Clearing OBD2 codes can be a simple task with the right tools and knowledge. OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN provides comprehensive guidance and tools to help you diagnose and resolve car issues efficiently. This guide will walk you through the process, ensuring you can confidently address check engine lights and other diagnostic alerts.
Contents
- 1. What Are OBD2 Codes and Why Clear Them?
- 2. Understanding the Check Engine Light
- 3. Essential Tools for Clearing OBD2 Codes
- 4. Step-by-Step Guide: How to Clear OBD2 Codes
- 4.1. Locate the OBD2 Port
- 4.2. Connect the OBD2 Scanner
- 4.3. Turn On the Ignition
- 4.4. Scan for Codes
- 4.5. Interpret the Codes
- 4.6. Address the Issue
- 4.7. Clear the Codes
- 4.8. Verify the Fix
- 4.9. Disconnect the Scanner
- 4.10. Turn Off the Ignition
- 4.11. Start the Engine and Check for Light
- 5. Common OBD2 Codes and Their Solutions
- 6. What to Do If the Check Engine Light Returns
- 7. Potential Problems and How to Avoid Them
- 8. OBD2 Scanner Recommendations
- 9. Advanced OBD2 Functions
- 10. The Future of OBD2 Technology
- 11. OBD2 and Emission Testing
- 12. Benefits of Using OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
- 13. Real-World Examples of Clearing OBD2 Codes
- 14. Maintaining Your Vehicle to Prevent OBD2 Codes
- 15. Contact OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for Assistance
- 16. Safety Precautions When Clearing OBD2 Codes
- 17. Understanding Vehicle Diagnostic Reports
- 18. The Role of OBD2 in Vehicle Performance
- 19. Tips for Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner
- 20. Clearing OBD2 Codes and DIY Car Repairs
- 21. How to Use an OBD2 Scanner to Improve Fuel Efficiency
- 22. The Importance of Regular Vehicle Inspections
- 23. The Future of Automotive Diagnostics
- 24. Troubleshooting Common OBD2 Scanner Issues
- 25. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques with OBD2 Scanners
- 26. Utilizing Online Resources for OBD2 Code Information
- 27. OBD2 Scanner Apps for Smartphones
- 28. Staying Updated with OBD2 Technology
- 29. Using OBD2 Scanners for Fleet Management
- 30. Final Thoughts: Mastering OBD2 Codes for Vehicle Health
- FAQ: Clearing OBD2 Codes
- What is an OBD2 scanner?
- How do I find the OBD2 port in my car?
- Can I clear OBD2 codes without a scanner?
- Will clearing OBD2 codes erase important data?
- How do I reset the readiness monitors after clearing OBD2 codes?
- What does it mean if the check engine light comes back on after clearing the codes?
- Is it safe to drive with the check engine light on?
- How do I interpret OBD2 codes?
- What are some common OBD2 codes?
- Where can I find more information about OBD2 technology?
1. What Are OBD2 Codes and Why Clear Them?
OBD2 (On-Board Diagnostics II) codes are standardized codes used to identify issues within your vehicle’s systems. Why should you clear these codes?
- To Reset the Check Engine Light: The most common reason is to turn off the check engine light after a repair.
- To Verify Repairs: Clearing the code and seeing if it returns confirms whether the issue has been resolved.
- To Prepare for Emission Tests: Some states require a “clean” OBD2 system (no recent codes) to pass emission tests.
According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), OBD2 systems were standardized in 1996 to monitor the performance of critical engine components and reduce emissions. Knowing how to manage these codes is essential for vehicle maintenance and compliance.
2. Understanding the Check Engine Light
The check engine light (CEL) can be both confusing and alarming. It indicates that your car’s onboard diagnostic system has detected a problem. The light doesn’t always mean a severe issue, but it should always be investigated. Clearing the OBD2 codes can help you determine if the problem is resolved after you’ve taken corrective action.
- Severity: The CEL can indicate anything from a loose gas cap to a major engine malfunction.
- Initial Steps: Before clearing codes, ensure you understand the underlying problem and have addressed it.
- Benefits: Clearing the code allows you to monitor if the issue recurs, helping you ensure the repair was effective.
3. Essential Tools for Clearing OBD2 Codes
To clear OBD2 codes, you’ll need the right tools. The most important of these is an OBD2 scanner.
- OBD2 Scanner: This device plugs into your car’s OBD2 port and allows you to read and clear diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
- Smartphone Apps: Many OBD2 scanners now connect to smartphones via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi, providing user-friendly interfaces and advanced features.
- Repair Manual: A repair manual specific to your vehicle can help you understand the meaning of specific codes and guide you through the repair process.
According to a study by Grand View Research, the global automotive diagnostic scan tools market is expected to grow significantly, reaching $9.1 billion by 2027. This growth underscores the importance of having the right tools for vehicle diagnostics and maintenance.
4. Step-by-Step Guide: How to Clear OBD2 Codes
Here’s a detailed guide on How To Clear Obd2 Codes using a scanner:
4.1. Locate the OBD2 Port
The OBD2 port is usually located under the dashboard on the driver’s side. Common locations include:
- Under the Steering Wheel: Often found near the center console.
- Near the Driver’s Knee: Sometimes located to the left of the steering column.
- Inside the Glove Compartment: Less common but still a possibility.
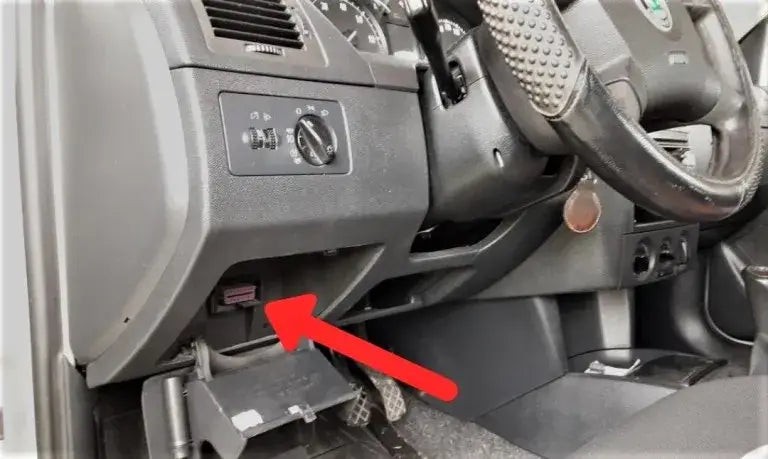 Locating the OBDII Port: Standard Location Under Dashboard
Locating the OBDII Port: Standard Location Under Dashboard
4.2. Connect the OBD2 Scanner
Plug the OBD2 scanner into the port. Ensure it’s securely connected.
- Check the Connection: The scanner should light up or indicate it’s receiving power.
- Troubleshooting: If the scanner doesn’t power on, check the port for any obstructions or damage.
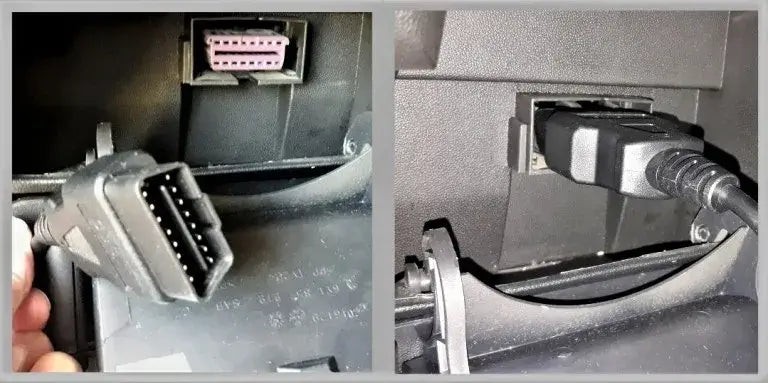 Connecting the OBD Code Reader: Secure Connection to Vehicle Port
Connecting the OBD Code Reader: Secure Connection to Vehicle Port
4.3. Turn On the Ignition
Turn the ignition to the “ON” position without starting the engine. This provides power to the car’s electrical systems, allowing the scanner to communicate with the computer.
- Key Position: Turn the key to the position just before starting the engine.
- Power Indication: Ensure that dashboard lights are on, indicating the system is powered.
 Turning On the Ignition: Powering Vehicle's Electrical System
Turning On the Ignition: Powering Vehicle's Electrical System
4.4. Scan for Codes
Follow the scanner’s instructions to initiate a scan. The scanner will retrieve any stored diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
- Menu Navigation: Use the scanner’s menu to select “Read Codes” or a similar option.
- Wait for Scan: Allow the scanner to complete the scan, which may take a few minutes.
 Scanning for Error Codes: OBDII Scan Tool Performing Diagnostics
Scanning for Error Codes: OBDII Scan Tool Performing Diagnostics
4.5. Interpret the Codes
Write down any codes you find. Use the scanner’s built-in database, a repair manual, or online resources to understand what each code means.
- Code Definitions: Common codes include P0300 (random misfire), P0171 (lean fuel mixture), and P0420 (catalyst system efficiency below threshold).
- Resource Utilization: Websites like OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN offer extensive databases to help you interpret codes accurately.
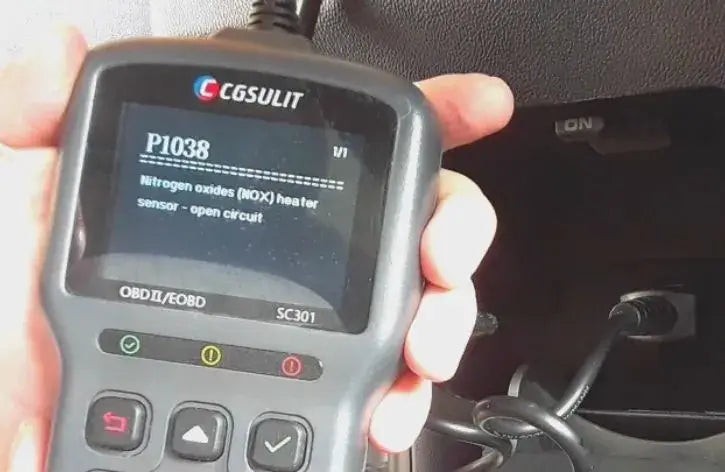 Reading Codes on OBD2 Reader: Interpreting Diagnostic Trouble Codes
Reading Codes on OBD2 Reader: Interpreting Diagnostic Trouble Codes
4.6. Address the Issue
Before clearing the codes, address the underlying problem. Clearing codes without fixing the issue will only result in the check engine light returning.
- Diagnostic Steps: Use the code information to diagnose the root cause.
- Repair or Replace: Perform necessary repairs, such as replacing a faulty sensor, fixing a vacuum leak, or replacing a worn-out component.
4.7. Clear the Codes
Navigate to the “Clear Codes” or “Erase Codes” option in the scanner’s menu. Confirm your selection when prompted.
- Confirmation Prompt: The scanner will ask you to confirm that you want to clear the codes.
- Post-Clearing: After clearing, the check engine light should turn off.
 Clearing Codes via DTC Library: Erasing Diagnostic Trouble Codes
Clearing Codes via DTC Library: Erasing Diagnostic Trouble Codes
4.8. Verify the Fix
Start the engine and drive the car. Monitor the check engine light to see if it returns.
- Driving Cycle: Complete a full driving cycle, which includes a mix of city and highway driving.
- Monitoring: Use the OBD2 scanner to monitor the car’s systems for any new or recurring codes.
4.9. Disconnect the Scanner
Once you’ve verified that the codes are cleared and the check engine light is off, disconnect the scanner.
- Proper Removal: Gently remove the scanner from the OBD2 port to avoid damaging the connector.
- Storage: Store the scanner in a safe place for future use.
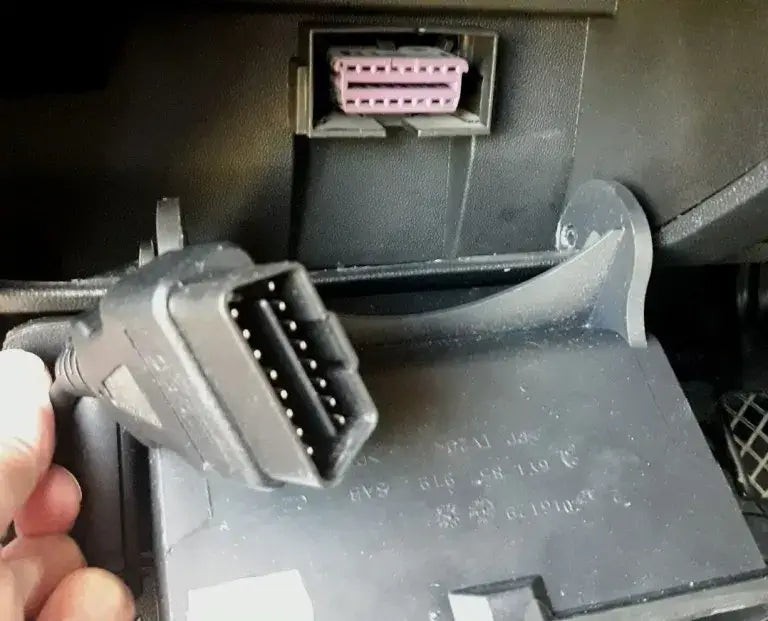 Disconnecting the OBD Code Reader: Safely Removing Scanner from Port
Disconnecting the OBD Code Reader: Safely Removing Scanner from Port
4.10. Turn Off the Ignition
Turn the ignition off after disconnecting the OBD2 scanner.
- Complete Shutdown: Ensure all systems are powered down.
- Final Check: Verify no warning lights remain on the dashboard.
 Turning Off the Ignition: Completing OBD2 Scan Process
Turning Off the Ignition: Completing OBD2 Scan Process
4.11. Start the Engine and Check for Light
Start the engine one last time to ensure the check engine light remains off. If the light stays off, you’ve successfully cleared the OBD2 codes and addressed the underlying issue.
- Final Verification: Confirm that the check engine light does not reappear after starting the engine.
- Continued Monitoring: Keep an eye on the dashboard for any future warning lights.
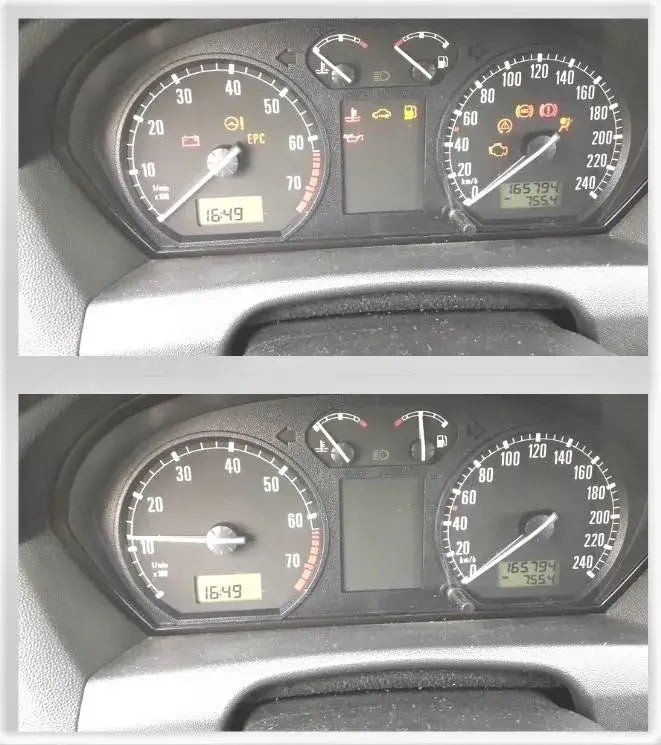 Starting Engine After Reset: Verifying Check Engine Light Is Off
Starting Engine After Reset: Verifying Check Engine Light Is Off
5. Common OBD2 Codes and Their Solutions
Here’s a table of common OBD2 codes, their meanings, and potential solutions:
| Code | Description | Possible Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| P0171 | System Too Lean (Bank 1) | Check for vacuum leaks, clean or replace MAF sensor, inspect fuel injectors, check fuel pump, replace oxygen sensor. |
| P0300 | Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected | Replace spark plugs, replace ignition coils, check for vacuum leaks, inspect fuel injectors, check compression. |
| P0420 | Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1) | Replace catalytic converter, check for exhaust leaks, replace oxygen sensors, inspect engine for misfires. |
| P0442 | Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (Small Leak) | Check gas cap, inspect EVAP hoses and canister, replace purge valve. |
| P0505 | Idle Air Control System Malfunction | Clean or replace idle air control valve, check for vacuum leaks, inspect throttle body. |
| P0113 | Intake Air Temperature Sensor Circuit High Input | Replace intake air temperature sensor, check wiring and connectors. |
| P0301 | Cylinder 1 Misfire Detected | Replace spark plug in cylinder 1, replace ignition coil in cylinder 1, check fuel injector in cylinder 1, check compression. |
| P0011 | “A” Camshaft Position – Timing Over-Advanced or System Performance (Bank 1) | Check oil level and condition, replace camshaft position sensor, inspect timing chain or belt, check for issues with variable valve timing (VVT) system. |
| P0102 | Mass or Volume Air Flow Circuit Low Input | Clean or replace mass air flow (MAF) sensor, check for vacuum leaks, inspect wiring and connectors. |
| P0135 | O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1, Sensor 1) | Replace oxygen sensor, check wiring and connectors. |
| B0001 | Front airbag deployment loop open | Check front airbag, replace front airbag. |
| B0002 | Front airbag deployment loop short to ground | Check front airbag, replace front airbag. |
6. What to Do If the Check Engine Light Returns
If the check engine light comes back on after clearing the codes, it indicates that the underlying issue was not fully resolved.
- Re-scan: Use the OBD2 scanner to read the codes again.
- Further Diagnosis: Perform a more thorough diagnosis based on the new codes.
- Professional Help: If you’re unable to resolve the issue yourself, seek assistance from a qualified mechanic.
According to the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), ongoing training and certification are essential for mechanics to stay current with the latest automotive technologies. Ensure that any mechanic you consult is ASE-certified.
7. Potential Problems and How to Avoid Them
Clearing OBD2 codes can sometimes lead to unintended consequences if not done correctly.
- Erasing Important Data: Clearing codes can erase freeze frame data, which provides a snapshot of the car’s condition when the code was triggered.
- Readiness Monitors: Clearing codes resets the readiness monitors, which can prevent your car from passing an emissions test until they are reset through normal driving.
- Incorrect Diagnosis: Clearing codes without addressing the underlying issue can mask serious problems and lead to further damage.
To avoid these issues:
- Record Codes: Always write down the codes before clearing them.
- Address the Root Cause: Ensure you’ve properly diagnosed and repaired the issue.
- Allow Time for Reset: Give the car time to complete a full driving cycle to reset the readiness monitors.
8. OBD2 Scanner Recommendations
Choosing the right OBD2 scanner can make a significant difference in your ability to diagnose and clear codes effectively. Here are some recommendations:
- Basic Scanners: These are inexpensive and can read and clear basic codes. An example is the CGSULIT SC301.
- Mid-Range Scanners: These offer more features, such as live data, freeze frame data, and enhanced code definitions.
- Professional-Grade Scanners: These provide advanced diagnostics, bidirectional control, and access to manufacturer-specific codes.
When selecting a scanner, consider the following factors:
- Compatibility: Ensure the scanner is compatible with your vehicle’s make and model.
- Features: Choose a scanner with the features you need, such as live data, freeze frame, and enhanced code definitions.
- Ease of Use: Look for a scanner with a user-friendly interface and clear instructions.
9. Advanced OBD2 Functions
Beyond reading and clearing codes, many OBD2 scanners offer advanced functions that can help you diagnose and repair more complex issues.
- Live Data: View real-time data from the car’s sensors, such as engine temperature, RPM, and oxygen sensor readings.
- Freeze Frame: Capture a snapshot of the car’s condition when a code was triggered, providing valuable diagnostic information.
- Bidirectional Control: Activate or deactivate specific components to test their functionality.
Using these advanced functions requires a deeper understanding of automotive systems, but it can greatly enhance your diagnostic capabilities.
10. The Future of OBD2 Technology
OBD2 technology is constantly evolving to meet the demands of modern vehicles.
- OBD3: The next generation of OBD systems will likely include enhanced monitoring capabilities and the ability to transmit diagnostic data wirelessly.
- Electric Vehicles: OBD systems are being adapted to monitor the unique components of electric vehicles, such as batteries and electric motors.
- Cybersecurity: As cars become more connected, cybersecurity is becoming an increasingly important consideration for OBD systems.
Staying informed about the latest advancements in OBD2 technology can help you keep your car running smoothly and efficiently.
11. OBD2 and Emission Testing
OBD2 systems play a critical role in ensuring that vehicles meet emission standards. During an emission test, technicians will typically check the OBD2 system for any stored codes and verify that the readiness monitors are set.
- Readiness Monitors: These monitors indicate whether the car’s emission control systems have been tested and are functioning properly.
- Test Failure: If there are any stored codes or if the readiness monitors are not set, the car will fail the emission test.
- Preparation: Before taking your car for an emission test, ensure that you’ve addressed any check engine lights and allowed the car time to complete a full driving cycle to reset the readiness monitors.
According to the U.S. Department of Transportation, regular vehicle maintenance and emission testing are essential for reducing air pollution and improving public health.
12. Benefits of Using OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN offers a wealth of resources to help you understand and utilize OBD2 technology effectively.
- Comprehensive Guides: Detailed guides on how to use OBD2 scanners, interpret codes, and perform basic repairs.
- Code Database: An extensive database of OBD2 codes with definitions, possible causes, and solutions.
- Product Reviews: Reviews of the latest OBD2 scanners and diagnostic tools.
- Community Forum: A forum where you can ask questions, share your experiences, and get advice from other car owners and experts.
By utilizing the resources available at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, you can save money on repairs, improve your car’s performance, and ensure that it meets emission standards.
13. Real-World Examples of Clearing OBD2 Codes
Let’s look at a few real-world scenarios where clearing OBD2 codes can be beneficial.
- Scenario 1: Loose Gas Cap
- Problem: The check engine light comes on, and the OBD2 scanner shows code P0442 (Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected).
- Solution: Check and tighten the gas cap. Clear the code. If the light stays off, the problem is solved.
- Scenario 2: Faulty Oxygen Sensor
- Problem: The check engine light is on, and the OBD2 scanner shows code P0135 (O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Malfunction).
- Solution: Replace the faulty oxygen sensor. Clear the code. Monitor the car to ensure the light doesn’t return.
- Scenario 3: Misfiring Engine
- Problem: The check engine light flashes, and the OBD2 scanner shows code P0300 (Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected).
- Solution: Replace the spark plugs and ignition coils. Clear the code. Test drive the car to confirm the misfire is resolved.
These examples illustrate how understanding and addressing OBD2 codes can help you quickly identify and resolve common car problems.
14. Maintaining Your Vehicle to Prevent OBD2 Codes
Preventative maintenance is key to avoiding frequent check engine lights and OBD2 codes.
- Regular Oil Changes: Keep the engine properly lubricated to prevent wear and tear.
- Air Filter Replacement: Ensure the engine receives clean air for optimal combustion.
- Spark Plug Maintenance: Replace spark plugs at recommended intervals to prevent misfires.
- Fluid Checks: Regularly check and top off fluids like coolant, brake fluid, and transmission fluid.
- Tire Maintenance: Maintain proper tire pressure and alignment for optimal fuel efficiency and safety.
By following a regular maintenance schedule, you can keep your car running smoothly and reduce the likelihood of triggering OBD2 codes.
15. Contact OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for Assistance
If you’re having trouble clearing OBD2 codes or diagnosing a check engine light, don’t hesitate to contact OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for assistance. Our team of experts is here to help you with all your automotive diagnostic needs.
- Phone Support: Call us at +1 (641) 206-8880 for immediate assistance.
- WhatsApp: Chat with us on WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880 for quick answers to your questions.
- Website: Visit our website at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for detailed guides, product reviews, and a comprehensive code database.
- Location: Visit us at 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States.
We are committed to providing you with the best possible service and support.
16. Safety Precautions When Clearing OBD2 Codes
When working on your car, it’s essential to take proper safety precautions.
- Wear Safety Glasses: Protect your eyes from debris and chemicals.
- Use Gloves: Protect your hands from dirt, grease, and chemicals.
- Work in a Well-Ventilated Area: Avoid breathing in harmful fumes.
- Disconnect the Battery: Before working on electrical components, disconnect the negative battery terminal to prevent electrical shocks.
- Use Jack Stands: When lifting the car, always use jack stands to support it safely.
By following these safety precautions, you can minimize the risk of injury while working on your car.
17. Understanding Vehicle Diagnostic Reports
A vehicle diagnostic report provides a comprehensive overview of your car’s systems.
- Code Interpretation: Understand the meaning of each code and its potential impact on your vehicle.
- System Analysis: Identify any underlying issues that need to be addressed.
- Maintenance Recommendations: Follow the recommendations for preventative maintenance to keep your car running smoothly.
Reviewing and understanding your vehicle’s diagnostic reports can help you make informed decisions about repairs and maintenance.
18. The Role of OBD2 in Vehicle Performance
OBD2 systems not only help with diagnostics but also play a critical role in optimizing vehicle performance.
- Fuel Efficiency: By monitoring the engine’s performance, the OBD2 system helps ensure optimal fuel efficiency.
- Engine Health: Regular monitoring can help detect and address potential problems before they cause serious damage.
- Smooth Operation: Proper functioning of the OBD2 system contributes to a smoother and more reliable driving experience.
Understanding the role of OBD2 in vehicle performance can motivate you to keep your car well-maintained and functioning optimally.
19. Tips for Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner
Selecting the best OBD2 scanner for your needs involves considering several factors.
- Compatibility: Ensure the scanner is compatible with your car’s make and model.
- Features: Choose a scanner with the features you need, such as live data, freeze frame, and bidirectional control.
- Ease of Use: Look for a scanner with a user-friendly interface and clear instructions.
- Price: Set a budget and choose a scanner that offers the best value for your money.
- Reviews: Read online reviews to get feedback from other users.
Taking these factors into account will help you choose an OBD2 scanner that meets your needs and budget.
20. Clearing OBD2 Codes and DIY Car Repairs
Clearing OBD2 codes is often part of the DIY car repair process.
- Diagnose the Problem: Use the OBD2 scanner to identify the issue.
- Research the Repair: Consult repair manuals, online forums, and video tutorials to learn how to perform the repair.
- Gather Tools and Parts: Collect all the necessary tools and parts for the repair.
- Perform the Repair: Follow the instructions carefully to complete the repair.
- Clear the Codes: Use the OBD2 scanner to clear the codes and turn off the check engine light.
- Test the Car: Test drive the car to ensure the problem is resolved.
By following these steps, you can successfully perform DIY car repairs and save money on labor costs.
21. How to Use an OBD2 Scanner to Improve Fuel Efficiency
An OBD2 scanner can be a valuable tool for improving your car’s fuel efficiency.
- Monitor Fuel Trim: Use the scanner to monitor short-term and long-term fuel trim values, which indicate how the engine is adjusting the fuel mixture.
- Identify Problems: Look for issues like vacuum leaks, faulty oxygen sensors, or clogged fuel injectors that can affect fuel efficiency.
- Address Issues: Repair or replace any faulty components to restore optimal fuel efficiency.
- Monitor Performance: Use the scanner to monitor fuel efficiency after making repairs to ensure the problem is resolved.
By using an OBD2 scanner to monitor and optimize your car’s performance, you can save money on gas and reduce your carbon footprint.
22. The Importance of Regular Vehicle Inspections
Regular vehicle inspections are essential for maintaining your car’s safety and performance.
- Identify Problems Early: Inspections can help detect potential problems before they cause serious damage.
- Ensure Safety: Regular inspections can help ensure that your car is safe to drive.
- Maintain Value: Keeping your car well-maintained can help preserve its value.
- Comply with Regulations: Many states require regular vehicle inspections to ensure compliance with safety and emission standards.
Schedule regular inspections with a qualified mechanic to keep your car running smoothly and safely.
23. The Future of Automotive Diagnostics
Automotive diagnostics is continually evolving, with new technologies and techniques emerging all the time.
- Artificial Intelligence: AI is being used to analyze diagnostic data and identify potential problems more quickly and accurately.
- Remote Diagnostics: Remote diagnostics allows technicians to diagnose and repair cars remotely, reducing the need for in-person visits.
- Predictive Maintenance: Predictive maintenance uses data analytics to predict when a car component is likely to fail, allowing for proactive repairs.
Staying informed about the latest advancements in automotive diagnostics can help you keep your car running smoothly and efficiently.
24. Troubleshooting Common OBD2 Scanner Issues
Even with the best OBD2 scanner, you may encounter some common issues. Here are some troubleshooting tips:
- Scanner Won’t Connect: Ensure the scanner is properly plugged into the OBD2 port and that the ignition is turned on.
- Incorrect Codes: Verify that the scanner is compatible with your car’s make and model.
- Scanner Won’t Clear Codes: Ensure you have addressed the underlying issue before attempting to clear the codes.
- Scanner Freezes: Try resetting the scanner or updating its firmware.
If you’re unable to resolve the issue, consult the scanner’s user manual or contact the manufacturer for assistance.
25. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques with OBD2 Scanners
For experienced users, OBD2 scanners can be used for more advanced diagnostic techniques.
- Component Testing: Use the scanner to activate or deactivate specific components to test their functionality.
- Data Logging: Record data over time to analyze trends and identify intermittent problems.
- Custom Parameters: Configure the scanner to monitor specific parameters that are relevant to your car’s performance.
These advanced techniques require a deeper understanding of automotive systems but can provide valuable insights into your car’s performance.
26. Utilizing Online Resources for OBD2 Code Information
The internet is a valuable resource for OBD2 code information.
- OBD2 Code Databases: Websites like OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN offer extensive databases of OBD2 codes with definitions, possible causes, and solutions.
- Online Forums: Participate in online forums to ask questions, share your experiences, and get advice from other car owners and experts.
- Video Tutorials: Watch video tutorials to learn how to use OBD2 scanners, diagnose problems, and perform repairs.
By utilizing these online resources, you can expand your knowledge of OBD2 technology and improve your ability to diagnose and repair car problems.
27. OBD2 Scanner Apps for Smartphones
Many OBD2 scanners now connect to smartphones via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi, providing user-friendly interfaces and advanced features.
- Real-Time Data: View real-time data from your car’s sensors on your smartphone screen.
- Code Definitions: Access a comprehensive database of OBD2 codes with definitions, possible causes, and solutions.
- Custom Dashboards: Create custom dashboards to monitor specific parameters that are relevant to your car’s performance.
- Data Logging: Record data over time to analyze trends and identify intermittent problems.
These smartphone apps can greatly enhance your ability to diagnose and repair car problems.
28. Staying Updated with OBD2 Technology
OBD2 technology is constantly evolving, so it’s important to stay updated with the latest advancements.
- Read Industry Publications: Subscribe to automotive industry publications to stay informed about new technologies and techniques.
- Attend Training Seminars: Attend training seminars to learn about the latest diagnostic tools and techniques.
- Participate in Online Forums: Participate in online forums to share your experiences and learn from other car owners and experts.
- Follow OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN: Regularly visit OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for the latest news, reviews, and guides on OBD2 technology.
By staying updated with OBD2 technology, you can ensure that you’re using the most effective tools and techniques for diagnosing and repairing car problems.
29. Using OBD2 Scanners for Fleet Management
OBD2 scanners can be a valuable tool for fleet management, helping to improve efficiency and reduce costs.
- Track Vehicle Performance: Monitor the performance of each vehicle in the fleet to identify potential problems early.
- Optimize Fuel Efficiency: Monitor fuel efficiency to identify and address issues that can increase fuel consumption.
- Schedule Maintenance: Schedule maintenance based on vehicle performance data to prevent breakdowns and extend vehicle life.
- Improve Driver Behavior: Monitor driver behavior, such as speeding and hard braking, to improve safety and reduce wear and tear on vehicles.
By using OBD2 scanners for fleet management, you can improve efficiency, reduce costs, and extend the life of your vehicles.
30. Final Thoughts: Mastering OBD2 Codes for Vehicle Health
Mastering the skill of clearing OBD2 codes is essential for every car owner who wants to maintain their vehicle’s health and performance. By understanding what these codes mean and how to address them, you can save money on repairs, improve your car’s fuel efficiency, and ensure that it meets emission standards. Remember, OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN is here to support you with comprehensive guides, expert advice, and the tools you need to keep your car running smoothly. Don’t hesitate to contact us for assistance, and take the first step towards becoming a more informed and empowered car owner today.
Is the check engine light causing you stress? Contact OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN now via Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880 or call us. Let our expertise guide you to resolve your car issues efficiently. Visit OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN at 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States.
FAQ: Clearing OBD2 Codes
What is an OBD2 scanner?
An OBD2 scanner is a device used to read and clear diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) from a vehicle’s onboard computer. It connects to the OBD2 port, typically located under the dashboard, and allows you to access valuable information about your car’s systems.
How do I find the OBD2 port in my car?
The OBD2 port is usually located under the dashboard on the driver’s side. Common locations include under the steering wheel, near the driver’s knee, or inside the glove compartment.
Can I clear OBD2 codes without a scanner?
While some methods exist, such as disconnecting the car battery, they are not recommended. Using an OBD2 scanner is the most reliable and safe way to clear codes and monitor your car’s systems.
Will clearing OBD2 codes erase important data?
Clearing codes can erase freeze frame data, which provides a snapshot of the car’s condition when the code was triggered. Always record the codes before clearing them.
How do I reset the readiness monitors after clearing OBD2 codes?
To reset the readiness monitors, you need to complete a full driving cycle, which includes a mix of city and highway driving.
What does it mean if the check engine light comes back on after clearing the codes?
If the check engine light comes back on, it indicates that the underlying issue was not fully resolved. Re-scan for codes and perform further diagnosis.
Is it safe to drive with the check engine light on?
It depends on the severity of the issue. If the light is flashing, it indicates a serious problem that could damage the engine. In such cases, it’s best to avoid driving and seek professional help.
How do I interpret OBD2 codes?
Use the scanner’s built-in database, a repair manual, or online resources like OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN to understand what each code means.
What are some common OBD2 codes?
Common codes include P0171 (system too lean), P0300 (random misfire), and P0420 (catalyst system efficiency below threshold).
Where can I find more information about OBD2 technology?
Visit OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for detailed guides, product reviews, and a comprehensive code database.

