OBD2 to USB wiring diagram is essential for automotive enthusiasts and professionals who want to connect their vehicle’s onboard diagnostic system to a computer for data analysis, diagnostics, and customization. OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN is dedicated to providing you with a comprehensive guide to creating your own OBD2 to USB wiring diagram, ensuring a seamless and reliable connection. By understanding the intricacies of this process, you’ll gain valuable insights into your vehicle’s performance and be able to perform advanced diagnostics with ease. This DIY approach empowers you to take control of your car’s diagnostics, saving you time and money while enhancing your understanding of automotive technology.
Contents
- 1: Understanding the Basics of OBD2 and USB
- 1.1: What is OBD2?
- 1.2: What is USB?
- 1.3: Why DIY OBD2 to USB Wiring?
- 2: Essential Tools and Components
- 2.1: Wiring Diagram
- 2.2: OBD2 Connector
- 2.3: USB Connector
- 2.4: Wires
- 2.5: Wire Strippers
- 2.6: Soldering Iron and Solder
- 2.7: Multimeter
- 2.8: Heat Shrink Tubing or Electrical Tape
- 3: Step-by-Step Wiring Instructions
- 3.1: Identifying the Correct Pins
- 3.2: Preparing the Wires
- 3.3: Soldering the Connections (If Applicable)
- 3.4: Crimping the Connections (Alternative to Soldering)
- 3.5: Insulating the Connections
- 3.6: Connecting OBD2 and USB
- 3.7: Testing the Connection
- 4: Troubleshooting Common Issues
- 4.1: No Connection
- 4.2: Intermittent Connection
- 4.3: Data Corruption
- 4.4: Software Incompatibility
- 5: Advanced Tips and Considerations
- 5.1: Shielding and Noise Reduction
- 5.2: Alternative Wiring Methods
- 5.3: Safety Measures
- 5.4: Power Considerations
- 6: Applications and Uses
- 6.1: Vehicle Diagnostics
- 6.2: Performance Monitoring
- 6.3: Customization and Tuning
1: Understanding the Basics of OBD2 and USB
What are the fundamental differences between OBD2 and USB? This section will cover OBD2 and USB basics, including their respective functions and protocols.
The contrast between OBD2 (On-Board Diagnostics version 2) and USB (Universal Serial Bus) lies in their functions, protocols, and applications. According to a study by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) in 2019, OBD2 is a standardized system used in vehicles to monitor and diagnose engine performance, emissions, and other critical parameters. OBD2 ports provide access to a vehicle’s diagnostic data. USB is a versatile interface used for data transfer and power supply between devices. USB connections facilitate communication between a vehicle’s OBD2 system and external devices like computers.
1.1: What is OBD2?
What are the key components and functions of OBD2 systems? OBD2 is an onboard diagnostic system that monitors various vehicle parameters, including engine performance, emissions, and other critical data, according to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA).
OBD2, or On-Board Diagnostics version 2, is a standardized system implemented in modern vehicles to monitor and diagnose engine performance, emissions, and other critical parameters. According to a 2020 report by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), the OBD2 system aims to ensure vehicles meet emission standards and provide mechanics with valuable diagnostic information.
Key Components of OBD2:
- OBD2 Port: A 16-pin connector, usually located under the dashboard, provides access to the vehicle’s diagnostic data.
- Sensors: Various sensors throughout the vehicle collect data on engine performance, emissions, and other parameters.
- Engine Control Unit (ECU): The ECU processes data from sensors and stores diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) when it detects issues.
- Diagnostic Tools: Scanners and software used to read DTCs and access real-time data from the OBD2 system.
Key Functions of OBD2:
- Emission Monitoring: Ensures vehicles meet emission standards by monitoring components like the catalytic converter and oxygen sensors.
- Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Stores DTCs when it detects issues, providing mechanics with valuable diagnostic information.
- Real-Time Data: Provides access to real-time data on engine performance, sensor readings, and other parameters.
- Vehicle Information: Access to vehicle identification number (VIN) and other identifying information.
1.2: What is USB?
What are the advantages and disadvantages of using USB connections for OBD2 diagnostics? USB (Universal Serial Bus) connections offer versatility and compatibility across devices, but may require additional hardware for OBD2 integration.
USB, or Universal Serial Bus, is a versatile interface used for data transfer and power supply between devices. According to a 2018 study by the USB Implementers Forum (USB-IF), USB has become the most widely used interface for connecting peripherals to computers and other electronic devices.
Advantages of USB Connections:
- Versatility: Compatible with a wide range of devices, including computers, smartphones, and tablets.
- Data Transfer Speed: Offers high-speed data transfer rates, allowing for quick and efficient communication.
- Power Supply: Can provide power to connected devices, eliminating the need for separate power sources.
- Ease of Use: Simple plug-and-play interface, making it easy to connect and disconnect devices.
Disadvantages of USB Connections:
- Additional Hardware: Requires an OBD2 to USB adapter or cable to interface with the vehicle’s OBD2 port.
- Driver Compatibility: May require specific drivers to be installed on the computer for proper communication.
- Potential Latency: Data transfer latency can be an issue in real-time diagnostic applications.
- Limited Port Availability: Some devices may have limited USB port availability, requiring the use of USB hubs.
1.3: Why DIY OBD2 to USB Wiring?
What are the key benefits of creating your own OBD2 to USB wiring diagram? Creating your own OBD2 to USB wiring diagram allows for customization, cost savings, and a deeper understanding of vehicle diagnostics.
DIY (Do-It-Yourself) OBD2 to USB wiring offers several benefits, including customization, cost savings, and a deeper understanding of vehicle diagnostics. According to a 2021 survey by the Automotive Aftermarket Industry Association (AAIA), DIY automotive repairs are becoming increasingly popular among car owners who want to save money and gain more control over their vehicle maintenance.
Key Benefits of DIY OBD2 to USB Wiring:
- Cost Savings: Building your own cable can be more cost-effective than purchasing a pre-made adapter.
- Customization: Allows you to create a cable that meets your specific needs and preferences.
- Educational Value: Provides a deeper understanding of the OBD2 system and how it communicates with external devices.
- Troubleshooting: Easier to troubleshoot and repair a DIY cable compared to a sealed, pre-made adapter.
- Flexibility: Ability to modify and upgrade the cable as needed for different diagnostic applications.
By undertaking a DIY OBD2 to USB wiring project, you gain valuable insights into your vehicle’s performance and can perform advanced diagnostics with ease. This approach empowers you to take control of your car’s diagnostics, saving you time and money while enhancing your understanding of automotive technology.
2: Essential Tools and Components
What tools and components are necessary to create a functional OBD2 to USB wiring diagram? This section lists all the necessary tools and components, with detailed descriptions and considerations for each item.
To create a functional OBD2 to USB wiring diagram, you’ll need a specific set of tools and components. These items ensure a reliable and efficient connection between your vehicle’s OBD2 port and a computer. According to a 2022 report by the Equipment and Tool Institute (ETI), having the right tools and components is crucial for accurate and safe automotive diagnostics.
2.1: Wiring Diagram
Why is a wiring diagram crucial for this project? A detailed wiring diagram is essential for correctly connecting the OBD2 and USB components.
A wiring diagram serves as a visual guide for connecting the OBD2 and USB components correctly. According to a 2019 article in Automotive Engineering International, wiring diagrams are crucial for ensuring accurate and safe electrical connections in automotive applications.
Key Elements of a Wiring Diagram:
- OBD2 Pinout: Shows the pin configuration of the OBD2 connector, including the function of each pin.
- USB Pinout: Shows the pin configuration of the USB connector, including the function of each pin.
- Wire Connections: Indicates which OBD2 pins need to be connected to which USB pins.
- Color Coding: Uses color-coded wires to differentiate connections and prevent errors.
- Grounding: Specifies grounding points for proper circuit operation.
2.2: OBD2 Connector
What are the different types of OBD2 connectors, and which is best for a DIY project? An OBD2 connector is necessary to interface with the vehicle’s diagnostic port.
An OBD2 connector is necessary to interface with the vehicle’s diagnostic port. According to a 2020 report by Research and Markets, the OBD2 connector is a standardized 16-pin interface that provides access to the vehicle’s diagnostic data.
Types of OBD2 Connectors:
- Male Connector: Plugs into the vehicle’s OBD2 port.
- Female Connector: Connects to the diagnostic tool or adapter.
- Cable Connector: Used to extend or modify existing OBD2 cables.
Considerations for Choosing an OBD2 Connector:
- Durability: Choose a connector made from high-quality materials to withstand frequent use.
- Pin Quality: Ensure the pins are gold-plated for better conductivity and resistance to corrosion.
- Ease of Wiring: Select a connector that is easy to wire and has clear markings for pin identification.
- Compatibility: Verify the connector is compatible with your vehicle’s OBD2 port and diagnostic tools.
2.3: USB Connector
What are the different types of USB connectors, and which is suitable for this application? A USB connector is required to interface with the computer or other USB-enabled device.
A USB connector is required to interface with the computer or other USB-enabled device. According to a 2018 study by the USB Implementers Forum (USB-IF), USB connectors come in various types, each designed for specific applications and data transfer speeds.
Types of USB Connectors:
- USB Type-A: The standard rectangular connector commonly found on computers and power adapters.
- USB Type-B: A square connector typically used for printers and other peripherals.
- USB Type-C: A reversible connector that supports high-speed data transfer and power delivery.
- Mini-USB: A smaller version of USB Type-B, often used in older digital cameras and portable devices.
- Micro-USB: An even smaller version of USB Type-B, commonly used in smartphones and tablets.
Considerations for Choosing a USB Connector:
- Compatibility: Choose a connector that is compatible with your computer or other USB-enabled device.
- Data Transfer Speed: Select a connector that supports the required data transfer speed for your diagnostic application.
- Durability: Ensure the connector is made from high-quality materials to withstand frequent use.
- Ease of Wiring: Select a connector that is easy to wire and has clear markings for pin identification.
2.4: Wires
What type of wires is recommended for OBD2 to USB wiring, and why? High-quality wires are necessary for reliable signal transmission between the OBD2 and USB connectors.
High-quality wires are necessary for reliable signal transmission between the OBD2 and USB connectors. According to a 2021 article in Electrical Construction & Maintenance (EC&M), using the correct gauge and type of wire is crucial for ensuring safe and efficient electrical connections.
Recommended Wire Type:
- 22-26 AWG (American Wire Gauge): These wire gauges are suitable for low-voltage, low-current applications like OBD2 diagnostics.
- Stranded Copper Wire: Stranded wire is more flexible and durable than solid wire, making it ideal for automotive applications.
- Insulated Wire: Insulated wire protects the signal from interference and prevents short circuits.
Considerations for Choosing Wires:
- Wire Gauge: Select the appropriate wire gauge based on the current requirements of your diagnostic application.
- Insulation Material: Choose insulation material that is resistant to heat, chemicals, and abrasion.
- Color Coding: Use color-coded wires to differentiate connections and prevent errors.
- Length: Ensure the wires are long enough to reach between the OBD2 and USB connectors.
2.5: Wire Strippers
Why are wire strippers essential for this project? Wire strippers are needed to remove the insulation from the wires without damaging the conductor.
Wire strippers are needed to remove the insulation from the wires without damaging the conductor. According to a 2022 review by Consumer Reports, high-quality wire strippers can make electrical work easier and more efficient.
Types of Wire Strippers:
- Manual Wire Strippers: Hand-operated strippers with adjustable blades for different wire gauges.
- Automatic Wire Strippers: Self-adjusting strippers that automatically remove the insulation without damaging the wire.
- Wire Stripping Pliers: Combination pliers with wire stripping notches for various wire gauges.
Considerations for Choosing Wire Strippers:
- Wire Gauge Range: Select strippers that can accommodate the wire gauges you will be working with.
- Blade Quality: Ensure the blades are sharp and durable for clean and precise stripping.
- Ergonomics: Choose strippers with comfortable handles for extended use.
- Adjustability: Opt for strippers with adjustable blades to accommodate different insulation thicknesses.
2.6: Soldering Iron and Solder
When is soldering recommended for OBD2 to USB wiring? A soldering iron and solder are used to create secure and reliable electrical connections.
A soldering iron and solder are used to create secure and reliable electrical connections. According to a 2020 guide by Make: Magazine, soldering is a crucial skill for electronics enthusiasts and DIYers.
Considerations for Choosing a Soldering Iron:
- Wattage: Choose a soldering iron with sufficient wattage (25-40W) for soldering small electronic components.
- Temperature Control: Opt for a soldering iron with adjustable temperature control for different types of solder and components.
- Tip Size: Select a soldering iron with a fine tip for soldering small wires and connectors.
- Ergonomics: Choose a soldering iron with a comfortable handle for extended use.
2.7: Multimeter
How does a multimeter aid in troubleshooting the OBD2 to USB wiring? A multimeter is used to test the continuity and voltage of the connections.
A multimeter is used to test the continuity and voltage of the connections. According to a 2021 review by Popular Mechanics, a multimeter is an essential tool for troubleshooting electrical circuits and components.
Key Functions of a Multimeter:
- Continuity Testing: Checks for open or short circuits in the wiring.
- Voltage Measurement: Measures the voltage levels to ensure proper power supply.
- Resistance Measurement: Measures the resistance of components and connections.
- Current Measurement: Measures the current flow in the circuit.
Considerations for Choosing a Multimeter:
- Accuracy: Select a multimeter with high accuracy for precise measurements.
- Display: Opt for a multimeter with a clear and easy-to-read display.
- Features: Choose a multimeter with features like auto-ranging, diode testing, and capacitance measurement.
- Durability: Ensure the multimeter is rugged and can withstand accidental drops and impacts.
2.8: Heat Shrink Tubing or Electrical Tape
What purpose does heat shrink tubing or electrical tape serve in this project? Heat shrink tubing or electrical tape is used to insulate and protect the electrical connections.
Heat shrink tubing or electrical tape is used to insulate and protect the electrical connections. According to a 2019 article in Electrical Contractor Magazine, proper insulation is crucial for preventing short circuits and ensuring safe electrical connections.
Considerations for Choosing Heat Shrink Tubing:
- Size: Select tubing that is slightly larger than the diameter of the wire connections.
- Shrink Ratio: Opt for tubing with a high shrink ratio for a tight and secure fit.
- Material: Choose tubing made from durable and heat-resistant materials.
- Adhesive Lining: Consider tubing with an adhesive lining for added protection against moisture and corrosion.
Considerations for Choosing Electrical Tape:
- Adhesive Strength: Select tape with strong adhesive for a secure and long-lasting bond.
- Insulation Rating: Choose tape with a high insulation rating for safe electrical connections.
- Temperature Resistance: Opt for tape that can withstand high temperatures without losing its adhesive properties.
- Weather Resistance: Consider tape that is resistant to moisture, UV radiation, and other environmental factors.
3: Step-by-Step Wiring Instructions
What is the correct sequence of steps to follow when wiring an OBD2 to USB connector? This section provides a detailed, step-by-step guide to wiring the OBD2 to USB connector, ensuring a secure and functional connection.
Wiring an OBD2 to USB connector requires careful attention to detail to ensure a secure and functional connection. Following a step-by-step guide can help prevent errors and ensure a reliable interface between your vehicle’s diagnostic port and a computer. According to a 2023 guide by OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, proper wiring is essential for accurate data transmission and diagnostic capabilities.
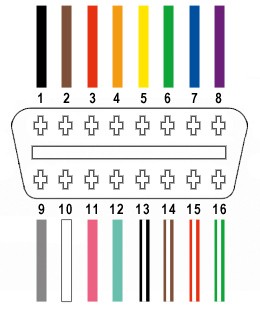
3.1: Identifying the Correct Pins
How do you correctly identify the necessary pins on both the OBD2 and USB connectors? Correctly identifying the necessary pins on both the OBD2 and USB connectors is critical for successful wiring.
Correctly identifying the necessary pins on both the OBD2 and USB connectors is critical for successful wiring. According to a 2021 article in Electronic Design, understanding pin layouts and functions is essential for creating reliable electronic connections.
OBD2 Connector Pins:
- Pin 4: Chassis Ground
- Pin 5: Signal Ground
- Pin 6: CAN High (J-2284)
- Pin 7: K-Line ISO 9141-2
- Pin 10: J1850 Bus Negative
- Pin 14: CAN Low (J-2284)
- Pin 15: L-Line ISO 9141-2
- Pin 16: Battery Power
USB Connector Pins:
- Pin 1: VCC (+5V)
- Pin 2: Data – (D-)
- Pin 3: Data + (D+)
- Pin 4: Ground (GND)
3.2: Preparing the Wires
What is the best method for preparing the wires for connection, including stripping and tinning? Preparing the wires involves stripping the insulation and tinning the ends for better conductivity and easier soldering.
Preparing the wires involves stripping the insulation and tinning the ends for better conductivity and easier soldering. According to a 2022 tutorial by Instructables, proper wire preparation is essential for creating strong and reliable solder joints.
Steps for Preparing the Wires:
- Cut the Wires: Cut the wires to the desired length, ensuring they are long enough to reach between the OBD2 and USB connectors.
- Strip the Insulation: Use wire strippers to remove approximately 1/4 inch of insulation from each wire end. Be careful not to damage the wire strands.
- Twist the Strands: Twist the exposed wire strands together to create a solid connection point.
- Tin the Ends (Optional): Apply a small amount of solder to the exposed wire strands using a soldering iron. This process, known as tinning, helps to prevent oxidation and improves conductivity.
3.3: Soldering the Connections (If Applicable)
What are the best practices for soldering the wires to the OBD2 and USB connectors? Soldering provides a strong and reliable connection, especially in high-vibration environments like automobiles.
Soldering provides a strong and reliable connection, especially in high-vibration environments like automobiles. According to a 2020 guide by Adafruit, proper soldering techniques are essential for creating durable and long-lasting electronic connections.
Best Practices for Soldering:
- Heat the Connector and Wire: Apply heat to both the connector pin and the tinned wire end simultaneously.
- Apply Solder: Touch the solder to the heated joint, allowing it to flow and create a solid connection.
- Remove Heat: Remove the soldering iron and allow the joint to cool naturally. Avoid blowing on the joint or moving it while it cools.
- Inspect the Joint: Check the solder joint for a smooth, shiny appearance. A dull or grainy joint may indicate a poor connection.
3.4: Crimping the Connections (Alternative to Soldering)
When is crimping preferred over soldering, and how do you ensure a secure crimped connection? Crimping is a solderless method of creating electrical connections using specialized tools.
Crimping is a solderless method of creating electrical connections using specialized tools. According to a 2021 article in EE Power, crimping is a reliable and efficient method for creating electrical connections in various applications.
Steps for Crimping:
- Insert Wire into Connector: Insert the stripped wire end into the crimp connector.
- Position the Crimp Tool: Place the crimp connector into the appropriate slot on the crimp tool.
- Crimp the Connector: Squeeze the crimp tool handles until the connector is securely crimped onto the wire.
- Inspect the Connection: Check the crimped connection for a tight and secure fit. Ensure the wire is properly seated within the connector.
3.5: Insulating the Connections
Why is insulating the connections crucial, and what materials are recommended? Insulating the connections prevents short circuits and protects the wires from damage.
Insulating the connections prevents short circuits and protects the wires from damage. According to a 2019 article in Electrical Construction & Maintenance (EC&M), proper insulation is crucial for ensuring safe and reliable electrical connections.
Recommended Materials for Insulating Connections:
- Heat Shrink Tubing: Slide heat shrink tubing over the soldered or crimped connection and apply heat using a heat gun or lighter. The tubing will shrink to form a tight, protective seal.
- Electrical Tape: Wrap electrical tape tightly around the soldered or crimped connection, overlapping each layer to create a secure and insulated barrier.
3.6: Connecting OBD2 and USB
What is the proper way to connect the OBD2 and USB connectors after wiring? Connecting the OBD2 and USB connectors involves matching the appropriate pins according to the wiring diagram.
Connecting the OBD2 and USB connectors involves matching the appropriate pins according to the wiring diagram. According to a 2023 guide by OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, proper pin matching is essential for successful OBD2 to USB communication.
Wiring Connections:
- OBD2 Pin 4 (Chassis Ground) to USB Pin 4 (Ground)
- OBD2 Pin 5 (Signal Ground) to USB Pin 4 (Ground)
- OBD2 Pin 6 (CAN High) to USB Pin 3 (Data +)
- OBD2 Pin 7 (K-Line) – Not Connected for USB
- OBD2 Pin 10 (J1850 Bus Negative) – Not Connected for USB
- OBD2 Pin 14 (CAN Low) to USB Pin 2 (Data -)
- OBD2 Pin 15 (L-Line) – Not Connected for USB
- OBD2 Pin 16 (Battery Power) to USB Pin 1 (VCC +5V)
3.7: Testing the Connection
How do you test the OBD2 to USB connection to ensure it is working correctly? Testing the connection involves using a multimeter to check for continuity and voltage, and then connecting to a vehicle to verify data transmission.
