Clearing OBD2 codes is crucial for maintaining your vehicle’s health, and understanding how to do it is essential. You can clear OBD2 codes without a scanner by trying methods such as disconnecting the battery, using the fuse box, completing a drive cycle, or using a Bluetooth OBD2 adapter with a smartphone app; for more detailed guidance and professional diagnostics, visit OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN. These alternative methods offer ways to address diagnostic trouble codes without needing a dedicated scanning tool.
Contents
- 1. Why Resetting OBD2 Codes Might Be Necessary
- 2. Methods to Clear OBD2 Codes Without a Scanner
- 2.1. Disconnecting the Car Battery
- 2.2. Using the Fuse Box
- 2.3. Performing a Drive Cycle
- 2.4. Using a Third-Party App with a Bluetooth OBD2 Adapter
- 3. Understanding OBD2 Codes and Their Meanings
- 3.1. Common OBD2 Code Categories
- 3.2. Example of Common OBD2 Codes
- 3.3. Importance of Proper Diagnosis
- 4. Potential Risks of Resetting Codes Without Addressing the Underlying Issue
- 5. The Role of OBD2 Scanners in Accurate Diagnostics
- 5.1. Benefits of Using an OBD2 Scanner
- 5.2. Types of OBD2 Scanners
- 5.3. Choosing the Right Scanner for Your Needs
- 6. Maintaining Your Vehicle After Clearing OBD2 Codes
- 6.1. Regular Maintenance Tasks
- 6.2. Importance of Routine Inspections
- 6.3. Keeping Accurate Records
- 7. When to Seek Professional Help
- 7.1. Complex Diagnostic Issues
- 7.2. Safety-Related Problems
- 7.3. Emission System Problems
- 8. Contact OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for Expert Assistance
- 8.1. Comprehensive Diagnostic Services
- 8.2. Expert Repair Solutions
- 8.3. Contact Information and Location
- 9. FAQs About Clearing OBD2 Codes Without a Scanner
- 9.1. Can I reset my car’s check engine light without a scanner?
- 9.2. Will resetting codes without a scanner affect my car’s performance?
- 9.3. How long does it take to reset car codes without a scanner?
- 9.4. Is it safe to disconnect the car battery to reset OBD2 codes?
- 9.5. Can a drive cycle clear all types of OBD2 codes?
- 9.6. What is the best app to use with a Bluetooth OBD2 adapter?
- 9.7. How do I find the ECU fuse in my car’s fuse box?
- 9.8. What should I do if the check engine light comes back on after resetting it?
- 9.9. Can resetting OBD2 codes help me pass an emissions test?
- 9.10. Are there any risks to resetting OBD2 codes without fixing the problem?
1. Why Resetting OBD2 Codes Might Be Necessary
Resetting your vehicle’s diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) can be necessary for several reasons. Understanding these reasons can help you decide when and how to clear these codes effectively. Here are some key reasons to reset OBD2 codes:
- Clearing Resolved Error Codes: Once a car issue has been fixed, the error code remains in the system. Resetting the codes clears these old messages from your dashboard, preventing confusion with new or unresolved issues.
- Preparing for Emissions Tests: Many states require vehicles to pass emissions tests. The check engine light, triggered by OBD2 codes, can cause a vehicle to fail, even if the underlying problem has been resolved. Resetting the codes after repairs can help ensure a successful test. According to the EPA, all vehicles manufactured after 1996 are equipped with OBD2 systems to monitor emissions-related components continuously.
- Temporary Diagnostic Measure: In situations where a permanent repair is not immediately possible, resetting the codes can temporarily turn off the check engine light. This provides a temporary reprieve while you plan and schedule the necessary repairs, avoiding constant distractions.
 Car Diagnostic Error Codes | Foxwell
Car Diagnostic Error Codes | Foxwell
2. Methods to Clear OBD2 Codes Without a Scanner
While an OBD2 scanner is a direct way to read and clear codes, several alternative methods can be used. These methods range from simple manual techniques to using alternative tools.
2.1. Disconnecting the Car Battery
One of the simplest methods to reset OBD2 codes is by disconnecting the car battery. This process cuts power to the car’s computer, effectively resetting it.
Step-by-Step Guide:
- Turn Off the Ignition: Before starting, ensure the car is completely turned off. This prevents electrical surges that could damage the vehicle’s electronics.
- Locate the Battery: Open the hood and find the car battery. It is typically located near the front of the engine bay.
- Disconnect the Negative Terminal: Use a wrench to loosen the nut on the negative terminal (marked with a “-” sign) and carefully remove the cable. This prevents accidental short circuits during the reset process.
- Wait for 15-30 Minutes: Allowing sufficient time ensures the car’s computer fully resets. Some mechanics recommend pressing the brake pedal to drain any remaining power from the system.
- Reconnect the Battery: After waiting, reconnect the negative terminal and tighten the nut with the wrench. Ensure the connection is secure to avoid any issues.
- Turn On the Ignition: Start the car and check if the check engine light is off. If it is, the reset was successful.
Important Considerations:
- Radio and Clock Settings: Disconnecting the battery will reset your radio and clock settings. Be prepared to reset these systems after reconnecting the battery.
- Potential Risks: While generally safe, disconnecting the battery can sometimes cause issues with other electronic systems in older vehicles. Always consult your car’s manual for specific warnings or recommendations.
2.2. Using the Fuse Box
Another method to reset OBD2 codes involves removing the fuse that powers the car’s Engine Control Unit (ECU).
Detailed Instructions:
- Turn Off the Ignition: Make sure the car is turned off to prevent electrical surges when removing the fuse.
- Locate the Fuse Box: Consult your car’s manual to find the location of the fuse box. It is usually located under the dashboard or in the engine compartment.
- Identify the ECU Fuse: Use the manual to identify the fuse for the ECU. The fuse layout diagram will help you locate the correct fuse.
- Remove the Fuse: Use a fuse puller or pliers to gently remove the fuse. Avoid using excessive force, which could damage the fuse or the fuse box.
- Wait for 15-30 Minutes: Allow the system to reset by waiting for a sufficient period.
- Reinsert the Fuse: Put the fuse back into its slot, ensuring it is securely in place.
- Turn On the Ignition: Start the car and check if the codes have been reset. If the check engine light is off, the process was successful.
Important Considerations:
- Fuse Box Diagram: Always refer to your car’s manual for the correct fuse box diagram. Removing the wrong fuse can cause other issues.
- Fuse Puller: Using a fuse puller is recommended to avoid damaging the fuse or the fuse box.
2.3. Performing a Drive Cycle
A drive cycle involves driving your car in a specific manner to allow the car’s computer to run diagnostics and reset certain codes. This method is particularly useful for resetting emissions-related codes.
Step-by-Step Drive Cycle Process:
- Cold Start: Start the car after it has been off for at least 8 hours to ensure all components are at ambient temperature.
- Idle for 2 Minutes: Let the car idle in park or neutral for two minutes to allow the engine to stabilize.
- Drive at a Steady Speed: Drive at a steady speed of around 45-55 mph for about 10-15 minutes. This helps the system to run checks under normal driving conditions.
- Stop and Go: Drive in stop-and-go traffic for another 5-10 minutes to simulate urban driving conditions.
- Idle for 2 Minutes: Let the car idle again for a couple of minutes before turning it off. This completes the diagnostic checks.
Additional Notes:
- Variations: The exact drive cycle can vary depending on the car manufacturer. Refer to your car’s manual for the specific drive cycle recommended for your vehicle.
- Effectiveness: Completing this drive cycle can reset the emissions system and clear minor codes. If the check engine light turns off, the process was successful.
2.4. Using a Third-Party App with a Bluetooth OBD2 Adapter
Using a third-party app with a Bluetooth OBD2 adapter is a low-cost alternative to a dedicated scanner. Although it requires a small investment in the adapter, it provides a convenient way to read and reset codes using your smartphone.
How to Use This Method:
- Plug in the OBD2 Adapter: Insert the Bluetooth OBD2 adapter into the OBD2 port, usually located under the dashboard near the steering column.
- Download a Smartphone App: Download a compatible app such as Torque (for Android) or OBD Fusion (for iOS) on your smartphone.
- Pair the Adapter with Your Phone: Use Bluetooth to connect the adapter to your phone, following the app’s instructions.
- Use the App to Reset Codes: Follow the app’s instructions to read and reset the codes. These apps typically have user-friendly interfaces.
Benefits of This Method:
- Cost-Effective: Bluetooth OBD2 adapters are relatively inexpensive compared to professional-grade scanners.
- Convenient: Using a smartphone app makes it easy to read and reset codes on the go.
- Additional Features: Many apps offer additional features such as real-time monitoring of engine parameters and diagnostic information.
 Vehicle Diagnostic Scan With Car Scanner | Foxwell
Vehicle Diagnostic Scan With Car Scanner | Foxwell
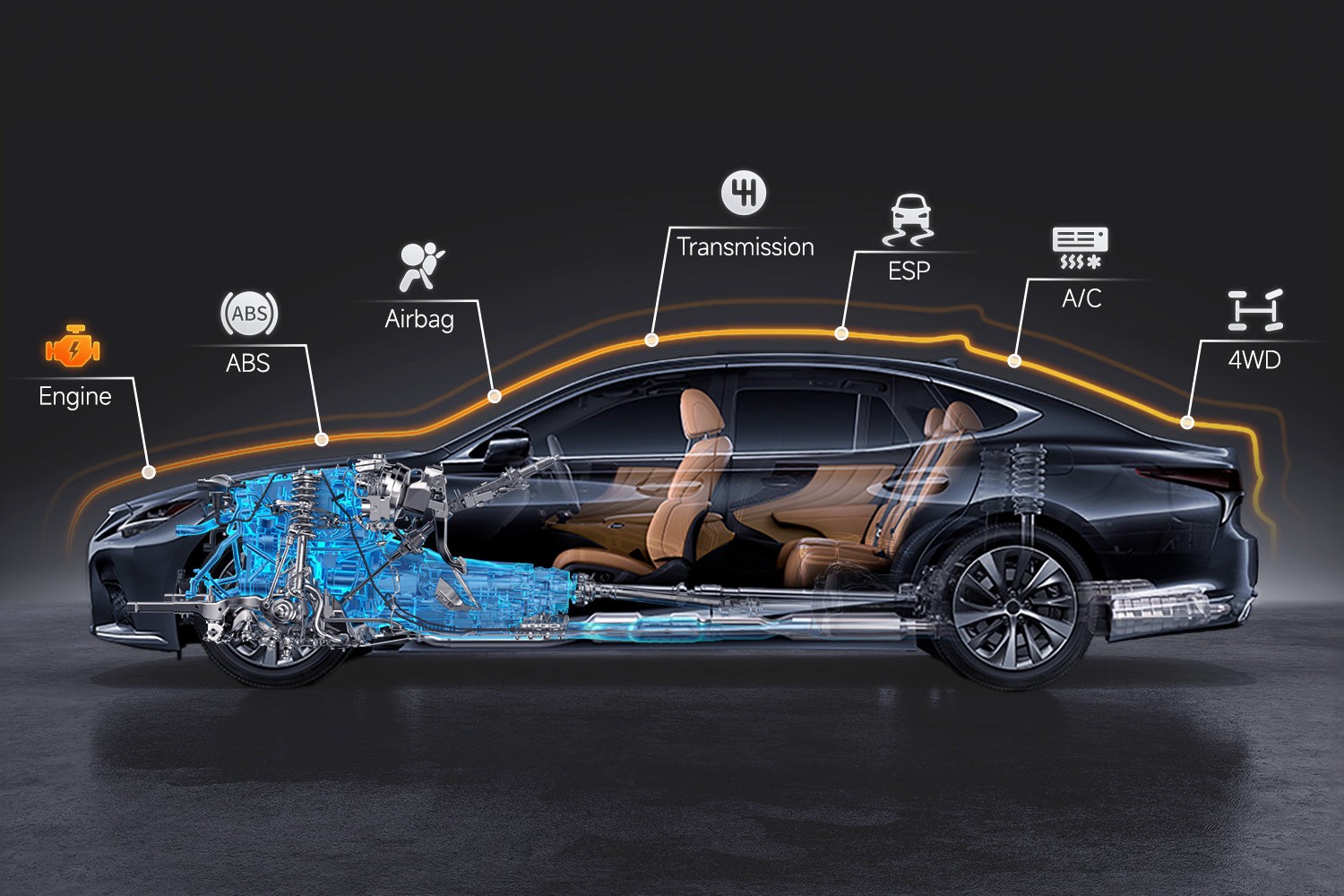
3. Understanding OBD2 Codes and Their Meanings
OBD2 codes are standardized codes used to diagnose issues within a vehicle. These codes provide valuable information about the nature and location of a problem.
3.1. Common OBD2 Code Categories
OBD2 codes are categorized to help identify the specific system or component that is experiencing an issue. The main categories include:
- P0XXX: Powertrain Codes (Engine and Transmission)
- P1XXX: Manufacturer-Specific Powertrain Codes
- B0XXX: Body Codes (e.g., Airbags, Central Locking)
- C0XXX: Chassis Codes (e.g., ABS, Traction Control)
- U0XXX: Network Communication Codes
3.2. Example of Common OBD2 Codes
Here is a table with common OBD2 codes, their descriptions, and potential causes:
| Code | Description | Possible Causes |
|---|---|---|
| P0171 | System Too Lean (Bank 1) | Vacuum leak, faulty oxygen sensor, dirty mass airflow sensor |
| P0300 | Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected | Faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, fuel injectors |
| P0420 | Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1) | Failing catalytic converter, exhaust leaks, faulty oxygen sensors |
| P0401 | Exhaust Gas Recirculation Flow Insufficient Detected | Clogged EGR valve, faulty EGR sensor, vacuum leaks |
| P0113 | Intake Air Temperature Sensor Circuit High Input | Faulty IAT sensor, wiring issues |
3.3. Importance of Proper Diagnosis
While resetting OBD2 codes can clear the check engine light, it is crucial to properly diagnose and address the underlying issue. Ignoring the root cause can lead to further damage and costly repairs. According to the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), accurate diagnosis requires a combination of technical knowledge, diagnostic tools, and systematic troubleshooting.
4. Potential Risks of Resetting Codes Without Addressing the Underlying Issue
Resetting OBD2 codes without addressing the underlying issue can lead to several risks:
- Recurring Problems: The check engine light will likely reappear if the underlying problem persists, causing repeated inconvenience.
- Further Damage: Ignoring mechanical or electrical issues can cause further damage to the vehicle, leading to more expensive repairs in the long run.
- Safety Concerns: Some issues, such as brake problems or airbag malfunctions, can pose safety risks if not properly addressed.
- Failed Emissions Tests: The vehicle may fail emissions tests if the underlying issue affects emissions control systems.
- Voided Warranty: Repeatedly resetting codes without proper repairs can void the vehicle’s warranty, as manufacturers may view it as neglect.
5. The Role of OBD2 Scanners in Accurate Diagnostics
While alternative methods can reset OBD2 codes, OBD2 scanners are invaluable for accurate diagnostics. Scanners provide detailed information about the codes and allow for real-time monitoring of engine parameters.
5.1. Benefits of Using an OBD2 Scanner
- Detailed Code Information: Scanners provide specific information about the code, helping to pinpoint the exact problem.
- Real-Time Data: Scanners can monitor real-time engine parameters, such as temperature, pressure, and sensor readings, aiding in diagnosis.
- Advanced Diagnostics: Many scanners offer advanced diagnostic features, such as freeze frame data and live data graphing.
- User-Friendly Interface: Modern scanners come with user-friendly interfaces that make it easy to read and interpret data.
- Cost Savings: By accurately diagnosing issues, scanners can help prevent unnecessary repairs and save money in the long run.
5.2. Types of OBD2 Scanners
There are several types of OBD2 scanners available, ranging from basic code readers to professional-grade diagnostic tools:
- Basic Code Readers: These are simple, low-cost devices that read and clear OBD2 codes.
- Mid-Range Scanners: These scanners offer additional features such as live data monitoring and freeze frame data.
- Professional-Grade Scanners: These are advanced diagnostic tools used by mechanics and technicians. They offer comprehensive diagnostic capabilities, including advanced coding and programming functions.
- Wireless Scanners: These scanners connect to smartphones or tablets via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi, offering convenient diagnostics on the go.
5.3. Choosing the Right Scanner for Your Needs
Selecting the right OBD2 scanner depends on your needs and budget. For basic code reading and clearing, a simple code reader may suffice. However, for more advanced diagnostics and real-time data monitoring, a mid-range or professional-grade scanner may be necessary. Consider factors such as compatibility, features, ease of use, and price when making your decision.
6. Maintaining Your Vehicle After Clearing OBD2 Codes
After clearing OBD2 codes, proper maintenance is crucial to prevent future issues. Regular maintenance can extend the life of your vehicle and ensure optimal performance.
6.1. Regular Maintenance Tasks
- Oil Changes: Regular oil changes keep the engine lubricated and prevent wear.
- Fluid Checks: Check and top off fluids such as coolant, brake fluid, and power steering fluid regularly.
- Tire Maintenance: Ensure tires are properly inflated and rotated to prevent uneven wear.
- Brake Inspections: Inspect brake pads and rotors regularly to ensure safe braking performance.
- Tune-Ups: Perform regular tune-ups, including spark plug replacement and air filter changes, to keep the engine running smoothly.
6.2. Importance of Routine Inspections
Routine inspections can help identify potential problems before they become major issues. Schedule regular inspections with a qualified mechanic to check the vehicle’s systems and components.
6.3. Keeping Accurate Records
Maintaining accurate records of maintenance and repairs can help track the vehicle’s history and identify recurring issues. Keep receipts, invoices, and maintenance logs organized for future reference.
7. When to Seek Professional Help
While many OBD2 code issues can be resolved with DIY methods, certain situations require professional help.
7.1. Complex Diagnostic Issues
If you are unable to diagnose the underlying issue or the check engine light continues to reappear, seek professional help. Complex diagnostic issues may require specialized tools and expertise.
7.2. Safety-Related Problems
Issues related to safety systems, such as brakes, airbags, or steering, should be addressed by a qualified mechanic. Do not attempt to repair these systems yourself, as improper repairs can pose safety risks.
7.3. Emission System Problems
Emission system problems can be complex and may require specialized diagnostic equipment. If you suspect an emission system issue, seek professional help to ensure proper diagnosis and repair.
8. Contact OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for Expert Assistance
While various methods exist to clear OBD2 codes, accurate diagnosis and proper repairs are essential for maintaining your vehicle’s health and safety. If you encounter complex diagnostic issues or need expert assistance, OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN is here to help.
8.1. Comprehensive Diagnostic Services
At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we offer comprehensive diagnostic services to accurately identify and address any issues with your vehicle. Our experienced technicians use state-of-the-art diagnostic tools to provide precise and reliable results.
8.2. Expert Repair Solutions
We provide expert repair solutions to address the underlying causes of OBD2 codes. Our skilled mechanics have the knowledge and expertise to perform a wide range of repairs, ensuring your vehicle is running smoothly and efficiently.
8.3. Contact Information and Location
- Address: 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
- Website: OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
Don’t wait until a minor issue becomes a major problem. Contact OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN today for expert diagnostics and reliable repair solutions. Let us help you keep your vehicle running at its best.
9. FAQs About Clearing OBD2 Codes Without a Scanner
9.1. Can I reset my car’s check engine light without a scanner?
Yes, you can reset the check engine light by disconnecting the car battery for a few minutes, removing the ECU fuse, or performing a drive cycle. However, these methods may not address the underlying issue causing the light.
9.2. Will resetting codes without a scanner affect my car’s performance?
Resetting codes typically does not affect performance if the underlying issue is resolved. However, if the problem persists, the check engine light will likely reappear, and performance may be affected.
9.3. How long does it take to reset car codes without a scanner?
It usually takes around 15-30 minutes to reset the codes without a scanner, depending on the method used. Disconnecting the battery or removing the ECU fuse requires waiting for a period to allow the system to reset.
9.4. Is it safe to disconnect the car battery to reset OBD2 codes?
Disconnecting the car battery is generally safe, but it can reset other electronic systems, such as the radio and clock. Ensure you know the potential consequences and have the necessary information to reset these systems.
9.5. Can a drive cycle clear all types of OBD2 codes?
A drive cycle is most effective for clearing emissions-related codes. Other types of codes may require different diagnostic and repair procedures.
9.6. What is the best app to use with a Bluetooth OBD2 adapter?
Popular apps include Torque (for Android) and OBD Fusion (for iOS). These apps offer a user-friendly interface and a range of diagnostic features.
9.7. How do I find the ECU fuse in my car’s fuse box?
Consult your car’s manual for the fuse box diagram. The diagram will identify the location of the ECU fuse.
9.8. What should I do if the check engine light comes back on after resetting it?
If the check engine light reappears, it indicates that the underlying issue has not been resolved. Seek professional help for accurate diagnosis and repair.
9.9. Can resetting OBD2 codes help me pass an emissions test?
Resetting OBD2 codes can help you pass an emissions test if the underlying issues have been resolved. However, if the issues persist, the vehicle will likely fail the test.
9.10. Are there any risks to resetting OBD2 codes without fixing the problem?
Yes, there are risks. The check engine light will likely reappear, and ignoring the underlying issue can lead to further damage, safety concerns, and failed emissions tests.