Ford Police Interceptor Obd Obd2 Codes can seem complex, but OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN simplifies the process of diagnosing and resolving issues in your vehicle, ensuring optimal performance and emission readiness. We provide expert guidance and resources for interpreting these codes, helping you to effectively troubleshoot your Ford Police Interceptor. With our support, you’ll confidently navigate the complexities of vehicle diagnostics, keeping your ride smooth and efficient. Explore solutions for check engine light, diagnostic trouble codes, and automotive repair needs.
Contents
- 1. Understanding OBD2 and Your Ford Police Interceptor
- 2. Decoding Ford Police Interceptor OBD2 Codes
- 2.1. Using an OBD2 Scanner
- 2.2. Understanding DTC Structure
- 2.3. Common Ford Police Interceptor OBD2 Codes
- 2.4. Diagnostic Approach
- 3. Common OBD2 Trouble Codes in Ford Police Interceptors
- 3.1. O2 Sensor Codes
- 3.2. Catalytic Converter Codes
- 3.3. Misfire Codes
- 3.4. EVAP System Codes
- 3.5. Other Common Codes
- 4. Diagnosing O2 Sensor Readiness Issues
- 4.1. Verifying Sensor Functionality
- 4.2. Checking for Exhaust Leaks
- 4.3. Ensuring Proper Engine Operating Temperature
- 4.4. Performing a Ford-Specific Drive Cycle
- 4.5. Addressing Underlying Issues
- 5. Step-by-Step Guide to Clearing OBD2 Codes
- 5.1. Connecting the OBD2 Scanner
- 5.2. Reading the Stored Codes
- 5.3. Addressing the Underlying Issues
- 5.4. Clearing the Codes with the Scanner
- 5.5. Verifying the Repair
- 5.6. Addressing Recurring Codes
- 6. Ford Police Interceptor Specific Drive Cycles
- 6.1. Understanding Drive Cycles
- 6.2. Importance of Ford-Specific Drive Cycles
- 6.3. Common Ford Drive Cycle Steps
- 6.4. Tips for Performing Drive Cycles
- 6.5. Resources for Ford Drive Cycles
- 7. The Role of a Professional Mechanic
- 7.1. Expertise and Experience
- 7.2. Specialized Tools and Equipment
- 7.3. Complex Diagnostic Procedures
- 7.4. Time Constraints
- 7.5. When to Seek Professional Help
- 8. Maintaining Your Ford Police Interceptor’s OBD2 System
- 8.1. Regular Inspections
- 8.2. Promptly Addressing Issues
- 8.3. Using Quality Parts
- 8.4. Keeping Software Updated
- 8.5. Regular Maintenance
- 8.6. Benefits of Proactive Maintenance
- 9. Ford Police Interceptor OBD2 Resources
- 9.1. Online OBD2 Code Databases
- 9.2. Ford Service Manuals
- 9.3. OBD2 Scanner Guides
- 9.4. Online Forums and Communities
- 9.5. Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs)
- 10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 10.1. What is an OBD2 Scanner?
- 10.2. How Do I Read OBD2 Codes?
- 10.3. What Are Common Automotive Errors and How Can They Be Fixed?
- 10.4. Can I Clear OBD2 Codes Myself?
- 10.5. What Does the Check Engine Light Mean?
- 10.6. How Often Should I Scan My Car for OBD2 Codes?
- 10.7. Where Can I Find Reliable OBD2 Information for My Ford Police Interceptor?
- 10.8. What Are Ford-Specific OBD2 Codes?
- 10.9. How Do Drive Cycles Help in OBD2 Diagnostics?
- 10.10. Why Is My Ford Police Interceptor Failing Emissions Tests Despite No Active Codes?
1. Understanding OBD2 and Your Ford Police Interceptor
Do you know what OBD2 is and why it’s important for your Ford Police Interceptor? Yes, OBD2, or On-Board Diagnostics II, is crucial for monitoring your Ford Police Interceptor’s performance and diagnosing potential issues. This system acts as the vehicle’s health monitor, tracking various parameters and alerting you to any malfunctions.
OBD2, standardized in the mid-1990s, is a universal system across all cars and light trucks sold in the United States, as mandated by the Clean Air Act Amendments of 1990. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), this standardization ensures that vehicles meet strict emissions standards. This system includes a standardized connector, a set of diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), and a communication protocol, enabling technicians and vehicle owners to diagnose issues efficiently.
The OBD2 system monitors components such as the engine, transmission, O2 sensors, and catalytic converters. When a problem is detected, the system generates a DTC and illuminates the check engine light. These codes can be read using an OBD2 scanner, providing valuable insights into the nature and location of the problem.
For Ford Police Interceptors, understanding OBD2 is particularly important due to their demanding usage. Regular monitoring using an OBD2 scanner can help identify issues early, preventing costly repairs and ensuring the vehicle operates efficiently. Additionally, proper diagnosis using OBD2 codes can aid in maintaining compliance with emission standards, which is essential for passing inspections.
2. Decoding Ford Police Interceptor OBD2 Codes
Want to know how to decode Ford Police Interceptor OBD2 codes effectively? To decode Ford Police Interceptor OBD2 codes, utilize an OBD2 scanner to retrieve the Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs), consult a reliable code database, and follow a systematic diagnostic approach to pinpoint the underlying issue.
2.1. Using an OBD2 Scanner
The first step in decoding OBD2 codes is to use an OBD2 scanner. These scanners plug into the OBD2 port, typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side. Once connected, the scanner reads the DTCs stored in the vehicle’s computer. There are numerous OBD2 scanners available, ranging from basic models that only read and clear codes to advanced units that offer live data streaming and bidirectional control.
2.2. Understanding DTC Structure
DTCs are structured in a specific format. According to the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), a DTC consists of five characters:
-
First Character: Indicates the system related to the code:
- P: Powertrain (engine, transmission)
- B: Body (airbags, power windows)
- C: Chassis (ABS, suspension)
- U: Network (communication systems)
-
Second Character: Specifies whether the code is generic or manufacturer-specific:
- 0: Generic (SAE standard)
- 1: Manufacturer-specific
-
Third Character: Indicates the subsystem:
- 1: Fuel and air metering
- 2: Fuel and air metering (injector circuit)
- 3: Ignition system
- 4: Auxiliary emission controls
- 5: Vehicle speed controls and idle control system
- 6: Computer output system
- 7: Transmission
- 8: Transmission
-
Fourth and Fifth Characters: Provide specific information about the fault.
For example, a code like P0300 indicates a generic powertrain code (P0) related to a random or multiple cylinder misfire (300).
2.3. Common Ford Police Interceptor OBD2 Codes
Several OBD2 codes are commonly encountered in Ford Police Interceptors due to their specific usage patterns. Some of the most frequent codes include:
-
P0171/P0174: System Too Lean (Bank 1/Bank 2)
These codes indicate that the engine is running with too little fuel or too much air. This can be caused by vacuum leaks, faulty MAF sensors, or fuel delivery issues.
-
P0300-P030X: Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected
Misfires can result from faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, fuel injectors, or compression issues.
-
P0420/P0430: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1/Bank 2)
These codes suggest that the catalytic converter is not functioning efficiently, potentially due to age, damage, or upstream engine issues.
-
P0401: Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Flow Insufficient Detected
This code indicates a problem with the EGR system, which can be caused by a clogged EGR valve or faulty sensors.
-
P0455: Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (Gross Leak)
This code points to a large leak in the evaporative emission control system, often due to a loose or damaged fuel cap, or issues with the EVAP system components.
2.4. Diagnostic Approach
Once you have the DTC, a systematic diagnostic approach is crucial. Start by verifying the code using a reliable database like those provided by OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN or the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE). Then, perform a visual inspection of the related components, checking for obvious damage or leaks.
Next, use the OBD2 scanner to monitor live data, such as sensor readings, fuel trims, and O2 sensor voltages. Compare these readings to the expected values to identify any discrepancies. Perform specific tests recommended for the DTC, such as testing the MAF sensor with a multimeter or checking for vacuum leaks with a smoke machine.
Following a logical and step-by-step diagnostic process will help you pinpoint the root cause of the problem and implement the appropriate repair.
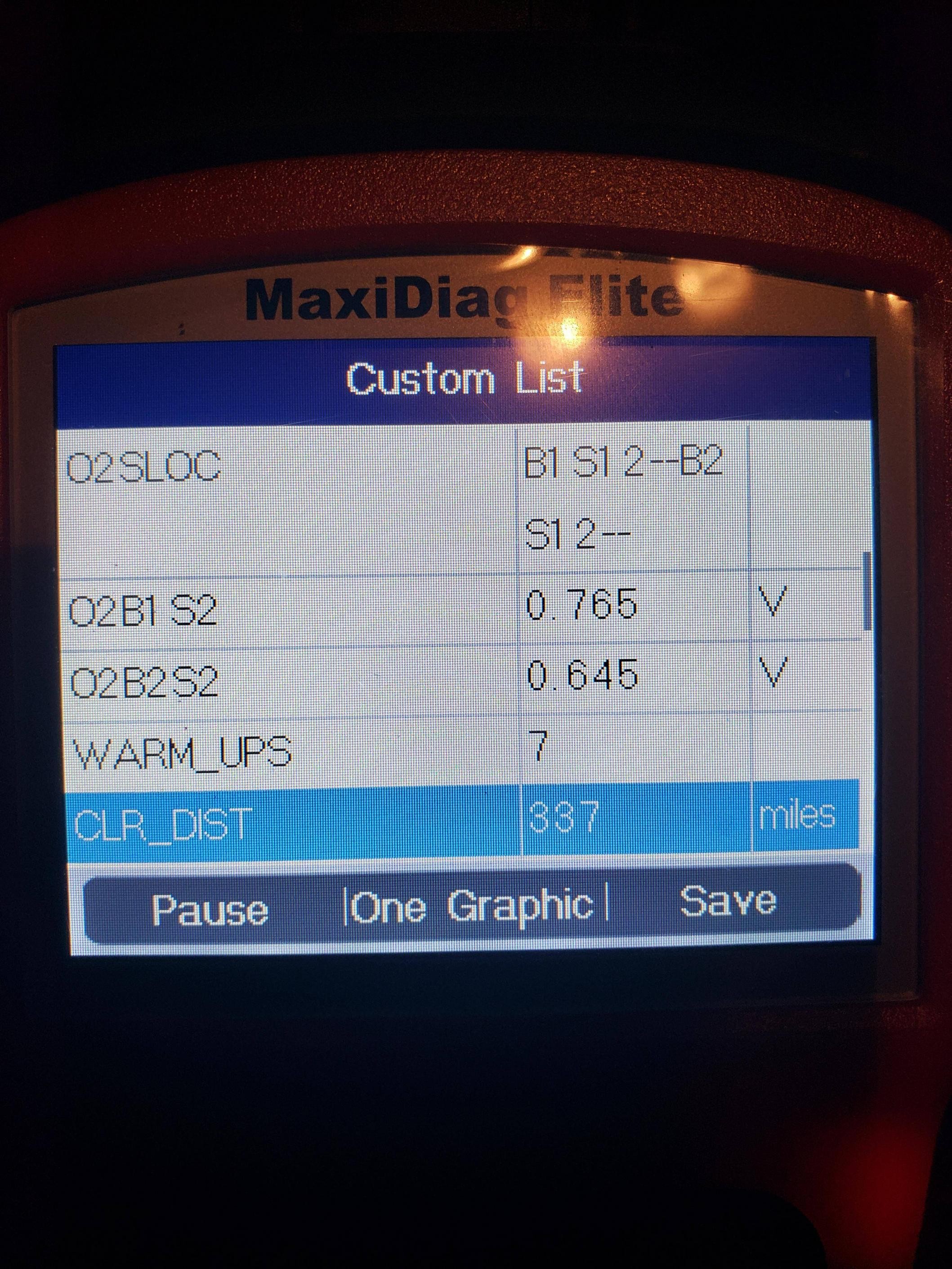 Ford Police Interceptor O2 Sensor Data
Ford Police Interceptor O2 Sensor Data
3. Common OBD2 Trouble Codes in Ford Police Interceptors
What are the common OBD2 trouble codes you might find in your Ford Police Interceptor? Common OBD2 trouble codes in Ford Police Interceptors include those related to O2 sensors, catalytic converters, misfires, and EVAP system leaks, which often arise due to the vehicle’s demanding operational conditions.
