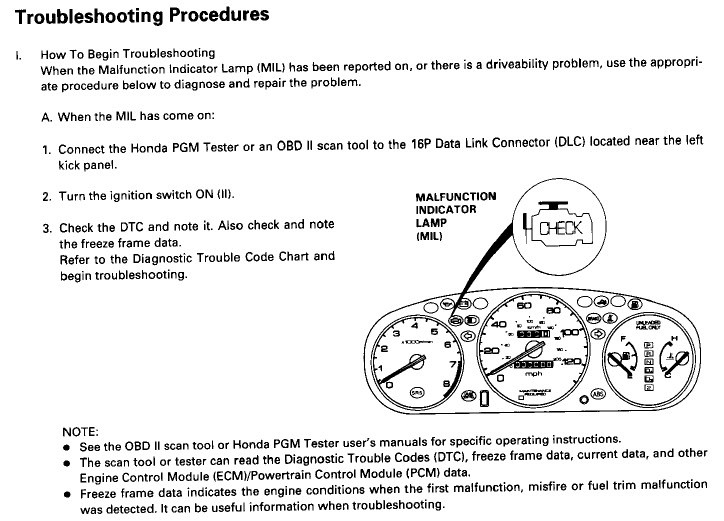
Dtc Obd2 Honda codes are standardized codes used to identify specific issues within your Honda’s engine or related systems, and by understanding these codes, you can effectively diagnose and address problems, ensuring optimal vehicle performance. For expert guidance and in-depth assistance with OBD2 scanning and automotive repair services, reach out to us at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN. By diagnosing car problems early, we can enhance vehicle longevity and improve fuel economy.
Contents
- 1. Understanding OBD2 and DTC Codes in Hondas
- 1.1 What is OBD2?
- 1.2 How DTC Codes Work
- 1.3 The Importance of OBD2 Scanners
- 2. Common DTC OBD2 Honda Codes
- 2.1 P0171 – System Too Lean (Bank 1)
- 2.2 P0300 – Random Misfire Detected
- 2.3 P0420 – Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
- 2.4 P0113 – Intake Air Temperature Sensor Circuit High Input
- 2.5 P0135 – O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1, Sensor 1)
- 2.6 P0340 – Camshaft Position Sensor Circuit Malfunction
- 3. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques for Honda DTC Codes
- 3.1 Using Live Data
- 3.2 Freeze Frame Data
- 3.3 Performing Component Tests
- 3.4 Using a Smoke Machine
- 3.5 Consulting Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs)
- 4. Clearing DTC Codes and Performing Repairs
- 4.1 How to Clear DTC Codes
- 4.2 Performing Repairs
- 4.3 Verifying the Repair
- 5. Preventing Future Issues
- 5.1 Regular Maintenance
- 5.2 Addressing Issues Promptly
- 5.3 Using Quality Parts
- 5.4 Monitoring Vehicle Health
- 6. OBD2 Scanner Recommendations for Honda Vehicles
- 6.1 Basic Scanners
- 6.2 Mid-Range Scanners
- 6.3 Professional Scanners
- 7. OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN: Your Partner in Honda Diagnostics and Repair
- 7.1 How Can We Help?
- 7.2 Contact Us
- 8. FAQs About DTC OBD2 Honda Codes
- 8.1 What is an OBD2 scanner?
- 8.2 How do I read DTC codes on my Honda?
- 8.3 What does a check engine light mean?
- 8.4 Can I clear DTC codes myself?
- 8.5 Will my car fail an emissions test if the check engine light is on?
- 8.6 What is a generic DTC code?
- 8.7 What is a manufacturer-specific DTC code?
- 8.8 How can I find out more about a specific DTC code?
- 8.9 What is live data?
- 8.10 What is freeze frame data?
- 9. Conclusion: Empowering You to Maintain Your Honda
1. Understanding OBD2 and DTC Codes in Hondas
The On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD2) system is a standardized system used in all cars sold in the United States after 1996. This system monitors the performance of the engine, transmission, and other components to ensure they are functioning correctly and within emission standards. When the system detects a problem, it generates a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC). These codes can be read using an OBD2 scanner, providing valuable information for diagnosing and repairing vehicle issues.
