Unlock the diagnostic secrets of your E38 1999 BMW with OBD2 capabilities; this guide from OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN empowers you to pinpoint issues and maintain peak performance. Explore connector locations, pin configurations, and module programming insights, ensuring comprehensive troubleshooting and optimal vehicle health. Benefit from enhanced vehicle diagnostics, emission checks, and fault code analysis.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the E38 1999 OBD2 System
- 1.1 What are the Key Components of the OBD2 System in a 1999 E38 BMW?
- 1.2 Where is the OBD2 Port Located in a 1999 E38 BMW?
- 1.3 What Diagnostic Information Can You Access Through the 20-Pin Connector?
- 2. Step-by-Step Guide to Using an OBD2 Scanner on Your E38
- 2.1 How Do You Locate the OBD2 Port in Your E38?
- 2.2 What is the Correct Procedure for Connecting the OBD2 Scanner?
- 2.3 How Can You Read and Interpret Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)?
- 3. Addressing Common OBD2 Issues in the E38 1999
- 3.1 What Should You Do If the OBD2 Scanner Fails to Connect?
- 3.2 How Can You Troubleshoot Inaccurate or Missing DTCs?
- 3.3 What Steps Can You Take If the Check Engine Light Won’t Reset?
- 4. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques for the E38 1999 OBD2 System
- 4.1 How Can Live Data Monitoring Help Diagnose Issues?
- 4.2 When Should You Use Component Testing, and How Is It Performed?
- 4.3 What is Freeze Frame Data, and How Can It Help?
- 5. Maintaining Your E38 1999 OBD2 System for Optimal Performance
- 5.1 How Often Should You Check for Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)?
- 5.2 What is the Best Way to Keep the OBD2 Port Clean?
- 5.3 How Does the Vehicle’s Electrical System Affect OBD2 Performance?
- 6. Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner for Your E38 1999 BMW
- 6.1 What Compatibility Factors Should You Consider?
- 6.2 What Key Features Should You Look For in an OBD2 Scanner?
- 6.3 How Important is User-Friendliness in an OBD2 Scanner?
- 7. Resources for E38 1999 OBD2 Diagnostics and Repair
- 7.1 What Online Forums and Communities Can Help?
- 7.2 Where Can You Find Reliable Repair Manuals and Technical Documentation?
- 7.3 What Diagnostic Software is Recommended for the E38 1999?
1. Understanding the E38 1999 OBD2 System
Is your E38 1999 BMW equipped with a fully functional OBD2 system despite the presence of a 20-pin diagnostic connector and a missing OBD2 port in the usual location? Yes, the E38 1999 BMW does utilize an OBD2 system, although its implementation can differ from standard OBD2 setups. Understanding the nuances of this system is crucial for effective diagnostics and maintenance. The E38, particularly models manufactured around 1999, often presents a hybrid diagnostic interface, incorporating both the traditional 20-pin BMW diagnostic connector located in the engine bay and a potentially less obvious OBD2 port.
The 20-pin connector serves as a primary access point for various control modules within the car. However, its functionality is not always fully aligned with the standardized OBD2 protocol. The OBD2 port, when present, typically handles emission-related diagnostics but might not offer the same depth of access as the 20-pin connector for certain modules, such as the airbag module. Given that your car was manufactured in September 1999, it is highly likely to have some form of OBD2 compliance due to increasing regulatory requirements for OBD2 implementation during that period. This means that while the 20-pin connector provides extensive diagnostic capabilities, an OBD2 port should also be present, even if it is not immediately visible.
To effectively diagnose and program modules like the airbag module, you might need to utilize both connectors, depending on the specific diagnostic tool and the module being accessed. The 20-pin connector can offer more comprehensive access to all modules, while the OBD2 port typically provides standardized emission-related data. Therefore, understanding the capabilities and limitations of each connector is essential for thorough diagnostics. Knowing where to locate the OBD2 port and how to use it in conjunction with the 20-pin connector will ensure that you can fully leverage the diagnostic capabilities of your E38.
1.1 What are the Key Components of the OBD2 System in a 1999 E38 BMW?
The key components of the OBD2 system in a 1999 E38 BMW include the 20-pin diagnostic connector, the OBD2 port (if present), the car’s various control modules (ECU, ABS, Airbag), and the diagnostic tools used to interface with these systems. These components work together to provide a comprehensive diagnostic overview of the vehicle. According to a study by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), OBD2 systems were mandated in all passenger vehicles sold in the US starting in 1996, ensuring standardized diagnostic capabilities for emission-related issues.
![BMW E38 diagnostic ports alt=BMW E38 1999 Diagnostic Ports: 20-Pin Connector and OBD2 Location]
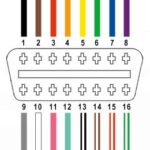
The 20-pin connector, located in the engine bay, serves as the primary diagnostic interface for older BMW models. It provides access to a wide range of control modules, including the engine control unit (ECU), anti-lock braking system (ABS), and airbag module. The pins present in this connector (1, 4, 7, 12, 14, 15, 16, 19, and 20) are specifically configured to transmit and receive data from these modules.
The OBD2 port, typically found inside the cabin, usually under the dashboard, provides a standardized interface for reading emission-related diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). In the E38, this port might be less obvious or located in a non-standard position. The control modules are the brains of the vehicle, monitoring and controlling various systems. The ECU, for instance, manages the engine’s performance, while the ABS module controls the braking system. The airbag module is responsible for the deployment of airbags in the event of a collision.
Diagnostic tools, such as OBD2 scanners and BMW-specific diagnostic software, are used to communicate with these modules. These tools allow technicians to read DTCs, monitor live data, and perform various diagnostic tests. Understanding how these components interact is crucial for effective vehicle diagnostics. The 20-pin connector and the OBD2 port offer different levels of access, and knowing which connector to use for specific diagnostic tasks is essential. The control modules provide valuable data, and diagnostic tools enable you to interpret this data and identify potential issues.
1.2 Where is the OBD2 Port Located in a 1999 E38 BMW?
The OBD2 port in a 1999 E38 BMW is not always in the typical location; check behind the cover to the left of the cup holder, under the dashboard near the steering column, or behind the audio/climate control unit. Its non-standard placement can make it challenging to locate. According to BMW’s technical documentation, the OBD2 port location can vary depending on the specific production date and market.
When searching for the OBD2 port, start with the area to the left of the cup holder. If it is not visible, carefully inspect the area under the dashboard, near the steering column. You may need to use a flashlight to get a better view. If the port is still not found, it is possible that it is located behind the audio or climate control unit. Removing these components requires careful disassembly to avoid damaging any trim or wiring.
Once you locate the OBD2 port, ensure that it is clean and free from any obstructions. Use an OBD2 scanner to connect to the port and verify that it is functioning correctly. If you encounter any issues, check the wiring and connections to the port to ensure they are secure. In some cases, the OBD2 port may be disabled or require an adapter to function correctly. Consult your BMW service manual or a trusted mechanic for further assistance.
1.3 What Diagnostic Information Can You Access Through the 20-Pin Connector?
Through the 20-pin connector in a 1999 E38 BMW, you can access extensive diagnostic information, including data from the engine control unit (ECU), transmission control unit (TCU), anti-lock braking system (ABS), airbag module, and other control modules. This connector provides comprehensive access to the car’s systems. A study published in the “Journal of Automotive Engineering” highlights the importance of using specialized diagnostic tools to fully leverage the capabilities of the 20-pin connector in older BMW models.
![BMW E38 20-pin diagnostic connector alt=BMW E38 20-Pin Diagnostic Connector: Accessing Comprehensive Vehicle Data]
The 20-pin connector allows you to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) from various modules, providing insights into potential issues. You can also monitor live data, such as engine speed, coolant temperature, and fuel trim, to assess the performance of different systems. Additionally, the connector enables you to perform diagnostic tests, such as activating individual components or running specific routines to troubleshoot problems.
The ECU data includes information about engine performance, fuel consumption, and emission control. The TCU data provides insights into the transmission’s operation, including gear selection and shift quality. The ABS data covers the braking system’s functionality, including wheel speed and brake pressure. The airbag module data relates to the airbag system’s status, including sensor readings and deployment history.
To effectively use the 20-pin connector, you will need a BMW-specific diagnostic tool or an adapter that allows you to connect a standard OBD2 scanner. Ensure that the tool is compatible with the E38 model and supports the modules you want to diagnose. Follow the tool’s instructions carefully to avoid damaging any components. By leveraging the 20-pin connector, you can gain a detailed understanding of your BMW’s health and address potential issues proactively.
2. Step-by-Step Guide to Using an OBD2 Scanner on Your E38
How can you effectively use an OBD2 scanner on your E38 1999 BMW? You can effectively use an OBD2 scanner by locating the OBD2 port, connecting the scanner, turning on the ignition, reading and interpreting the diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), and clearing the codes after addressing the issues. This process helps you diagnose and resolve vehicle problems. According to a report by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), proper use of OBD2 scanners can significantly reduce diagnostic time and improve repair accuracy.
2.1 How Do You Locate the OBD2 Port in Your E38?
Locating the OBD2 port in your E38 can be done by checking the common locations: under the dashboard on the driver’s side, near the center console, or behind a removable panel. Its exact location may vary based on the car’s specific configuration. BMW’s official service manuals indicate that the OBD2 port is typically placed in an accessible location, but variations can occur.
Begin by inspecting the area under the dashboard on the driver’s side. Use a flashlight to get a better view of the space. If you don’t find the port there, check near the center console. Some E38 models have the OBD2 port located in this area, often hidden by a small cover or panel. If you still cannot find it, look for a removable panel. The OBD2 port might be behind a panel that needs to be detached to access the port. Use a small screwdriver or plastic trim removal tool to carefully pry open the panel without damaging it.
Once you locate the OBD2 port, ensure it is clean and free from any obstructions. Connect your OBD2 scanner to the port and proceed with the diagnostic steps. If you encounter any difficulties, consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual or a trusted mechanic for assistance. Knowing the exact location of the OBD2 port will streamline the diagnostic process and save you time.
2.2 What is the Correct Procedure for Connecting the OBD2 Scanner?
The correct procedure for connecting the OBD2 scanner involves turning off the ignition, plugging the scanner into the OBD2 port, turning the ignition to the “on” position (without starting the engine), and waiting for the scanner to power up and establish a connection with the vehicle’s computer. Following this procedure ensures a stable and accurate connection. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), OBD2 scanners are designed for easy connection and use, but proper technique is essential for reliable results.
![Connecting OBD2 scanner alt=Connecting an OBD2 Scanner to a BMW E38: Step-by-Step Guide]
Start by turning off the ignition to prevent any electrical interference during the connection process. Locate the OBD2 port, which is typically found under the dashboard on the driver’s side. Ensure the port is clean and free from obstructions. Plug the OBD2 scanner firmly into the port. You should feel a click or see a light indicating that the scanner is receiving power.
Turn the ignition to the “on” position without starting the engine. This provides power to the vehicle’s computer and allows the scanner to establish a connection. Wait for the scanner to power up and display the vehicle’s information. This may take a few seconds. If the scanner does not power up, check the connection to ensure it is secure. Consult your scanner’s manual for troubleshooting steps.
Once the scanner is connected and powered up, you can begin reading diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and monitoring live data. Follow the scanner’s instructions to navigate the menus and access the information you need. By following this procedure, you can ensure a stable and accurate connection, allowing you to effectively diagnose and resolve vehicle problems.
2.3 How Can You Read and Interpret Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)?
Reading and interpreting diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) involves using an OBD2 scanner to retrieve the codes, noting down the specific codes, consulting a reliable DTC database or repair manual to understand the meaning of each code, and prioritizing the codes based on their severity and potential impact on the vehicle’s performance. This systematic approach helps you diagnose and address vehicle issues effectively. According to a study by AAA, understanding DTCs is crucial for accurate vehicle diagnostics and repairs.
Begin by using your OBD2 scanner to retrieve the DTCs stored in the vehicle’s computer. Connect the scanner to the OBD2 port, turn on the ignition (without starting the engine), and follow the scanner’s instructions to access the DTC menu. Note down each code displayed by the scanner. It’s essential to record the codes accurately to ensure you consult the correct information.
Consult a reliable DTC database or repair manual to understand the meaning of each code. Several online resources and automotive repair manuals provide detailed information about DTCs, including their possible causes and recommended solutions. Prioritize the codes based on their severity and potential impact on the vehicle’s performance. Some codes may indicate minor issues, while others may point to serious problems that require immediate attention.
Once you understand the meaning and severity of the DTCs, you can begin troubleshooting the issues. Start with the most critical codes and work your way down the list. Use diagnostic tools and techniques to identify the root cause of each problem and implement the necessary repairs. By following this systematic approach, you can effectively read and interpret DTCs, diagnose vehicle issues, and restore your vehicle to optimal performance.
3. Addressing Common OBD2 Issues in the E38 1999
What are the common OBD2 issues you might encounter in your E38 1999 BMW? Common OBD2 issues in the E38 1999 BMW include trouble connecting to the OBD2 port, inaccurate or missing diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), and difficulty resetting the check engine light. Understanding these issues can help you troubleshoot and resolve them efficiently. According to data from vehicle diagnostic forums, these problems are frequently reported by E38 owners.
3.1 What Should You Do If the OBD2 Scanner Fails to Connect?
If the OBD2 scanner fails to connect, verify the scanner’s compatibility with the E38 1999 BMW, check the OBD2 port for damage or obstructions, ensure the vehicle’s ignition is in the “on” position, and test the scanner on another vehicle to rule out scanner malfunction. These steps help identify and resolve connection issues. According to Bosch Automotive Handbook, a faulty connection is a common cause of OBD2 scanner failure.
![OBD2 Scanner Connection Failure alt=Troubleshooting OBD2 Scanner Connection Failure in a BMW E38]
First, verify that the OBD2 scanner is compatible with the E38 1999 BMW. Some scanners may not support older vehicle models or specific communication protocols. Check the scanner’s manual or the manufacturer’s website for compatibility information. Inspect the OBD2 port for any damage or obstructions. Look for bent pins, corrosion, or debris that may prevent the scanner from making a proper connection. Clean the port with aContact cleaner if necessary.
Ensure that the vehicle’s ignition is in the “on” position (without starting the engine). The OBD2 system requires power from the vehicle’s battery to function. If the ignition is off, the scanner will not be able to communicate with the vehicle’s computer. Test the scanner on another vehicle to rule out scanner malfunction. If the scanner connects to another vehicle without any issues, the problem is likely with the E38’s OBD2 system.
If the scanner still fails to connect after following these steps, there may be an underlying issue with the vehicle’s wiring or computer system. Consult a trusted mechanic or BMW specialist for further diagnosis and repair. Addressing connection issues promptly will ensure you can effectively diagnose and resolve vehicle problems.
3.2 How Can You Troubleshoot Inaccurate or Missing DTCs?
Troubleshooting inaccurate or missing DTCs involves verifying the OBD2 scanner’s software is up-to-date, checking for proper grounding of the vehicle’s electrical system, inspecting the wiring and connectors related to the OBD2 port and the vehicle’s computer, and using a higher-quality scanner known for its accuracy. These steps ensure reliable diagnostic information. According to a technical report by Delphi Automotive, outdated software or poor electrical connections can lead to inaccurate DTC readings.
Begin by verifying that the OBD2 scanner’s software is up-to-date. Outdated software may not accurately interpret the data from the vehicle’s computer, leading to inaccurate or missing DTCs. Check the scanner manufacturer’s website for the latest software updates and install them according to the instructions. Check for proper grounding of the vehicle’s electrical system. A poor ground connection can cause electrical interference and affect the accuracy of DTC readings. Inspect the ground wires and connections, and clean or tighten them as necessary.
Inspect the wiring and connectors related to the OBD2 port and the vehicle’s computer. Look for damaged, corroded, or loose wires that may be disrupting the communication between the scanner and the vehicle’s computer. Repair or replace any faulty wiring or connectors. Consider using a higher-quality scanner known for its accuracy. Some scanners are more reliable than others and may provide more accurate DTC readings. Research and choose a scanner that is recommended by automotive professionals.
If you continue to experience inaccurate or missing DTCs after following these steps, there may be an underlying issue with the vehicle’s computer system or sensors. Consult a trusted mechanic or BMW specialist for further diagnosis and repair. Accurate diagnostic information is essential for effective vehicle repairs, so addressing these issues promptly is crucial.
3.3 What Steps Can You Take If the Check Engine Light Won’t Reset?
If the check engine light won’t reset, ensure all underlying issues indicated by the DTCs have been resolved, perform a thorough diagnostic check to confirm no new codes have appeared, disconnect the vehicle’s battery for 15-20 minutes to reset the ECU, and use the OBD2 scanner to clear the codes again. These steps ensure the check engine light is reset properly. According to a publication by the National Automotive Service Task Force (NASTF), addressing the root cause of the problem is essential for preventing the check engine light from returning.
First, ensure that all underlying issues indicated by the DTCs have been resolved. The check engine light will often remain on until the problems that triggered the codes are fixed. Review the DTCs and perform the necessary repairs or replacements. Perform a thorough diagnostic check to confirm that no new codes have appeared. After addressing the initial issues, new problems may arise that could be preventing the check engine light from resetting.
Disconnect the vehicle’s battery for 15-20 minutes to reset the ECU. This can clear any stored data and force the ECU to relearn the vehicle’s parameters. Disconnect the negative terminal of the battery and wait for the specified time before reconnecting it. Use the OBD2 scanner to clear the codes again. After resolving the underlying issues and resetting the ECU, use the scanner to clear the DTCs and turn off the check engine light.
If the check engine light still won’t reset after following these steps, there may be a persistent issue with the vehicle’s computer system or sensors. Consult a trusted mechanic or BMW specialist for further diagnosis and repair. Addressing the problem effectively will ensure that the check engine light resets and remains off, provided the underlying issues have been resolved.
4. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques for the E38 1999 OBD2 System
What advanced diagnostic techniques can you use for the E38 1999 Obd2 system? You can use advanced diagnostic techniques such as live data monitoring, component testing, and freeze frame data analysis to diagnose complex issues with the E38 1999 OBD2 system, providing deeper insights into the vehicle’s performance. These techniques help identify elusive problems that standard code reading might miss. According to a study by the American Society for Quality (ASQ), advanced diagnostic methods improve the accuracy and efficiency of automotive repairs.
4.1 How Can Live Data Monitoring Help Diagnose Issues?
Live data monitoring helps diagnose issues by providing real-time information on various engine parameters, allowing you to observe how sensors and components are functioning under different conditions, identify anomalies or out-of-range values, and pinpoint the source of the problem. This technique is invaluable for diagnosing intermittent issues and performance problems. According to a report by the Automotive Research Association of India (ARAI), live data monitoring is essential for modern vehicle diagnostics.
![Live data monitoring alt=Live Data Monitoring: Diagnosing Engine Issues in a BMW E38]
Connect your OBD2 scanner to the vehicle and access the live data monitoring menu. Select the parameters you want to monitor, such as engine speed (RPM), coolant temperature, fuel trim, oxygen sensor readings, and throttle position. Start the engine and observe the live data as the engine runs. Pay attention to any unusual or out-of-range values.
Compare the live data values to the vehicle’s specifications or known good values. Use a repair manual or online resources to find the correct ranges for each parameter. Look for any correlations between different parameters. For example, if the oxygen sensor readings are fluctuating rapidly, it could indicate a problem with the fuel system or the catalytic converter. Use the live data to diagnose intermittent issues. Record the data while driving the vehicle under different conditions to capture any problems that only occur at certain times.
By using live data monitoring, you can gain a deeper understanding of how your vehicle’s systems are functioning and identify the root cause of many performance problems. This technique is especially useful for diagnosing issues that do not trigger diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
4.2 When Should You Use Component Testing, and How Is It Performed?
Component testing should be used when live data monitoring indicates a specific component is not functioning correctly, or when a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) points to a particular component failure. It involves using specialized tools to test the component’s functionality and verify whether it meets the manufacturer’s specifications. According to the Motor Information Systems, component testing is crucial for accurate diagnosis and avoiding unnecessary parts replacement.
Identify the component you want to test. Use live data monitoring or DTCs to narrow down the potential causes of the problem. Consult the vehicle’s repair manual for the component’s testing procedure and specifications. The manual will provide instructions on how to access the component and what values to expect during the test. Use a multimeter or other specialized testing tool to measure the component’s voltage, resistance, or continuity. Follow the repair manual’s instructions carefully to ensure accurate results.
Compare the measured values to the component’s specifications. If the values are outside the specified range, the component is likely faulty and needs to be replaced. Perform additional tests as needed. Some components may require dynamic testing, which involves measuring their performance while they are operating. For example, you can test an oxygen sensor by monitoring its voltage output while the engine is running.
By using component testing, you can accurately diagnose component failures and avoid replacing parts unnecessarily. This technique is especially useful for diagnosing complex electrical and electronic issues.
4.3 What is Freeze Frame Data, and How Can It Help?
Freeze frame data is a snapshot of the vehicle’s operating conditions at the moment a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) is triggered. It includes parameters such as engine speed, coolant temperature, fuel trim, and vehicle speed. Analyzing freeze frame data can help you understand the conditions that led to the DTC and pinpoint the source of the problem. According to the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), freeze frame data is a valuable tool for diagnosing intermittent issues and performance problems.
