The Obd2 Interface V1.5 is a valuable tool for diagnosing car problems, providing access to your vehicle’s onboard computer to read diagnostic trouble codes and monitor performance. OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN offers comprehensive guides and services to help you effectively utilize this interface, ensuring accurate diagnostics and efficient repairs. By understanding the capabilities of the OBD2 interface V1.5, you can save time and money on car maintenance while improving your vehicle’s performance through diagnostic tools, scan tools, and vehicle diagnostics.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the OBD2 Interface V1.5
- 1.1. What is OBD2?
- 1.2. Key Features of OBD2 Interface V1.5
- 1.3. Why Choose the V1.5 Version?
- 2. Compatibility: What Vehicles Can You Use It On?
- 2.1. Vehicle Coverage by Region
- 2.2. Compatibility with Different Car Brands
- 2.3. Exceptions and Limitations
- 3. Functions: What Can You Do With The OBD2 Interface V1.5?
- 3.1. Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 3.1.1. Generic vs. Manufacturer-Specific Codes
- 3.1.2. Understanding Code Definitions
- 3.2. Clearing Trouble Codes
- 3.3. Monitoring Real-Time Data
- 3.3.1. Key Parameters to Monitor
- 3.4. Performing Diagnostic Tests
- 3.5. Accessing Vehicle Information
- 4. How to Use the OBD2 Interface V1.5: A Step-by-Step Guide
- 4.1. Locating the OBD2 Port
- 4.2. Connecting the OBD2 Interface
- 4.3. Pairing with Your Android Device via Bluetooth
- 4.4. Choosing the Right App
- 4.5. Reading and Interpreting Data
- 4.6. Troubleshooting Connection Issues
- 5. Best Apps and Software for OBD2 Interface V1.5
- 5.1. Top Android Apps
- 5.1.1. Torque Pro
- 5.1.2. DashCommand
- 5.1.3. OBD Car Doctor
- 5.2. PC Software Options
- 5.2.1. ScanMaster-ELM
- 5.2.2. ScanTool.net
- 5.2.3. PCMSCAN ELM
- 5.3. Software Compatibility
- 6. Common Issues and Troubleshooting
- 6.1. Connection Problems
- 6.1.1. Bluetooth Pairing Issues
- 6.1.2. Interface Not Recognized by App
- 6.2. Incorrect Data Readings
- 6.2.1. Inaccurate Sensor Data
- 6.2.2. Error Codes Not Displaying
- 6.3. Software Compatibility Issues
- 6.3.1. App Crashes or Freezes
- 6.3.2. Incompatible Protocols
- 7. Advanced Tips and Tricks
- 7.1. Using Enhanced Diagnostic Modes
- 7.1.1. Accessing Manufacturer-Specific Data
- 7.1.2. Performing Advanced Tests
- 7.2. Creating Custom Dashboards
- 7.2.1. Selecting Relevant Parameters
- 7.2.2. Customizing Gauges and Graphs
- 7.3. Data Logging and Analysis
- 7.3.1. Recording Data
- 7.3.2. Analyzing Data
- 8. OBD2 Interface V1.5 vs. Other Versions
- 8.1. Key Differences
- 8.1.1. Firmware Stability
- 8.1.2. Vehicle Compatibility
- 8.1.3. Feature Set
- 8.2. Advantages of V1.5
- 8.3. Disadvantages of V1.5
- 9. Safety Precautions
- 9.1. Safe Environment
- 9.2. Avoiding Distractions
- 9.3. Electrical Safety
- 9.4. Data Security
- 10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 10.1. What is an OBD2 Scanner?
- 10.2. How Do I Read OBD2 Error Codes?
- 10.3. What Common Car Problems Can an OBD2 Scanner Detect?
- 10.4. Is the OBD2 Interface V1.5 Suitable for Beginners?
- 10.5. Can I Use the OBD2 Interface V1.5 on Multiple Vehicles?
- 10.6. How Often Should I Scan My Car with an OBD2 Scanner?
- 10.7. Will Clearing OBD2 Codes Solve My Car Problem?
- 10.8. What Are the Limitations of the OBD2 Interface V1.5?
- 10.9. How Can I Update the Firmware of My OBD2 Interface V1.5?
- 10.10. Is It Safe to Buy a Used OBD2 Interface V1.5?
1. Understanding the OBD2 Interface V1.5
What exactly is the OBD2 interface V1.5, and why is it important for car diagnostics? The OBD2 (On-Board Diagnostics II) interface V1.5 is a hardware and software standard used to access data from a vehicle’s onboard computer. It’s important because it allows mechanics and car owners to diagnose problems, monitor performance, and ensure vehicles meet emissions standards, leading to quicker repairs, better fuel efficiency, and reduced environmental impact, according to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA).
1.1. What is OBD2?
OBD2 is a standardized system that allows external devices to communicate with a vehicle’s computer, accessing data related to engine performance, emissions, and other critical systems. According to the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), the OBD2 standard ensures that all vehicles manufactured after 1996 are equipped with a universal port and protocol for diagnostics.
1.2. Key Features of OBD2 Interface V1.5
The OBD2 interface V1.5 is known for its stable firmware and compatibility with various vehicles. Key features include:
- PIC18F25K80 Chipset: Ensures reliable performance and compatibility.
- Bluetooth Connectivity: Allows wireless connection to Android devices for easy data access.
- Support for OBD-II Protocols: Compatible with all standard OBD-II protocols for comprehensive diagnostics.
- Generic and Manufacturer-Specific Codes: Reads and interprets both generic and manufacturer-specific diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
- Real-time Data Monitoring: Provides live data streams from various sensors and systems within the vehicle.
- User-Friendly Interface: Designed to be easy to use, even for beginners.
1.3. Why Choose the V1.5 Version?
The V1.5 version of the OBD2 interface is often preferred due to its enhanced stability and broader vehicle compatibility compared to older versions. It offers a reliable connection and accurate data retrieval, making it a dependable tool for both professional mechanics and DIY enthusiasts.
2. Compatibility: What Vehicles Can You Use It On?
Understanding which vehicles are compatible with the OBD2 interface V1.5 is crucial for effective diagnostics. Generally, it works with most cars manufactured after 1996 in the United States, after 2001 in Europe, and after 2002 in Asia. However, there are exceptions, so it’s always best to verify compatibility.
2.1. Vehicle Coverage by Region
The OBD2 interface V1.5 supports a wide range of vehicles from different regions:
- American Cars: Generally supports cars manufactured after 1998.
- European Cars: Typically supports cars manufactured after 2000.
- Asian Cars: Usually supports cars manufactured after 2002, including Japanese, Korean, and Chinese models.
- Russian Cars: Supports cars manufactured after 2012 (e.g., VAZ, UAZ, GAZ).
2.2. Compatibility with Different Car Brands
Different car brands adhere to OBD2 standards with slight variations. Here’s a general guide:
- Ford: Compatible with most models manufactured after 1996.
- Chevrolet: Compatible with most models manufactured after 1996.
- Toyota: Compatible with most models manufactured after 1998.
- Honda: Compatible with most models manufactured after 1998.
- BMW: Compatible with most models manufactured after 2000.
- Mercedes-Benz: Compatible with most models manufactured after 2000.
2.3. Exceptions and Limitations
Despite broad compatibility, there are exceptions:
- 24V Diesel or Trucks: The OBD2 interface V1.5 typically does not support 24V diesel vehicles or trucks.
- Vehicles without a 16-Pin Adapter: It cannot be used on cars without a 16-pin OBD2 adapter port.
- Hybrid and Electric Vehicles: While many hybrid and electric vehicles use OBD2, some functions may be limited or require specialized tools.
- Older Vehicles: Vehicles manufactured before the standardization of OBD2 may not be compatible.
3. Functions: What Can You Do With The OBD2 Interface V1.5?
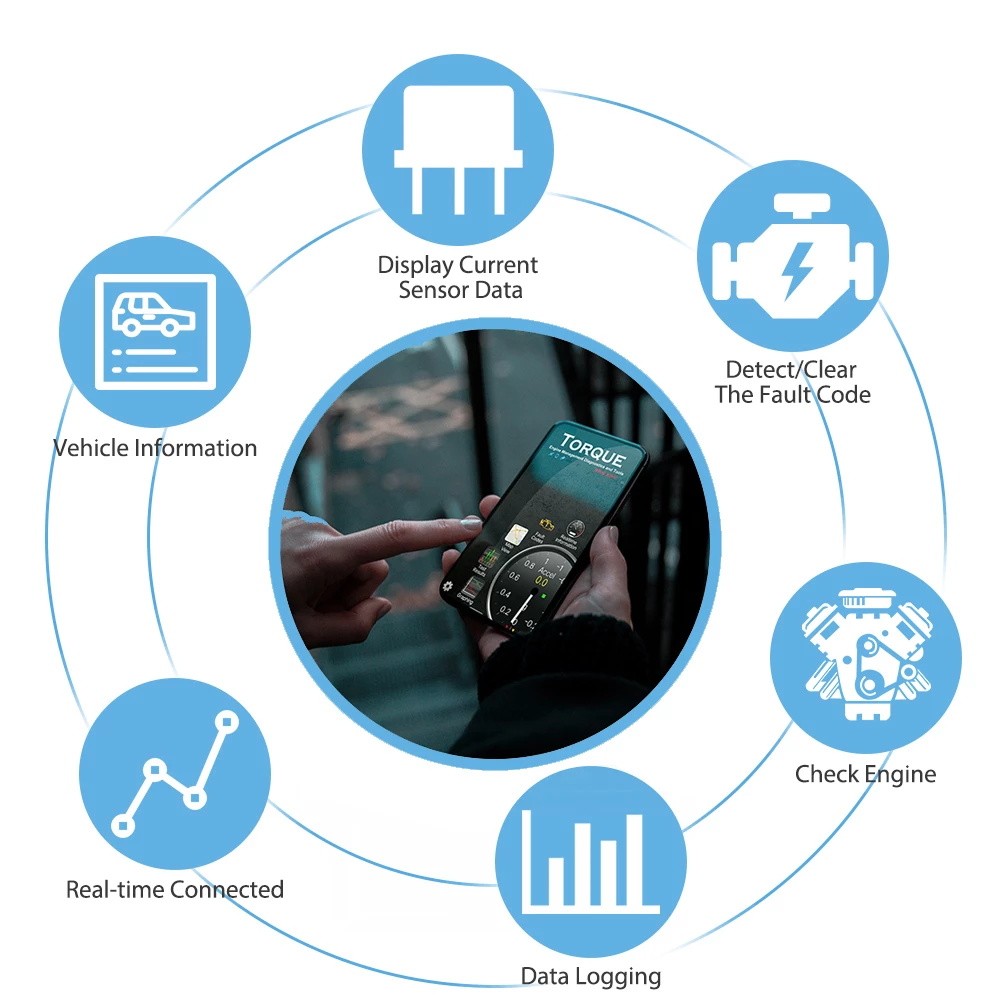
What functions can you perform using the OBD2 interface V1.5, and how can these functions help in diagnosing and maintaining your vehicle? The OBD2 interface V1.5 allows you to read diagnostic trouble codes, clear these codes, monitor real-time data, and perform various diagnostic tests. These functions help identify problems, understand your vehicle’s performance, and ensure it runs efficiently.
3.1. Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
One of the primary functions of the OBD2 interface V1.5 is reading diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). These codes are generated by the vehicle’s computer when it detects a problem.
3.1.1. Generic vs. Manufacturer-Specific Codes
- Generic Codes: These are standard codes defined by the OBD2 standard and are the same across all vehicle makes and models. They typically start with the letters P0, P2, C0, B0, or U0.
- Manufacturer-Specific Codes: These codes are specific to the vehicle manufacturer and provide more detailed information about the problem. They usually start with P1, P3, C1, B1, or U1.
3.1.2. Understanding Code Definitions
Each DTC has a specific definition that describes the problem. For example:
- P0300: Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected
- P0171: System Too Lean (Bank 1)
- P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
3.2. Clearing Trouble Codes
After identifying and fixing a problem, you can use the OBD2 interface V1.5 to clear the trouble codes and turn off the Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL), also known as the “Check Engine” light. Clearing codes can also help reset the vehicle’s computer after repairs.
3.3. Monitoring Real-Time Data
The OBD2 interface V1.5 allows you to monitor real-time data from various sensors and systems in your vehicle. This data can help you understand how your vehicle is performing and identify potential problems before they trigger a DTC.
3.3.1. Key Parameters to Monitor
- Engine RPM: Revolutions per minute, indicating engine speed.
- Vehicle Speed: Current speed of the vehicle.
- Coolant Temperature: Temperature of the engine coolant.
- Intake Air Temperature: Temperature of the air entering the engine.
- Mass Air Flow (MAF): Measures the amount of air entering the engine.
- Oxygen Sensor Readings: Measures the oxygen content in the exhaust.
- Fuel Trim: Adjustments made to the fuel mixture by the engine control unit (ECU).
- Battery Voltage: Voltage of the vehicle’s battery.
3.4. Performing Diagnostic Tests
Some OBD2 scanners and software allow you to perform specific diagnostic tests, such as:
- Oxygen Sensor Test: Checks the performance of the oxygen sensors.
- Evaporative Emission Control System (EVAP) Test: Checks for leaks in the EVAP system.
- Catalyst Monitor Test: Checks the efficiency of the catalytic converter.
3.5. Accessing Vehicle Information
The OBD2 interface V1.5 can also provide access to important vehicle information, such as:
- Vehicle Identification Number (VIN): A unique identifier for the vehicle.
- Calibration Identification (CALID): Identifies the software version installed in the ECU.
- Calibration Verification Number (CVN): A checksum value used to verify the integrity of the software.
4. How to Use the OBD2 Interface V1.5: A Step-by-Step Guide
How do you connect and use the OBD2 interface V1.5 to diagnose your car problems effectively? Using the OBD2 interface V1.5 involves connecting the device to your car’s OBD2 port, pairing it with your Android device via Bluetooth, and using a compatible app to read and interpret the data. Following these steps ensures accurate diagnostics and helps you understand your vehicle’s condition.
4.1. Locating the OBD2 Port
The first step is to locate the OBD2 port in your vehicle. It is typically found under the dashboard on the driver’s side. Common locations include:
- Under the steering wheel column
- Near the center console
- Inside the glove compartment
4.2. Connecting the OBD2 Interface
Once you have located the OBD2 port, plug the OBD2 interface V1.5 into the port. Ensure it is securely connected.
4.3. Pairing with Your Android Device via Bluetooth
- Enable Bluetooth: Turn on Bluetooth on your Android device.
- Search for Devices: Go to the Bluetooth settings and search for available devices.
- Select “OBD II”: Find the device named “OBD II” or a similar name in the list of available devices and select it.
- Enter the Pairing Code: When prompted, enter the Bluetooth pairing code, which is typically “1234”.
- Pair the Devices: Complete the pairing process.
4.4. Choosing the Right App
There are many OBD2 apps available for Android devices. Some popular options include:
- Torque Pro: A comprehensive app with many features and customization options.
- DashCommand: A visually appealing app with customizable dashboards and gauges.
- OBD Car Doctor: A free app with basic diagnostic features.
- Auto Doctor: Another free app with a user-friendly interface.
- EOBD Facile: An app focused on European vehicles with enhanced diagnostic capabilities.
4.5. Reading and Interpreting Data
- Launch the App: Open the OBD2 app on your Android device.
- Connect to the OBD2 Interface: In the app settings, select the Bluetooth connection type and choose the “OBD II” device.
- Read Diagnostic Trouble Codes: Navigate to the section for reading diagnostic trouble codes. The app will display any stored DTCs and their definitions.
- Monitor Real-Time Data: Go to the real-time data section to view live data streams from various sensors and systems in your vehicle.
- Perform Diagnostic Tests: If the app supports it, perform specific diagnostic tests to further analyze your vehicle’s performance.
4.6. Troubleshooting Connection Issues
If you encounter problems connecting the OBD2 interface V1.5 to your Android device, try the following:
- Verify Bluetooth Connection: Ensure that Bluetooth is enabled on your Android device and that it is properly paired with the OBD2 interface.
- Check App Settings: Make sure the app is configured to use the correct Bluetooth device.
- Restart Devices: Try restarting both your Android device and the vehicle.
- Check OBD2 Port: Ensure that the OBD2 interface is securely plugged into the OBD2 port and that the port is clean and free of debris.
- Test with Another App: Try using a different OBD2 app to see if the problem is with the app itself.
5. Best Apps and Software for OBD2 Interface V1.5
What are the best apps and software to use with the OBD2 interface V1.5, and what features do they offer to help you diagnose and monitor your vehicle? The best apps and software for the OBD2 interface V1.5 include Torque Pro, DashCommand, and OBD Car Doctor, offering features like real-time data monitoring, DTC reading and clearing, and customizable dashboards. Choosing the right app can enhance your diagnostic capabilities and provide valuable insights into your vehicle’s performance.
5.1. Top Android Apps
5.1.1. Torque Pro
Torque Pro is a popular and comprehensive OBD2 app for Android devices. It offers a wide range of features, including:
- Real-time Data Monitoring: Displays live data from various sensors and systems.
- Diagnostic Trouble Codes: Reads and clears DTCs.
- Customizable Dashboards: Allows you to create custom dashboards with gauges and graphs.
- Data Logging: Records data for later analysis.
- GPS Tracking: Tracks your vehicle’s location and speed.
- Plugin Support: Supports plugins for enhanced functionality.
5.1.2. DashCommand
DashCommand is another popular OBD2 app known for its visually appealing interface and customizable dashboards. Key features include:
- Real-time Data Monitoring: Displays live data with customizable gauges and graphs.
- Diagnostic Trouble Codes: Reads and clears DTCs.
- Performance Monitoring: Tracks vehicle performance metrics such as acceleration, braking, and horsepower.
- Fuel Economy Analysis: Provides detailed fuel economy analysis.
- Data Logging: Records data for later analysis.
5.1.3. OBD Car Doctor
OBD Car Doctor is a free OBD2 app that offers basic diagnostic features. It is a good option for beginners or those who only need basic functionality. Key features include:
- Real-time Data Monitoring: Displays live data from basic sensors.
- Diagnostic Trouble Codes: Reads and clears DTCs.
- Trip Logging: Records trip data such as distance, time, and fuel consumption.
5.2. PC Software Options
5.2.1. ScanMaster-ELM
ScanMaster-ELM is a popular PC software for OBD2 diagnostics. It offers a wide range of features and is compatible with various OBD2 interfaces. Key features include:
- Real-time Data Monitoring: Displays live data from various sensors and systems.
- Diagnostic Trouble Codes: Reads and clears DTCs.
- Advanced Diagnostic Tests: Supports advanced diagnostic tests such as oxygen sensor tests and EVAP tests.
- Data Logging: Records data for later analysis.
- Reporting: Generates detailed diagnostic reports.
5.2.2. ScanTool.net
ScanTool.net offers both software and hardware solutions for OBD2 diagnostics. Their software is compatible with various OBD2 interfaces and offers a range of features. Key features include:
- Real-time Data Monitoring: Displays live data from various sensors and systems.
- Diagnostic Trouble Codes: Reads and clears DTCs.
- Customizable Dashboards: Allows you to create custom dashboards with gauges and graphs.
- Data Logging: Records data for later analysis.
- Reporting: Generates detailed diagnostic reports.
5.2.3. PCMSCAN ELM
PCMSCAN ELM is a PC software designed for advanced OBD2 diagnostics. It offers a range of features for both beginners and advanced users. Key features include:
- Real-time Data Monitoring: Displays live data from various sensors and systems.
- Diagnostic Trouble Codes: Reads and clears DTCs.
- Graphical Display: Displays data in graphical format for easy analysis.
- Data Logging: Records data for later analysis.
- Reporting: Generates detailed diagnostic reports.
5.3. Software Compatibility
When choosing an OBD2 app or software, it’s important to ensure that it is compatible with your OBD2 interface and your vehicle. Check the app or software documentation for compatibility information.
6. Common Issues and Troubleshooting
What are some common issues you might encounter while using the OBD2 interface V1.5, and how can you troubleshoot them effectively? Common issues include connection problems, incorrect data readings, and software compatibility issues. Troubleshooting these problems involves verifying the Bluetooth connection, ensuring app compatibility, and checking the OBD2 port for damage.
6.1. Connection Problems
6.1.1. Bluetooth Pairing Issues
If you are having trouble pairing the OBD2 interface with your Android device via Bluetooth, try the following:
- Verify Bluetooth is Enabled: Make sure Bluetooth is turned on in your Android device settings.
- Ensure Device is Discoverable: Some devices require you to make them discoverable in the Bluetooth settings.
- Enter the Correct Pairing Code: The default pairing code is usually “1234”.
- Restart Devices: Try restarting both your Android device and the vehicle.
- Clear Bluetooth Cache: Clear the Bluetooth cache on your Android device.
6.1.2. Interface Not Recognized by App
If the app is not recognizing the OBD2 interface, try the following:
- Check App Settings: Make sure the app is configured to use the correct Bluetooth device.
- Reinstall the App: Try uninstalling and reinstalling the app.
- Update the App: Make sure you are using the latest version of the app.
- Try Another App: Try using a different OBD2 app to see if the problem is with the app itself.
6.2. Incorrect Data Readings
6.2.1. Inaccurate Sensor Data
If you are getting inaccurate sensor data, try the following:
- Check Sensor Connections: Make sure the sensors are properly connected and functioning correctly.
- Verify Vehicle Compatibility: Ensure that the OBD2 interface and app are compatible with your vehicle.
- Update Firmware: Check for firmware updates for the OBD2 interface.
- Calibrate Sensors: Some apps allow you to calibrate sensors for more accurate readings.
6.2.2. Error Codes Not Displaying
If the app is not displaying error codes, try the following:
- Ensure Check Engine Light is On: The check engine light must be illuminated for the app to read error codes.
- Clear Existing Codes: Clear any existing codes and then drive the vehicle to see if new codes are generated.
- Check OBD2 Port: Make sure the OBD2 interface is securely plugged into the OBD2 port.
- Try Another Vehicle: Test the OBD2 interface on another vehicle to see if the problem is with the interface or the vehicle.
6.3. Software Compatibility Issues
6.3.1. App Crashes or Freezes
If the app is crashing or freezing, try the following:
- Close Background Apps: Close any unnecessary apps running in the background.
- Clear App Cache: Clear the app cache in the Android device settings.
- Reinstall the App: Try uninstalling and reinstalling the app.
- Update the App: Make sure you are using the latest version of the app.
- Check Device Compatibility: Ensure that the app is compatible with your Android device.
6.3.2. Incompatible Protocols
If the app is not compatible with your vehicle’s OBD2 protocols, try the following:
- Check Vehicle Compatibility: Make sure the app supports the OBD2 protocols used by your vehicle.
- Try Another App: Try using a different OBD2 app that supports your vehicle’s protocols.
- Update Firmware: Check for firmware updates for the OBD2 interface.
7. Advanced Tips and Tricks
What are some advanced tips and tricks for using the OBD2 interface V1.5 to get the most out of your car diagnostics? Advanced tips include using enhanced diagnostic modes, creating custom dashboards, and logging data for in-depth analysis. These techniques can provide a deeper understanding of your vehicle’s performance and help you diagnose complex issues effectively.
7.1. Using Enhanced Diagnostic Modes
Some OBD2 apps and software offer enhanced diagnostic modes that provide access to manufacturer-specific data and tests. These modes can provide more detailed information about your vehicle’s performance and help you diagnose problems that are not detectable with standard OBD2 protocols.
7.1.1. Accessing Manufacturer-Specific Data
To access manufacturer-specific data, you may need to enter a special code or select your vehicle’s make and model in the app or software settings. Once you have accessed the enhanced diagnostic mode, you can view data from various systems and sensors that are specific to your vehicle.
7.1.2. Performing Advanced Tests
Enhanced diagnostic modes may also allow you to perform advanced tests, such as:
- ABS Tests: Tests the anti-lock braking system.
- Airbag Tests: Tests the airbag system.
- Transmission Tests: Tests the transmission system.
- Body Control Module (BCM) Tests: Tests the BCM.
7.2. Creating Custom Dashboards
Many OBD2 apps and software allow you to create custom dashboards with gauges and graphs that display real-time data from your vehicle. This can be a useful way to monitor specific parameters that are important to you.
7.2.1. Selecting Relevant Parameters
When creating a custom dashboard, select the parameters that are most relevant to your needs. For example, if you are interested in monitoring engine performance, you may want to include parameters such as:
- Engine RPM
- Vehicle Speed
- Coolant Temperature
- Intake Air Temperature
- Mass Air Flow (MAF)
- Oxygen Sensor Readings
- Fuel Trim
7.2.2. Customizing Gauges and Graphs
Customize the gauges and graphs to display the data in a way that is easy to understand. You can choose different types of gauges and graphs, set minimum and maximum values, and add labels and colors.
7.3. Data Logging and Analysis
Data logging allows you to record data from your vehicle over time. This can be useful for diagnosing intermittent problems or for analyzing your vehicle’s performance under different driving conditions.
7.3.1. Recording Data
Most OBD2 apps and software have a data logging feature that allows you to record data to a file. You can typically specify the parameters to record, the recording interval, and the file format.
7.3.2. Analyzing Data
Once you have recorded the data, you can analyze it using a spreadsheet program or a dedicated data analysis tool. Look for patterns or anomalies in the data that may indicate a problem.
8. OBD2 Interface V1.5 vs. Other Versions
How does the OBD2 interface V1.5 compare to other versions, and what are the advantages and disadvantages of using it? The OBD2 interface V1.5 offers improved stability and broader compatibility compared to older versions, making it a reliable choice for most users. However, newer versions may offer additional features and support for the latest vehicle models.
8.1. Key Differences
8.1.1. Firmware Stability
The V1.5 version is known for its stable firmware, which ensures reliable performance and accurate data readings. Older versions may have firmware issues that can lead to connection problems or inaccurate data.
8.1.2. Vehicle Compatibility
The V1.5 version has broad vehicle compatibility, supporting most cars manufactured after 1996 in the United States, after 2001 in Europe, and after 2002 in Asia. Newer versions may offer even broader compatibility, including support for the latest vehicle models.
8.1.3. Feature Set
Newer versions of the OBD2 interface may offer additional features, such as support for more advanced diagnostic tests, enhanced data logging capabilities, and integration with cloud-based services.
8.2. Advantages of V1.5
- Stability: Reliable performance due to stable firmware.
- Compatibility: Broad vehicle compatibility.
- Cost-Effective: Often more affordable than newer versions.
8.3. Disadvantages of V1.5
- Limited Features: May not offer all the features of newer versions.
- No Support for Latest Models: May not support the latest vehicle models.
9. Safety Precautions
What safety precautions should you take when using the OBD2 interface V1.5 to ensure your safety and prevent damage to your vehicle? Safety precautions include using the device in a safe environment, avoiding distractions while driving, and ensuring the device is properly connected to prevent electrical damage. Following these precautions will help you use the OBD2 interface V1.5 safely and effectively.
9.1. Safe Environment
Always use the OBD2 interface in a safe environment. Avoid using it in areas with flammable materials or explosive gases.
9.2. Avoiding Distractions
Do not use the OBD2 interface while driving. It can be distracting and increase the risk of an accident. Pull over to a safe location before using the interface.
9.3. Electrical Safety
Ensure that the OBD2 interface is properly connected to the OBD2 port. Do not force the connector or use excessive force. This can damage the connector or the vehicle’s electrical system.
9.4. Data Security
Be aware of the potential security risks associated with connecting to your vehicle’s computer. Use a reputable OBD2 app or software and avoid downloading software from untrusted sources.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
10.1. What is an OBD2 Scanner?
An OBD2 scanner is a device used to read and interpret data from a vehicle’s onboard computer system, providing diagnostic information about the vehicle’s health and performance. It connects to the OBD2 port, typically located under the dashboard, and retrieves diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), which indicate specific issues within the vehicle’s systems. According to a study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), using OBD2 scanners can significantly reduce diagnostic time and improve repair accuracy.
10.2. How Do I Read OBD2 Error Codes?
To read OBD2 error codes, connect an OBD2 scanner to the vehicle’s OBD2 port, turn on the ignition, and use the scanner’s interface to access the diagnostic menu. The scanner will display any stored DTCs, which can then be looked up in a database to understand their meaning. Many scanners also provide a brief description of the code’s meaning. For example, a P0300 code indicates a random or multiple cylinder misfire.
10.3. What Common Car Problems Can an OBD2 Scanner Detect?
An OBD2 scanner can detect a wide range of common car problems, including engine misfires, issues with the oxygen sensors, problems with the catalytic converter, fuel system malfunctions, and issues with the evaporative emission control system (EVAP). By reading and interpreting the DTCs, you can pinpoint the source of the problem and take appropriate action.
10.4. Is the OBD2 Interface V1.5 Suitable for Beginners?
Yes, the OBD2 interface V1.5 is suitable for beginners due to its user-friendly design and straightforward functionality. When paired with a compatible app, it provides an easy way to read and clear diagnostic trouble codes, monitor real-time data, and perform basic diagnostic tests. Many apps offer intuitive interfaces and helpful guides, making it accessible for those with limited automotive knowledge.
10.5. Can I Use the OBD2 Interface V1.5 on Multiple Vehicles?
Yes, the OBD2 interface V1.5 can be used on multiple vehicles, provided that they are OBD2 compliant and fall within the supported vehicle coverage. However, it is essential to ensure that the interface and the chosen app are compatible with each vehicle’s specific make, model, and year to ensure accurate diagnostics.
10.6. How Often Should I Scan My Car with an OBD2 Scanner?
It is recommended to scan your car with an OBD2 scanner whenever the “Check Engine” light comes on or if you notice any unusual behavior or performance issues. Regular scanning, even without apparent problems, can help identify potential issues early and prevent more severe damage.
10.7. Will Clearing OBD2 Codes Solve My Car Problem?
Clearing OBD2 codes will not solve the underlying problem with your car. It only resets the system and turns off the “Check Engine” light. The code will likely reappear if the issue is not addressed. It is essential to diagnose and repair the root cause of the problem before clearing the codes.
10.8. What Are the Limitations of the OBD2 Interface V1.5?
The limitations of the OBD2 interface V1.5 include its inability to support 24V diesel vehicles or trucks, its incompatibility with vehicles lacking a 16-pin adapter, and its limited functionality with some hybrid and electric vehicles. Additionally, it may not provide access to advanced manufacturer-specific data or tests available with more advanced scanners.
10.9. How Can I Update the Firmware of My OBD2 Interface V1.5?
The process for updating the firmware of your OBD2 interface V1.5 varies depending on the manufacturer. Some interfaces can be updated via a USB connection to a computer, while others may require a dedicated app or software. Check the manufacturer’s website or user manual for specific instructions on how to update the firmware.
10.10. Is It Safe to Buy a Used OBD2 Interface V1.5?
It is generally safe to buy a used OBD2 interface V1.5, but it is essential to ensure that the device is in good working condition and comes with all necessary accessories. Test the interface on a compatible vehicle before purchasing to verify its functionality. Also, be cautious of counterfeit devices, which may not perform accurately or reliably.
Understanding and utilizing the OBD2 interface V1.5 can greatly enhance your ability to diagnose and maintain your vehicle. With the right tools and knowledge, you can save time and money while ensuring your car runs smoothly.
Are you facing challenges in diagnosing your car problems or understanding how to use the OBD2 scanner effectively? At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we offer expert guidance and comprehensive repair services to help you get the most out of your OBD2 scanner. Contact us today via Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for personalized assistance. Our location is 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States.
 elm327 with chip fitting
elm327 with chip fitting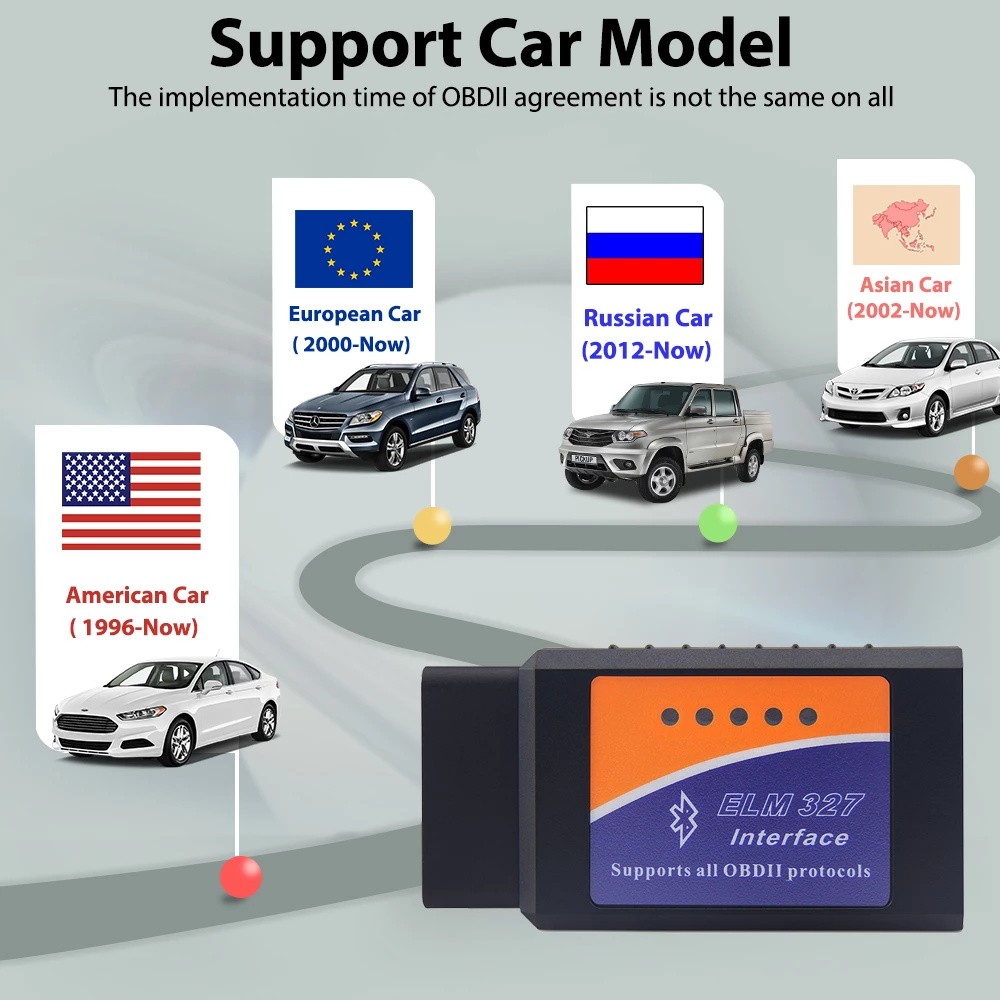 elm327 with chip model
elm327 with chip model elm327 Bluetooth adapter for OBDII protocols
elm327 Bluetooth adapter for OBDII protocols vehicle OBDII scanner for Android phone
vehicle OBDII scanner for Android phone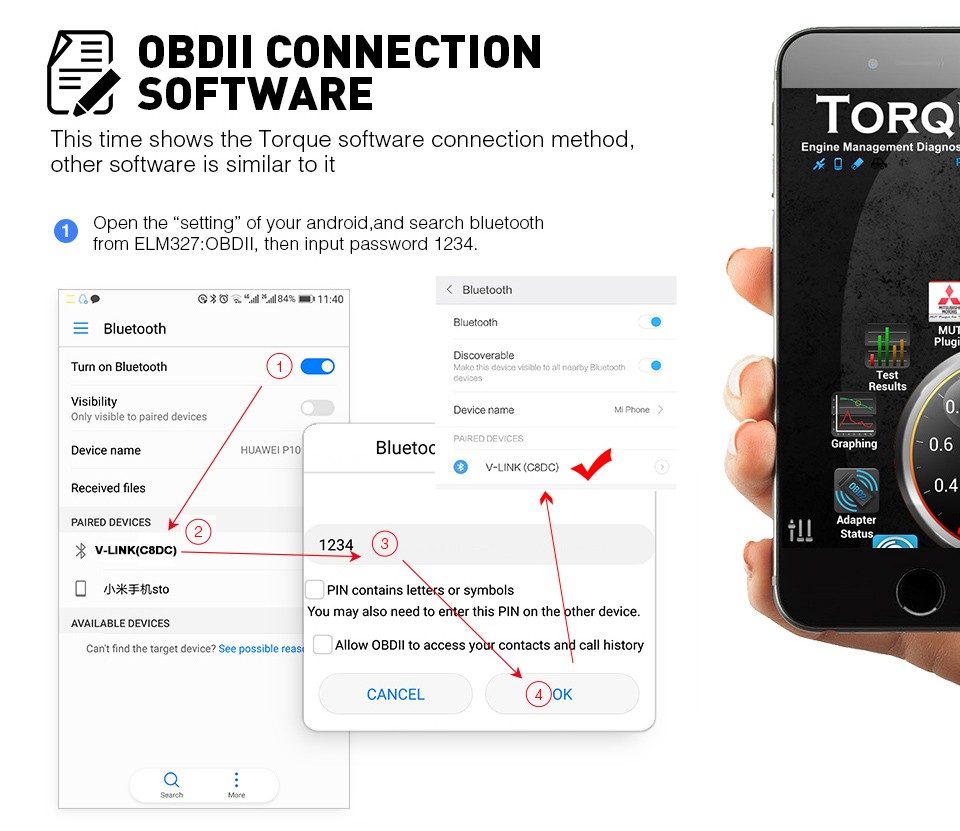 bluetooth setup on Android device for OBD2 scanner
bluetooth setup on Android device for OBD2 scanner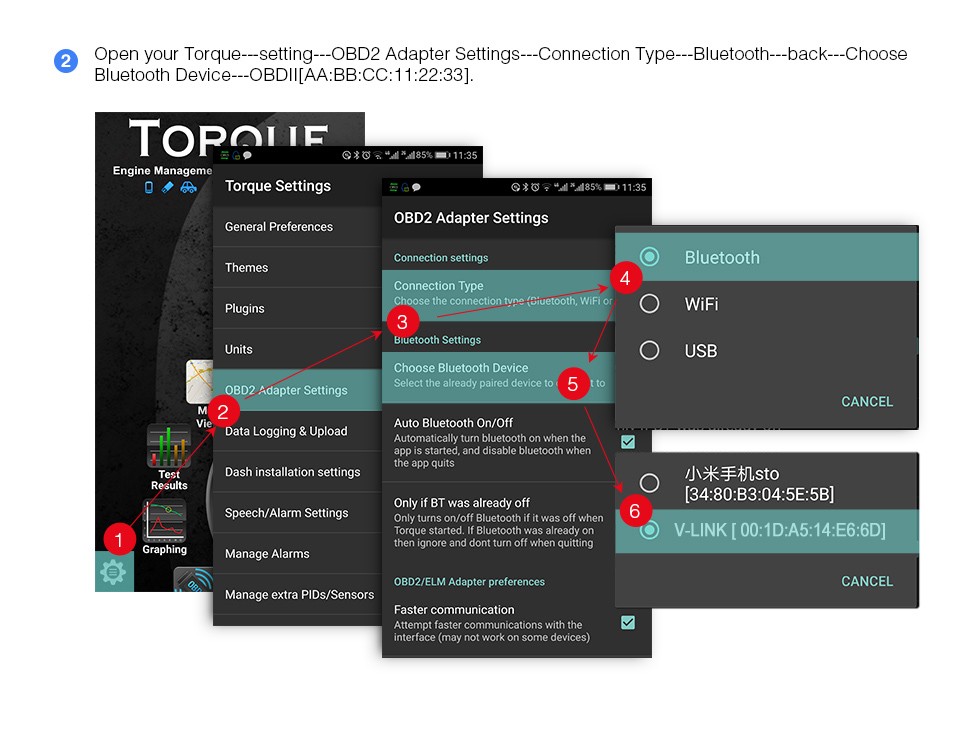 connecting an ELM327 to a vehicle
connecting an ELM327 to a vehicle