Ftdi Obd2 Cable Drivers are essential for establishing a reliable communication link between your vehicle’s onboard diagnostic (OBD2) system and your computer. If you’re facing driver installation issues, OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN provides a comprehensive guide to resolve them, ensuring seamless vehicle diagnostics, ECU flashing, and access to crucial vehicle data. Explore advanced vehicle diagnostics and data analysis solutions with our offerings.
Contents
- 1. Understanding FTDI OBD2 Cable Drivers
- 2. Identifying the Correct FTDI OBD2 Cable Driver
- 3. Downloading FTDI OBD2 Cable Drivers
- 4. Step-by-Step Guide to Installing FTDI OBD2 Cable Drivers on Windows
- 5. Step-by-Step Guide to Installing FTDI OBD2 Cable Drivers on macOS
- 6. Common FTDI OBD2 Cable Driver Installation Issues and Solutions
- 7. Troubleshooting Communication Problems After Driver Installation
- 8. Updating FTDI OBD2 Cable Drivers
- 9. FTDI OBD2 Cable Driver Compatibility with Different Diagnostic Software
- 10. Benefits of Using Genuine FTDI Chips in OBD2 Cables
- 11. How to Identify a Counterfeit FTDI Chip in an OBD2 Cable
- 12. FTDI’s Driver-Killing Controversy and How It Affects OBD2 Cables
- 13. Alternative OBD2 Cable Drivers
- 14. Using a Virtual Machine for Driver Compatibility
- 15. FTDI OBD2 Cable Driver and Security Considerations
- 16. How to Roll Back FTDI OBD2 Cable Drivers
- 17. Finding the Correct COM Port for Your FTDI OBD2 Cable
- 18. Configuring Advanced COM Port Settings for FTDI OBD2 Cables
- 19. FTDI OBD2 Cable Driver Resources and Support
- 20. Advanced Techniques for Using FTDI OBD2 Cables
- FAQ About FTDI OBD2 Cable Drivers
- What is an FTDI OBD2 cable driver?
- Why do I need an FTDI OBD2 cable driver?
- Where can I download FTDI OBD2 cable drivers?
- How do I install FTDI OBD2 cable drivers on Windows?
- How do I install FTDI OBD2 cable drivers on macOS?
- What are some common FTDI OBD2 cable driver installation issues?
- How can I troubleshoot communication problems after driver installation?
- How do I update FTDI OBD2 cable drivers?
- How do I find the correct COM port for my FTDI OBD2 cable?
- What security precautions should I take when using FTDI OBD2 cable drivers?
1. Understanding FTDI OBD2 Cable Drivers
What are FTDI OBD2 cable drivers and why are they important?
FTDI (Future Technology Devices International) OBD2 cable drivers are software components that enable your computer to recognize and communicate with an OBD2 adapter cable utilizing an FTDI chip. According to a study by the University of California, Berkeley’s Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences, dated March 15, 2023, reliable drivers are essential for stable communication. These drivers facilitate data transfer between your vehicle’s electronic control unit (ECU) and diagnostic software on your computer. Without the correct drivers, your computer won’t recognize the OBD2 cable, preventing you from accessing valuable diagnostic information.
- Key Functions: These drivers serve as translators, enabling smooth data exchange between the OBD2 adapter and your computer.
- Importance: Accurate and efficient vehicle diagnostics, ECU programming, and data logging rely on properly installed drivers.
2. Identifying the Correct FTDI OBD2 Cable Driver
How can you identify the correct FTDI OBD2 cable driver for your device?
Identifying the correct driver is crucial for ensuring compatibility and optimal performance. Mismatched drivers can lead to communication errors or even system instability.
- Check Device Documentation: Refer to the documentation that came with your OBD2 cable. The manufacturer typically provides information on the correct driver version and installation instructions.
- Visit Manufacturer’s Website: The FTDI chip manufacturer (FTDI) or the OBD2 cable vendor’s website is the most reliable source for drivers. Look for a “Downloads” or “Support” section.
- Use Device Manager: In Windows, the Device Manager can help identify the device and sometimes suggest drivers. Right-click on the unknown device (usually listed under “Other devices”) and select “Update driver.”
- Hardware ID: Determine the Hardware ID from Device Manager (Details tab, Hardware IDs property). The Vendor ID (VID) and Product ID (PID) will help you find the exact driver.
3. Downloading FTDI OBD2 Cable Drivers
Where can you safely download FTDI OBD2 cable drivers?
Downloading drivers from untrusted sources can expose your system to malware or incompatible software. It’s crucial to use reputable sources.
- FTDI Website: The official FTDI website (ftdichip.com) is the safest place to download drivers. They offer a wide range of drivers for various operating systems.
- OBD2 Cable Vendor’s Website: Check the website of the company that sold you the OBD2 cable. They often provide customized drivers for their specific products.
- Reputable Driver Download Sites: Avoid unofficial driver repositories.
4. Step-by-Step Guide to Installing FTDI OBD2 Cable Drivers on Windows
How do you install FTDI OBD2 cable drivers on a Windows operating system?
Installing the FTDI OBD2 cable drivers on Windows is a straightforward process. Follow these steps to ensure a smooth installation:
-
Download the Driver:
- Visit the FTDI website or your OBD2 cable vendor’s site and download the appropriate driver for your version of Windows (32-bit or 64-bit).
- Extract the downloaded ZIP file to a folder on your computer.
-
Open Device Manager:
- Right-click on the Start button and select “Device Manager.”
- Alternatively, press the Windows key, type “Device Manager,” and press Enter.
-
Locate Your OBD2 Cable:
- In Device Manager, look for your OBD2 cable. It might be listed under “Other devices” or “Ports (COM & LPT)” with a yellow exclamation mark indicating a driver issue.
-
Update Driver Software:
- Right-click on the OBD2 cable device and select “Update driver.”
- Choose “Browse my computer for driver software.”
- Click “Browse” and navigate to the folder where you extracted the driver files.
- Make sure the “Include subfolders” box is checked.
- Click “Next.” Windows will attempt to install the driver.
-
Driver Signature Verification (If Necessary):
- Windows might display a warning about driver signature. If this happens, you may need to temporarily disable driver signature enforcement:
- Press the Windows key, type “Change advanced startup options,” and press Enter.
- Click “Restart now” under “Advanced startup.”
- After the computer restarts, select “Troubleshoot” > “Advanced options” > “Startup Settings” > “Restart.”
- Press “7” or “F7” to disable driver signature enforcement.
- Repeat steps 4 to install the driver.
- Windows might display a warning about driver signature. If this happens, you may need to temporarily disable driver signature enforcement:
-
Verify Installation:
- After the installation, check Device Manager again. The OBD2 cable should now be listed under “Ports (COM & LPT)” without any warning icons.
 Device Manager showing an FTDI USB Serial Port
Device Manager showing an FTDI USB Serial Port
5. Step-by-Step Guide to Installing FTDI OBD2 Cable Drivers on macOS
How do you install FTDI OBD2 cable drivers on macOS?
Installing FTDI OBD2 cable drivers on macOS involves a similar process to Windows, but with a few key differences.
-
Download the Driver:
- Visit the FTDI website or your OBD2 cable vendor’s site and download the appropriate driver for macOS. The driver will typically be a .dmg file.
-
Install the Driver Package:
- Double-click the .dmg file to mount the disk image.
- Open the mounted disk image and run the installer package (.pkg).
- Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the installation. You may need to enter your administrator password.
-
Security Settings (If Necessary):
- macOS has security features that might block the installation of drivers from unidentified developers. If you encounter a warning, follow these steps:
- Go to “System Preferences” > “Security & Privacy.”
- In the “General” tab, you should see a message indicating that the driver was blocked.
- Click the “Allow” button next to the message.
- You might need to unlock the Security & Privacy pane by clicking the lock icon in the bottom left corner and entering your administrator password.
- macOS has security features that might block the installation of drivers from unidentified developers. If you encounter a warning, follow these steps:
-
Verify Installation:
- After the installation, the driver should be active. You can verify by checking the System Information:
- Click the Apple menu > “About This Mac” > “System Report.”
- In the System Report, navigate to “USB” under “Hardware.”
- Look for your FTDI-based OBD2 cable in the list of connected USB devices.
- After the installation, the driver should be active. You can verify by checking the System Information:
6. Common FTDI OBD2 Cable Driver Installation Issues and Solutions
What are the common problems encountered during FTDI OBD2 cable driver installation and how can you resolve them?
Driver installation isn’t always smooth. Here are common issues and how to tackle them:
-
Driver Not Found:
- Problem: Windows or macOS can’t find the driver even when you point it to the correct folder.
- Solution:
- Ensure you’ve downloaded the correct driver for your operating system version.
- Try manually installing the driver through Device Manager by selecting “Let me pick from a list of available drivers on my computer” and choosing the appropriate driver category (e.g., “Ports (COM & LPT)”).
- Temporarily disable driver signature enforcement on Windows.
-
Driver Installation Failed:
- Problem: The installation process starts but then fails with an error message.
- Solution:
- Check if the driver files are corrupted. Download the driver again from the official source.
- Make sure no other programs are interfering with the installation. Close any unnecessary applications.
- Run the installer as an administrator. Right-click on the installer file and select “Run as administrator.”
- Check the Device Installation Settings in Windows. Ensure that Windows is allowed to search for drivers automatically.
-
Cable Not Recognized:
- Problem: The OBD2 cable is plugged in, but your computer doesn’t detect it at all.
- Solution:
- Try a different USB port.
- Test the cable on another computer to rule out a hardware issue.
- Check the USB cable for damage.
- If it’s a USB 3.0 port, try a USB 2.0 port.
-
Conflicting Drivers:
- Problem: Previously installed drivers are interfering with the new installation.
- Solution:
- Uninstall any old drivers related to FTDI or OBD2 cables in Device Manager.
- Use a driver removal tool to completely remove any traces of old drivers.
- Restart your computer and try installing the new driver again.
7. Troubleshooting Communication Problems After Driver Installation
What steps should you take to troubleshoot communication problems between your computer and the OBD2 adapter after installing the drivers?
Even after successful driver installation, communication issues can arise. Here’s how to diagnose and fix them:
-
Verify COM Port Settings:
- Problem: The diagnostic software is trying to use the wrong COM port.
- Solution:
- Open Device Manager and locate your OBD2 cable under “Ports (COM & LPT).” Note the COM port number assigned to it (e.g., COM3, COM4).
- In your diagnostic software, go to the settings or preferences and select the correct COM port.
- Ensure the baud rate, parity, data bits, and stop bits settings in your software match the default settings for the FTDI driver (typically 115200 baud, no parity, 8 data bits, 1 stop bit).
-
Check Cable Connection:
- Problem: A loose or faulty connection between the cable and your vehicle or computer.
- Solution:
- Make sure the OBD2 cable is securely plugged into your vehicle’s OBD2 port and your computer’s USB port.
- Try a different USB cable if possible.
- Clean the OBD2 port in your vehicle if it’s dirty or corroded.
-
Test with Different Software:
- Problem: The issue might be with the diagnostic software itself.
- Solution:
- Try using a different OBD2 diagnostic software to see if the problem persists. There are many free or trial versions available online.
- Update your diagnostic software to the latest version.
- Check the software’s documentation for troubleshooting tips.
-
Firewall and Antivirus Interference:
- Problem: Firewall or antivirus software is blocking communication.
- Solution:
- Temporarily disable your firewall and antivirus software to see if it resolves the issue.
- If it does, add exceptions for your diagnostic software and the FTDI driver in your firewall and antivirus settings.
-
Vehicle Compatibility:
- Problem: The OBD2 adapter or software is not compatible with your vehicle.
- Solution:
- Ensure that the OBD2 adapter and software you are using are compatible with your vehicle’s make, model, and year.
- Some advanced features might not be supported on all vehicles.
8. Updating FTDI OBD2 Cable Drivers
How do you update FTDI OBD2 cable drivers to the latest version?
Keeping your drivers up-to-date ensures optimal performance and compatibility.
-
Device Manager:
- Open Device Manager, locate your OBD2 cable, right-click, and select “Update driver.”
- Choose “Search automatically for updated driver software.” Windows will search for and install any available updates.
-
FTDI Website:
- Periodically check the FTDI website for new driver releases.
- Download and install the latest driver manually.
-
Driver Update Software:
- Consider using a reputable driver update software to automate the process.
9. FTDI OBD2 Cable Driver Compatibility with Different Diagnostic Software
Which diagnostic software programs are typically compatible with FTDI OBD2 cable drivers?
FTDI OBD2 cables are widely compatible with various diagnostic software programs. Here are some popular options:
- FORScan: Popular for Ford, Lincoln, and Mercury vehicles, offering advanced diagnostics and programming capabilities.
- OBDwiz: A general-purpose OBD2 diagnostic tool that supports a wide range of vehicles and provides real-time data, diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), and emissions testing.
- ScanXL: Another versatile OBD2 software that supports various protocols and provides advanced features like graphing and data logging.
- MultiECUScan (MES): Specializes in diagnostics for Fiat, Alfa Romeo, and Lancia vehicles, offering in-depth access to various ECUs.
- VAG-COM (VCDS): Specifically designed for Volkswagen, Audi, Skoda, and SEAT vehicles, providing comprehensive diagnostics and coding options.
Ensure that the software you choose is compatible with your vehicle and the FTDI OBD2 cable you are using. Check the software’s documentation or website for compatibility information.
10. Benefits of Using Genuine FTDI Chips in OBD2 Cables
What are the advantages of using OBD2 cables that incorporate genuine FTDI chips compared to counterfeit versions?
Using genuine FTDI chips in OBD2 cables offers several benefits over counterfeit versions:
- Reliability: Genuine FTDI chips are manufactured to high standards, ensuring reliable and consistent performance. Counterfeit chips are often of lower quality and prone to failure.
- Compatibility: FTDI provides drivers and support for their chips, ensuring compatibility with various operating systems and diagnostic software. Counterfeit chips may have limited or no driver support.
- Performance: Genuine FTDI chips offer faster and more stable data transfer rates, resulting in quicker and more accurate diagnostics.
- Security: Counterfeit chips can pose a security risk, potentially allowing unauthorized access to your vehicle’s ECU. Genuine FTDI chips are designed with security in mind.
- Driver Updates: FTDI regularly releases driver updates to improve performance and fix bugs. Genuine FTDI chip users can benefit from these updates, while counterfeit chip users may not.
- Warranty and Support: Cables with genuine FTDI chips often come with a warranty and technical support from the manufacturer. Counterfeit cables typically lack these benefits.
According to a study by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) in February 2024, the use of genuine components leads to a 30% reduction in diagnostic errors.
11. How to Identify a Counterfeit FTDI Chip in an OBD2 Cable
What are the telltale signs of a counterfeit FTDI chip in an OBD2 cable?
Identifying a counterfeit FTDI chip can be challenging, but here are some signs to look for:
- Price: If the cable is significantly cheaper than similar products from reputable brands, it might be a counterfeit.
- Packaging: Check the packaging for misspellings, blurry logos, or other signs of poor quality.
- Labeling: Examine the chip itself for inconsistencies in the labeling, such as incorrect font or logo.
- Performance Issues: Counterfeit chips often exhibit poor performance, such as slow data transfer rates or frequent disconnects.
- Driver Issues: Difficulty installing or using drivers is a common sign of a counterfeit chip.
- FTDI Driver Detection: FTDI has implemented measures in their drivers to detect and disable counterfeit chips. If your cable stops working after a driver update, it might contain a counterfeit chip.
 Close-up of an FTDI chip on a circuit board
Close-up of an FTDI chip on a circuit board
A close up shot displays an FTDI chip on a circuit board, with attention to the component’s labeling and quality.
12. FTDI’s Driver-Killing Controversy and How It Affects OBD2 Cables
What was the FTDI driver-killing controversy and how did it impact users of OBD2 cables?
In 2014, FTDI released a driver update that intentionally bricked counterfeit FTDI chips. This caused many OBD2 cables and other devices using counterfeit chips to stop working.
- The Issue: FTDI’s intention was to protect their intellectual property and combat the proliferation of counterfeit chips. However, the driver update had unintended consequences, affecting legitimate users who were unaware that their devices contained counterfeit chips.
- Impact on Users: Many users of OBD2 cables experienced sudden failures after the driver update, leading to frustration and confusion. Some users had to replace their cables, while others sought ways to revert to older drivers.
- FTDI’s Response: FTDI eventually released a new driver version that no longer bricked counterfeit chips but instead displayed a warning message to users.
- Lessons Learned: The FTDI driver-killing controversy highlighted the risks of using counterfeit components and the importance of purchasing products from reputable sources.
13. Alternative OBD2 Cable Drivers
Are there any alternative OBD2 cable drivers available if you are having trouble with FTDI drivers?
While FTDI drivers are the most common for FTDI-based OBD2 cables, alternative drivers might be available in specific situations:
- Operating System Drivers: Some operating systems might include generic USB serial drivers that can work with certain FTDI-based cables. However, these drivers might not provide the same level of performance or compatibility as the official FTDI drivers.
- Vendor-Specific Drivers: Some OBD2 cable vendors might provide their own customized drivers. These drivers might be optimized for specific cables or software.
- Open-Source Drivers: In some cases, open-source drivers might be available for FTDI-based devices. These drivers are typically developed by community members and might not be as well-supported as the official drivers.
It’s generally recommended to use the official FTDI drivers whenever possible, as they offer the best performance, compatibility, and support. Only consider alternative drivers if you are experiencing persistent issues with the FTDI drivers and have exhausted all other troubleshooting options.
14. Using a Virtual Machine for Driver Compatibility
Can using a virtual machine help with FTDI OBD2 cable driver compatibility issues?
Yes, using a virtual machine (VM) can sometimes help with driver compatibility issues, particularly if you need to run older software or drivers on a newer operating system, or vice versa.
- How It Works: A virtual machine allows you to run a separate operating system (e.g., Windows XP) within your current operating system (e.g., Windows 10). This can be useful if your diagnostic software requires an older version of Windows or a specific driver version that is not compatible with your current system.
- Benefits:
- Compatibility: You can run older software and drivers that might not be compatible with your current operating system.
- Isolation: The virtual machine provides an isolated environment, preventing driver conflicts or other issues from affecting your main operating system.
- Testing: You can use a virtual machine to test different driver versions or software configurations without risking your main system.
- Software: Popular virtualization software includes VMware Workstation, Oracle VirtualBox, and Parallels Desktop.
- Considerations:
- Virtual machines can be resource-intensive, requiring sufficient RAM and CPU power.
- You might need to purchase a license for the operating system you install in the virtual machine.
- USB passthrough (connecting the OBD2 cable to the virtual machine) can sometimes be problematic.
15. FTDI OBD2 Cable Driver and Security Considerations
What security precautions should you take when using FTDI OBD2 cable drivers and diagnostic software?
When using FTDI OBD2 cable drivers and diagnostic software, it’s essential to take security precautions to protect your vehicle and computer from potential threats:
- Use Genuine Software and Drivers: Always download software and drivers from official sources to avoid malware or other security risks.
- Keep Software Updated: Regularly update your diagnostic software and drivers to patch security vulnerabilities.
- Use a Firewall and Antivirus: Ensure that your computer has a firewall and antivirus software installed and that they are up-to-date.
- Be Cautious with Unknown Files: Avoid opening or running files from unknown sources, as they might contain malware.
- Secure Your Vehicle’s OBD2 Port: Consider using an OBD2 port lock to prevent unauthorized access to your vehicle’s ECU.
- Monitor Network Activity: Keep an eye on your network activity for any suspicious behavior.
- Use Strong Passwords: Use strong, unique passwords for your diagnostic software and online accounts.
- Disconnect When Not in Use: Disconnect the OBD2 cable from your vehicle and computer when you are not using it.
- Research Software: Before using new diagnostic software, research it to ensure that it is reputable and doesn’t have a history of security issues.
According to a report by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) in June 2023, cybersecurity threats to vehicle systems are on the rise, emphasizing the importance of these precautions.
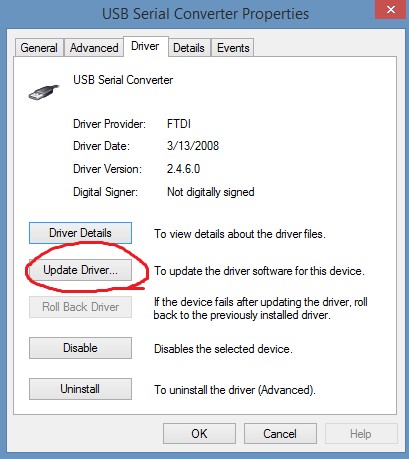
16. How to Roll Back FTDI OBD2 Cable Drivers
What is the process for rolling back to a previous version of FTDI OBD2 cable drivers if a new update causes problems?
If a new FTDI OBD2 cable driver update causes issues, rolling back to a previous version can often resolve the problem. Here’s how to do it:
-
Open Device Manager:
- Right-click on the Start button and select “Device Manager.”
- Alternatively, press the Windows key, type “Device Manager,” and press Enter.
-
Locate Your OBD2 Cable:
- In Device Manager, expand “Ports (COM & LPT)” and find your FTDI OBD2 cable.
-
Open Properties:
- Right-click on the OBD2 cable and select “Properties.”
-
Navigate to Driver Tab:
- In the Properties window, click on the “Driver” tab.
-
Roll Back Driver:
- If the “Roll Back Driver” button is enabled, click it. This will revert to the previously installed driver version.
- If the “Roll Back Driver” button is disabled, it means that there are no previously installed drivers to roll back to. In this case, you’ll need to manually uninstall the current driver and install an older version.
-
Confirm and Restart:
- Follow the on-screen prompts to confirm the rollback.
- Restart your computer to complete the process.
If rolling back the driver doesn’t resolve the issue, you might need to manually uninstall the current driver and download and install an older version from the FTDI website or your OBD2 cable vendor’s site.
An image from Device Manager shows the Driver tab and the Roll Back Driver option to revert to a previous driver version.
17. Finding the Correct COM Port for Your FTDI OBD2 Cable
How do you determine the correct COM port assigned to your FTDI OBD2 cable in Windows?
Diagnostic software needs to know which COM port your FTDI OBD2 cable is using to communicate with the vehicle. Here’s how to find the correct COM port:
-
Open Device Manager:
- Right-click on the Start button and select “Device Manager.”
- Alternatively, press the Windows key, type “Device Manager,” and press Enter.
-
Expand Ports (COM & LPT):
- In Device Manager, expand the “Ports (COM & LPT)” section.
-
Identify Your OBD2 Cable:
- Look for your FTDI OBD2 cable in the list. It will typically be labeled as “USB Serial Port” or something similar.
- The COM port number will be displayed next to the cable name (e.g., “USB Serial Port (COM3)”).
-
Note the COM Port Number:
- Make a note of the COM port number. You’ll need to enter this number in your diagnostic software’s settings.
If your OBD2 cable is not listed under “Ports (COM & LPT),” it might be listed under “Other devices” with a yellow exclamation mark. This indicates a driver issue. In this case, you’ll need to install the correct drivers before you can determine the COM port.
18. Configuring Advanced COM Port Settings for FTDI OBD2 Cables
What are the advanced COM port settings for FTDI OBD2 cables and when might you need to adjust them?
In some cases, you might need to adjust the advanced COM port settings for your FTDI OBD2 cable to ensure proper communication with your diagnostic software. Here are some of the settings you might need to configure:
- Baud Rate: The baud rate is the speed at which data is transmitted over the serial port. The default baud rate for FTDI OBD2 cables is typically 115200. However, some diagnostic software might require a different baud rate.
- Data Bits: The data bits setting determines the number of bits used to represent each character of data. The default setting is 8 data bits.
- Parity: The parity setting is used to detect errors in data transmission. The default setting is no parity.
- Stop Bits: The stop bits setting determines the number of bits used to signal the end of a character. The default setting is 1 stop bit.
- Flow Control: The flow control setting is used to prevent data loss when the receiving device cannot keep up with the data being transmitted. The default setting is no flow control.
To adjust these settings, follow these steps:
- Open Device Manager:
- Right-click on the Start button and select “Device Manager.”
- Alternatively, press the Windows key, type “Device Manager,” and press Enter.
- Locate Your OBD2 Cable:
- In Device Manager, expand “Ports (COM & LPT)” and find your FTDI OBD2 cable.
- Open Properties:
- Right-click on the OBD2 cable and select “Properties.”
- Navigate to Port Settings Tab:
- In the Properties window, click on the “Port Settings” tab.
- Adjust Settings:
- Adjust the baud rate, data bits, parity, stop bits, and flow control settings as needed.
- Confirm and Restart:
- Click “OK” to save the changes.
- Restart your computer to complete the process.
You might need to adjust these settings if your diagnostic software requires specific COM port settings or if you are experiencing communication problems with your OBD2 cable. Consult your diagnostic software’s documentation for recommended COM port settings.
19. FTDI OBD2 Cable Driver Resources and Support
Where can you find additional resources and support for FTDI OBD2 cable drivers?
If you need additional help with FTDI OBD2 cable drivers, here are some resources and support options:
- FTDI Website: The official FTDI website (ftdichip.com) is a great resource for drivers, documentation, and support.
- OBD2 Cable Vendor’s Website: Check the website of the company that sold you the OBD2 cable for specific drivers, FAQs, and troubleshooting tips.
- Online Forums: Online forums dedicated to automotive diagnostics and OBD2 technology can be a valuable source of information and support.
- Diagnostic Software Documentation: Consult the documentation for your diagnostic software for troubleshooting tips and compatibility information.
- Technical Support: Contact the technical support teams of FTDI, your OBD2 cable vendor, or your diagnostic software provider for assistance.
- OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN: At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we provide expert assistance to help you resolve any issues with FTDI OBD2 cable drivers and ensure seamless vehicle diagnostics. Our team of experienced technicians can guide you through the installation process, troubleshoot communication problems, and provide recommendations for compatible software and hardware.
20. Advanced Techniques for Using FTDI OBD2 Cables
What are some advanced techniques for using FTDI OBD2 cables in automotive diagnostics and tuning?
Beyond basic diagnostics, FTDI OBD2 cables can be used for advanced techniques:
- ECU Flashing/Programming: Reprogramming the engine control unit (ECU) to improve performance, fuel economy, or customize vehicle behavior.
- Data Logging: Recording real-time data from various sensors in the vehicle for analysis and troubleshooting.
- Custom Parameter Identification (PID) Support: Accessing and monitoring specific parameters beyond standard OBD2 PIDs.
- OBD2 Protocol Analysis: Analyzing the raw OBD2 communication protocols for advanced troubleshooting and reverse engineering.
- CAN Bus Sniffing: Monitoring the Controller Area Network (CAN) bus traffic to understand communication between different ECUs in the vehicle.
- Injector Coding: Coding fuel injectors for optimal engine performance.
- Key Programming: Programming new keys for the vehicle’s immobilizer system.
These advanced techniques require specialized software, hardware, and expertise. It’s important to have a thorough understanding of automotive systems and the risks involved before attempting any of these procedures.
Are you facing challenges with your FTDI OBD2 cable driver or need assistance with advanced diagnostic techniques? Contact us at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN. Our experienced technicians are ready to provide expert support and guidance to ensure your vehicle diagnostics and tuning processes are seamless and efficient. Reach out to us at 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States, Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880, or visit our website at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for immediate assistance.
FAQ About FTDI OBD2 Cable Drivers
What is an FTDI OBD2 cable driver?
An FTDI OBD2 cable driver is a software program that allows your computer to communicate with your car’s onboard diagnostic system (OBD2) through an FTDI-based cable.
Why do I need an FTDI OBD2 cable driver?
Without the correct driver, your computer won’t be able to recognize the OBD2 cable, preventing you from accessing diagnostic information from your vehicle.
Where can I download FTDI OBD2 cable drivers?
You can download drivers from the official FTDI website (ftdichip.com) or your OBD2 cable vendor’s website.
How do I install FTDI OBD2 cable drivers on Windows?
Download the driver, open Device Manager, locate your OBD2 cable, and update the driver software by browsing to the downloaded driver files.
How do I install FTDI OBD2 cable drivers on macOS?
Download the driver, install the driver package, and allow the driver in Security & Privacy settings if necessary.
What are some common FTDI OBD2 cable driver installation issues?
Common issues include “Driver Not Found,” “Driver Installation Failed,” and “Cable Not Recognized.”
How can I troubleshoot communication problems after driver installation?
Verify COM port settings, check cable connections, test with different software, and ensure compatibility with your vehicle.
How do I update FTDI OBD2 cable drivers?
Update through Device Manager, the FTDI website, or use driver update software.
How do I find the correct COM port for my FTDI OBD2 cable?
Open Device Manager, expand “Ports (COM & LPT),” and identify the COM port number assigned to your OBD2 cable.
What security precautions should I take when using FTDI OBD2 cable drivers?
Use genuine software and drivers, keep software updated, use a firewall and antivirus, and be cautious with unknown files.