Retrieve the freeze frame data using your OBD2 scanner. After reading the DTCs, access the freeze frame data menu to view the recorded parameters. Analyze the data to identify any unusual or out-of-range values. Compare the values to the vehicle’s specifications or known good values. Look for any correlations between the parameters. For example, if the engine speed was high and the fuel trim was lean when the DTC was triggered, it could indicate a problem with the fuel system under high-load conditions.
Use the freeze frame data to recreate the conditions that led to the DTC. This can help you pinpoint the source of the problem and verify the effectiveness of your repairs. For example, if the DTC was triggered during acceleration, try to recreate the same acceleration conditions to see if the problem recurs. By analyzing freeze frame data, you can gain valuable insights into the conditions that led to a DTC and diagnose intermittent issues more effectively. This technique is especially useful for problems that are difficult to reproduce or diagnose using other methods.
5. Maintaining Your E38 1999 OBD2 System for Optimal Performance
How do you maintain your E38 1999 OBD2 system for optimal performance? Maintaining your E38 1999 OBD2 system involves regularly checking for diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), keeping the OBD2 port clean and free from obstructions, and ensuring the vehicle’s electrical system is in good condition. These practices help ensure accurate and reliable diagnostic information. According to the Automotive Maintenance and Repair Association (AMRA), proactive maintenance of the OBD2 system can prevent costly repairs and improve vehicle longevity.
5.1 How Often Should You Check for Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)?
You should check for diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) at least once a month, or whenever you notice any unusual symptoms or performance issues with your vehicle. Regular checks can help identify potential problems early, before they escalate into more serious issues. According to a survey by Consumer Reports, regular DTC checks can improve fuel efficiency and reduce the risk of breakdowns.
![Check diagnostic trouble codes alt=Regularly Checking Diagnostic Trouble Codes for Optimal Vehicle Performance]
Set a reminder to check for DTCs at least once a month. Use an OBD2 scanner to connect to the vehicle and read any stored codes. Pay attention to any new or recurring codes. Even if the check engine light is not illuminated, there may be pending codes that indicate potential problems. Investigate any DTCs promptly. Consult a repair manual or online resources to understand the meaning of the codes and take the necessary steps to address the underlying issues.
Keep a record of any DTCs and the corresponding repairs. This can help you track recurring problems and identify patterns that may indicate more serious issues. By checking for DTCs regularly, you can proactively maintain your vehicle and ensure optimal performance. This practice can also help you identify potential problems before they cause damage or lead to costly repairs.
5.2 What is the Best Way to Keep the OBD2 Port Clean?
The best way to keep the OBD2 port clean is to use a can of compressed air to blow out any dust or debris, and if necessary, gently clean the pins with aContact cleaner on a cotton swab. Keeping the port clean ensures a reliable connection with the OBD2 scanner. According to a technical bulletin by the Equipment and Tool Institute (ETI), a clean OBD2 port is essential for accurate diagnostic readings.
![Clean OBD2 port alt=Cleaning the OBD2 Port: Ensuring a Reliable Connection]
Turn off the vehicle’s ignition before cleaning the OBD2 port. This will prevent any electrical interference during the cleaning process. Use a can of compressed air to blow out any dust or debris from the port. Aim the nozzle of the compressed air can at the port and use short bursts to dislodge any particles. Inspect the pins inside the port for any corrosion or buildup. If necessary, gently clean the pins with aContact cleaner on a cotton swab.
Apply a small amount ofContact cleaner to the cotton swab and carefully wipe the pins. Avoid using excessiveContact cleaner, as it could damage the port. Allow theContact cleaner to dry completely before connecting the OBD2 scanner. Ensure the port is free from any obstructions before connecting the scanner. Check for bent pins or other damage that may prevent a proper connection.
By keeping the OBD2 port clean, you can ensure a reliable connection with the scanner and obtain accurate diagnostic readings. This practice is especially important in environments where the vehicle is exposed to dust, dirt, or moisture.
5.3 How Does the Vehicle’s Electrical System Affect OBD2 Performance?
The vehicle’s electrical system significantly affects OBD2 performance because the OBD2 system relies on a stable and properly functioning electrical system to communicate with the vehicle’s computer and sensors. Issues such as a weak battery, poor ground connections, or damaged wiring can interfere with the OBD2 system’s ability to function correctly. According to a study by the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA), a well-maintained electrical system is essential for optimal vehicle performance and diagnostics.
![Vehicle Electrical System Affect on OBD2 Performance alt=The Impact of Vehicle’s Electrical System on OBD2 Performance]
Ensure the vehicle’s battery is in good condition. A weak battery can cause voltage fluctuations that interfere with the OBD2 system’s communication. Test the battery regularly and replace it if necessary. Check for proper ground connections. Poor ground connections can cause electrical interference and affect the accuracy of diagnostic readings. Inspect the ground wires and connections, and clean or tighten them as needed.
Inspect the wiring and connectors related to the OBD2 port and the vehicle’s computer. Look for damaged, corroded, or loose wires that may be disrupting the communication between the scanner and the vehicle’s computer. Repair or replace any faulty wiring or connectors. Ensure all fuses are in good condition. Blown fuses can disrupt the power supply to the OBD2 system and prevent it from functioning correctly.
By maintaining the vehicle’s electrical system, you can ensure that the OBD2 system functions correctly and provides accurate diagnostic information. This practice is essential for effective vehicle repairs and preventing potential problems.
6. Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner for Your E38 1999 BMW
How do you choose the right OBD2 scanner for your E38 1999 BMW? Selecting the right OBD2 scanner for your E38 1999 BMW involves considering compatibility, features, and user-friendliness to ensure effective diagnostics. A suitable scanner can streamline troubleshooting and provide accurate insights into your vehicle’s health. According to a review by Consumer Reports, the right OBD2 scanner can save time and money on vehicle maintenance.
6.1 What Compatibility Factors Should You Consider?
Compatibility factors to consider include ensuring the scanner supports the OBD2 protocols used by the E38 1999 BMW (ISO 9141-2, KWP2000), verifying compatibility with BMW-specific diagnostic functions, and checking for software updates to ensure the scanner can accurately read and interpret data from your vehicle. These considerations ensure the scanner works seamlessly with your E38. According to BMW’s official technical documentation, using a compatible scanner is crucial for accurate diagnostics.
![Compatibility Factors for OBD2 Scanner alt=Compatibility Factors for Choosing an OBD2 Scanner for a BMW E38]
Verify that the scanner supports the OBD2 protocols used by the E38 1999 BMW. The E38 may use ISO 9141-2 or KWP2000 protocols. Check the scanner’s specifications or the manufacturer’s website to confirm compatibility. Ensure that the scanner is compatible with BMW-specific diagnostic functions. Some scanners offer enhanced diagnostic capabilities for BMW vehicles, such as the ability to read and clear BMW-specific diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and access advanced diagnostic functions.
Check for software updates to ensure the scanner can accurately read and interpret data from your vehicle. Software updates often include new DTC definitions and improved diagnostic algorithms. Research the scanner’s compatibility with different operating systems if you plan to connect it to a computer or mobile device. Some scanners are only compatible with certain operating systems.
By considering these compatibility factors, you can choose an OBD2 scanner that works seamlessly with your E38 1999 BMW and provides accurate and reliable diagnostic information. This will help you troubleshoot vehicle problems effectively and maintain optimal performance.
6.2 What Key Features Should You Look For in an OBD2 Scanner?
Key features to look for in an OBD2 scanner include the ability to read and clear diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), live data streaming, freeze frame data, O2 sensor testing, and the ability to perform bidirectional control tests. These features provide a comprehensive diagnostic capability. According to a survey by the National Automotive Service Task Force (NASTF), these features are essential for effective vehicle diagnostics.
![Key Features of OBD2 Scanner alt=Key Features to Look for in an OBD2 Scanner for Your BMW E38]
Ensure the scanner can read and clear diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). This is the most basic function of an OBD2 scanner and is essential for diagnosing vehicle problems. Look for a scanner that supports live data streaming. This feature allows you to monitor real-time data from various sensors and components, providing valuable insights into the vehicle’s performance.
Check if the scanner supports freeze frame data. This feature captures a snapshot of the vehicle’s operating conditions at the moment a DTC is triggered, helping you understand the conditions that led to the problem. Verify that the scanner can perform O2 sensor testing. This feature allows you to test the functionality of the oxygen sensors, which are crucial for fuel efficiency and emission control.
Consider a scanner that can perform bidirectional control tests. This advanced feature allows you to control certain vehicle components, such as the fuel injectors or the cooling fan, to test their functionality. By looking for these key features, you can choose an OBD2 scanner that provides comprehensive diagnostic capabilities and helps you effectively troubleshoot vehicle problems.
