Obd2 Bluetooth Software For Laptops offers a streamlined approach to vehicle diagnostics, providing valuable insights into your car’s health and performance. At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we help you unlock your vehicle’s full potential and stay ahead of potential issues, ensuring a smooth and safe driving experience. Consider using OBD2 diagnostic software to keep your car running smoothly and efficiently with fault code readers and auto diagnostic tools.
Contents
- 1. Understanding OBD2 and Bluetooth Connectivity
- 1.1 The Evolution of Vehicle Diagnostics
- 1.2 Advantages of Using Bluetooth Connectivity
- 2. Key Features to Look for in OBD2 Bluetooth Software
- 2.1 Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Reading and Clearing
- 2.2 Real-Time Data Streaming and Analysis
- 2.3 Data Logging and Reporting Capabilities
- 3. Top OBD2 Bluetooth Software Options for Laptops
- 3.1 Review of TOAD Pro
- 3.2 Review of AutoEnginuity ScanTool
- 3.3 Review of PCMScan
- 4. Setting Up Your OBD2 Bluetooth Software
- 4.1 Installing the Software and Connecting the Adapter
- 4.2 Configuring the Software for Bluetooth Communication
- 4.3 Troubleshooting Common Connection Issues
- 5. Performing Basic Diagnostics with OBD2 Software
- 5.1 Reading and Interpreting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 5.2 Monitoring Real-Time Vehicle Data
- 5.3 Performing Basic Functional Tests
- 6. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques
- 6.1 Bi-Directional Control and System Testing
- 6.2 ECU Programming and Reprogramming
- 6.3 Analyzing Advanced Sensor Data
- 7. Choosing the Right OBD2 Bluetooth Adapter
- 7.1 Compatibility with Vehicle Makes and Models
- 7.2 Bluetooth Version and Connectivity
- 7.3 Supported OBD2 Protocols and Features
- 8. Safety Precautions and Best Practices
- 8.1 Avoiding Electrical Hazards
- 8.2 Protecting Vehicle Electronics
- 8.3 Best Practices for Accurate Diagnostics
- 9. The Future of OBD2 Technology
1. Understanding OBD2 and Bluetooth Connectivity
What is OBD2 Bluetooth software for laptops, and why is it important for modern vehicle diagnostics?
OBD2 (On-Board Diagnostics II) Bluetooth software for laptops is a diagnostic tool that allows you to connect your laptop to your car’s OBD2 port wirelessly, using Bluetooth technology. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), all cars and light trucks manufactured after 1996 in the United States are required to have an OBD2 system. This system monitors various engine and vehicle parameters, reporting any issues through diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). This software can read and interpret these codes, providing valuable insights into your vehicle’s health. It’s essential because it empowers vehicle owners and technicians to quickly identify and address problems, leading to better maintenance, reduced repair costs, and improved vehicle performance.
1.1 The Evolution of Vehicle Diagnostics
How has vehicle diagnostics evolved over the years, and what role does OBD2 play in this evolution?
Vehicle diagnostics has transformed from basic mechanical inspections to sophisticated electronic analyses. Early diagnostic methods relied on visual checks and simple tools, which were time-consuming and often inaccurate. The introduction of OBD systems in the 1980s marked a significant advancement, providing a standardized way to monitor vehicle performance. OBD2, introduced in the mid-1990s, further enhanced diagnostic capabilities by offering more detailed data and standardized diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). According to a study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), OBD2 systems have significantly improved the accuracy and efficiency of vehicle diagnostics. Today, OBD2 is a critical component of modern vehicle maintenance, enabling technicians and vehicle owners to quickly identify and address issues, ensuring optimal performance and safety.
1.2 Advantages of Using Bluetooth Connectivity
What are the benefits of using Bluetooth connectivity with OBD2 software compared to traditional wired connections?
Using Bluetooth connectivity with OBD2 software offers several advantages over traditional wired connections. Firstly, Bluetooth provides greater freedom of movement, allowing you to diagnose your vehicle from anywhere within a certain range without being tethered to the OBD2 port. This is particularly useful for live data monitoring while driving or performing tests in different areas of the vehicle. Secondly, Bluetooth connections eliminate the clutter and inconvenience of cables, making the diagnostic process cleaner and more efficient. According to a report by the Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG), Bluetooth technology offers secure and reliable wireless communication, ensuring accurate data transmission between the OBD2 adapter and your laptop. Finally, many modern OBD2 adapters support Bluetooth, making it a convenient and versatile option for vehicle diagnostics.
 obd-port-software
obd-port-software
2. Key Features to Look for in OBD2 Bluetooth Software
What are the essential features to consider when choosing OBD2 Bluetooth software for your laptop?