3.1. O2 Sensor Codes
O2 sensor codes are frequent in Ford Police Interceptors due to the constant engine operation and varying driving conditions. These codes often include:
-
P0130-P0167: O2 Sensor Circuit Malfunction
These codes indicate issues with the O2 sensor circuit, such as open circuits, short circuits, or sensor failure.
-
P0171/P0174: System Too Lean (Bank 1/Bank 2)
These codes can also be related to faulty O2 sensors providing incorrect readings, leading the engine to run lean.
-
P0135/P0141/P0155/P0161: O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Malfunction
These codes indicate problems with the O2 sensor heater circuit, which is essential for the sensor to reach operating temperature quickly.
According to a study by the EPA, faulty O2 sensors can significantly impact fuel efficiency and emissions. Replacing O2 sensors at recommended intervals (typically every 60,000 to 100,000 miles) can help maintain optimal engine performance.
3.2. Catalytic Converter Codes
Catalytic converter codes are also common, particularly in older vehicles. The primary codes include:
-
P0420/P0430: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1/Bank 2)
These codes suggest that the catalytic converter is not efficiently reducing emissions. This can be caused by a degraded converter, exhaust leaks, or upstream engine issues.
Catalytic converters play a crucial role in reducing harmful emissions. A malfunctioning catalytic converter can lead to increased pollution and potential failure to pass emissions inspections. Regular inspections and addressing upstream engine issues can help prolong the life of the catalytic converter.
3.3. Misfire Codes
Misfire codes can occur due to various reasons, impacting engine performance and potentially causing damage. Common misfire codes include:
- P0300: Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected
- P0301-P030X: Cylinder X Misfire Detected (where X is the cylinder number)
Misfires can be caused by faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, fuel injectors, vacuum leaks, or compression issues. Diagnosing misfires involves checking each of these components to identify the root cause. A study by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) found that misfires can lead to increased emissions and potential engine damage if not addressed promptly.
3.4. EVAP System Codes
EVAP (Evaporative Emission Control System) codes indicate issues with the system that prevents fuel vapors from escaping into the atmosphere. Common EVAP codes include:
- P0440: Evaporative Emission Control System Malfunction
- P0455: Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (Gross Leak)
- P0456: Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (Very Small Leak)
These codes can be caused by a loose or damaged fuel cap, leaks in the EVAP lines, or issues with the EVAP canister or purge valve. A properly functioning EVAP system is crucial for reducing emissions and maintaining air quality.
3.5. Other Common Codes
In addition to the above, other common OBD2 codes in Ford Police Interceptors include:
-
P0101: Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor Circuit Range/Performance
This code indicates a problem with the MAF sensor, which measures the amount of air entering the engine.
-
P0113: Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor Circuit High Input
This code indicates a problem with the IAT sensor, which measures the temperature of the air entering the engine.
-
P0505: Idle Air Control (IAC) System Malfunction
This code indicates a problem with the IAC system, which controls the engine’s idle speed.
Understanding these common OBD2 codes and their potential causes can help you diagnose and repair your Ford Police Interceptor more effectively. Regular maintenance and timely repairs are essential for maintaining optimal performance and compliance with emissions standards.
4. Diagnosing O2 Sensor Readiness Issues
Are you struggling with O2 sensor readiness issues on your Ford Police Interceptor? To diagnose O2 sensor readiness issues on a Ford Police Interceptor, verify sensor functionality with an OBD2 scanner, check for exhaust leaks, ensure proper engine operating temperature, and perform a Ford-specific drive cycle.
4.1. Verifying Sensor Functionality
Start by using an OBD2 scanner to check the live data from the O2 sensors. The scanner should display the sensor voltages, which should fluctuate between approximately 0.1 and 0.9 volts when the engine is running. According to Bosch, a leading manufacturer of O2 sensors, these fluctuations indicate that the sensors are actively monitoring the exhaust gas composition.
If the sensor voltages are flat or unresponsive, it could indicate a faulty sensor. Additionally, check the heater circuit resistance. The heater circuit helps the sensor reach operating temperature quickly, which is essential for accurate readings. Use a multimeter to measure the resistance of the heater circuit, comparing the reading to the manufacturer’s specifications.
4.2. Checking for Exhaust Leaks
Exhaust leaks can introduce extra oxygen into the exhaust stream, affecting the O2 sensor readings and preventing the readiness monitors from setting. Inspect the exhaust system for any signs of leaks, such as rust, cracks, or loose connections. Pay particular attention to the areas around the exhaust manifold, catalytic converter, and O2 sensors.
You can use a smoke machine to identify small exhaust leaks. The smoke will escape from any leaks, making them easier to locate. Addressing exhaust leaks is crucial for ensuring accurate O2 sensor readings and proper readiness monitor operation.
4.3. Ensuring Proper Engine Operating Temperature
The engine must reach and maintain its normal operating temperature for the O2 sensor readiness monitors to run. Check the engine coolant temperature using an OBD2 scanner or the vehicle’s temperature gauge. The engine should reach a temperature of around 195-220°F (90-104°C) for the monitors to function correctly.
If the engine is not reaching the proper temperature, it could indicate a faulty thermostat or cooling system issue. Replacing the thermostat or addressing cooling system problems can help ensure the engine reaches the necessary temperature for the readiness monitors to set.
4.4. Performing a Ford-Specific Drive Cycle
Ford vehicles often require a specific drive cycle to set the O2 sensor readiness monitors. A drive cycle involves a series of driving conditions that allow the vehicle’s computer to run the necessary diagnostic tests. According to Ford Motor Company, a typical Ford drive cycle includes the following steps:
- Cold Start: Ensure the engine is completely cold (has not been run for at least eight hours).
- Idle: Start the engine and allow it to idle for two minutes.
- Acceleration: Accelerate to 45 mph (72 km/h) at a moderate rate.
- Cruise: Maintain a steady speed of 45 mph (72 km/h) for five minutes.
- Deceleration: Decelerate to 20 mph (32 km/h) without using the brakes.
- Acceleration: Accelerate back to 45 mph (72 km/h).
- Cruise: Maintain a steady speed of 45 mph (72 km/h) for five minutes.
- Deceleration: Decelerate and come to a complete stop.
- Idle: Allow the engine to idle for two minutes.
Repeat this drive cycle several times, if necessary. Use an OBD2 scanner to check the readiness monitor status after each drive cycle. The O2 sensor monitors should eventually set to “Ready” or “Complete.”
4.5. Addressing Underlying Issues
If the O2 sensor readiness monitors still do not set after performing the drive cycle and verifying sensor functionality, there may be underlying issues affecting the engine’s performance. These issues could include vacuum leaks, fuel delivery problems, or exhaust leaks.
Perform a thorough inspection of the engine and related systems to identify and address any potential problems. Addressing these underlying issues can help ensure the O2 sensor readiness monitors set correctly and the vehicle passes emissions inspections.
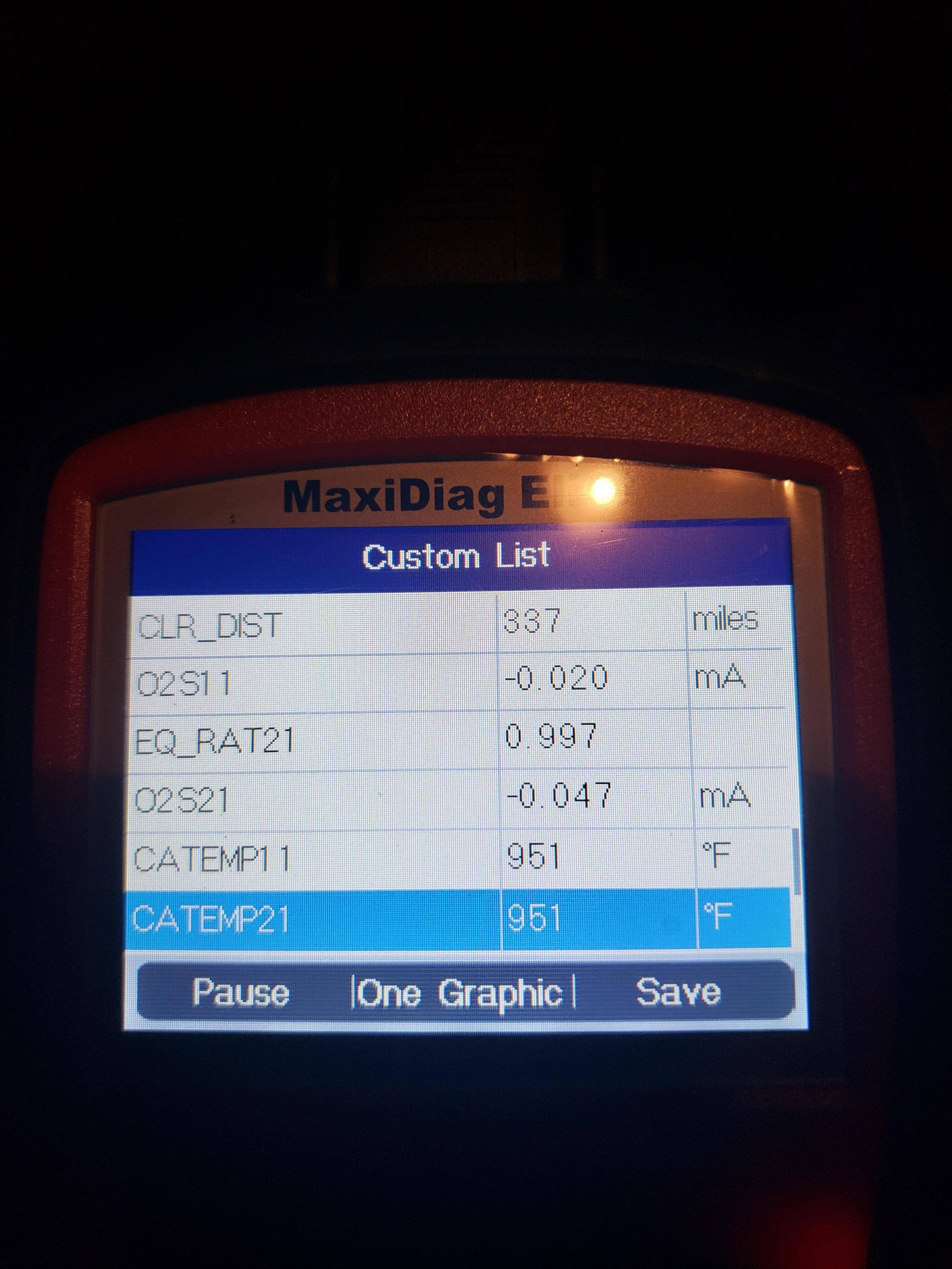 Ford Police Interceptor Sensor Data
Ford Police Interceptor Sensor Data
5. Step-by-Step Guide to Clearing OBD2 Codes
Need a clear, step-by-step guide to clearing OBD2 codes on your Ford Police Interceptor? To clear OBD2 codes on your Ford Police Interceptor, connect an OBD2 scanner, read the stored codes, address the underlying issues, and use the scanner to clear the codes and verify the repair.
5.1. Connecting the OBD2 Scanner
The first step in clearing OBD2 codes is to connect an OBD2 scanner to the vehicle’s OBD2 port. This port is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side. Turn the ignition key to the “on” position without starting the engine to provide power to the scanner.
Ensure the scanner is securely connected and powered on. The scanner will then communicate with the vehicle’s computer to retrieve stored diagnostic information.
5.2. Reading the Stored Codes
Once the scanner is connected and powered on, navigate to the “Read Codes” or “Diagnostic Codes” option in the scanner’s menu. The scanner will display a list of Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) stored in the vehicle’s computer.
Record all the DTCs displayed by the scanner. These codes provide valuable information about the issues that have been detected by the vehicle’s computer. Use a reliable database, such as those provided by OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN or the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), to look up the meaning of each code.
5.3. Addressing the Underlying Issues
Clearing OBD2 codes without addressing the underlying issues is only a temporary solution. The codes will likely reappear if the problems are not resolved. Based on the DTCs retrieved from the scanner, diagnose and repair the underlying issues.
For example, if the scanner displays a code related to a faulty O2 sensor, replace the sensor. If the code indicates a vacuum leak, locate and repair the leak. Addressing the root cause of the problems is crucial for preventing the codes from recurring and ensuring the vehicle operates properly.
5.4. Clearing the Codes with the Scanner
After addressing the underlying issues, you can clear the OBD2 codes using the scanner. Navigate to the “Clear Codes” or “Erase Codes” option in the scanner’s menu. The scanner will prompt you to confirm that you want to clear the codes.
Confirm the action, and the scanner will send a command to the vehicle’s computer to clear the stored DTCs. Once the codes are cleared, the check engine light should turn off.
5.5. Verifying the Repair
After clearing the codes, it’s important to verify that the repair was successful and the codes do not reappear. Start the engine and let it run for a few minutes. Then, use the scanner to read the codes again.
If no new codes appear, the repair was likely successful. However, it’s a good idea to drive the vehicle under various conditions to ensure the issue is fully resolved. Monitor the vehicle’s performance and check the readiness monitors using the scanner. The readiness monitors should set to “Ready” or “Complete,” indicating that the vehicle has passed all the necessary diagnostic tests.
5.6. Addressing Recurring Codes
If the OBD2 codes reappear after clearing them and driving the vehicle, it indicates that the underlying issues were not fully resolved. In this case, further diagnosis and repair are necessary.
Recheck the DTCs and perform a more thorough inspection of the related systems. Consult a qualified mechanic if you are unable to diagnose and repair the issues yourself. Addressing recurring codes promptly is essential for maintaining the vehicle’s performance and preventing potential damage.
6. Ford Police Interceptor Specific Drive Cycles
Why are Ford Police Interceptor specific drive cycles essential for diagnosing OBD2 issues? Ford Police Interceptor specific drive cycles are essential because they allow the vehicle’s onboard diagnostics to run specific tests under controlled conditions, ensuring accurate and reliable diagnosis of OBD2-related issues.
6.1. Understanding Drive Cycles
A drive cycle is a specific set of driving conditions designed to allow the vehicle’s onboard diagnostics to run various tests and verify the functionality of different systems. These tests are crucial for setting the readiness monitors, which indicate whether the vehicle is ready for an emissions inspection.
Drive cycles typically involve a combination of idling, accelerating, cruising, and decelerating under specific conditions. The exact steps required for a drive cycle can vary depending on the vehicle make, model, and year.
6.2. Importance of Ford-Specific Drive Cycles
Ford vehicles, including the Police Interceptor, often require specific drive cycles to set the readiness monitors. Using the correct drive cycle ensures that the vehicle’s computer can run the necessary diagnostic tests and accurately assess the functionality of various systems.
According to Ford Motor Company, using a non-specific or incorrect drive cycle may result in the readiness monitors not setting, leading to failed emissions inspections. Ford-specific drive cycles are tailored to the unique characteristics of Ford vehicles, ensuring that the diagnostic tests are performed under the appropriate conditions.
6.3. Common Ford Drive Cycle Steps
While the exact steps may vary slightly, a common Ford drive cycle typically includes the following:
- Cold Start: Ensure the engine is completely cold (has not been run for at least eight hours).
- Idle: Start the engine and allow it to idle for two minutes.
- Acceleration: Accelerate to 45 mph (72 km/h) at a moderate rate.
- Cruise: Maintain a steady speed of 45 mph (72 km/h) for five minutes.
- Deceleration: Decelerate to 20 mph (32 km/h) without using the brakes.
- Acceleration: Accelerate back to 45 mph (72 km/h).
- Cruise: Maintain a steady speed of 45 mph (72 km/h) for five minutes.
- Deceleration: Decelerate and come to a complete stop.
- Idle: Allow the engine to idle for two minutes.
Repeat this drive cycle several times, if necessary. Use an OBD2 scanner to check the readiness monitor status after each drive cycle.
6.4. Tips for Performing Drive Cycles
To ensure the drive cycle is performed correctly, follow these tips:
- Use a Safe Location: Perform the drive cycle on a road with minimal traffic and distractions.
- Follow Speed Limits: Adhere to all speed limits and traffic laws while performing the drive cycle.
- Monitor the OBD2 Scanner: Use an OBD2 scanner to monitor the readiness monitor status and ensure the tests are running.
- Repeat if Necessary: If the readiness monitors do not set after the first drive cycle, repeat the process several times.
- Consult the Vehicle’s Service Manual: Refer to the vehicle’s service manual for specific instructions and recommendations for performing drive cycles.
6.5. Resources for Ford Drive Cycles
Several resources are available to help you find the correct drive cycle for your Ford Police Interceptor:
- OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN: Provides information and resources for performing drive cycles on various vehicles.
- Ford Motor Company: Offers service manuals and technical information for Ford vehicles.
- National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE): Provides training and certification for automotive technicians, including information on drive cycles.
Using these resources can help you ensure you are performing the correct drive cycle and accurately diagnosing OBD2-related issues on your Ford Police Interceptor.
7. The Role of a Professional Mechanic
When should you consider seeking help from a professional mechanic for OBD2 issues on your Ford Police Interceptor? Consider seeking help from a professional mechanic for OBD2 issues on your Ford Police Interceptor when you lack the expertise, tools, or time to diagnose and repair complex problems effectively.
7.1. Expertise and Experience
Professional mechanics possess the expertise and experience necessary to diagnose and repair complex OBD2 issues. They have extensive training and knowledge of vehicle systems, allowing them to accurately identify the root cause of problems.
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, automotive service technicians and mechanics require formal training and certification to stay current with the latest technologies and repair procedures. Professional mechanics undergo rigorous training programs, such as those offered by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), to develop their skills and knowledge.
7.2. Specialized Tools and Equipment
Diagnosing and repairing OBD2 issues often requires specialized tools and equipment, such as advanced OBD2 scanners, multimeters, smoke machines, and diagnostic software. Professional mechanics have access to these tools and know how to use them effectively.
These specialized tools allow mechanics to perform comprehensive diagnostic tests and accurately pinpoint the source of the problem. For example, an advanced OBD2 scanner can provide live data streaming, bidirectional control, and access to manufacturer-specific diagnostic codes, enabling mechanics to diagnose complex issues more efficiently.
7.3. Complex Diagnostic Procedures
Some OBD2 issues require complex diagnostic procedures that may be beyond the capabilities of the average vehicle owner. These procedures may involve testing various components, analyzing sensor data, and troubleshooting electrical circuits.
Professional mechanics are trained to perform these complex diagnostic procedures and have the knowledge to interpret the results accurately. They can use diagnostic flowcharts, wiring diagrams, and technical service bulletins to guide their diagnostic process and identify the underlying cause of the problem.
7.4. Time Constraints
Diagnosing and repairing OBD2 issues can be time-consuming, especially if you lack the necessary expertise and tools. Professional mechanics can often diagnose and repair problems more quickly due to their experience and access to specialized equipment.
If you have time constraints or prefer to leave the repairs to a professional, seeking help from a mechanic is a wise decision. They can efficiently diagnose and repair the issues, allowing you to get back on the road as soon as possible.
7.5. When to Seek Professional Help
Consider seeking help from a professional mechanic in the following situations:
- You are unsure how to diagnose the OBD2 codes.
- You lack the necessary tools and equipment.
- The problem is complex and requires specialized diagnostic procedures.
- You have time constraints and prefer to leave the repairs to a professional.
- You have attempted to repair the issue yourself but have been unsuccessful.
By seeking help from a professional mechanic, you can ensure that the OBD2 issues on your Ford Police Interceptor are accurately diagnosed and repaired, maintaining the vehicle’s performance and reliability.
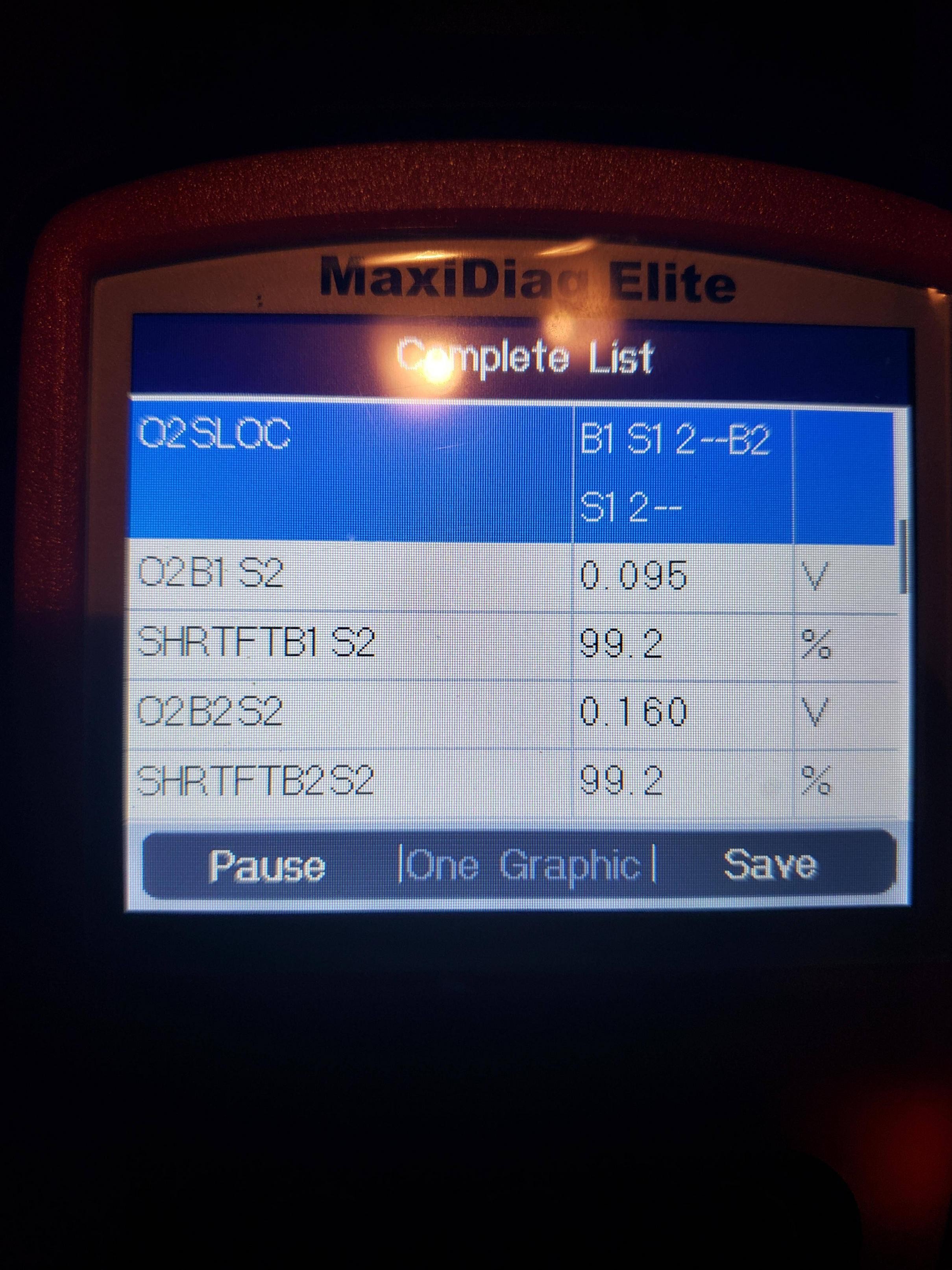 Ford Police Interceptor Sensor Data
Ford Police Interceptor Sensor Data
8. Maintaining Your Ford Police Interceptor’s OBD2 System
How can you proactively maintain your Ford Police Interceptor’s OBD2 system to prevent issues? To proactively maintain your Ford Police Interceptor’s OBD2 system, perform regular inspections, address issues promptly, use quality parts, and keep software updated to prevent potential problems.
8.1. Regular Inspections
Regular inspections are essential for maintaining the health of your Ford Police Interceptor’s OBD2 system. These inspections should include:
- Visual Inspection: Check for any obvious signs of damage, such as frayed wires, loose connections, or damaged sensors.
- OBD2 Scan: Use an OBD2 scanner to check for any stored or pending DTCs.
- Sensor Monitoring: Monitor the performance of key sensors, such as O2 sensors, MAF sensors, and temperature sensors, using an OBD2 scanner.
- Exhaust System Check: Inspect the exhaust system for leaks, rust, or damage.
Performing these inspections regularly can help identify potential issues early, before they escalate into more significant problems.
8.2. Promptly Addressing Issues
Addressing OBD2 issues promptly is crucial for preventing further damage and maintaining the vehicle’s performance. Ignoring DTCs or delaying repairs can lead to more costly problems down the road.
When a DTC is detected, diagnose and repair the underlying issue as soon as possible. This may involve replacing faulty sensors, repairing vacuum leaks, or addressing engine performance problems.
8.3. Using Quality Parts
Using quality parts is essential for ensuring the reliability and longevity of your Ford Police Interceptor’s OBD2 system. Cheap or substandard parts may fail prematurely, leading to recurring issues and potential damage to other components.
When replacing sensors, valves, or other components, use OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) parts or high-quality aftermarket parts from reputable brands. These parts are designed to meet the vehicle’s specifications and provide reliable performance.
8.4. Keeping Software Updated
Keeping the vehicle’s software updated is crucial for maintaining the proper functioning of the OBD2 system. Manufacturers often release software updates to address known issues, improve performance, and enhance diagnostic capabilities.
Check with your Ford dealer or a qualified mechanic to ensure that your vehicle has the latest software updates installed. These updates can help prevent potential problems and ensure the OBD2 system functions correctly.
8.5. Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance, such as oil changes, tune-ups, and fluid replacements, can also help maintain the health of the OBD2 system. Properly maintained engines and systems are less likely to experience issues that trigger DTCs.
Follow the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule and address any maintenance needs promptly. This can help prevent potential problems and ensure the vehicle operates smoothly.
8.6. Benefits of Proactive Maintenance
Proactively maintaining your Ford Police Interceptor’s OBD2 system offers several benefits:
- Prevents Costly Repairs: Identifying and addressing issues early can prevent more significant and costly repairs down the road.
- Maintains Vehicle Performance: A properly functioning OBD2 system helps ensure the vehicle operates at its optimal performance.
- Ensures Compliance with Emissions Standards: A healthy OBD2 system helps maintain compliance with emissions standards, allowing the vehicle to pass inspections.
- Extends Vehicle Lifespan: Proactive maintenance can help extend the lifespan of the vehicle and its components.
By following these tips and proactively maintaining your Ford Police Interceptor’s OBD2 system, you can prevent potential problems and ensure the vehicle operates reliably for years to come.
9. Ford Police Interceptor OBD2 Resources
What are the best OBD2 resources available specifically for Ford Police Interceptors? The best OBD2 resources available specifically for Ford Police Interceptors include online databases, Ford service manuals, OBD2 scanner guides, and online forums for specialized support.
9.1. Online OBD2 Code Databases
Online OBD2 code databases are valuable resources for identifying and understanding DTCs. These databases provide detailed information about the meaning of each code, potential causes, and recommended troubleshooting steps.
Some popular online OBD2 code databases include:
- OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN: Offers a comprehensive database of OBD2 codes, including Ford-specific codes, along with troubleshooting tips and repair information.
- AutoCodes.com: Provides detailed information about OBD2 codes, technical service bulletins, and diagnostic procedures.
- OBD-Codes.com: Offers a searchable database of OBD2 codes, along with user-submitted solutions and repair tips.
These online databases can help you quickly identify the meaning of DTCs and develop a diagnostic strategy.
9.2. Ford Service Manuals
Ford service manuals are essential resources for understanding the intricacies of the Ford Police Interceptor’s OBD2 system. These manuals provide detailed information about the vehicle’s components, systems, and diagnostic procedures.
Ford service manuals typically include:
- Wiring Diagrams: Detailed wiring diagrams for the vehicle’s electrical systems, including the OBD2 system.
- Component Locations: Information about the location of various components, such as sensors, valves, and control modules.
- Diagnostic Procedures: Step-by-step diagnostic procedures for troubleshooting OBD2 codes and other issues.
- Repair Procedures: Detailed repair procedures for replacing components and repairing damaged systems.
Ford service manuals can be obtained from your local Ford dealer or purchased online from reputable sources.
9.3. OBD2 Scanner Guides
OBD2 scanner guides provide valuable information about using and interpreting the data from OBD2 scanners. These guides can help you understand how to use the scanner effectively and interpret the data accurately.
OBD2 scanner guides typically include:
- Scanner Operation: Instructions on how to connect and operate the scanner.
- Data Interpretation: Information about interpreting the data displayed by the scanner, such as sensor readings, fuel trims, and readiness monitor status.
- Troubleshooting Tips: Tips for troubleshooting common OBD2 issues using the scanner.
- Advanced Features: Information about using advanced scanner features, such as live data streaming and bidirectional control.
OBD2 scanner guides can be obtained from the scanner manufacturer or found online through various automotive forums and websites.
9.4. Online Forums and Communities
Online forums and communities are valuable resources for connecting with other Ford Police Interceptor owners and sharing information about OBD2 issues. These forums can provide a wealth of knowledge and support from experienced vehicle owners and mechanics.
Some popular online forums and communities for Ford Police Interceptors include:
- Ford Police Interceptor Forums: Dedicated forums for discussing Ford Police Interceptor issues, including OBD2 problems, performance upgrades, and maintenance tips.
- Automotive Forums: General automotive forums where you can ask questions and share information about OBD2 issues on Ford vehicles.
- Social Media Groups: Social media groups dedicated to Ford Police Interceptors, where you can connect with other owners and share experiences.
These online forums and communities can provide valuable support and information for troubleshooting OBD2 issues on your Ford Police Interceptor.
9.5. Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs)
Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs) are documents issued by manufacturers to provide information about common issues and recommended repair procedures. TSBs can be valuable resources for diagnosing and repairing OBD2 issues on your Ford Police Interceptor.
TSBs typically include:
- Problem Description: A description of the issue being addressed.
- Affected Vehicles: A list of vehicles affected by the issue.
- Cause of the Problem: An explanation of the underlying cause of the issue.
- Recommended Repair Procedure: A step-by-step repair procedure for resolving the issue.
TSBs can be obtained from your local Ford dealer or accessed online through various automotive databases.
By utilizing these resources, you can gain a better understanding of your Ford Police Interceptor’s OBD2 system and effectively troubleshoot any issues that may arise.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
10.1. What is an OBD2 Scanner?
An OBD2 scanner is a diagnostic tool used to read and interpret data from a vehicle’s On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD2) system, helping to identify potential issues.
10.2. How Do I Read OBD2 Codes?
Connect the OBD2 scanner to the OBD2 port, typically located under the dashboard, turn on the ignition, and use the scanner’s interface to read and record the displayed Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs).
10.3. What Are Common Automotive Errors and How Can They Be Fixed?
Common automotive errors include misfires, O2 sensor failures, and EVAP system leaks. Fixes vary but often involve replacing faulty sensors, repairing leaks, or addressing engine performance issues.
10.4. Can I Clear OBD2 Codes Myself?
Yes, you can clear OBD2 codes using a scanner after addressing the underlying issues, but it’s crucial to fix the root cause to prevent the codes from recurring.
10.5. What Does the Check Engine Light Mean?
The check engine light indicates that the vehicle’s computer has detected a problem, which could range from minor to severe. An OBD2 scan can help identify the specific issue.
10.6. How Often Should I Scan My Car for OBD2 Codes?
Regular scanning, especially when you notice unusual performance, is recommended to catch potential issues early and prevent costly repairs.
10.7. Where Can I Find Reliable OBD2 Information for My Ford Police Interceptor?
Reliable sources include Ford service manuals, online OBD2 code databases, automotive forums, and expert advice from professional mechanics at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN.
10.8. What Are Ford-Specific OBD2 Codes?
Ford-specific OBD2 codes are diagnostic trouble codes unique to Ford vehicles, providing more detailed information about the issue than generic codes.
10.9. How Do Drive Cycles Help in OBD2 Diagnostics?
Drive cycles allow the vehicle’s onboard diagnostics to run specific tests under controlled conditions, ensuring accurate and reliable diagnosis of OBD2-related issues.
10.10. Why Is My Ford Police Interceptor Failing Emissions Tests Despite No Active Codes?
This could be due to readiness monitors not being set. Performing a Ford-specific drive cycle and ensuring all systems are functioning correctly can help resolve this issue.
Do you need expert assistance with your Ford Police Interceptor OBD OBD2 codes? At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we understand the challenges of diagnosing and repairing modern vehicles. Our team of experienced technicians is here to provide the guidance and support you need. Whether you’re dealing with a stubborn check engine light, O2 sensor issues, or any other OBD2-related problem, we can help you pinpoint the root cause and find the right solution. Contact us today at 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States, Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880, or visit our website at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for expert assistance and reliable service. Let us help you keep your Ford Police Interceptor running smoothly and efficiently.