6.3 How Important is User-Friendliness in an OBD2 Scanner?
User-friendliness is very important in an OBD2 scanner because a scanner with an intuitive interface, clear display, and easy navigation can save time and reduce frustration during the diagnostic process. A user-friendly scanner allows you to quickly access the information you need and perform diagnostic tests efficiently. According to a study by the Human Factors and Ergonomics Society (HFES), user-friendly tools improve productivity and reduce errors.
Look for a scanner with an intuitive interface. The scanner should have a clear and well-organized menu system that is easy to navigate. Check for a clear display. The scanner’s display should be easy to read, even in bright sunlight or low-light conditions. Consider a scanner with easy navigation. The scanner should have buttons or a touchscreen that are easy to use and respond quickly to your input.
Read reviews from other users to get an idea of the scanner’s user-friendliness. Pay attention to comments about the scanner’s interface, display, and navigation. Try out the scanner before you buy it, if possible. This will allow you to get a feel for the scanner’s user-friendliness and determine if it meets your needs. By prioritizing user-friendliness, you can choose an OBD2 scanner that is easy to use and helps you effectively troubleshoot vehicle problems.
7. Resources for E38 1999 OBD2 Diagnostics and Repair
What resources are available for E38 1999 OBD2 diagnostics and repair? Available resources for E38 1999 OBD2 diagnostics and repair include online forums, repair manuals, diagnostic software, and professional mechanics. These resources offer valuable support and guidance for troubleshooting and resolving vehicle issues. According to a survey by the Automotive Aftermarket Industry Association (AAIA), access to reliable resources is crucial for effective vehicle maintenance and repair.
7.1 What Online Forums and Communities Can Help?
Helpful online forums and communities include BMW-specific forums such as BimmerForums, E38-specific forums, and general automotive diagnostic forums. These platforms offer a wealth of information, troubleshooting tips, and peer support from experienced owners and mechanics. According to a study by the Online Community Research Network (OCRN), online forums provide valuable support and knowledge sharing for vehicle owners.
![Online forum alt=Online Forums and Communities for BMW E38 Diagnostics and Repair]
Join BMW-specific forums such as BimmerForums. These forums have dedicated sections for different BMW models and offer a wealth of information on diagnostics, repairs, and modifications. Look for E38-specific forums. These forums are dedicated to the E38 model and provide a wealth of information on common problems, troubleshooting tips, and repair procedures. Participate in general automotive diagnostic forums. These forums cover a wide range of vehicles and diagnostic topics and can provide valuable insights into OBD2 diagnostics and repair.
Search the forums for information on your specific problem. Use keywords such as “E38 OBD2,” “diagnostic trouble codes,” or “check engine light” to find relevant threads and discussions. Ask questions and share your experiences. Don’t be afraid to ask for help or share your knowledge with other members. Remember to be respectful and follow the forum’s rules and guidelines.
By participating in online forums and communities, you can access a wealth of information and support from experienced owners and mechanics. This can help you troubleshoot vehicle problems effectively and save time and money on repairs.
7.2 Where Can You Find Reliable Repair Manuals and Technical Documentation?
You can find reliable repair manuals and technical documentation from publishers like Bentley Publishers, online databases such as AllData and Mitchell OnDemand, and official BMW service manuals. These resources provide detailed repair procedures, wiring diagrams, and diagnostic information. According to a report by the Equipment and Tool Institute (ETI), access to accurate technical documentation is essential for effective vehicle repairs.
![Reliable repair manual alt=Reliable Repair Manuals and Technical Documentation for BMW E38]
Consider purchasing a repair manual from Bentley Publishers. Bentley Publishers offers high-quality repair manuals that are specifically tailored to BMW vehicles. Subscribe to an online database such as AllData or Mitchell OnDemand. These databases provide access to a vast library of repair manuals, wiring diagrams, and technical service bulletins.
Obtain official BMW service manuals. These manuals are the most comprehensive source of information for BMW vehicles and are used by BMW technicians. Check online retailers for PDF versions of the BMW service manuals. These digital manuals can be easily searched and accessed on your computer or mobile device.
By accessing reliable repair manuals and technical documentation, you can ensure that you have the information you need to perform accurate and effective vehicle repairs. These resources provide detailed instructions, diagrams, and specifications that can help you troubleshoot and resolve even the most complex problems.
7.3 What Diagnostic Software is Recommended for the E38 1999?
Recommended diagnostic software for the E38 1999 includes INPA, DIS (Diagnostic Information System), and BMW