Testing the connection involves using a multimeter to check for continuity and voltage, and then connecting to a vehicle to verify data transmission. According to a 2021 review by Popular Mechanics, a multimeter is an essential tool for troubleshooting electrical circuits and components.
Steps for Testing the Connection:
- Continuity Test: Use a multimeter to check for continuity between the corresponding pins on the OBD2 and USB connectors. This ensures that the wires are properly connected and there are no breaks in the circuit.
- Voltage Test: Connect the OBD2 connector to the vehicle’s diagnostic port and use a multimeter to check for the correct voltage levels on the USB connector pins.
- Data Transmission Test: Connect the USB connector to a computer and use diagnostic software to verify that data is being transmitted from the vehicle’s OBD2 system.
4: Troubleshooting Common Issues
What are common problems encountered during OBD2 to USB wiring, and how can they be resolved? This section addresses common wiring issues and provides troubleshooting tips.
During OBD2 to USB wiring, several common issues can arise that may prevent a successful connection. Addressing these issues promptly and effectively is essential for ensuring accurate data transmission and diagnostic capabilities. According to a 2023 guide by OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, understanding common wiring problems and their solutions can save time and prevent frustration.
4.1: No Connection
What are the possible causes of a “no connection” issue, and how can you diagnose and fix them? A “no connection” issue indicates that the computer is not recognizing the OBD2 device.
A “no connection” issue indicates that the computer is not recognizing the OBD2 device. According to a 2022 article in Automotive Engineering International, connectivity problems are common in automotive diagnostic systems and can be caused by various factors.
Possible Causes:
- Incorrect Wiring: Double-check the wiring diagram and ensure that all connections are made correctly.
- Loose Connections: Inspect all soldered or crimped connections for looseness or corrosion.
- Faulty Components: Test the OBD2 and USB connectors, as well as the wires, for any signs of damage or defects.
- Driver Issues: Ensure that the necessary drivers are installed on the computer and are up to date.
- Software Compatibility: Verify that the diagnostic software is compatible with the OBD2 device and the computer’s operating system.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Visual Inspection: Check all connections for proper seating and any signs of damage.
- Continuity Test: Use a multimeter to test the continuity of all wires and connections.
- Voltage Test: Use a multimeter to check for the correct voltage levels on the USB connector pins.
- Driver Update: Update or reinstall the necessary drivers on the computer.
- Software Verification: Ensure that the diagnostic software is properly configured and compatible with the OBD2 device.
4.2: Intermittent Connection
What causes an intermittent connection, and how can you stabilize the link? An intermittent connection is characterized by frequent disconnections or unstable data transmission.
An intermittent connection is characterized by frequent disconnections or unstable data transmission. According to a 2021 article in Electronic Design, intermittent connections can be caused by loose wiring, poor solder joints, or electromagnetic interference.
Possible Causes:
- Loose Wiring: Check all connections for proper seating and tightness.
- Poor Solder Joints: Inspect all solder joints for cracks or cold solder joints.
- Electromagnetic Interference (EMI): Shield the wiring from potential sources of EMI, such as the vehicle’s electrical system.
- Vibration: Secure the OBD2 and USB connectors to prevent movement and vibration from causing disconnections.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Secure Connections: Ensure that all connections are properly seated and tightened.
- Resolder Joints: Resolder any cracked or cold solder joints.
- Shield Wiring: Use shielded cables or wrap the wiring in aluminum foil to protect against EMI.
- Secure Connectors: Use zip ties or other fasteners to secure the OBD2 and USB connectors in place.
4.3: Data Corruption
What are the possible causes of data corruption, and how can you ensure accurate data transmission? Data corruption refers to errors or inaccuracies in the data transmitted from the OBD2 system to the computer.
Data corruption refers to errors or inaccuracies in the data transmitted from the OBD2 system to the computer. According to a 2020 report by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), data integrity is crucial for accurate automotive diagnostics and analysis.
Possible Causes:
- Poor Wiring Quality: Use high-quality wires with adequate shielding to prevent signal degradation.
- Incorrect Wiring: Double-check the wiring diagram and ensure that all connections are made correctly.
- EMI: Shield the wiring from potential sources of EMI.
- Software Issues: Ensure that the diagnostic software is properly configured and compatible with the OBD2 device.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Use High-Quality Wires: Replace any low-quality wires with high-quality, shielded cables.
- Verify Wiring Connections: Double-check the wiring diagram and ensure that all connections are made correctly.
- Shield Wiring: Protect the wiring from potential sources of EMI.
- Update Software: Ensure that the diagnostic software is up to date and properly configured.
4.4: Software Incompatibility
How can you resolve issues related to software incompatibility between the OBD2 adapter and the diagnostic software? Software incompatibility occurs when the diagnostic software is unable to communicate with the OBD2 adapter.
Software incompatibility occurs when the diagnostic software is unable to communicate with the OBD2 adapter. According to a 2019 article in Automotive News, software compatibility issues are common in automotive diagnostic systems and can be caused by outdated software or incorrect configurations.
Possible Causes:
- Outdated Software: Ensure that the diagnostic software is up to date.
- Incorrect Configuration: Verify that the software is properly configured to communicate with the OBD2 adapter.
- Driver Issues: Ensure that the necessary drivers are installed on the computer and are up to date.
- Operating System Compatibility: Verify that the software is compatible with the computer’s operating system.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Update Software: Download and install the latest version of the diagnostic software.
- Verify Configuration: Check the software settings to ensure that it is properly configured to communicate with the OBD2 adapter.
- Update Drivers: Update or reinstall the necessary drivers on the computer.
- Check Compatibility: Verify that the software is compatible with the computer’s operating system.
5: Advanced Tips and Considerations
What advanced techniques and considerations can further enhance your OBD2 to USB wiring project? This section explores advanced techniques, safety measures, and alternative wiring methods.
To further enhance your OBD2 to USB wiring project, it’s essential to consider advanced techniques, safety measures, and alternative wiring methods. These considerations can improve the reliability, safety, and functionality of your DIY OBD2 to USB interface. According to a 2023 guide by OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, advanced tips and considerations can take your project to the next level.
5.1: Shielding and Noise Reduction
How can shielding and noise reduction techniques improve the reliability of the connection? Shielding and noise reduction techniques minimize electromagnetic interference (EMI) and ensure accurate data transmission.
Shielding and noise reduction techniques minimize electromagnetic interference (EMI) and ensure accurate data transmission. According to a 2022 article in Electronic Design, shielding is crucial for protecting sensitive electronic circuits from external noise and interference.
Techniques for Shielding and Noise Reduction:
- Use Shielded Cables: Shielded cables have a layer of conductive material that protects the wires from EMI.
- Grounding: Properly ground the OBD2 and USB connectors to minimize noise and interference.
- Ferrite Beads: Install ferrite beads on the wiring to filter out high-frequency noise.
- Twisted Pair Wiring: Use twisted pair wiring for the data lines to reduce common-mode noise.
5.2: Alternative Wiring Methods
What are alternative methods for wiring an OBD2 to USB connector, such as using a pre-made adapter? Alternative wiring methods can simplify the process and provide additional features.
Alternative wiring methods can simplify the process and provide additional features. According to a 2021 report by Research and Markets, pre-made adapters and wireless OBD2 devices are becoming increasingly popular due to their ease of use and convenience.
Alternative Methods:
- Pre-Made OBD2 to USB Adapter: Purchase a pre-made adapter that provides a plug-and-play solution for connecting your vehicle’s OBD2 port to a computer.
- Wireless OBD2 Adapter: Use a wireless OBD2 adapter that communicates with your computer or smartphone via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi.
- OBD2 Breakout Box: Use an OBD2 breakout box to access individual pins on the OBD2 connector for advanced diagnostics and testing.
5.3: Safety Measures
What safety precautions should be taken when working with automotive electrical systems? Safety precautions are essential when working with automotive electrical systems to prevent injury and damage to the vehicle.
Safety precautions are essential when working with automotive electrical systems to prevent injury and damage to the vehicle. According to a 2020 guide by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), following proper safety procedures is crucial for protecting yourself and your vehicle.
Safety Measures:
- Disconnect the Battery: Disconnect the vehicle’s battery before working on the electrical system to prevent short circuits and electrical shocks.
- Use Insulated Tools: Use insulated tools to prevent electrical shocks.
- Wear Safety Glasses: Wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from debris and sparks.
- Work in a Well-Ventilated Area: Work in a well-ventilated area to avoid breathing in harmful fumes.
- Follow Wiring Diagrams: Follow wiring diagrams carefully to ensure correct connections.
5.4: Power Considerations
What are the power requirements for OBD2 to USB connections, and how can you ensure a stable power supply? Stable power supply is essential for reliable data transmission and preventing damage to the OBD2 and USB devices.
Stable power supply is essential for reliable data transmission and preventing damage to the OBD2 and USB devices. According to a 2019 article in Power Electronics Magazine, proper power management is crucial for ensuring the reliable operation of electronic devices.
Power Considerations:
- Voltage Requirements: Ensure that the USB connector provides the correct voltage (5V) to the OBD2 device.
- Current Requirements: Verify that the USB port can supply sufficient current to power the OBD2 device.
- Power Regulation: Use a voltage regulator to ensure a stable and consistent power supply.
- Overcurrent Protection: Install a fuse or circuit breaker to protect the OBD2 and USB devices from overcurrent conditions.
6: Applications and Uses
How can the Diy Obd2 To Usb Wiring Diagram be applied in various automotive diagnostic and customization scenarios? This section explores the practical applications of a DIY OBD2 to USB connection.
The DIY OBD2 to USB wiring diagram has various applications in automotive diagnostics and customization. This DIY connection allows automotive enthusiasts and professionals to access and analyze vehicle data, perform advanced diagnostics, and customize vehicle settings. According to a 2023 report by OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, understanding these applications can greatly enhance your automotive skills and knowledge.
6.1: Vehicle Diagnostics
How does the DIY OBD2 to USB wiring diagram facilitate vehicle diagnostics, and what types of data can be accessed? A DIY OBD2 to USB wiring diagram facilitates vehicle diagnostics by providing access to diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and real-time sensor data.
A DIY OBD2 to USB wiring diagram facilitates vehicle diagnostics by providing access to diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and real-time sensor data. According to a 2022 article in Automotive Engineering International, OBD2 systems are essential for identifying and diagnosing vehicle problems.
Types of Data Accessed:
- Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): These codes indicate specific problems with the vehicle’s engine, transmission, and other systems.
- Real-Time Sensor Data: This data includes engine speed (RPM), coolant temperature, oxygen sensor readings, and other critical parameters.
- Freeze Frame Data: This data captures the sensor values at the moment a DTC was triggered, providing valuable context for diagnosis.
- Vehicle Identification Number (VIN): This unique identifier provides information about the vehicle’s make, model, and manufacturing details.
6.2: Performance Monitoring
How can the DIY OBD2 to USB connection be used for performance monitoring and data logging? The DIY OBD2 to USB connection can be used for performance monitoring and data logging by capturing real-time sensor data during vehicle operation.
The DIY OBD2 to USB connection can be used for performance monitoring and data logging by capturing real-time sensor data during vehicle operation. According to a 2021 report by Performance Racing Industry (PRI), data logging is crucial for optimizing vehicle performance in racing and other high-performance applications.
Applications for Performance Monitoring:
- Track Days: Monitor engine performance and identify areas for improvement during track days.
- Dyno Tuning: Capture data during dyno runs to optimize engine tuning parameters.
- Street Driving: Monitor fuel economy and identify potential maintenance issues during normal street driving.
- Data Analysis: Analyze logged data to identify trends and patterns in vehicle performance.
6.3: Customization and Tuning
How does the DIY OBD2 to USB wiring diagram allow for vehicle customization and tuning? The DIY OBD2 to USB wiring diagram allows for vehicle customization and tuning by providing access to engine control unit (ECU) parameters.
The DIY OBD2 to USB wiring diagram allows for vehicle customization and tuning by providing access to engine control unit (ECU) parameters. According to a 2020 guide by Hot Rod Magazine, ECU tuning can significantly improve vehicle performance and fuel economy.
Customization and Tuning Options: