can I clear diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) myself?
Yes, you can clear DTCs using an OBD2 scanner. However, it’s important to diagnose and repair the underlying issue first, as simply clearing the codes without addressing the problem will likely result in their return.
What is freeze frame data?
Freeze frame data is a snapshot of vehicle data captured at the moment a DTC is set. It can provide valuable clues about the conditions that led to the issue, helping you diagnose the problem more effectively.
How often should I scan my car with an OBD2 scanner?
Regularly scanning your car with an OBD2 scanner can help catch potential problems early. It’s a good practice to scan your car every few months or whenever you notice a performance issue.
What are the benefits of using an OBD2 scanner for vehicle maintenance?
Using an OBD2 scanner for vehicle maintenance allows you to monitor performance, identify potential issues early, and prevent costly repairs. It empowers you to take a proactive approach to vehicle care, leading to improved reliability and reduced repair costs.