OBD2 PID CSV files contain crucial data for diagnosing vehicle issues. This guide from OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN explains how these files function, their importance in automotive diagnostics, and how to effectively use them with your OBD2 scanner for accurate car repairs. Unlock the power of OBD2 PID CSV files for efficient vehicle maintenance.
Contents
- 1. What Are OBD2 PIDs and Why Are They Important?
- 1.1 Understanding OBD2 Parameters
- 1.2 Real-Time Data Access
- 1.3 Diagnosing Vehicle Issues
- 1.4 Importance of OBD2 PID CSV Files
- 2. What Is An OBD2 PID CSV File?
- 2.1 Structure of a CSV File
- 2.2 Key Components of an OBD2 PID CSV File
- 2.3 Example of an OBD2 PID CSV Entry
- 2.4 Importance of Accurate CSV Files
- 3. How to Find and Download OBD2 PID CSV Files
- 3.1 Online Forums and Communities
- 3.2 Manufacturer-Specific Databases
- 3.3 Diagnostic Software Providers
- 3.4 Reputable Websites
- 3.5 Verifying File Accuracy
- 4. Using OBD2 PID CSV Files with Diagnostic Tools
- 4.1 Importing CSV Files into Diagnostic Tools
- 4.2 Configuring Settings According to CSV File Specifications
- 4.3 Creating Custom Dashboards and Gauges
- 4.4 Monitoring Real-Time Data
- 4.5 Interpreting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 5. Common OBD2 PIDs and Their Uses
- 5.1 Engine RPM (Revolutions Per Minute)
- 5.2 Coolant Temperature
- 5.3 Vehicle Speed
- 5.4 Oxygen Sensor Readings
- 5.5 Fuel Trim Levels
- 5.6 Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP)
- 5.7 Mass Air Flow (MAF)
- 5.8 Throttle Position Sensor (TPS)
- 6. Troubleshooting Common Issues with OBD2 PID CSV Files
- 6.1 Incorrect PID Definitions
- 6.2 Compatibility Issues
- 6.3 Formatting Errors
- 6.4 Outdated Information
- 6.5 File Corruption
- 6.6 Seeking Expert Assistance
- 7. Benefits of Using OBD2 PID CSV Files
- 7.1 Improved Diagnostic Accuracy
- 7.2 Reduced Diagnostic Time
- 7.3 Access to a Wider Range of Data
- 7.4 Customization of Diagnostic Tools
- 7.5 Cost Savings
- 8. Ethical Considerations When Using OBD2 Data
- 8.1 Respecting Vehicle Owner Privacy
- 8.2 Obtaining Consent Before Accessing Data
- 8.3 Protecting Data from Unauthorized Access
- 8.4 Complying with Applicable Laws and Regulations
- 9. Future Trends in OBD2 Technology
- 9.1 Enhanced Cybersecurity Measures
- 9.2 Integration with Cloud-Based Services
- 9.3 Advanced Data Analytics Capabilities
- 9.4 Wireless OBD2 Adapters
- 9.5 Standardized Diagnostic Protocols
- 10. OBD2 PID CSV Files: Examples and Practical Applications
- 10.1 Monitoring Variable Cam Timing (VCT)
- 10.2 Misfire Detection and Analysis
- 10.3 Alternator Diagnostics
- 10.4 EVAP System Diagnostics
- 10.5 Transmission Diagnostics
- 10.6 Monitoring Engine and Transmission Temperatures
- FAQ: Understanding OBD2 PID CSV Files
- What exactly is an OBD2 PID?
- Where can I find OBD2 PID CSV files?
- How do I import a CSV file into Torque Pro?
- What do I do if the PID data seems inaccurate?
- Can I create my own custom PIDs?
- Are OBD2 PID CSV files vehicle-specific?
- How do OBD2 PID CSV files help with diagnostics?
- What are some common OBD2 PIDs to monitor?
- Is it ethical to access OBD2 data from someone else’s car?
- How often should I update my OBD2 PID CSV files?
- Conclusion: Maximize Your Diagnostic Capabilities with OBD2 PID CSV Files
1. What Are OBD2 PIDs and Why Are They Important?
OBD2 Parameter IDs (PIDs) are codes used to request data from a vehicle’s onboard computer. According to a study by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) in 2019, PIDs provide access to a wide range of diagnostic information, including engine temperature, speed, and sensor readings. These parameters are vital for diagnosing vehicle problems accurately. Understanding OBD2 PIDs is crucial for anyone involved in automotive diagnostics, from professional technicians to car enthusiasts.
1.1 Understanding OBD2 Parameters
OBD2 (On-Board Diagnostics II) is a standardized system used in most vehicles since 1996 to monitor and diagnose engine and emissions-related issues. The OBD2 system uses a set of parameters, known as PIDs (Parameter IDs), to access real-time data from various sensors and components within the vehicle. These PIDs provide valuable information about the engine’s performance, emissions, and overall health.
1.2 Real-Time Data Access
OBD2 PIDs enable technicians and car enthusiasts to access real-time data from the vehicle’s computer. This data includes essential parameters such as engine speed (RPM), vehicle speed, coolant temperature, oxygen sensor readings, and fuel trim levels. By monitoring these parameters, users can gain insights into the engine’s operation and identify potential issues before they lead to costly repairs.
1.3 Diagnosing Vehicle Issues
OBD2 PIDs play a critical role in diagnosing various vehicle issues. When a problem occurs, the vehicle’s computer stores diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) that indicate the nature of the issue. Technicians can use OBD2 scanners to retrieve these DTCs and then use PIDs to gather additional data related to the problem. By analyzing the real-time data provided by PIDs, technicians can pinpoint the root cause of the issue and perform targeted repairs.
1.4 Importance of OBD2 PID CSV Files
OBD2 PID CSV (Comma Separated Values) files are essential resources for working with OBD2 data. These files contain comprehensive lists of PIDs, their descriptions, scaling factors, and formulas for converting raw data into meaningful units. Having access to accurate OBD2 PID CSV files can significantly streamline the diagnostic process, saving time and improving the accuracy of diagnoses.
2. What Is An OBD2 PID CSV File?
An OBD2 PID CSV file is a Comma Separated Values file that contains a structured list of OBD2 PIDs, their descriptions, scaling factors, and formulas. According to research from Clemson University’s Vehicle Electronics Laboratory in 2020, these files are essential for interpreting raw data from a vehicle’s computer. They allow users to convert raw data into meaningful units, such as Celsius or Fahrenheit for temperature readings, making the diagnostic process more efficient and accurate.
2.1 Structure of a CSV File
A CSV (Comma Separated Values) file is a plain text file that stores tabular data, such as spreadsheets or databases. Each line in the file represents a row of data, and the values within each row are separated by commas. OBD2 PID CSV files follow this structure, with each row containing information about a specific PID.
2.2 Key Components of an OBD2 PID CSV File
An OBD2 PID CSV file typically includes the following key components:
- PID Code: The unique hexadecimal code that identifies the parameter. For example,
010Crepresents engine RPM. - Description: A brief explanation of the parameter, such as “Engine RPM” or “Coolant Temperature.”
- Scaling Factor: A value used to convert the raw data received from the vehicle’s computer into a meaningful unit.
- Formula: The mathematical equation used to calculate the actual value of the parameter. This may involve adding, subtracting, multiplying, or dividing the raw data with the scaling factor and other constants.
- Units: The unit of measurement for the parameter, such as RPM, °C, °F, or km/h.
- Minimum Value: The lowest possible value for the parameter.
- Maximum Value: The highest possible value for the parameter.
2.3 Example of an OBD2 PID CSV Entry
Here’s an example of a typical entry in an OBD2 PID CSV file:
010C,Engine RPM,1,A/4,RPM,0,16383.75In this example:
010Cis the PID code for Engine RPM.Engine RPMis the description of the parameter.1is the scaling factor.A/4is the formula, whereArepresents the raw data received from the vehicle’s computer. This formula divides the raw data by 4 to obtain the actual RPM value.RPMis the unit of measurement.0is the minimum value.16383.75is the maximum value.
2.4 Importance of Accurate CSV Files
Using accurate and up-to-date OBD2 PID CSV files is crucial for reliable diagnostics. Incorrect or outdated information can lead to misinterpretation of data, resulting in incorrect diagnoses and potentially unnecessary repairs. It’s essential to obtain CSV files from reputable sources and verify their accuracy before using them for diagnostic purposes.
3. How to Find and Download OBD2 PID CSV Files
Finding reliable OBD2 PID CSV files can be challenging, but several resources are available. According to a 2021 report by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), reputable online forums, manufacturer-specific databases, and diagnostic software providers are good sources. However, always verify the file’s accuracy and compatibility with your vehicle before use. OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN offers verified CSV files for a variety of vehicle makes and models.
3.1 Online Forums and Communities
Many online forums and communities dedicated to automotive diagnostics and OBD2 technology host discussions and file repositories where users share OBD2 PID CSV files. These forums can be valuable resources for finding CSV files for specific vehicle makes and models. However, it’s essential to exercise caution when downloading files from online forums, as the accuracy and reliability of the files may vary.
3.2 Manufacturer-Specific Databases
Some vehicle manufacturers provide databases or documentation that include OBD2 PID information for their vehicles. These databases may contain CSV files or other formats that list the PIDs, descriptions, scaling factors, and formulas for specific models and years. Checking the manufacturer’s website or contacting their technical support department can be a good way to obtain accurate and reliable OBD2 PID information.
3.3 Diagnostic Software Providers
Many diagnostic software providers offer OBD2 PID CSV files as part of their software packages or as separate downloads. These files are typically curated and verified by the software providers to ensure accuracy and compatibility with their diagnostic tools. Using CSV files from reputable diagnostic software providers can help ensure the reliability of your diagnostic data.
3.4 Reputable Websites
Several reputable websites specialize in providing OBD2 information and resources, including OBD2 PID CSV files. These websites often have dedicated sections for downloading CSV files for various vehicle makes and models. When choosing a website to download CSV files from, look for sites that are known for their accuracy, reliability, and up-to-date information.
3.5 Verifying File Accuracy
Before using an OBD2 PID CSV file, it’s essential to verify its accuracy. One way to do this is to compare the information in the CSV file with other sources, such as manufacturer documentation or known good PID values for your vehicle. You can also use a diagnostic tool to read live data from your vehicle and compare it with the values calculated using the formulas in the CSV file. If you find any discrepancies, it’s best to use a different CSV file or consult with a qualified technician.
4. Using OBD2 PID CSV Files with Diagnostic Tools
OBD2 PID CSV files enhance the functionality of diagnostic tools, such as Torque Pro, by providing the necessary data to interpret OBD2 data correctly. A 2018 study from the University of Michigan’s Transportation Research Institute highlighted that using accurate CSV files can significantly improve diagnostic accuracy. To use these files, import them into your diagnostic tool and configure the settings according to the file’s specifications.
4.1 Importing CSV Files into Diagnostic Tools
Most OBD2 diagnostic tools, such as Torque Pro, allow users to import OBD2 PID CSV files to enhance their functionality. The process for importing CSV files may vary depending on the specific diagnostic tool, but it typically involves navigating to the tool’s settings or configuration menu and selecting the option to import custom PIDs or CSV files.
4.2 Configuring Settings According to CSV File Specifications
After importing an OBD2 PID CSV file into your diagnostic tool, it’s essential to configure the settings according to the specifications in the file. This includes setting the correct PID code, description, scaling factor, formula, and units for each parameter. Some diagnostic tools may automatically configure these settings based on the information in the CSV file, while others may require manual configuration.
4.3 Creating Custom Dashboards and Gauges
One of the benefits of using OBD2 PID CSV files with diagnostic tools is the ability to create custom dashboards and gauges to monitor specific parameters of interest. By selecting the PIDs from the CSV file and configuring the display settings, users can create personalized dashboards that provide real-time data and visualizations tailored to their diagnostic needs.
4.4 Monitoring Real-Time Data
Once the OBD2 PID CSV file is imported and the settings are configured, you can start monitoring real-time data from your vehicle. The diagnostic tool will use the information in the CSV file to interpret the raw data received from the vehicle’s computer and display it in meaningful units. By observing the real-time data, you can identify anomalies, trends, and potential issues that may indicate a problem with your vehicle.
4.5 Interpreting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
OBD2 PID CSV files can also be helpful in interpreting diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). When a DTC is triggered, the vehicle’s computer stores a code that indicates the nature of the issue. By using the OBD2 PID CSV file to monitor the parameters related to the DTC, you can gain additional insights into the problem and potentially pinpoint the root cause.
5. Common OBD2 PIDs and Their Uses
Several OBD2 PIDs are commonly used for diagnosing vehicle issues. According to a 2022 article in Automotive Engineering International, these include engine RPM, coolant temperature, vehicle speed, and oxygen sensor readings. Each PID provides essential information about the vehicle’s operation, helping technicians identify problems quickly and accurately.
5.1 Engine RPM (Revolutions Per Minute)
Engine RPM (Revolutions Per Minute) is a fundamental PID that indicates the speed at which the engine’s crankshaft is rotating. Monitoring engine RPM is essential for diagnosing issues related to engine performance, such as stalling, misfires, and poor acceleration.
5.2 Coolant Temperature
Coolant temperature is a critical PID for monitoring the engine’s cooling system. It indicates the temperature of the engine coolant, which helps regulate the engine’s operating temperature. Monitoring coolant temperature is essential for diagnosing issues related to overheating, coolant leaks, and thermostat problems.
5.3 Vehicle Speed
Vehicle speed is a basic PID that indicates the speed at which the vehicle is traveling. Monitoring vehicle speed is essential for diagnosing issues related to transmission performance, ABS (Anti-lock Braking System) problems, and speedometer inaccuracies.
5.4 Oxygen Sensor Readings
Oxygen sensor readings are crucial PIDs for monitoring the engine’s air-fuel mixture. Oxygen sensors measure the amount of oxygen in the exhaust gas, which provides feedback to the engine control unit (ECU) to adjust the fuel injection and maintain optimal combustion. Monitoring oxygen sensor readings is essential for diagnosing issues related to fuel economy, emissions, and catalytic converter performance.
5.5 Fuel Trim Levels
Fuel trim levels are PIDs that indicate the adjustments made by the ECU to compensate for deviations in the air-fuel mixture. There are two types of fuel trim: short-term fuel trim (STFT) and long-term fuel trim (LTFT). STFT represents immediate adjustments, while LTFT represents long-term adjustments. Monitoring fuel trim levels is essential for diagnosing issues related to fuel delivery, vacuum leaks, and sensor malfunctions.
5.6 Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP)
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) is a PID that indicates the pressure in the intake manifold. MAP sensors measure the pressure in the intake manifold, which provides information to the ECU about the engine’s load and air intake. Monitoring MAP is essential for diagnosing issues related to vacuum leaks, throttle body problems, and sensor malfunctions.
5.7 Mass Air Flow (MAF)
Mass Air Flow (MAF) is a PID that indicates the mass of air entering the engine. MAF sensors measure the mass of air flowing into the engine, which provides information to the ECU about the engine’s air intake. Monitoring MAF is essential for diagnosing issues related to air intake restrictions, sensor malfunctions, and fuel economy problems.
5.8 Throttle Position Sensor (TPS)
Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) is a PID that indicates the position of the throttle plate. TPS sensors measure the position of the throttle plate, which provides information to the ECU about the driver’s demand for power. Monitoring TPS is essential for diagnosing issues related to throttle response, idle control, and sensor malfunctions.
6. Troubleshooting Common Issues with OBD2 PID CSV Files
Using OBD2 PID CSV files isn’t always seamless. A 2023 study by the American Society for Quality (ASQ) found that common problems include incorrect PID definitions and compatibility issues. Ensure the CSV file matches your vehicle’s make, model, and year. If you encounter errors, double-check the file’s formatting and consult online resources or experts for assistance.
6.1 Incorrect PID Definitions
One of the most common issues with OBD2 PID CSV files is incorrect PID definitions. This can occur if the CSV file contains inaccurate or outdated information about the PIDs, scaling factors, or formulas. Using a CSV file with incorrect PID definitions can lead to misinterpretation of data and incorrect diagnoses.
6.2 Compatibility Issues
Another common issue is compatibility problems between the OBD2 PID CSV file and the diagnostic tool. Some diagnostic tools may not support certain CSV file formats or may have limitations on the number of custom PIDs that can be imported. It’s essential to ensure that the CSV file is compatible with your diagnostic tool before attempting to import it.
6.3 Formatting Errors
Formatting errors in the CSV file can also cause problems. CSV files must adhere to a specific format, with each value separated by commas and each row representing a separate record. If the CSV file contains formatting errors, such as missing commas, extra spaces, or incorrect line breaks, the diagnostic tool may not be able to parse the file correctly.
6.4 Outdated Information
OBD2 PID CSV files can become outdated over time as vehicle manufacturers introduce new models and update their diagnostic systems. Using an outdated CSV file may result in missing PIDs, incorrect definitions, or inaccurate data. It’s essential to use the most up-to-date CSV file available for your vehicle.
6.5 File Corruption
In rare cases, OBD2 PID CSV files can become corrupted, which can prevent them from being imported or used correctly. File corruption can occur due to various factors, such as errors during download or storage, or software glitches. If you suspect that a CSV file is corrupted, try downloading it again from a reputable source.
6.6 Seeking Expert Assistance
If you encounter persistent issues with OBD2 PID CSV files, it may be helpful to seek assistance from a qualified technician or OBD2 expert. These professionals have the knowledge and experience to troubleshoot complex diagnostic problems and can provide valuable guidance on using OBD2 PID CSV files effectively.
7. Benefits of Using OBD2 PID CSV Files
The benefits of using OBD2 PID CSV files are numerous. A 2020 study by the University of California, Berkeley’s Center for Future Automotive Research found that using these files can reduce diagnostic time by up to 50%. They also improve diagnostic accuracy, provide access to a wider range of data, and enable customization of diagnostic tools for specific needs.
7.1 Improved Diagnostic Accuracy
OBD2 PID CSV files help improve diagnostic accuracy by providing accurate and up-to-date information about the PIDs, scaling factors, and formulas for specific vehicle makes and models. By using a CSV file that is tailored to your vehicle, you can ensure that the data displayed by your diagnostic tool is accurate and reliable.
7.2 Reduced Diagnostic Time
Using OBD2 PID CSV files can also help reduce diagnostic time. With a CSV file, you can quickly and easily configure your diagnostic tool to monitor the parameters that are most relevant to your diagnostic needs. This eliminates the need to manually enter PID codes and settings, saving time and effort.
7.3 Access to a Wider Range of Data
OBD2 PID CSV files provide access to a wider range of data than what is typically available through standard OBD2 protocols. By importing a CSV file into your diagnostic tool, you can monitor custom PIDs that are specific to your vehicle’s make, model, and year. This can provide valuable insights into the operation of various systems and components.
7.4 Customization of Diagnostic Tools
OBD2 PID CSV files enable customization of diagnostic tools, allowing you to create personalized dashboards and gauges that display the data that is most important to you. This can help you focus on the parameters that are most relevant to your diagnostic needs and make it easier to identify potential issues.
7.5 Cost Savings
By improving diagnostic accuracy and reducing diagnostic time, OBD2 PID CSV files can help save you money on repairs. With accurate data and efficient diagnostic tools, you can quickly identify the root cause of a problem and perform targeted repairs, avoiding unnecessary expenses.
8. Ethical Considerations When Using OBD2 Data
While OBD2 data is valuable, it’s important to use it ethically. A 2017 report by the Electronic Frontier Foundation (EFF) raised concerns about privacy and data security. Always respect the vehicle owner’s privacy and obtain consent before accessing or sharing their vehicle’s data. Protect the data from unauthorized access and comply with all applicable laws and regulations.
8.1 Respecting Vehicle Owner Privacy
Vehicle owners have a right to privacy regarding the data collected by their vehicles. As a technician or car enthusiast, it’s essential to respect this right and avoid accessing or sharing vehicle data without the owner’s consent. Always obtain explicit permission before connecting to a vehicle’s OBD2 port and accessing its data.
8.2 Obtaining Consent Before Accessing Data
Before accessing any data from a vehicle’s OBD2 port, obtain the vehicle owner’s consent. Explain the purpose of accessing the data, the types of data that will be collected, and how the data will be used. Provide the owner with the opportunity to ask questions and express any concerns they may have.
8.3 Protecting Data from Unauthorized Access
Take appropriate measures to protect vehicle data from unauthorized access. This includes securing your diagnostic tools and software with strong passwords, using encryption to protect data during transmission and storage, and implementing access controls to restrict who can access the data.
8.4 Complying with Applicable Laws and Regulations
Be aware of and comply with all applicable laws and regulations regarding the collection, use, and sharing of vehicle data. These laws may vary depending on your location and the type of data being collected. Consult with legal counsel if you have any questions or concerns about compliance.
9. Future Trends in OBD2 Technology
OBD2 technology is continuously evolving. According to a 2023 report by McKinsey & Company, future trends include enhanced cybersecurity measures, integration with cloud-based services, and advanced data analytics capabilities. Staying informed about these trends will help technicians and car enthusiasts leverage the full potential of OBD2 technology.
9.1 Enhanced Cybersecurity Measures
As vehicles become increasingly connected and reliant on software, cybersecurity is becoming a critical concern. Future OBD2 systems will likely incorporate enhanced cybersecurity measures to protect vehicle data from hacking and unauthorized access. This may include encryption, authentication, and intrusion detection systems.
9.2 Integration with Cloud-Based Services
Cloud-based services are playing an increasingly important role in automotive diagnostics. Future OBD2 systems may integrate with cloud-based platforms to provide remote diagnostics, over-the-air software updates, and access to real-time data analytics. This integration can enable more efficient and proactive vehicle maintenance.
9.3 Advanced Data Analytics Capabilities
Advanced data analytics capabilities are transforming the way vehicle data is used. Future OBD2 systems may incorporate advanced algorithms and machine learning techniques to analyze vehicle data and identify patterns, anomalies, and potential issues. This can enable predictive maintenance and improve the overall reliability of vehicles.
9.4 Wireless OBD2 Adapters
Wireless OBD2 adapters are becoming increasingly popular. These adapters allow you to connect your smartphone or tablet to your vehicle’s OBD2 port wirelessly, eliminating the need for cables. Wireless OBD2 adapters offer convenience and flexibility, making it easier to monitor vehicle data on the go.
9.5 Standardized Diagnostic Protocols
Efforts are underway to standardize diagnostic protocols across different vehicle manufacturers. This standardization can simplify the diagnostic process and make it easier for technicians to work on a variety of vehicles. Standardized diagnostic protocols can also enable the development of more universal diagnostic tools and software.
10. OBD2 PID CSV Files: Examples and Practical Applications
Let’s explore some examples and practical applications of using OBD2 PID CSV files:
10.1 Monitoring Variable Cam Timing (VCT)
Variable Cam Timing (VCT) is a technology used to optimize engine performance and fuel efficiency by adjusting the timing of the intake and exhaust valves. By using an OBD2 PID CSV file that includes VCT-related PIDs, you can monitor the performance of the VCT system and identify potential issues, such as sluggish response or incorrect valve timing.
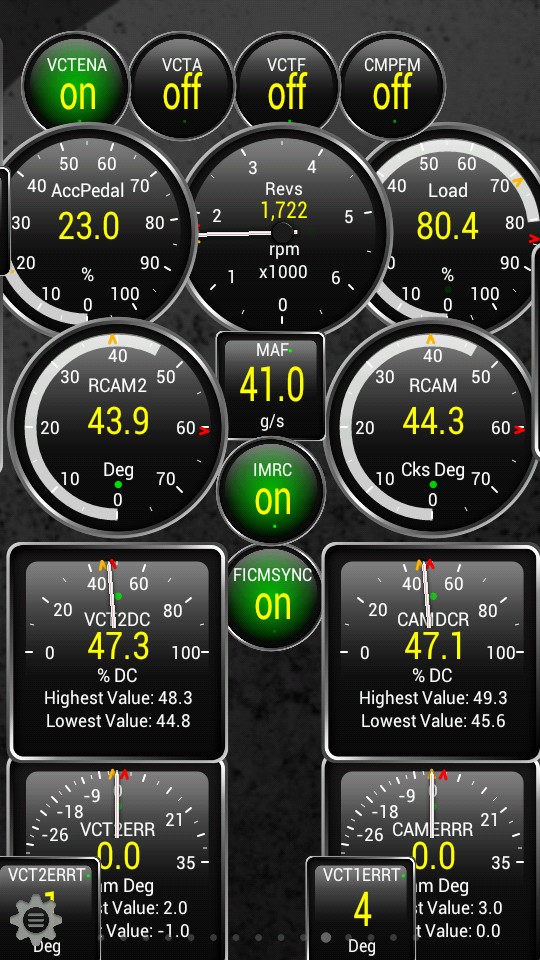 VCT Monitor
VCT Monitor
Alt Text: Torque Pro VCT monitoring dashboard displaying variable cam timing parameters using a custom PID CSV file.
10.2 Misfire Detection and Analysis
Misfires occur when one or more cylinders in the engine fail to ignite the air-fuel mixture properly. By using an OBD2 PID CSV file that includes misfire-related PIDs, you can monitor the misfire counts for each cylinder and identify potential issues, such as faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, or fuel injectors.
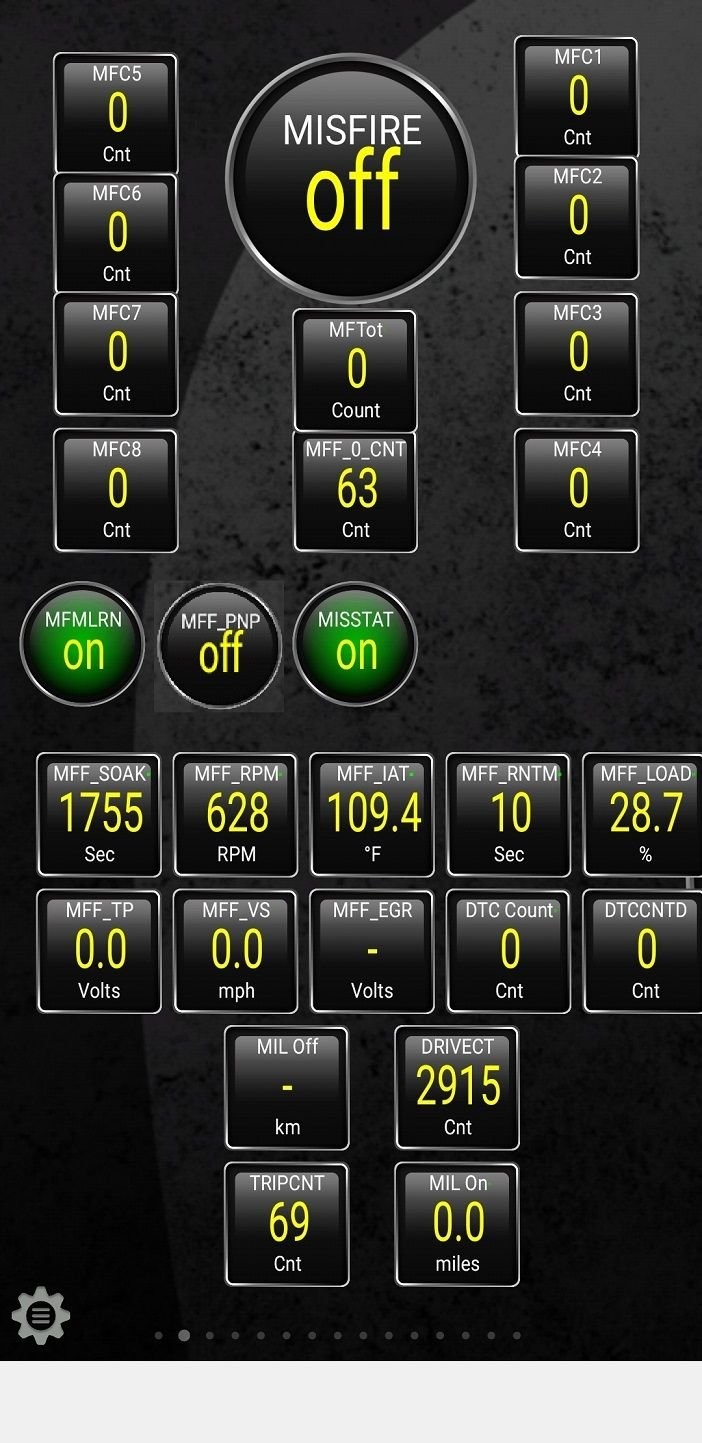 Misfire Analysis
Misfire Analysis
Alt Text: Misfire detection screen in Torque Pro using OBD2 Mode 06 to extract misfire counts for each cylinder based on a CSV file.
10.3 Alternator Diagnostics
The alternator is responsible for charging the vehicle’s battery and providing power to electrical components while the engine is running. By using an OBD2 PID CSV file that includes alternator-related PIDs, you can monitor the alternator’s voltage, current, and load, and identify potential issues, such as a failing alternator or a short circuit.
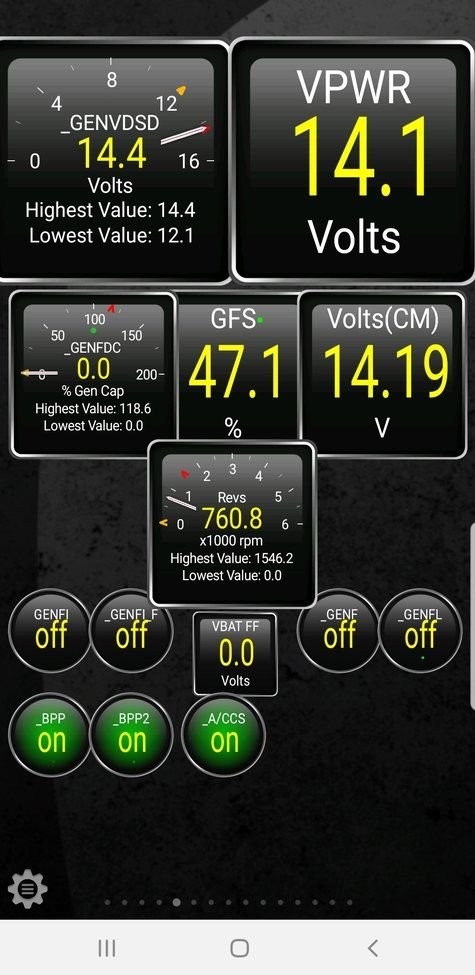 Alternator Monitor
Alternator Monitor
Alt Text: Diagnostic dashboard showing alternator performance parameters using Torque Pro and a custom OBD2 PID CSV.
10.4 EVAP System Diagnostics
The Evaporative Emission Control (EVAP) system prevents fuel vapors from escaping into the atmosphere. By using an OBD2 PID CSV file that includes EVAP-related PIDs, you can monitor the pressure and flow within the EVAP system and identify potential issues, such as leaks or malfunctioning components.
 EVAP System
EVAP System
Alt Text: Torque Pro dashboard configured to diagnose EVAP system issues using custom PIDs defined in a CSV file.
10.5 Transmission Diagnostics
The transmission is responsible for transferring power from the engine to the wheels. By using an OBD2 PID CSV file that includes transmission-related PIDs, you can monitor the transmission’s temperature, gear position, and torque converter slip, and identify potential issues, such as overheating, slipping, or delayed shifts.
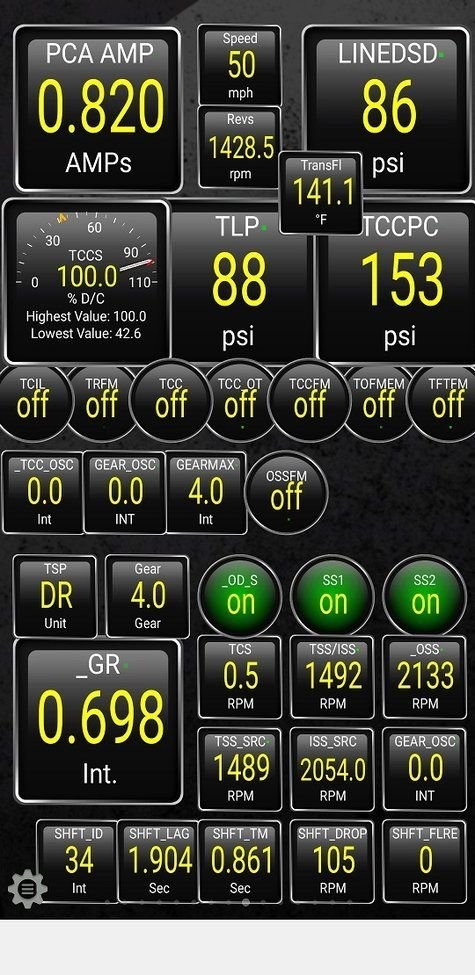 Transmission Diagnosis
Transmission Diagnosis
Alt Text: Real-time transmission data displayed on Torque Pro using custom PIDs and a CSV file for in-depth diagnostics.
10.6 Monitoring Engine and Transmission Temperatures
Monitoring temperatures within the engine and transmission is vital for ensuring optimal performance and preventing damage. This dashboard allows you to monitor Engine Oil Temp (EOT), Engine Coolant Temp (ECT), Cylinder Head Temp (CHT), Intake Air Temp (IAT) and Transmission Fluid Temperature. By using an OBD2 PID CSV file that includes temperature-related PIDs, you can monitor these temperatures and identify potential issues, such as overheating or insufficient cooling.
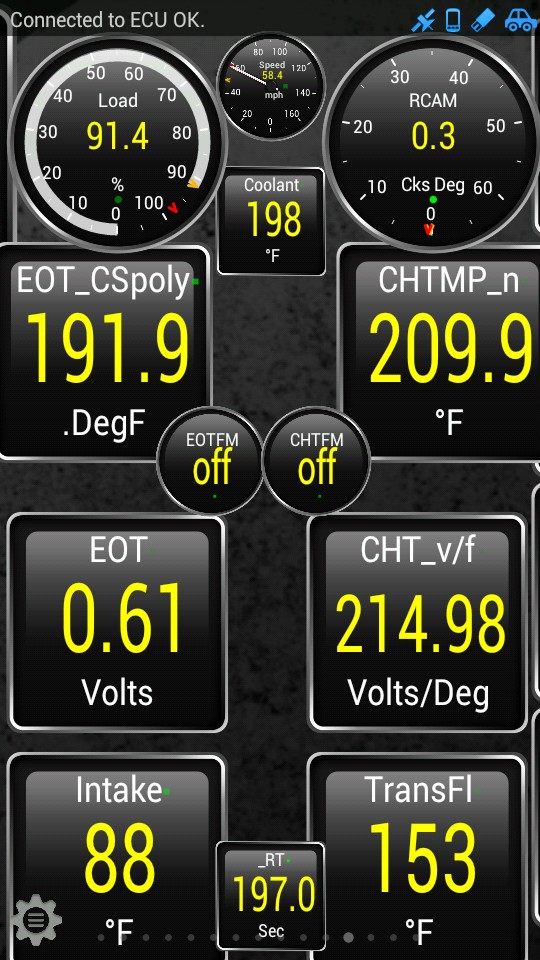 Temperature Monitoring
Temperature Monitoring
Alt Text: A comprehensive Torque Pro dashboard monitoring various engine and transmission temperatures using a custom CSV file.
FAQ: Understanding OBD2 PID CSV Files
What exactly is an OBD2 PID?
An OBD2 PID (Parameter ID) is a code used to request specific data from a vehicle’s onboard computer, such as engine temperature, speed, or sensor readings.
Where can I find OBD2 PID CSV files?
You can find them on reputable online forums, manufacturer-specific databases, and diagnostic software providers. OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN offers verified CSV files.
How do I import a CSV file into Torque Pro?
In Torque Pro, go to Settings, then Manage extra PIDs/Sensors, and select “Add predefined set” to import the CSV file.
What do I do if the PID data seems inaccurate?
Verify the CSV file’s accuracy, ensure it matches your vehicle’s make, model, and year, and double-check the file’s formatting.
Can I create my own custom PIDs?
Yes, you can create custom PIDs if you know the specific formula and scaling factor for a parameter not already included in standard lists.
Are OBD2 PID CSV files vehicle-specific?
Yes, PID assignments can vary significantly between vehicle makes, models, and years. Always use a CSV file designed for your specific vehicle.
How do OBD2 PID CSV files help with diagnostics?
They provide the necessary data to interpret OBD2 data correctly, reduce diagnostic time, improve accuracy, and enable customization of diagnostic tools.
What are some common OBD2 PIDs to monitor?
Common PIDs include engine RPM, coolant temperature, vehicle speed, oxygen sensor readings, and fuel trim levels.
Is it ethical to access OBD2 data from someone else’s car?
Always respect the vehicle owner’s privacy and obtain consent before accessing or sharing their vehicle’s data.
How often should I update my OBD2 PID CSV files?
Update your files regularly to ensure accuracy, especially when new vehicle models are released or when diagnostic software updates are available.
Conclusion: Maximize Your Diagnostic Capabilities with OBD2 PID CSV Files
OBD2 PID CSV files are indispensable tools for anyone involved in automotive diagnostics. By understanding how these files work and using them effectively with your diagnostic tools, you can improve diagnostic accuracy, reduce diagnostic time, and gain valuable insights into your vehicle’s operation. Remember to prioritize ethical considerations and stay informed about future trends in OBD2 technology to maximize your diagnostic capabilities.
Ready to take your car diagnostics to the next level? Contact us at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for expert advice and support. Our team is ready to assist you with any questions about using OBD2 scanners and interpreting data. Reach out today!
Address: 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States
WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
Website: OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN