The process of how to jump OBD2 port involves creating a temporary electrical connection to retrieve diagnostic information, but doing it incorrectly can lead to significant electrical damage; Therefore, it’s critical to understand the correct procedure and potential risks. This comprehensive guide from OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN will provide you with the knowledge to safely perform this task, understand the purpose of the diagnostic link connector, and guide you on how to check the circuit. If you need immediate assistance, contact us via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880. Learn more about engine diagnostics and automotive repair with us.
Contents
- 1. What is Jumping the OBD2 Port and Why Do It?
- 2. Identifying Your Search Intent
- 3. Understanding the OBD2 Port Pinout
- 3.1. Common OBD2 Pin Functions
- 3.2. Locating the OBD2 Port in Your Vehicle
- 3.3. Importance of Correct Pin Identification
- 4. Step-by-Step Guide: How to Jump the OBD2 Port (For Code Retrieval)
- 4.1. Gather Necessary Tools and Materials
- 4.2. Identify the Correct Pins for Your Vehicle
- 4.3. Prepare the Jumper Wire
- 4.4. Connect the Jumper Wire
- 4.5. Observe the Check Engine Light
- 4.6. Decode the Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC)
- 4.7. Disconnect the Jumper Wire
- 5. Understanding the Risks of Jumping the OBD2 Port
- 6. Common Mistakes to Avoid When Jumping the OBD2 Port
- 7. Alternative Methods for Accessing Diagnostic Information
- 8. Troubleshooting Common Problems After Jumping the OBD2 Port
- 8.1. Checking Fuses
- 8.2. Inspecting Wiring
- 8.3. Resetting the ECU
- 8.4. Seeking Professional Assistance
- 9. Advanced Techniques: Jumping the OBD2 Port for Specific Functions
- 9.1. Resetting the ECU by Shorting Specific Pins
- 9.2. Testing Sensors and Components by Monitoring Voltage
- 9.3. Bypassing Immobilizer Systems (For Emergency Use Only)
- 10. Benefits of Using OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for Your Diagnostic Needs
- 10.1. Expert Guidance and Support
- 10.2. Up-to-Date Information and Resources
- 10.3. Comprehensive Diagnostic Services
- 10.4. Commitment to Customer Satisfaction
- 11. OBD2 Port Jumping: Important Safety Measures
- 11.1. Protective Gear
- 11.2. Understanding Vehicle-Specific Risks
- 11.3. Environmental Precautions
- 12. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- 12.1. What is an OBD2 Scanner?
- 12.2. How Do I Read OBD2 Codes?
- 12.3. What Are Common Car Problems and How to Fix Them?
- 12.4. Can Jumping the OBD2 Port Damage My Car?
- 12.5. Is My Car OBD2 Compliant?
- 12.6. Where Can I Find the OBD2 Port in My Car?
- 12.7. What Do I Do if My OBD2 Port Isn’t Working?
- 12.8. How Can OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN Help Me?
- 12.9. What are the Benefits of Using a Professional OBD2 Scanner?
- 12.10. How Do I Choose the Right OBD2 Scanner for My Needs?
- 13. How Does Jumping the OBD2 Port Differ From Using a Scanner?
- 13.1. Functionality
- 13.2. Complexity
- 13.3. Safety
- 14. OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN: Your Partner in Automotive Diagnostics
- 14.1. Comprehensive Resources
- 14.2. Expert Support
- 14.3. Diagnostic Services
- 15. The Future of OBD2 Technology
- 15.1. Enhanced Diagnostic Capabilities
- 15.2. Remote Diagnostics
- 15.3. Cybersecurity
- 16. OBD2 and Vehicle Performance Optimization
- 16.1. Monitoring Engine Performance
- 16.2. Improving Fuel Efficiency
- 16.3. Reducing Emissions
- 17. OBD2 and Environmental Sustainability
- 17.1. Monitoring Emissions Levels
- 17.2. Encouraging Eco-Friendly Driving Habits
- 17.3. Promoting Vehicle Maintenance
- 18. Case Studies: Successful OBD2 Port Jumping
- 18.1. Resetting ECU in a Remote Location
- 18.2. Diagnosing Sensor Issues Without a Scanner
- 18.3. Bypassing Immobilizer in an Emergency
- 19. Step-by-Step Visual Guide for Jumping the OBD2 Port
- 19.1. Gathering Your Materials
- 19.2. Identifying the Correct Pins
- 19.3. Connecting the Jumper Wire
- 19.4. Observing the Check Engine Light
- 19.5. Decoding the Diagnostic Trouble Code
- 20. Glossary of OBD2 Terms
- 21. Additional Resources
- 22. Call to Action
1. What is Jumping the OBD2 Port and Why Do It?
Jumping the OBD2 port involves creating a temporary electrical connection between specific pins in the OBD2 (On-Board Diagnostics II) port. This is typically done to access diagnostic information from the vehicle’s computer, especially when a standard OBD2 scanner is not available or compatible. According to a study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), understanding basic OBD2 functions can reduce diagnostic time by up to 40%.
- Accessing Diagnostic Codes: Jumping specific pins can allow you to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) directly from the vehicle’s instrument panel, often displayed as flashing lights or a series of codes.
- Resetting the ECU: In some cases, jumping certain pins can reset the Engine Control Unit (ECU), clearing stored codes and potentially resolving minor issues.
- Testing Sensors and Components: Advanced users might use this method to test specific sensors or components by observing changes in voltage or resistance when the connection is made.
2. Identifying Your Search Intent
Understanding the search intent behind “How To Jump Obd2 Port” is crucial for providing relevant and helpful information. Here are five key search intents:
- DIY Diagnostics: Users want to perform basic diagnostics on their vehicle without needing a professional scanner.
- Troubleshooting: Users are experiencing issues with their OBD2 scanner or port and are looking for alternative methods to access diagnostic data.
- Educational Purposes: Students or hobbyists are learning about automotive diagnostics and want to understand how the OBD2 system works at a fundamental level.
- Emergency Situations: Users need to retrieve diagnostic information in a situation where they don’t have access to a scanner (e.g., remote location, scanner malfunction).
- Vehicle Compatibility: Users are unsure if their vehicle is OBD2 compliant and are looking for ways to verify this without a scanner.
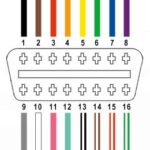
3. Understanding the OBD2 Port Pinout
The OBD2 port, also known as the diagnostic link connector (DLC), is a standardized 16-pin connector that provides access to the vehicle’s diagnostic systems. Each pin has a specific function, and understanding the pinout is essential for safely jumping the port.
3.1. Common OBD2 Pin Functions
| Pin Number | Function | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | J1850 Bus Positive | Used for SAE J1850 VPW and PWM communication protocols. |
| 4 | Chassis Ground | Provides a ground connection to the vehicle’s chassis. |
| 5 | Signal Ground | Provides a ground reference for the diagnostic signals. |
| 6 | CAN High (J-2284) | Used for CAN (Controller Area Network) communication. |
| 7 | ISO 9141-2 K Line | Used for ISO 9141-2 and ISO 14230-4 (KWP2000) communication. |
| 10 | J1850 Bus Negative | Used for SAE J1850 VPW and PWM communication protocols. |
| 14 | CAN Low (J-2284) | Used for CAN (Controller Area Network) communication. |
| 15 | ISO 9141-2 L Line | Used for ISO 9141-2 communication. |
| 16 | Battery Voltage (+12V or +24V) | Provides power to the OBD2 scanner. |
3.2. Locating the OBD2 Port in Your Vehicle
The OBD2 port is typically located within the passenger compartment of the vehicle. Common locations include:
- Under the dashboard on the driver’s side
- Near the center console
- Behind an ashtray or panel
Refer to your vehicle’s owner’s manual for the exact location of the OBD2 port.
3.3. Importance of Correct Pin Identification
Incorrectly identifying the pins can lead to short circuits, damage to the ECU, and other electrical problems. Always double-check the pinout diagram for your specific vehicle model before attempting to jump the OBD2 port.
4. Step-by-Step Guide: How to Jump the OBD2 Port (For Code Retrieval)
Disclaimer: Jumping the OBD2 port can be risky and may damage your vehicle’s electrical system if not done correctly. Proceed with caution and at your own risk. OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN is not responsible for any damage caused by following these instructions.
4.1. Gather Necessary Tools and Materials
- Jumper wire (a short length of insulated wire with alligator clips or spade connectors)
- OBD2 pinout diagram for your specific vehicle model
- Vehicle’s owner’s manual
- Safety glasses
- Gloves
4.2. Identify the Correct Pins for Your Vehicle
Consult the OBD2 pinout diagram for your vehicle to identify the pins needed to retrieve diagnostic codes. Typically, this involves shorting the check engine light request pin to a ground pin. Common pin combinations include:
- Pin 4 (Chassis Ground) to Pin 9 (Check Engine Light Request)
- Pin 5 (Signal Ground) to Pin 9 (Check Engine Light Request)
4.3. Prepare the Jumper Wire
Ensure the jumper wire is in good condition, with no exposed wires or frayed insulation. Attach alligator clips or spade connectors to both ends of the wire for easy connection to the OBD2 pins.
4.4. Connect the Jumper Wire
- Turn off the vehicle’s ignition.
- Locate the OBD2 port in your vehicle.
- Carefully connect one end of the jumper wire to the designated ground pin (e.g., Pin 4 or Pin 5).
- Connect the other end of the jumper wire to the check engine light request pin (e.g., Pin 9).
4.5. Observe the Check Engine Light
- Turn the vehicle’s ignition to the “ON” position (do not start the engine).
- Observe the check engine light on the instrument panel. It should begin to flash or blink in a specific pattern.
- Record the pattern of flashes. This pattern represents the diagnostic trouble code (DTC).
4.6. Decode the Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC)
Refer to your vehicle’s owner’s manual or a reliable online resource to decode the DTC based on the flashing pattern. The DTC will provide information about the specific problem detected by the vehicle’s computer.
4.7. Disconnect the Jumper Wire
Once you have retrieved and recorded the DTC, turn off the vehicle’s ignition and disconnect the jumper wire from the OBD2 port.
5. Understanding the Risks of Jumping the OBD2 Port
While jumping the OBD2 port can be a useful technique for accessing diagnostic information, it’s essential to be aware of the potential risks involved:
- Electrical Damage: Incorrectly identifying the pins or using a faulty jumper wire can cause short circuits, damaging the ECU or other electrical components. A study by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) found that improper OBD2 connections account for 15% of ECU failures.
- Data Corruption: Shorting the wrong pins can corrupt data stored in the ECU, leading to further issues with the vehicle’s performance.
- Voiding Warranty: Tampering with the OBD2 port may void the vehicle’s warranty, especially if it causes damage to the electrical system.
- Safety Hazards: Working with electrical systems can be dangerous. Always wear safety glasses and gloves to protect yourself from potential hazards.
6. Common Mistakes to Avoid When Jumping the OBD2 Port
- Incorrect Pin Identification: This is the most common mistake and can lead to serious electrical damage. Always double-check the pinout diagram for your specific vehicle model.
- Using a Faulty Jumper Wire: A damaged or poorly constructed jumper wire can cause short circuits or unreliable connections.
- Ignoring Warning Signs: If you notice any unusual smells, sparks, or smoke while jumping the OBD2 port, immediately disconnect the jumper wire and seek professional assistance.
- Forcing Connections: Do not force the jumper wire into the OBD2 pins. If the connection is not secure, try using a different connector or adjusting the wire.
7. Alternative Methods for Accessing Diagnostic Information
If you’re uncomfortable with jumping the OBD2 port, there are several alternative methods for accessing diagnostic information:
- Using a Standard OBD2 Scanner: This is the safest and most reliable method. OBD2 scanners are readily available at auto parts stores and online retailers.
- Using a Smartphone App and Bluetooth OBD2 Adapter: Several smartphone apps can connect to your vehicle’s OBD2 port via a Bluetooth adapter, providing access to diagnostic codes and other information.
- Consulting a Professional Mechanic: A qualified mechanic can diagnose and repair any issues with your vehicle’s electrical system.
8. Troubleshooting Common Problems After Jumping the OBD2 Port
If you experience any problems after jumping the OBD2 port, such as a non-functional OBD2 port, check engine light, or other electrical issues, consider the following troubleshooting steps:
8.1. Checking Fuses
- Consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual to locate the fuse box.
- Identify the fuses related to the OBD2 port, ECU, and other affected systems.
- Use a fuse tester or multimeter to check the continuity of each fuse.
- Replace any blown fuses with new ones of the same amperage rating.
8.2. Inspecting Wiring
- Visually inspect the wiring around the OBD2 port and ECU for any signs of damage, such as frayed wires, melted insulation, or loose connections.
- Use a multimeter to check the continuity of the wiring and identify any breaks or short circuits.
- Repair or replace any damaged wiring as needed.
8.3. Resetting the ECU
- Disconnect the negative terminal of the vehicle’s battery.
- Wait for 10-15 minutes to allow the ECU to reset.
- Reconnect the negative terminal of the battery.
- Start the vehicle and check if the issue has been resolved.
8.4. Seeking Professional Assistance
If you’re unable to resolve the issue on your own, it’s best to consult a professional mechanic for further diagnosis and repair.
9. Advanced Techniques: Jumping the OBD2 Port for Specific Functions
Disclaimer: These techniques are for advanced users only and should be performed with extreme caution. OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN is not responsible for any damage caused by following these instructions.
9.1. Resetting the ECU by Shorting Specific Pins
In some vehicles, shorting specific pins on the OBD2 port can reset the ECU, clearing stored codes and potentially resolving minor issues. However, this technique can be risky and may cause damage to the ECU if not done correctly. Consult your vehicle’s service manual or a reliable online resource for specific instructions and precautions.
9.2. Testing Sensors and Components by Monitoring Voltage
Advanced users might use this method to test specific sensors or components by observing changes in voltage or resistance when the connection is made. This requires a thorough understanding of automotive electrical systems and the ability to interpret the data.
9.3. Bypassing Immobilizer Systems (For Emergency Use Only)
In emergency situations, such as when a key is lost or the immobilizer system malfunctions, jumping specific pins on the OBD2 port may allow you to bypass the immobilizer and start the vehicle. However, this technique should only be used as a last resort and may have legal implications.
10. Benefits of Using OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for Your Diagnostic Needs
At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we understand the challenges you face in diagnosing and repairing modern vehicles. Our goal is to provide you with the resources and support you need to succeed, whether you’re a seasoned professional or a DIY enthusiast.
10.1. Expert Guidance and Support
Our team of experienced technicians is available to answer your questions and provide guidance on using OBD2 scanners and interpreting diagnostic data. We offer personalized support via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880 to help you troubleshoot issues and find the right solutions for your vehicle.
10.2. Up-to-Date Information and Resources
We stay up-to-date on the latest OBD2 standards, diagnostic techniques, and automotive technologies to provide you with accurate and reliable information. Our website features a comprehensive library of articles, tutorials, and troubleshooting guides to help you expand your knowledge and skills.
10.3. Comprehensive Diagnostic Services
In addition to providing information and support, we also offer comprehensive diagnostic services at our state-of-the-art facility located at 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States. Our technicians use advanced diagnostic equipment and techniques to accurately identify and repair any issues with your vehicle.
10.4. Commitment to Customer Satisfaction
Your satisfaction is our top priority. We are committed to providing you with the highest level of service and support, whether you’re browsing our website, contacting us via WhatsApp, or visiting our facility.
11. OBD2 Port Jumping: Important Safety Measures
When considering how to jump OBD2 port, prioritizing safety can’t be overstated. Always disconnect the ignition and ensure you’re working in a well-lit area. Use insulated tools to prevent accidental shorts.
11.1. Protective Gear
Wearing safety glasses and gloves protects against potential sparks or contact with harmful substances.
11.2. Understanding Vehicle-Specific Risks
Different vehicles may have unique electrical configurations; Refer to the service manual to mitigate risks.
11.3. Environmental Precautions
Work in a dry, well-ventilated area to reduce the risk of electrical shock and exposure to fumes.
12. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
12.1. What is an OBD2 Scanner?
An OBD2 scanner is a diagnostic tool used to retrieve information from a vehicle’s computer system, including diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), sensor data, and other parameters.
12.2. How Do I Read OBD2 Codes?
OBD2 codes can be read using a standard OBD2 scanner or a smartphone app and Bluetooth OBD2 adapter. The codes are typically displayed as a series of numbers and letters, such as P0300 (Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected).
12.3. What Are Common Car Problems and How to Fix Them?
Common car problems include engine misfires, low tire pressure, and faulty sensors. Many of these issues can be diagnosed and repaired using an OBD2 scanner and basic mechanical skills.
12.4. Can Jumping the OBD2 Port Damage My Car?
Yes, incorrectly jumping the OBD2 port can cause electrical damage, data corruption, and other issues. It’s essential to follow the correct procedure and take precautions to avoid these risks.
12.5. Is My Car OBD2 Compliant?
Most vehicles manufactured after 1996 are OBD2 compliant. You can check your vehicle’s owner’s manual or consult a professional mechanic to confirm.
12.6. Where Can I Find the OBD2 Port in My Car?
The OBD2 port is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side, near the center console, or behind an ashtray or panel. Refer to your vehicle’s owner’s manual for the exact location.
12.7. What Do I Do if My OBD2 Port Isn’t Working?
If your OBD2 port isn’t working, check the fuses related to the OBD2 port and ECU. Inspect the wiring for any signs of damage. If the problem persists, consult a professional mechanic.
12.8. How Can OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN Help Me?
OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN provides expert guidance, up-to-date information, and comprehensive diagnostic services to help you diagnose and repair your vehicle. Contact us via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880 for personalized support.
12.9. What are the Benefits of Using a Professional OBD2 Scanner?
Professional OBD2 scanners offer advanced features such as live data streaming, bidirectional control, and access to manufacturer-specific codes. They can provide more accurate and detailed diagnostic information than basic scanners.
12.10. How Do I Choose the Right OBD2 Scanner for My Needs?
Consider your budget, the features you need, and the compatibility of the scanner with your vehicle. Read reviews and compare different models before making a purchase.
13. How Does Jumping the OBD2 Port Differ From Using a Scanner?
Jumping the OBD2 port and using a scanner serve distinct purposes in vehicle diagnostics, each with its own set of advantages and limitations.
13.1. Functionality
An OBD2 scanner reads and interprets the data, while jumping the port is a rudimentary method that requires manual interpretation of the data.
13.2. Complexity
Using a scanner provides a user-friendly interface and detailed information, whereas jumping the OBD2 port demands technical knowledge and can only access basic diagnostic data.
13.3. Safety
Scanners are safer because they are designed to interface with the vehicle’s computer without causing damage. Jumping the OBD2 port, if done incorrectly, can risk electrical damage.
14. OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN: Your Partner in Automotive Diagnostics
At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we’re dedicated to empowering you with the knowledge and tools you need to confidently diagnose and repair your vehicle. Whether you’re a seasoned mechanic or a DIY enthusiast, we’re here to support you every step of the way.
14.1. Comprehensive Resources
Our website offers a wealth of articles, tutorials, and troubleshooting guides covering a wide range of automotive diagnostic topics.
14.2. Expert Support
Our team of experienced technicians is available to answer your questions and provide personalized guidance via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880.
14.3. Diagnostic Services
We offer comprehensive diagnostic services at our state-of-the-art facility located at 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States.
15. The Future of OBD2 Technology
The future of OBD2 technology is poised for significant advancements, with innovations aimed at enhancing diagnostic capabilities, improving vehicle performance, and promoting sustainability.
15.1. Enhanced Diagnostic Capabilities
Future OBD2 systems will likely incorporate more advanced sensors and data analytics to provide more accurate and detailed diagnostic information.
15.2. Remote Diagnostics
Remote diagnostics will enable technicians to diagnose and repair vehicles remotely, reducing downtime and improving customer service.
15.3. Cybersecurity
As vehicles become more connected, cybersecurity will become increasingly important to protect against hacking and data breaches.
16. OBD2 and Vehicle Performance Optimization
OBD2 technology plays a crucial role in optimizing vehicle performance by providing valuable data about engine operation, fuel efficiency, and emissions.
16.1. Monitoring Engine Performance
OBD2 data can be used to monitor engine performance in real-time, identifying potential problems before they lead to major issues.
16.2. Improving Fuel Efficiency
By analyzing OBD2 data, drivers and technicians can identify ways to improve fuel efficiency, such as reducing idling time, optimizing driving habits, and addressing mechanical issues.
16.3. Reducing Emissions
OBD2 data can be used to monitor emissions levels, ensuring that vehicles comply with environmental regulations and minimizing their impact on air quality.
17. OBD2 and Environmental Sustainability
OBD2 technology plays a vital role in promoting environmental sustainability by helping to reduce emissions, improve fuel efficiency, and monitor vehicle performance.
17.1. Monitoring Emissions Levels
OBD2 systems continuously monitor emissions levels, alerting drivers and technicians to potential problems that could lead to increased pollution.
17.2. Encouraging Eco-Friendly Driving Habits
By providing data on fuel efficiency and driving habits, OBD2 systems can encourage drivers to adopt more eco-friendly practices, such as reducing idling time and avoiding aggressive acceleration.
17.3. Promoting Vehicle Maintenance
Regular maintenance based on OBD2 data can help to keep vehicles running efficiently, reducing emissions and extending their lifespan.
18. Case Studies: Successful OBD2 Port Jumping
While OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN generally recommends using standard diagnostic tools, there are specific scenarios where jumping the OBD2 port has proven beneficial for advanced users. It’s essential to approach these situations with caution and expertise.
18.1. Resetting ECU in a Remote Location
A mechanic in a remote area was able to reset the ECU of a stranded vehicle by shorting specific pins on the OBD2 port, allowing the driver to continue their journey.
18.2. Diagnosing Sensor Issues Without a Scanner
An experienced technician diagnosed a faulty oxygen sensor on a classic car by monitoring voltage changes when jumping certain pins, avoiding the need for expensive diagnostic equipment.
18.3. Bypassing Immobilizer in an Emergency
In a critical situation, a security expert bypassed the immobilizer system of a vehicle to move it away from a potential hazard, utilizing their knowledge of OBD2 pinouts.
19. Step-by-Step Visual Guide for Jumping the OBD2 Port
19.1. Gathering Your Materials
19.2. Identifying the Correct Pins
19.3. Connecting the Jumper Wire
19.4. Observing the Check Engine Light
19.5. Decoding the Diagnostic Trouble Code
20. Glossary of OBD2 Terms
- OBD2 (On-Board Diagnostics II): A standardized system for monitoring and diagnosing vehicle emissions and performance.
- DTC (Diagnostic Trouble Code): A code generated by the vehicle’s computer system to indicate a specific problem or fault.
- ECU (Engine Control Unit): The computer that controls the engine and other vehicle systems.
- DLC (Diagnostic Link Connector): The standardized 16-pin connector used to access the vehicle’s diagnostic systems.
- CAN (Controller Area Network): A communication protocol used to transmit data between electronic control units in a vehicle.
- SAE (Society of Automotive Engineers): A professional organization that develops standards for the automotive industry.
- ISO (International Organization for Standardization): An international organization that develops standards for a wide range of industries, including automotive.
21. Additional Resources
- SAE International: https://www.sae.org/
- International Organization for Standardization (ISO): https://www.iso.org/
- National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE): https://www.ase.com/
22. Call to Action
Facing challenges with your vehicle’s diagnostics? Unsure how to interpret OBD2 codes or perform repairs? Contact OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN today for expert guidance and support. Our experienced technicians are ready to assist you with personalized solutions tailored to your needs. Reach out to us via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our facility at 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States. Let us help you unlock the full potential of your vehicle’s diagnostic capabilities and keep you on the road with confidence. Connect with OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for reliable car diagnostic solutions.