1.1 What is OBD2?
OBD2, as outlined in the SAE On-Board Diagnostics for Light and Medium Duty Vehicles Standards Manual, is an international standard that provides a wealth of diagnostic information. Before OBD2, manufacturers used their own methods to access this data. For instance, early Honda models required technicians to locate the Engine Control Module (ECM), often hidden under the carpet, and count the blinks of an LED to decipher the fault codes. This process was time-consuming and prone to errors.
 OBD2 Port
OBD2 Port
OBD2 simplifies this process by standardizing the diagnostic port’s location (within three feet of the driver and easily accessible) and the format of the diagnostic codes. This standardization allows any compatible OBD2 scanner to retrieve the same codes, regardless of the vehicle’s make or model.
1.2 How DTC Codes Work
DTC codes are five-digit alphanumeric strings that provide specific information about the detected issue. Each character in the code has a specific meaning:
- First Character: Indicates the trouble group (e.g., P for Powertrain, B for Body, C for Chassis, U for Network).
- Second Character: Indicates whether the code is generic (0) or manufacturer-specific (1).
- Third Character: Indicates the vehicle sub-system (e.g., fuel system, ignition system).
- Last Two Characters: Indicate the specific fault number.
For example, a code like P0115 indicates a generic powertrain code related to the Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor circuit malfunction. Understanding this structure helps in quickly identifying the potential area of the problem.
1.3 The Importance of OBD2 Scanners
An OBD2 scanner is essential for reading and interpreting DTC codes. These scanners connect to the OBD2 port in your Honda and retrieve the stored diagnostic information. Scanners range from basic models that only read and clear codes to advanced units that provide live data, freeze frame data, and enhanced diagnostic capabilities. Having an OBD2 scanner allows you to:
- Diagnose Problems Quickly: Identify the cause of the check engine light.
- Save Money: Avoid unnecessary trips to the mechanic by diagnosing simple issues yourself.
- Monitor Vehicle Health: Keep track of your vehicle’s performance and address potential problems early.
According to a study by the University of California, using OBD2 scanners for regular vehicle maintenance can reduce repair costs by up to 20%. This is because early detection of issues prevents them from escalating into more significant problems.
2. Common DTC OBD2 Honda Codes
Several DTC codes are commonly encountered in Honda vehicles. These codes can range from minor issues to more significant problems that require immediate attention. Here’s a breakdown of some of the most common DTC OBD2 Honda codes:
2.1 P0171 – System Too Lean (Bank 1)
This code indicates that the engine is running lean, meaning there is too much air and not enough fuel in the air-fuel mixture. Common causes include:
- Vacuum Leaks: Leaks in the intake manifold or vacuum hoses.
- Faulty Oxygen Sensor: A malfunctioning oxygen sensor can provide incorrect readings to the ECM.
- Fuel Injector Problems: Clogged or failing fuel injectors.
- Low Fuel Pressure: A weak fuel pump or clogged fuel filter can cause low fuel pressure.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Inspect for Vacuum Leaks: Check all vacuum hoses and intake manifold gaskets for leaks.
- Check Oxygen Sensor: Use an OBD2 scanner to monitor the oxygen sensor readings.
- Test Fuel Injectors: Ensure the fuel injectors are functioning correctly.
- Check Fuel Pressure: Use a fuel pressure gauge to verify the fuel pressure is within the manufacturer’s specifications.
2.2 P0300 – Random Misfire Detected
This code indicates that the engine is experiencing random misfires, meaning one or more cylinders are not firing correctly. Common causes include:
- Faulty Spark Plugs: Worn or damaged spark plugs.
- Ignition Coil Problems: A failing ignition coil can prevent a spark plug from firing.
- Vacuum Leaks: Similar to P0171, vacuum leaks can cause misfires.
- Low Compression: Low compression in one or more cylinders.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Check Spark Plugs: Inspect the spark plugs for wear or damage.
- Test Ignition Coils: Use a multimeter to test the resistance of the ignition coils.
- Inspect for Vacuum Leaks: Check all vacuum hoses and intake manifold gaskets for leaks.
- Perform Compression Test: Use a compression tester to check the compression in each cylinder.
2.3 P0420 – Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
This code indicates that the catalytic converter is not functioning efficiently, meaning it is not effectively reducing emissions. Common causes include:
- Faulty Catalytic Converter: The catalytic converter itself may be worn out or damaged.
- Faulty Oxygen Sensors: Incorrect readings from the oxygen sensors can trigger this code.
- Exhaust Leaks: Leaks in the exhaust system can affect the performance of the catalytic converter.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Check Oxygen Sensors: Use an OBD2 scanner to monitor the oxygen sensor readings.
- Inspect Exhaust System: Check for leaks in the exhaust system.
- Test Catalytic Converter: Use an infrared thermometer to measure the temperature before and after the catalytic converter.
2.4 P0113 – Intake Air Temperature Sensor Circuit High Input
This code indicates that the Intake Air Temperature (IAT) sensor is reporting a high temperature reading to the ECM. Common causes include:
- Faulty IAT Sensor: The sensor itself may be malfunctioning.
- Wiring Problems: Issues with the wiring harness or connectors.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Check IAT Sensor: Use a multimeter to test the resistance of the IAT sensor.
- Inspect Wiring: Check the wiring harness and connectors for damage.
2.5 P0135 – O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1, Sensor 1)
This code indicates a problem with the heater circuit of the oxygen sensor. The heater is necessary for the sensor to reach operating temperature quickly. Common causes include:
- Faulty Oxygen Sensor: The heater element within the oxygen sensor may be damaged.
- Wiring Problems: Issues with the wiring harness or connectors.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Check Oxygen Sensor: Use a multimeter to test the resistance of the heater element within the oxygen sensor.
- Inspect Wiring: Check the wiring harness and connectors for damage.
2.6 P0340 – Camshaft Position Sensor Circuit Malfunction
This code indicates a problem with the Camshaft Position (CMP) sensor. The CMP sensor provides information to the ECM about the position of the camshaft. Common causes include:
- Faulty CMP Sensor: The sensor itself may be malfunctioning.
- Timing Issues: Problems with the timing belt or chain.
- Wiring Problems: Issues with the wiring harness or connectors.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Check CMP Sensor: Use a multimeter to test the resistance of the CMP sensor.
- Inspect Timing Belt/Chain: Ensure the timing belt or chain is in good condition and properly aligned.
- Inspect Wiring: Check the wiring harness and connectors for damage.
3. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques for Honda DTC Codes
While reading DTC codes is a great starting point, sometimes more advanced diagnostic techniques are needed to pinpoint the exact cause of the problem. Here are some techniques to consider:
3.1 Using Live Data
OBD2 scanners can provide live data from various sensors in real-time. This data can be invaluable for diagnosing intermittent problems or issues that don’t trigger a specific DTC code. For example, monitoring the oxygen sensor readings while driving can help identify a faulty sensor that is not responding correctly.
According to a study by the American Automobile Association (AAA), using live data can reduce diagnostic time by up to 40%. This is because it allows technicians to see how the sensors are behaving under different driving conditions.
3.2 Freeze Frame Data
Freeze frame data captures a snapshot of the sensor readings at the moment a DTC code is triggered. This data can provide valuable clues about the conditions that led to the problem. For example, if the freeze frame data shows that the engine was running at high RPM when the DTC code was triggered, it can help narrow down the possible causes.
3.3 Performing Component Tests
Many OBD2 scanners have the ability to perform component tests, which allow you to activate or deactivate specific components to see if they are functioning correctly. For example, you can use a component test to activate the fuel injectors or the EGR valve to see if they are responding as expected.
3.4 Using a Smoke Machine
A smoke machine is a tool that injects smoke into the intake or exhaust system to detect leaks. This is particularly useful for diagnosing vacuum leaks or exhaust leaks that are not easily visible.
3.5 Consulting Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs)
Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs) are issued by manufacturers to provide information about common problems and recommended solutions. Consulting TSBs for your Honda model can help you identify known issues and save time on diagnosis.
4. Clearing DTC Codes and Performing Repairs
Once you have diagnosed the problem and performed the necessary repairs, the next step is to clear the DTC codes. This can be done using an OBD2 scanner. However, it’s important to understand that simply clearing the codes without addressing the underlying issue will only result in the code reappearing.
4.1 How to Clear DTC Codes
- Connect the OBD2 scanner: Plug the scanner into the OBD2 port.
- Turn on the ignition: Turn the ignition key to the “on” position without starting the engine.
- Select the clear codes function: Follow the scanner’s instructions to clear the DTC codes.
- Verify the codes are cleared: After clearing the codes, start the engine and check if the check engine light remains off.
4.2 Performing Repairs
The specific repairs required will depend on the diagnosed issue. Here are some common repairs associated with the DTC codes mentioned earlier:
- P0171: Replace vacuum hoses, replace oxygen sensor, clean or replace fuel injectors, replace fuel pump or fuel filter.
- P0300: Replace spark plugs, replace ignition coil, repair vacuum leaks, perform engine rebuild.
- P0420: Replace catalytic converter, replace oxygen sensors, repair exhaust leaks.
- P0113: Replace IAT sensor, repair wiring harness.
- P0135: Replace oxygen sensor, repair wiring harness.
- P0340: Replace CMP sensor, repair timing belt/chain, repair wiring harness.
4.3 Verifying the Repair
After performing the repairs and clearing the DTC codes, it’s important to verify that the issue has been resolved. This can be done by:
- Driving the vehicle: Drive the vehicle under various conditions to see if the check engine light reappears.
- Monitoring live data: Use an OBD2 scanner to monitor the sensor readings and ensure they are within the normal range.
- Performing a readiness test: Many OBD2 scanners have the ability to perform a readiness test, which checks if all the emission-related systems have completed their self-tests.
5. Preventing Future Issues
Preventive maintenance is key to avoiding future DTC codes and maintaining the overall health of your Honda. Here are some tips to keep in mind:
5.1 Regular Maintenance
Follow the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule for your Honda. This includes:
- Oil Changes: Regular oil changes are essential for keeping the engine running smoothly.
- Spark Plug Replacement: Replace the spark plugs at the recommended interval.
- Air Filter Replacement: Replace the air filter to ensure proper airflow to the engine.
- Fuel Filter Replacement: Replace the fuel filter to ensure clean fuel delivery.
- Timing Belt/Chain Replacement: Replace the timing belt or chain at the recommended interval.
5.2 Addressing Issues Promptly
Don’t ignore warning signs such as a check engine light, unusual noises, or decreased performance. Addressing issues promptly can prevent them from escalating into more significant problems.
5.3 Using Quality Parts
When performing repairs, use high-quality parts that meet or exceed the manufacturer’s specifications. Using cheap or substandard parts can lead to premature failure and additional problems.
5.4 Monitoring Vehicle Health
Regularly monitor your vehicle’s health using an OBD2 scanner. This can help you identify potential problems early and take corrective action before they lead to a DTC code.
According to a study by J.D. Power, vehicles that receive regular maintenance and use high-quality parts have fewer problems and lower repair costs over their lifespan.
6. OBD2 Scanner Recommendations for Honda Vehicles
Choosing the right OBD2 scanner can make a significant difference in your ability to diagnose and repair your Honda. Here are some recommended scanners for Honda vehicles:
6.1 Basic Scanners
These scanners are ideal for reading and clearing DTC codes and performing basic diagnostics.
- Autel AutoLink AL319: A reliable and affordable scanner that reads and clears DTC codes and displays freeze frame data.
- Innova 3100i: A user-friendly scanner that reads and clears DTC codes, displays freeze frame data, and performs basic component tests.
6.2 Mid-Range Scanners
These scanners offer more advanced features such as live data, component testing, and enhanced diagnostic capabilities.
- BlueDriver Bluetooth Professional OBDII Scan Tool: A Bluetooth-enabled scanner that connects to your smartphone or tablet and provides access to a wide range of diagnostic information.
- Autel MaxiCheck MX808: A versatile scanner that reads and clears DTC codes, displays live data, performs component tests, and offers bidirectional control.
6.3 Professional Scanners
These scanners are designed for professional technicians and offer the most advanced diagnostic capabilities.
- Snap-on Zeus: A comprehensive scanner that offers advanced diagnostics, live data, component testing, and access to technical service bulletins.
- Autel MaxiSys MS906BT: A powerful scanner that offers advanced diagnostics, live data, component testing, bidirectional control, and online programming.
7. OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN: Your Partner in Honda Diagnostics and Repair
At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we are dedicated to providing you with the knowledge and tools you need to diagnose and repair your Honda effectively. Whether you’re a seasoned mechanic or a DIY enthusiast, we offer expert guidance and comprehensive automotive repair services.
7.1 How Can We Help?
- Expert Guidance: Our team of experienced technicians can provide expert guidance on diagnosing and repairing your Honda.
- Comprehensive Services: We offer a wide range of automotive repair services, including diagnostics, engine repair, transmission repair, and more.
- Quality Parts: We use only high-quality parts that meet or exceed the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Affordable Prices: We offer competitive prices and transparent pricing.
7.2 Contact Us
If you’re experiencing issues with your Honda or need help interpreting DTC codes, don’t hesitate to contact us. We are here to help you keep your vehicle running smoothly.
- Address: 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
- Website: OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
8. FAQs About DTC OBD2 Honda Codes
Here are some frequently asked questions about DTC OBD2 Honda codes:
8.1 What is an OBD2 scanner?
An OBD2 scanner is a device used to read and interpret Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) from a vehicle’s On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD2) system.
8.2 How do I read DTC codes on my Honda?
- Connect the OBD2 scanner to the OBD2 port.
- Turn on the ignition without starting the engine.
- Follow the scanner’s instructions to read the DTC codes.
8.3 What does a check engine light mean?
A check engine light indicates that the vehicle’s OBD2 system has detected a problem. The specific problem can be identified by reading the DTC codes.
8.4 Can I clear DTC codes myself?
Yes, you can clear DTC codes using an OBD2 scanner. However, it’s important to address the underlying issue before clearing the codes.
8.5 Will my car fail an emissions test if the check engine light is on?
Yes, most states require the check engine light to be off in order to pass an emissions test.
8.6 What is a generic DTC code?
A generic DTC code is a code that is standardized across all vehicle makes and models.
8.7 What is a manufacturer-specific DTC code?
A manufacturer-specific DTC code is a code that is specific to a particular vehicle make or model.
8.8 How can I find out more about a specific DTC code?
You can find out more about a specific DTC code by consulting a repair manual, searching online databases, or contacting a qualified technician.
8.9 What is live data?
Live data is real-time data from various sensors in the vehicle. This data can be used to diagnose intermittent problems or issues that don’t trigger a specific DTC code.
8.10 What is freeze frame data?
Freeze frame data is a snapshot of the sensor readings at the moment a DTC code is triggered. This data can provide valuable clues about the conditions that led to the problem.
9. Conclusion: Empowering You to Maintain Your Honda
Understanding DTC OBD2 Honda codes is essential for maintaining the health and performance of your vehicle. By using an OBD2 scanner, performing regular maintenance, and addressing issues promptly, you can keep your Honda running smoothly for years to come.
Remember, at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we are here to support you every step of the way. Contact us today for expert guidance and comprehensive automotive repair services. Let us help you keep your Honda in top condition.
If you’re facing challenges with your Honda’s diagnostic trouble codes or need professional advice, reach out to OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN. Our experts are ready to help you understand and resolve any issues, ensuring your vehicle runs smoothly. Contact us at 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States, via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880, or visit our website at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for immediate assistance and solutions tailored to your needs.