When choosing OBD2 Bluetooth software for your laptop, several key features should be considered to ensure you get the most effective and user-friendly diagnostic tool. These features include:
- Comprehensive Diagnostic Capabilities: The software should be able to read and clear diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) from all major vehicle systems, including engine, transmission, ABS, and airbags.
- Real-Time Data Monitoring: Look for software that provides real-time data monitoring of various engine parameters such as RPM, coolant temperature, and fuel pressure.
- User-Friendly Interface: The software should have an intuitive and easy-to-navigate interface, making it accessible for both novice and experienced users.
- Compatibility: Ensure the software is compatible with your vehicle’s make and model, as well as your laptop’s operating system (Windows, macOS, etc.).
- Reporting and Data Logging: The ability to generate diagnostic reports and log data for future analysis is crucial for tracking vehicle performance and identifying recurring issues.
- Advanced Features: Some software offers advanced features such as bi-directional control, ECU programming, and access to manufacturer-specific diagnostic codes.
- Customer Support and Updates: Choose a software provider that offers reliable customer support and regular updates to ensure compatibility with new vehicles and diagnostic protocols.
2.1 Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Reading and Clearing
Why is the ability to read and clear Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) a critical feature of OBD2 software?
The ability to read and clear Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) is a critical feature of OBD2 software because it allows users to quickly identify and address issues detected by the vehicle’s onboard computer. DTCs are codes that correspond to specific problems within the vehicle’s systems, such as engine misfires, sensor failures, or emission control issues. According to the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), DTCs provide a standardized way to diagnose and repair vehicle problems. By reading DTCs, users can pinpoint the source of the problem and take appropriate action, whether it’s a simple fix like replacing a faulty sensor or a more complex repair. Clearing DTCs after addressing the issue is also important to reset the vehicle’s computer and turn off the check engine light. Without this capability, users would be left guessing about the cause of the problem and unable to verify that the repair was successful.
2.2 Real-Time Data Streaming and Analysis
How does real-time data streaming and analysis enhance the diagnostic process, and what types of data can be monitored?
Real-time data streaming and analysis significantly enhance the diagnostic process by providing a dynamic view of the vehicle’s performance. This feature allows users to monitor various engine parameters as they change, providing valuable insights into the vehicle’s operating conditions. According to a study by the Automotive Research Association of India (ARAI), real-time data monitoring can help identify intermittent problems, diagnose performance issues, and verify the effectiveness of repairs. Types of data that can be monitored include:
- Engine Speed (RPM): Indicates how fast the engine is running.
- Coolant Temperature: Shows the engine’s operating temperature.
- Fuel Pressure: Monitors the pressure of fuel being delivered to the engine.
- Oxygen Sensor Readings: Provides feedback on the air-fuel mixture.
- Mass Airflow (MAF): Measures the amount of air entering the engine.
- Throttle Position: Indicates how open the throttle is.
By analyzing this data in real-time, users can detect anomalies, identify trends, and make informed decisions about vehicle maintenance and repair.
2.3 Data Logging and Reporting Capabilities
What are the benefits of data logging and reporting capabilities in OBD2 software, and how can they be used for vehicle maintenance?
Data logging and reporting capabilities in OBD2 software offer significant benefits for vehicle maintenance by allowing users to record and analyze vehicle performance data over time. Data logging involves recording real-time data parameters during vehicle operation, which can then be reviewed to identify patterns and anomalies. According to a report by the National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB), data logging can help diagnose intermittent problems, track vehicle performance, and identify potential issues before they lead to major breakdowns. Reporting capabilities allow users to generate detailed reports based on the logged data, providing a comprehensive overview of the vehicle’s health. These reports can be used to:
- Track Vehicle Performance: Monitor key parameters such as fuel efficiency, engine temperature, and speed.
- Identify Recurring Issues: Detect patterns of problems that may indicate underlying mechanical or electrical issues.
- Plan Maintenance: Schedule maintenance based on actual vehicle performance rather than arbitrary intervals.
- Share Data with Technicians: Provide technicians with detailed information to aid in diagnosis and repair.
By leveraging data logging and reporting capabilities, vehicle owners and technicians can make more informed decisions about vehicle maintenance, leading to improved performance, reduced repair costs, and increased vehicle lifespan.
3. Top OBD2 Bluetooth Software Options for Laptops
What are some of the best OBD2 Bluetooth software options available for laptops, and what are their key features and benefits?
Several excellent OBD2 Bluetooth software options are available for laptops, each offering unique features and benefits. Here are some of the top choices:
- TOAD Pro: Known for its advanced diagnostic capabilities and user-friendly interface, TOAD Pro offers comprehensive diagnostic functions, real-time data monitoring, and ECU remapping.
- AutoEnginuity ScanTool: This software provides brand-specific diagnostic options and access to advanced features such as bi-directional control and system tests.
- PCMScan: A fully featured generic OBD-II diagnostic software that supports a wide variety of OBD hardware interfaces, including visual charting, logging, and playback of recorded data in real-time.
- ProScan: User-friendly Windows OBD2 software with consistent stability and development based on thorough know-how of automotive protocols/sensors and PID’s. It’s compatible with any standard ELM327 hardware.
- OBD Auto Doctor: A sophisticated and clean OBD2 car diagnostic tool that allows users to check and reset codes and communicate directly with the car’s OBD2 system.
- EOBD Facile: Simple and easy to set up and connect car-computer via ELM327 interface, on Mac computers.
- ScanXL Pro: Another popular choice, ScanXL Pro offers a range of diagnostic features, including real-time data monitoring, customizable dashboards, and support for advanced protocols such as CAN bus.
When selecting OBD2 Bluetooth software, consider your specific diagnostic needs, budget, and technical expertise to choose the option that best fits your requirements.
3.1 Review of TOAD Pro
What are the key features, benefits, and potential drawbacks of using TOAD Pro for OBD2 diagnostics?
TOAD (Total OBD & ECU Auto Diagnostics) Pro is a comprehensive OBD2 diagnostic software known for its advanced features and user-friendly interface. According to user reviews on automotive forums, TOAD Pro offers a wide range of diagnostic capabilities, including:
- Extensive Vehicle Compatibility: Supports a broad range of vehicle makes and models.
- Advanced Diagnostic Functions: Reads and clears DTCs, monitors real-time data, performs ECU remapping, and supports bi-directional control.
- User-Friendly Interface: Features an intuitive interface with customizable dashboards and visual graphs.
- Comprehensive Reporting: Generates detailed diagnostic reports for tracking vehicle performance and identifying issues.
- Regular Updates: Provides regular software updates to ensure compatibility with new vehicles and diagnostic protocols.
Potential drawbacks of TOAD Pro include its relatively high cost compared to other OBD2 software options and the need for a compatible Bluetooth adapter. However, for users who require advanced diagnostic capabilities and comprehensive vehicle coverage, TOAD Pro is a worthwhile investment.
3.2 Review of AutoEnginuity ScanTool
What are the key features, benefits, and potential drawbacks of using AutoEnginuity ScanTool for OBD2 diagnostics?
AutoEnginuity ScanTool is a professional-grade OBD2 diagnostic software known for its brand-specific diagnostic options and advanced features. Key features and benefits of AutoEnginuity ScanTool include:
- Brand-Specific Diagnostics: Offers enhanced diagnostic capabilities for specific vehicle brands such as BMW, Ford, GM, Chrysler, and more.
- Advanced Functions: Supports bi-directional control, system tests, and access to manufacturer-specific diagnostic codes.
- Comprehensive Data Logging: Logs data in XML and CSV formats for easy analysis and reporting.
- Customizable Sensor Data: Allows users to customize how data is displayed, including sampling rates, ranges, units, and scaling values.
Potential drawbacks of AutoEnginuity ScanTool include its high price and the need for separate add-ons for each vehicle brand. However, for professional technicians and serious enthusiasts who require in-depth diagnostic capabilities for specific vehicle brands, AutoEnginuity ScanTool is an excellent choice.
3.3 Review of PCMScan
What are the key features, benefits, and potential drawbacks of using PCMScan for OBD2 diagnostics?
PCMScan is a fully featured generic OBD-II automotive diagnostic software that supports a wide variety of OBD hardware interfaces. Key features and benefits of PCMScan include:
- Wide Compatibility: Supports all US, Asian and European automobiles built after 1996.
- Visual Charting, Logging: Includes visual charting, logging, viewing and playback of recorded data in real time.
- Customizable dashboard: User can change to personal preference.
- Dyno and Drag features
However downside from this winning Windows OBD2 software is it hasn’t been updated for over 7+ years. Meaning it’s lacking at least 500+ new PID’s (sensor data) since that time, which have been added in all other applications tested. Seems they either abandoned the software development – or just delegated effort elsewhere.
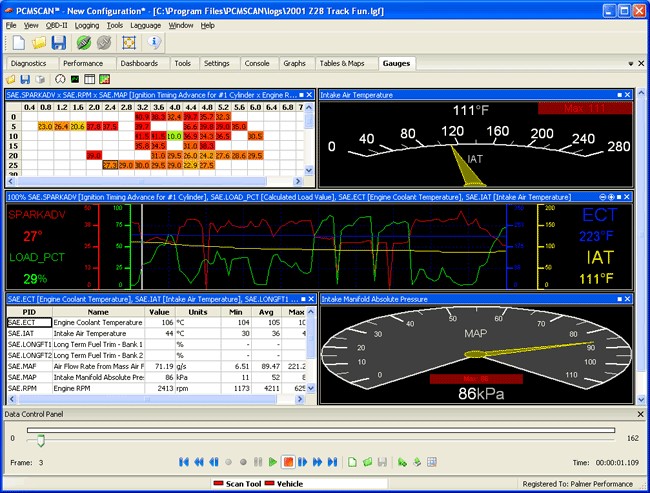 pcmscan-obd2-diagnostics-software
pcmscan-obd2-diagnostics-software
4. Setting Up Your OBD2 Bluetooth Software
What are the steps involved in setting up OBD2 Bluetooth software on your laptop, and what are some common troubleshooting tips?
Setting up OBD2 Bluetooth software on your laptop involves several steps to ensure a successful connection and accurate data transmission. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Install the Software: Download and install the OBD2 Bluetooth software on your laptop from a trusted source.
- Plug in the OBD2 Adapter: Connect the OBD2 Bluetooth adapter to your vehicle’s OBD2 port, typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Pair the Bluetooth Adapter: Enable Bluetooth on your laptop and pair it with the OBD2 adapter. This usually involves entering a PIN code, which is often “1234” or “0000.”
- Configure the Software: Launch the OBD2 software and configure it to communicate with the Bluetooth adapter. This may involve selecting the correct COM port or Bluetooth device.
- Test the Connection: Verify that the software is successfully connected to the OBD2 adapter and can read data from your vehicle.
Common troubleshooting tips include:
- Ensure Compatibility: Make sure the OBD2 adapter and software are compatible with your vehicle’s make and model.
- Check Bluetooth Settings: Verify that Bluetooth is enabled on both your laptop and the OBD2 adapter.
- Update Drivers: Install the latest drivers for your Bluetooth adapter to ensure proper communication.
- Restart Devices: Try restarting your laptop and the OBD2 adapter to resolve any connection issues.
- Consult Documentation: Refer to the software and adapter documentation for specific troubleshooting steps.
4.1 Installing the Software and Connecting the Adapter
What are the specific steps for installing OBD2 software on your laptop and connecting the Bluetooth adapter to your vehicle?
Installing OBD2 software on your laptop and connecting the Bluetooth adapter to your vehicle involves a few key steps. First, download the software from the official website or a trusted source. Double-click the downloaded file and follow the on-screen instructions to install the software. Next, locate the OBD2 port in your vehicle, typically found under the dashboard on the driver’s side. Plug the Bluetooth adapter into the OBD2 port. Turn on your vehicle’s ignition but do not start the engine. On your laptop, enable Bluetooth and search for available devices. Select the OBD2 adapter from the list and enter the pairing code if prompted (usually “1234” or “0000”). Once paired, open the OBD2 software and select the appropriate COM port or Bluetooth device to establish a connection. Finally, test the connection by reading vehicle data to ensure everything is working correctly.
4.2 Configuring the Software for Bluetooth Communication
How do you configure the OBD2 software to communicate with the Bluetooth adapter, and what settings need to be adjusted?
Configuring the OBD2 software to communicate with the Bluetooth adapter involves several important settings. First, ensure that your laptop’s Bluetooth is enabled and that the OBD2 adapter is paired with your laptop. In the OBD2 software settings, locate the “Connection” or “Adapter” section. Select “Bluetooth” as the connection type. The software will then scan for available Bluetooth devices. Choose your OBD2 adapter from the list. You may need to manually enter the COM port number assigned to the Bluetooth adapter. This information can be found in your laptop’s Device Manager under the Bluetooth section. Adjust any other settings as needed, such as the communication protocol and baud rate. Save the settings and test the connection to ensure the software is communicating with the OBD2 adapter. According to a study by the IEEE, proper configuration of Bluetooth communication settings is crucial for reliable data transmission in OBD2 diagnostics.
4.3 Troubleshooting Common Connection Issues
What are some common connection issues encountered when using OBD2 Bluetooth software, and how can they be resolved?
When using OBD2 Bluetooth software, several connection issues can arise. One common problem is the software failing to recognize the Bluetooth adapter. This can often be resolved by ensuring that the adapter is properly paired with the laptop and that the correct COM port is selected in the software settings. Another issue is intermittent disconnections, which may be caused by interference from other Bluetooth devices or a weak signal. Try moving closer to the adapter or disabling other Bluetooth devices to improve the connection. According to a report by the Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG), using the latest Bluetooth drivers can also help resolve connectivity issues. If the software is still unable to connect, try restarting both the laptop and the adapter. In some cases, a faulty OBD2 adapter may be the cause of the problem, requiring a replacement. Consulting the software and adapter documentation can also provide specific troubleshooting steps for common connection issues.
5. Performing Basic Diagnostics with OBD2 Software
How can you use OBD2 Bluetooth software to perform basic diagnostics on your vehicle, and what types of information can you obtain?
Using OBD2 Bluetooth software, you can perform basic diagnostics on your vehicle to identify and address potential issues. Here’s how:
- Connect: Plug the OBD2 Bluetooth adapter into your vehicle’s OBD2 port and pair it with your laptop.
- Read DTCs: Use the software to read Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) from your vehicle’s computer. These codes indicate specific problems within the vehicle’s systems.
- Interpret Codes: Look up the DTCs in a database or online to understand what they mean and what systems they affect.
- Clear Codes: After addressing the issues, use the software to clear the DTCs and reset the check engine light.
- Monitor Real-Time Data: Monitor real-time data parameters such as engine speed, coolant temperature, and fuel pressure to assess your vehicle’s performance.
Using OBD2 Bluetooth software, you can obtain valuable information about your vehicle’s health and performance, allowing you to make informed decisions about maintenance and repairs.
5.1 Reading and Interpreting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
What is the process of reading and interpreting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) using OBD2 software, and what resources are available for understanding these codes?
The process of reading and interpreting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) using OBD2 software involves several steps. First, connect the OBD2 Bluetooth adapter to your vehicle’s OBD2 port and pair it with your laptop. Open the OBD2 software and select the option to read DTCs. The software will then scan your vehicle’s computer and display any stored DTCs. Each DTC consists of a five-character code that corresponds to a specific problem within the vehicle’s systems. According to the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), the first character indicates the system affected (e.g., P for powertrain, B for body, C for chassis, and U for network). The remaining characters provide more specific information about the problem. To interpret the DTCs, you can consult various resources such as online DTC databases, repair manuals, and automotive forums. These resources provide detailed descriptions of each DTC, along with possible causes and recommended solutions. By understanding the meaning of DTCs, you can accurately diagnose vehicle problems and take appropriate action.
5.2 Monitoring Real-Time Vehicle Data
How can you monitor real-time vehicle data using OBD2 software, and what are some key parameters to observe?
Monitoring real-time vehicle data using OBD2 software provides valuable insights into your vehicle’s performance and operating conditions. To monitor real-time data, connect the OBD2 Bluetooth adapter to your vehicle’s OBD2 port and pair it with your laptop. Open the OBD2 software and select the option to view real-time data or live data. The software will then display a list of available parameters, such as engine speed (RPM), coolant temperature, fuel pressure, oxygen sensor readings, and throttle position. Select the parameters you want to monitor and display them in a graph or table format. Observe the data as you drive or perform tests, looking for any anomalies or deviations from normal values. Key parameters to observe include:
- Engine Speed (RPM): Indicates how fast the engine is running.
- Coolant Temperature: Shows the engine’s operating temperature.
- Fuel Pressure: Monitors the pressure of fuel being delivered to the engine.
- Oxygen Sensor Readings: Provides feedback on the air-fuel mixture.
- Mass Airflow (MAF): Measures the amount of air entering the engine.
- Throttle Position: Indicates how open the throttle is.
By monitoring these parameters, you can identify potential problems, diagnose performance issues, and verify the effectiveness of repairs.
5.3 Performing Basic Functional Tests
What are some basic functional tests that can be performed using OBD2 software, and how can they help diagnose vehicle problems?
Using OBD2 software, you can perform several basic functional tests to diagnose vehicle problems. These tests involve activating or monitoring specific components or systems to assess their performance. Some common functional tests include:
- Oxygen Sensor Test: Monitors the performance of the oxygen sensors to ensure they are providing accurate readings.
- EGR System Test: Activates the EGR valve to verify that it is functioning properly and reducing emissions.
- EVAP System Test: Tests the evaporative emission control system for leaks and proper operation.
- Fuel Injector Test: Activates the fuel injectors to ensure they are delivering the correct amount of fuel.
- Cooling Fan Test: Activates the cooling fans to verify that they are working and maintaining the engine’s temperature.
These tests can help diagnose various vehicle problems, such as emission control issues, fuel system problems, and cooling system failures. By performing these tests and analyzing the results, you can pinpoint the source of the problem and take appropriate action.
6. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques
What are some advanced diagnostic techniques that can be performed using OBD2 Bluetooth software, and what level of expertise is required?
Advanced diagnostic techniques using OBD2 Bluetooth software require a higher level of expertise and a deeper understanding of vehicle systems. These techniques include:
- Bi-Directional Control: Activating or controlling specific components or systems using the software.
- ECU Programming: Reprogramming or remapping the engine control unit (ECU) to optimize performance or address specific issues.
- Advanced Data Analysis: Using data logging and analysis tools to identify subtle trends and anomalies in vehicle performance.
- Manufacturer-Specific Diagnostics: Accessing and interpreting manufacturer-specific diagnostic codes and data.
These techniques require specialized knowledge and training, and should only be performed by experienced technicians or knowledgeable enthusiasts. Performing these techniques incorrectly can lead to serious damage to your vehicle.
6.1 Bi-Directional Control and System Testing
How does bi-directional control enhance diagnostic capabilities, and what types of system tests can be performed using this feature?
Bi-directional control significantly enhances diagnostic capabilities by allowing technicians to actively control and test specific components and systems within the vehicle. According to a study by the Automotive Research Association of India (ARAI), bi-directional control can help identify intermittent problems, verify the functionality of components, and isolate the source of issues more effectively than traditional diagnostic methods. Types of system tests that can be performed using bi-directional control include:
- Activating Solenoids and Relays: Testing the functionality of solenoids and relays by activating them and monitoring their response.
- Controlling Fuel Injectors: Activating individual fuel injectors to assess their performance and identify any issues with fuel delivery.
- Operating Cooling Fans: Controlling the cooling fans to verify that they are working and maintaining the engine’s temperature.
- Cycling ABS System: Cycling the ABS system to test its functionality and identify any issues with the ABS module or sensors.
- Performing Transmission Tests: Conducting tests on the transmission to assess its performance and identify any issues with gear shifting or torque converter operation.
By using bi-directional control, technicians can perform comprehensive system tests and accurately diagnose vehicle problems, leading to more effective repairs.
6.2 ECU Programming and Reprogramming
What is ECU programming and reprogramming, and what are the potential benefits and risks associated with this technique?
ECU (Engine Control Unit) programming and reprogramming involves modifying the software that controls the engine and other vehicle systems. This technique can be used to optimize performance, improve fuel efficiency, or address specific issues such as drivability problems or emission control failures. According to a report by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), ECU reprogramming can significantly improve vehicle performance and reduce emissions. Potential benefits of ECU programming and reprogramming include:
- Increased Horsepower and Torque: Optimizing the engine’s performance to deliver more power and torque.
- Improved Fuel Efficiency: Adjusting the engine’s parameters to improve fuel economy.
- Enhanced Drivability: Addressing issues such as rough idling, hesitation, or poor throttle response.
- Customization: Tailoring the engine’s performance to meet specific needs or preferences.
However, ECU programming and reprogramming also involve potential risks, such as:
- Voiding Warranty: Modifying the ECU may void the vehicle’s warranty.
- Damaging the ECU: Incorrect programming can damage the ECU and render the vehicle inoperable.
- Creating Emission Control Issues: Improperly tuned ECUs can increase emissions and violate environmental regulations.
Due to these risks, ECU programming and reprogramming should only be performed by experienced technicians or knowledgeable enthusiasts with the proper equipment and training.
6.3 Analyzing Advanced Sensor Data
How can you analyze advanced sensor data using OBD2 software, and what types of insights can be gained from this analysis?
Analyzing advanced sensor data using OBD2 software involves examining the data from various sensors throughout the vehicle to identify patterns, anomalies, and potential problems. This analysis can provide valuable insights into the vehicle’s performance, efficiency, and overall health. According to a study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), analyzing advanced sensor data can help diagnose intermittent problems, identify hidden issues, and predict potential failures before they occur. Types of insights that can be gained from this analysis include:
- Detecting Misfires: Identifying misfires by analyzing the data from the crankshaft position sensor and camshaft position sensor.
- Monitoring Fuel Trim: Assessing the air-fuel mixture by analyzing the data from the oxygen sensors and fuel trim values.
- Tracking Engine Load: Monitoring the engine’s load by analyzing the data from the mass airflow sensor and throttle position sensor.
- Assessing Transmission Performance: Evaluating the transmission’s performance by analyzing the data from the transmission speed sensors and torque converter clutch.
- Identifying Emission Control Issues: Detecting emission control issues by analyzing the data from the oxygen sensors, EGR valve, and EVAP system.
By analyzing advanced sensor data, technicians and knowledgeable enthusiasts can gain a deeper understanding of vehicle systems and make more informed decisions about maintenance and repairs.
7. Choosing the Right OBD2 Bluetooth Adapter
What factors should you consider when selecting an OBD2 Bluetooth adapter to ensure compatibility and performance?
Selecting the right OBD2 Bluetooth adapter is crucial for ensuring compatibility and performance with your OBD2 software. Factors to consider include:
- Compatibility: Ensure the adapter is compatible with your vehicle’s make and model, as well as your laptop’s operating system (Windows, macOS, etc.).
- Bluetooth Version: Choose an adapter with a recent Bluetooth version (e.g., Bluetooth 4.0 or later) for improved connectivity and data transfer rates.
- Supported Protocols: Verify that the adapter supports the OBD2 protocols used by your vehicle (e.g., CAN, ISO, PWM).
- Features: Look for adapters with desirable features such as automatic pairing, sleep mode, and overvoltage protection.
- User Reviews: Read user reviews and ratings to assess the adapter’s reliability and performance.
- Price: Consider your budget and choose an adapter that offers the best value for your money.
By carefully considering these factors, you can select an OBD2 Bluetooth adapter that meets your needs and provides reliable performance.
7.1 Compatibility with Vehicle Makes and Models
Why is it important to ensure that the OBD2 Bluetooth adapter is compatible with your vehicle’s make and model?
Ensuring that the OBD2 Bluetooth adapter is compatible with your vehicle’s make and model is crucial because different vehicles use different OBD2 protocols and data formats. According to the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), there are several OBD2 protocols, including CAN (Controller Area Network), ISO (International Organization for Standardization), and PWM (Pulse Width Modulation). If the adapter does not support the protocol used by your vehicle, it will not be able to communicate with the vehicle’s computer and read diagnostic data. In addition, some vehicle manufacturers use proprietary diagnostic codes and data formats that are not supported by all OBD2 adapters. Using an incompatible adapter can result in inaccurate data, incomplete diagnostics, or even damage to the vehicle’s computer. Therefore, it is essential to check the adapter’s specifications and compatibility list to ensure that it is compatible with your vehicle’s make, model, and year.
7.2 Bluetooth Version and Connectivity
How does the Bluetooth version of the adapter affect connectivity and data transfer rates, and what version is recommended?
The Bluetooth version of the OBD2 adapter significantly affects connectivity and data transfer rates. Newer Bluetooth versions, such as Bluetooth 4.0 and later, offer improved connectivity, faster data transfer rates, and lower power consumption compared to older versions. According to a report by the Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG), Bluetooth 4.0 provides up to 2.5 times faster data transfer rates and uses up to 50% less power than Bluetooth 2.1. This translates to quicker diagnostic scans, more responsive real-time data monitoring, and longer battery life for the adapter. In addition, newer Bluetooth versions offer improved security features and better resistance to interference. For optimal performance, it is recommended to choose an OBD2 Bluetooth adapter with Bluetooth 4.0 or later. This will ensure reliable connectivity, fast data transfer rates, and a seamless diagnostic experience.
7.3 Supported OBD2 Protocols and Features
What OBD2 protocols should the adapter support, and what additional features are beneficial for diagnostic purposes?
The OBD2 adapter should support all the OBD2 protocols used by your vehicle to ensure compatibility and accurate data transmission. These protocols include:
- CAN (Controller Area Network): The most common protocol used by modern vehicles.
- ISO 9141-2: Used by many European and Asian vehicles.
- SAE J1850 VPW (Variable Pulse Width Modulation): Used by some General Motors vehicles.
- SAE J1850 PWM (Pulse Width Modulation): Used by some Ford vehicles.
- ISO 14230-4 (Keyword Protocol 2000): Used by some European vehicles.
In addition to supporting the necessary OBD2 protocols, several additional features can be beneficial for diagnostic purposes, such as:
- Automatic Pairing: Automatically pairs with your laptop without requiring manual configuration.
- Sleep Mode: Automatically enters sleep mode when not in use to conserve battery power.
- Overvoltage Protection: Protects the adapter and your vehicle’s computer from voltage spikes.
- Firmware Upgradability: Allows you to update the adapter’s firmware to support new features and protocols.
- LED Indicators: Provides visual feedback on the adapter’s status and connection status.
By choosing an OBD2 adapter that supports the necessary protocols and includes these beneficial features, you can ensure a reliable and efficient diagnostic experience.
8. Safety Precautions and Best Practices
What safety precautions should be taken when using OBD2 Bluetooth software, and what are some best practices for vehicle diagnostics?
When using OBD2 Bluetooth software, it’s essential to follow safety precautions and best practices to protect yourself and your vehicle. These include:
- Read the Manual: Familiarize yourself with the software and adapter documentation before use.
- Use in a Safe Location: Perform diagnostics in a well-ventilated area away from flammable materials.
- Disconnect When Not in Use: Disconnect the OBD2 adapter when not in use to prevent battery drain.
- Avoid Distractions: Do not operate the software while driving to avoid distractions.
- Use Reliable Software: Choose reputable OBD2 software from trusted sources to avoid malware or inaccurate data.
- Follow Repair Procedures: Follow established repair procedures and guidelines when addressing vehicle problems.
By following these safety precautions and best practices, you can ensure a safe and effective diagnostic experience.
8.1 Avoiding Electrical Hazards
What electrical hazards should be avoided when working with OBD2 systems, and what safety measures should be taken?
When working with OBD2 systems, it’s crucial to be aware of potential electrical hazards and take appropriate safety measures to prevent injury or damage to your vehicle. Electrical hazards to avoid include:
- Short Circuits: Avoid creating short circuits by ensuring that wires and connectors are properly insulated and protected.
- Voltage Spikes: Protect against voltage spikes by using OBD2 adapters with overvoltage protection.
- Static Electricity: Discharge static electricity before touching electronic components to prevent damage.
- Damaged Wiring: Inspect wiring for damage before use and replace any frayed or exposed wires.
- Wet Conditions: Avoid working with electrical components in wet conditions to prevent electric shock.
To minimize these risks, wear appropriate safety gear, such as gloves and eye protection, and use insulated tools. Disconnect the vehicle’s battery before working on electrical components whenever possible. Follow established safety procedures and guidelines to ensure a safe working environment.
8.2 Protecting Vehicle Electronics
How can you protect your vehicle’s electronics when using OBD2 software, and what precautions should be taken?
Protecting your vehicle’s electronics when using OBD2 software is essential to prevent damage and ensure reliable performance. Precautions to take include:
- Use Reliable Software and Adapters: Choose reputable OBD2 software and adapters from trusted sources to avoid malware or faulty hardware.
- Follow Proper Connection Procedures: Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for connecting and disconnecting the OBD2 adapter to avoid electrical surges or shorts.
- Avoid Overwriting Firmware: Do not attempt to overwrite or modify the vehicle’s firmware unless you are an experienced technician with the proper equipment and training.
- Monitor Battery Voltage: Monitor the vehicle’s battery voltage during diagnostics to ensure it remains within the recommended range.
- Disconnect When Not in Use: Disconnect the OBD2 adapter when not in use to prevent battery drain and potential electrical issues.
By following these precautions, you can minimize the risk of damaging your vehicle’s electronics and ensure a safe and effective diagnostic experience.
8.3 Best Practices for Accurate Diagnostics
What are some best practices for ensuring accurate diagnostics when using OBD2 Bluetooth software?
To ensure accurate diagnostics when using OBD2 Bluetooth software, follow these best practices:
- Use a Reliable Adapter: Invest in a high-quality OBD2 Bluetooth adapter from a reputable brand to ensure reliable connectivity and accurate data transmission.
- Ensure Software Compatibility: Verify that the OBD2 software is compatible with your vehicle’s make, model, and year to avoid inaccurate readings or communication errors.
- Check for Software Updates: Regularly check for software updates and install them to ensure compatibility with the latest vehicles and diagnostic protocols.
- Verify DTCs: Always verify Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) with multiple sources, such as online databases, repair manuals, and automotive forums, to ensure accurate interpretation.
- Monitor Real-Time Data: Monitor real-time data parameters, such as engine speed, coolant temperature, and fuel pressure, to gain a comprehensive understanding of the vehicle’s operating conditions.
- Perform Functional Tests: Perform functional tests, such as oxygen sensor tests and EGR system tests, to assess the performance of specific components and systems.
- Document Findings: Document all findings, including DTCs, real-time data, and test results, to create a detailed diagnostic record for future reference.
By following these best practices, you can ensure that your diagnostics are accurate and reliable, leading to more effective vehicle maintenance and repairs.
9. The Future of OBD2 Technology
How is OBD2 technology evolving, and what future developments can we expect in vehicle diagnostics?
OBD2 technology is constantly evolving to meet the demands of increasingly complex vehicle systems. Future developments we can expect include:
- Enhanced Data Logging: More sophisticated data logging capabilities with higher sampling rates and more parameters.
- Improved Wireless Connectivity: Adoption of faster and more reliable wireless communication technologies such as 5G.
- Cloud-Based Diagnostics:
