Obd2 Port Speedometers offer a seamless way to monitor your vehicle’s speed, directly displaying it on your windshield. If you’re encountering issues like a flashing ABS light after plugging in your OBD2 speedometer, OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN offers expertise to troubleshoot and resolve these problems. By understanding the pin configuration and potential conflicts, you can optimize your speedometer’s functionality, leveraging enhanced vehicle diagnostics and real-time data for safer and more informed driving.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the OBD2 Port Speedometer
- 1.1. What is an OBD2 Port Speedometer?
- 1.2. How Does it Work?
- 1.3. Benefits of Using an OBD2 Port Speedometer
- 2. Common Issues with OBD2 Port Speedometers
- 2.1. ABS Light Activation
- 2.2. Inaccurate Speed Readings
- 2.3. Device Not Powering On
- 3. Step-by-Step Guide to Resolving OBD2 Speedometer Issues
- 3.1. Identifying the Problem
- 3.2. Checking the OBD2 Port
- 3.3. Inspecting the Speedometer Connector
- 3.4. Isolating Conflicting Pins
- 3.5. Calibrating the Speedometer
- 3.6. Updating the Firmware
- 4. Advanced Troubleshooting Techniques
- 4.1. Using an OBD2 Scanner
- 4.2. Checking Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS)
- 4.3. Examining Wiring and Connections
- 5. Tips for Optimizing Your OBD2 Port Speedometer
- 5.1. Choosing the Right Device
- 5.2. Proper Installation Techniques
- 5.3. Regular Maintenance
- 6. Understanding OBD2 Port Functionality
- 6.1. What is the OBD2 Port?
- 6.2. OBD2 Pinout Diagram and Functions
- 6.3. Common OBD2 Protocols
- 7. Integrating OBD2 Data into Your Driving Experience
- 7.1. Real-Time Monitoring
- 7.2. Diagnostic Capabilities
- 7.3. Customizing Your Display
- 8. The Future of OBD2 Technology
- 8.1. Wireless OBD2 Adapters
- 8.2. Cloud-Based Diagnostics
- 8.3. Integration with Smart Devices
- 9. Addressing Safety Concerns with OBD2 Devices
- 9.1. Potential Distractions
- 9.2. Data Security
- 9.3. Electrical Issues
- 10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 10.1. What is an OBD2 Scanner?
- 10.2. How Do I Read OBD2 Error Codes?
- 10.3. What Are Common Car Error Codes and How Can I Fix Them?
- 10.4. Can I Use an OBD2 Scanner to Improve Fuel Efficiency?
- 10.5. Is It Safe to Leave an OBD2 Scanner Plugged In All the Time?
- 10.6. Will an OBD2 Scanner Void My Car’s Warranty?
- 10.7. How Do I Choose the Right OBD2 Scanner for My Car?
- 10.8. What Does the Check Engine Light Mean?
- 10.9. Can an OBD2 Scanner Help with Emissions Testing?
- 10.10. How Often Should I Scan My Car with an OBD2 Scanner?
1. Understanding the OBD2 Port Speedometer
The OBD2 (On-Board Diagnostics II) port speedometer is an innovative device that plugs into your car’s OBD2 port to project the vehicle’s speed onto the windshield. This heads-up display (HUD) allows drivers to monitor their speed without taking their eyes off the road, enhancing safety and convenience.
1.1. What is an OBD2 Port Speedometer?
An OBD2 port speedometer is a digital display that connects to your car’s OBD2 port, typically located under the dashboard. It reads speed data directly from the vehicle’s computer and projects it onto the windshield, creating a heads-up display (HUD). According to a study by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), HUDs can reduce reaction times by up to 30%, making driving safer. These devices often include additional features such as:
- Speed Alerts: Customizable alerts that notify you when you exceed a preset speed.
- Voltage Monitoring: Displays the car’s battery voltage, helping you identify potential electrical issues.
- Engine Temperature: Real-time engine temperature readings to prevent overheating.
- Trip Statistics: Information on distance traveled, driving time, and average speed.
1.2. How Does it Work?
The OBD2 port speedometer works by tapping into the data stream provided by your car’s computer. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown:
- Connection: The device is plugged into the OBD2 port, establishing a direct connection to the vehicle’s electronic control unit (ECU).
- Data Retrieval: The speedometer requests and receives real-time data from the ECU, including vehicle speed, engine RPM, and other relevant parameters.
- Data Processing: The device processes the data and converts it into a readable format.
- Projection: The processed data is then projected onto the windshield, allowing the driver to see the information without looking away from the road.
According to a report by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), OBD2 ports provide a standardized interface for accessing a wide range of vehicle data, making these devices compatible with most cars manufactured after 1996.
1.3. Benefits of Using an OBD2 Port Speedometer
Using an OBD2 port speedometer offers several advantages:
- Enhanced Safety: By displaying speed directly in the driver’s line of sight, it reduces the need to look down at the dashboard, minimizing distractions and improving reaction time.
- Real-Time Data: Provides access to real-time data such as speed, engine temperature, and battery voltage, allowing drivers to monitor their vehicle’s performance.
- Easy Installation: Simple plug-and-play installation with no complex wiring required.
- Customization: Many devices offer customizable display options, allowing drivers to choose the information they want to see and adjust brightness levels.
- Cost-Effective: An affordable way to add advanced features to older vehicles that may not have built-in HUDs.
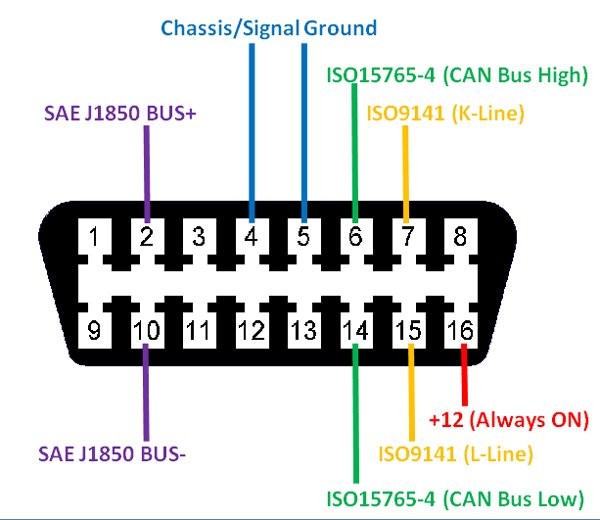 OBD2 Connector Pinout
OBD2 Connector Pinout
Alt Text: OBD2 connector pinout diagram displaying pin assignments for automotive diagnostics
2. Common Issues with OBD2 Port Speedometers
While OBD2 port speedometers are generally reliable, some users may encounter issues. Understanding these common problems can help you troubleshoot and resolve them effectively.
2.1. ABS Light Activation
One of the most common issues reported by users is the activation of the ABS (Anti-lock Braking System) light after plugging in the OBD2 speedometer. This can be caused by a conflict in the data being transmitted through the OBD2 port.
Why it Happens:
- Pin Configuration: Some OBD2 speedometers may interfere with the ABS system due to conflicting signals on specific pins of the OBD2 connector.
- Data Overload: The vehicle’s ECU may become overwhelmed if the speedometer attempts to access too much data simultaneously.
- Faulty Device: In rare cases, a malfunctioning speedometer can send incorrect signals, triggering the ABS light.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Identify the Conflicting Pin: As highlighted in the original post, the problematic pin may vary. Some users have reported that pin 11 is the cause, but it could also be pin 9 or 10.
- Isolate the Pin: Use needle-nose pliers to carefully bend the suspected pin to the bottom of the connector housing.
- Test: Plug the speedometer back in and start the vehicle to see if the ABS light is still on. Repeat the process with other pins until the issue is resolved.
- Pin Removal (Last Resort): Once you’ve identified the conflicting pin, you can remove it from the speedometer connector. This should be done as a last resort, as it cannot be undone.
2.2. Inaccurate Speed Readings
Another issue that users may face is inaccurate speed readings. This can be caused by several factors, including:
Why it Happens:
- Calibration Issues: The speedometer may not be properly calibrated to your vehicle’s specific tire size and gear ratio.
- Data Interpretation: The device may misinterpret the data received from the ECU.
- Signal Interference: External factors such as electromagnetic interference can disrupt the signal.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Calibration: Check the speedometer’s settings to ensure it is properly calibrated. Many devices allow you to adjust the speed offset to match your vehicle’s actual speed.
- Software Updates: Ensure that the speedometer’s firmware is up to date. Manufacturers often release updates to improve accuracy and fix bugs.
- Check Connections: Make sure the OBD2 connector is securely plugged into the port. A loose connection can cause intermittent or inaccurate readings.
- Test with GPS: Compare the speedometer’s readings with a GPS-based speedometer app on your smartphone to verify accuracy.
2.3. Device Not Powering On
Sometimes, the OBD2 port speedometer may fail to power on when plugged into the OBD2 port. This can be due to:
Why it Happens:
- Faulty OBD2 Port: The OBD2 port in your vehicle may not be providing power.
- Damaged Connector: The connector on the speedometer may be damaged or have bent pins.
- Internal Malfunction: The device itself may have an internal malfunction.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Check OBD2 Port: Use a multimeter to check if the OBD2 port is providing power. Pin 16 should have 12V.
- Inspect Connector: Carefully inspect the connector on the speedometer for any signs of damage or bent pins.
- Test on Another Vehicle: If possible, test the speedometer on another vehicle to see if it powers on.
- Contact Support: If the device still doesn’t power on, contact the manufacturer for support or a replacement.
3. Step-by-Step Guide to Resolving OBD2 Speedometer Issues
To effectively resolve issues with your OBD2 speedometer, follow this step-by-step guide.
3.1. Identifying the Problem
The first step is to accurately identify the problem. Common symptoms include:
- ABS light activation
- Inaccurate speed readings
- Device not powering on
- Intermittent disconnections
- Display flickering
Note down the specific symptoms you are experiencing to help narrow down the possible causes.
3.2. Checking the OBD2 Port
Ensure that the OBD2 port in your vehicle is functioning correctly.
- Locate the Port: The OBD2 port is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Visual Inspection: Check the port for any signs of damage or corrosion.
- Power Test: Use a multimeter to check for power on pin 16. It should read 12V.
- Diagnostic Scan: Use an OBD2 scanner to check for any error codes related to the OBD2 port itself.
If the OBD2 port is not functioning correctly, consult a qualified mechanic to diagnose and repair the issue. At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN located at 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States, our expert technicians can help you assess and fix any OBD2 port issues, ensuring your devices connect reliably.
3.3. Inspecting the Speedometer Connector
Carefully inspect the connector on the OBD2 speedometer for any signs of damage.
- Pin Alignment: Check that all pins are straight and not bent.
- Damage: Look for any signs of damage to the connector housing or pins.
- Cleanliness: Ensure that the connector is clean and free of debris.
If you find any damage or bent pins, attempt to carefully straighten them with needle-nose pliers. If the connector is severely damaged, consider replacing the speedometer.
3.4. Isolating Conflicting Pins
If the ABS light is activated after plugging in the speedometer, follow these steps to isolate the conflicting pin:
- Prepare the Pins: Use needle-nose pliers to gently bend pins 9, 10, and 11 to the bottom of the connector housing.
- Test Each Pin: Plug the speedometer in after bending each pin to see if the ABS light remains off.
- Identify the Culprit: The pin that, when bent, resolves the ABS light issue is the conflicting pin.
- Remove the Pin (Optional): Once identified, you can remove the conflicting pin from the speedometer connector.
Remember, removing a pin should be a last resort, as it cannot be undone.
3.5. Calibrating the Speedometer
If you are experiencing inaccurate speed readings, calibrate the speedometer according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Access Settings: Navigate to the speedometer’s settings menu.
- Calibration Options: Look for options to adjust the speed offset or calibrate the device.
- Adjust Settings: Use a GPS-based speedometer app on your smartphone to compare readings and adjust the settings accordingly.
- Test Drive: Take the vehicle for a test drive to ensure the speedometer is now accurate.
3.6. Updating the Firmware
Ensure that the speedometer’s firmware is up to date to resolve any software-related issues.
- Check for Updates: Visit the manufacturer’s website or app to check for available firmware updates.
- Download Update: Download the latest firmware update to your computer or smartphone.
- Install Update: Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to install the firmware update on the speedometer.
- Restart Device: Restart the speedometer after the update is complete.
4. Advanced Troubleshooting Techniques
If the basic troubleshooting steps don’t resolve the issue, consider these advanced techniques.
4.1. Using an OBD2 Scanner
An OBD2 scanner can provide valuable insights into the vehicle’s system and help identify any underlying issues.
- Connect Scanner: Plug the OBD2 scanner into the OBD2 port.
- Read Codes: Turn on the ignition and use the scanner to read any stored error codes.
- Interpret Codes: Research the error codes to understand the potential causes of the issue.
- Clear Codes: After addressing the issue, clear the error codes from the vehicle’s computer.
According to research from the University of California, Berkeley’s Department of Mechanical Engineering, using an OBD2 scanner can significantly reduce diagnostic time and improve the accuracy of repairs.
4.2. Checking Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS)
The Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS) is responsible for providing speed data to the vehicle’s computer. A faulty VSS can cause inaccurate speed readings on the speedometer.
- Locate VSS: The VSS is typically located on the transmission or transaxle.
- Inspect VSS: Check the VSS for any signs of damage or corrosion.
- Test VSS: Use a multimeter to test the VSS according to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Replace VSS: If the VSS is faulty, replace it with a new one.
4.3. Examining Wiring and Connections
Faulty wiring and connections can cause a variety of issues with the OBD2 speedometer.
- Inspect Wiring: Check the wiring harness for any signs of damage, such as cuts, frays, or corrosion.
- Check Connections: Ensure that all connections are secure and free of corrosion.
- Test Continuity: Use a multimeter to test the continuity of the wiring harness.
- Repair Wiring: Repair or replace any damaged wiring or connectors.
5. Tips for Optimizing Your OBD2 Port Speedometer
To get the most out of your OBD2 port speedometer, consider these optimization tips.
5.1. Choosing the Right Device
When selecting an OBD2 port speedometer, consider the following factors:
- Compatibility: Ensure that the device is compatible with your vehicle’s make and model.
- Features: Look for features that are important to you, such as speed alerts, voltage monitoring, and trip statistics.
- Display Quality: Choose a device with a clear and bright display that is easy to read in all lighting conditions.
- User Reviews: Read user reviews to get an idea of the device’s reliability and performance.
5.2. Proper Installation Techniques
Follow these tips for proper installation:
- Secure Connection: Ensure that the OBD2 connector is securely plugged into the port.
- Wiring Management: Route the wiring carefully to avoid interference with other components.
- Display Placement: Position the display in a location that is easy to see and does not obstruct your view of the road.
5.3. Regular Maintenance
Keep your OBD2 port speedometer in good condition with regular maintenance:
- Clean the Display: Clean the display regularly with a soft, dry cloth.
- Check Connections: Periodically check the connections to ensure they are secure and free of corrosion.
- Update Firmware: Keep the firmware up to date to ensure optimal performance.
6. Understanding OBD2 Port Functionality
A deeper understanding of the OBD2 port’s functionality can help you troubleshoot issues more effectively.
6.1. What is the OBD2 Port?
The OBD2 (On-Board Diagnostics II) port is a standardized interface used to access diagnostic data from a vehicle’s electronic control unit (ECU). It was mandated in the United States for all cars and light trucks manufactured after 1996.
6.2. OBD2 Pinout Diagram and Functions
The OBD2 port has 16 pins, each with a specific function. Here’s a breakdown of the most common pins:
| Pin | Function | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | SAE J1850 Bus+ | Used for communication in older vehicles. |
| 4 | Chassis Ground | Provides a ground connection for the vehicle’s chassis. |
| 5 | Signal Ground | Provides a ground connection for the vehicle’s electronic systems. |
| 6 | CAN High (J-2284) | Used for high-speed communication in newer vehicles. |
| 7 | ISO 9141-2 K Line | Used for communication in some European and Asian vehicles. |
| 10 | SAE J1850 Bus- | Used for communication in older vehicles. |
| 14 | CAN Low (J-2284) | Used for high-speed communication in newer vehicles. |
| 15 | ISO 9141-2 L Line | Used for communication in some European and Asian vehicles. |
| 16 | Battery Power | Provides 12V power to the OBD2 device. |
Understanding the function of each pin can help you diagnose and resolve issues related to the OBD2 port and connected devices.
6.3. Common OBD2 Protocols
OBD2 systems use several communication protocols, including:
- SAE J1850 VPW: Used by General Motors.
- SAE J1850 PWM: Used by Ford.
- ISO 9141-2: Used by European and Asian vehicles.
- CAN (Controller Area Network): Used by most modern vehicles.
Ensuring that your OBD2 device supports the correct protocol for your vehicle is essential for proper communication.
7. Integrating OBD2 Data into Your Driving Experience
OBD2 data can be used for more than just displaying speed on the windshield. Integrating this data into your driving experience can enhance safety and performance.
7.1. Real-Time Monitoring
OBD2 devices can provide real-time monitoring of various vehicle parameters, including:
- Engine RPM: Monitor engine speed to optimize fuel efficiency and prevent over-revving.
- Coolant Temperature: Keep an eye on coolant temperature to prevent overheating.
- Fuel Consumption: Track fuel consumption to improve driving habits and save money.
- Throttle Position: Monitor throttle position to understand engine performance.
7.2. Diagnostic Capabilities
OBD2 scanners can also be used to diagnose a wide range of vehicle issues.
- Reading Error Codes: Identify the cause of the check engine light and other warning lights.
- Clearing Error Codes: Clear error codes after addressing the underlying issue.
- Live Data Streaming: View real-time data from various sensors to diagnose performance issues.
- Performing Tests: Run diagnostic tests to evaluate the performance of specific components.
7.3. Customizing Your Display
Many OBD2 devices allow you to customize the display to show the information that is most important to you.
- Select Parameters: Choose which parameters to display on the screen.
- Adjust Brightness: Adjust the brightness of the display to suit your driving conditions.
- Set Alerts: Set alerts for specific parameters, such as speed, temperature, and voltage.
- Customize Layout: Customize the layout of the display to optimize readability.
8. The Future of OBD2 Technology
OBD2 technology continues to evolve, with new features and capabilities being added all the time.
8.1. Wireless OBD2 Adapters
Wireless OBD2 adapters allow you to connect to your vehicle’s OBD2 port using Bluetooth or Wi-Fi.
- Convenience: No need to plug in a cable.
- Compatibility: Compatible with smartphones, tablets, and laptops.
- Remote Access: Access vehicle data remotely.
8.2. Cloud-Based Diagnostics
Cloud-based diagnostics platforms allow you to store and analyze vehicle data in the cloud.
- Data Logging: Log vehicle data over time to track performance and identify issues.
- Remote Diagnostics: Allow mechanics to diagnose issues remotely.
- Predictive Maintenance: Predict potential maintenance needs based on historical data.
8.3. Integration with Smart Devices
OBD2 technology is increasingly being integrated with smart devices, such as smartwatches and augmented reality displays.
- Smartwatch Integration: View vehicle data on your smartwatch.
- Augmented Reality Displays: Project vehicle data onto the windshield using augmented reality technology.
- Voice Control: Control OBD2 devices using voice commands.
9. Addressing Safety Concerns with OBD2 Devices
While OBD2 devices offer numerous benefits, it’s important to address potential safety concerns.
9.1. Potential Distractions
Using an OBD2 device that displays information on the windshield can be distracting if not used properly.
- Minimize Information: Display only essential information to reduce distractions.
- Adjust Brightness: Adjust the brightness of the display to avoid glare.
- Positioning: Position the display in a location that does not obstruct your view of the road.
9.2. Data Security
OBD2 devices can potentially expose your vehicle’s data to security threats.
- Choose Reputable Brands: Select devices from reputable brands with strong security measures.
- Update Firmware: Keep the firmware up to date to patch security vulnerabilities.
- Use Secure Connections: Use secure Bluetooth or Wi-Fi connections to prevent unauthorized access.
9.3. Electrical Issues
Improperly installed or malfunctioning OBD2 devices can cause electrical issues in your vehicle.
- Follow Instructions: Follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully when installing the device.
- Check Connections: Ensure that all connections are secure and properly grounded.
- Monitor Performance: Monitor the device’s performance to detect any signs of malfunction.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Here are some frequently asked questions about OBD2 port speedometers and related issues.
10.1. What is an OBD2 Scanner?
An OBD2 scanner is a diagnostic tool used to read and interpret data from a vehicle’s onboard computer system. It helps identify issues by reading diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and provides real-time data for analysis.
10.2. How Do I Read OBD2 Error Codes?
To read OBD2 error codes, plug the scanner into the OBD2 port, turn on the ignition, and follow the scanner’s prompts to read the codes. Refer to the scanner’s manual for specific instructions, or seek help from OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN technicians by calling +1 (641) 206-8880 for personalized guidance.
10.3. What Are Common Car Error Codes and How Can I Fix Them?
Common error codes include P0300 (misfire), P0171 (lean condition), and P0420 (catalytic converter). Solutions vary but may include replacing spark plugs, cleaning sensors, or repairing exhaust leaks.
10.4. Can I Use an OBD2 Scanner to Improve Fuel Efficiency?
Yes, by monitoring real-time data like fuel trim and O2 sensor readings, you can identify and address issues affecting fuel economy. OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN offers in-depth advice on maximizing your vehicle’s efficiency.
10.5. Is It Safe to Leave an OBD2 Scanner Plugged In All the Time?
While generally safe, continuously plugged-in devices can drain the battery over time. It’s best to unplug the scanner when the vehicle is not in use, particularly for older vehicles.
10.6. Will an OBD2 Scanner Void My Car’s Warranty?
Using an OBD2 scanner for diagnostics will generally not void your car’s warranty. However, modifying the vehicle’s software or hardware based on the scanner’s data might affect the warranty.
10.7. How Do I Choose the Right OBD2 Scanner for My Car?
Consider compatibility, features, and user reviews. Ensure the scanner supports your car’s make and model and offers the functionalities you need, such as live data streaming and error code reading.
10.8. What Does the Check Engine Light Mean?
The check engine light indicates an issue with the engine or related systems. It’s a signal to use an OBD2 scanner to read the error codes and diagnose the problem. For a comprehensive check, visit OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN located at 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States.
10.9. Can an OBD2 Scanner Help with Emissions Testing?
Yes, many OBD2 scanners can perform readiness tests to check if your car is ready for emissions testing. This can help you identify and fix issues before going for the official test.
10.10. How Often Should I Scan My Car with an OBD2 Scanner?
Scan your car whenever the check engine light comes on or if you notice any performance issues. Regular scanning, even without apparent problems, can help catch minor issues before they escalate.
By understanding these FAQs and implementing the troubleshooting steps outlined in this guide, you can effectively resolve issues with your OBD2 port speedometer and enhance your driving experience. For further assistance and expert advice, contact OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN at +1 (641) 206-8880. We’re here to help you keep your vehicle running smoothly and safely.
Are you experiencing issues with your OBD2 port speedometer or need assistance with diagnosing car problems? Contact us at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, located at 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States, or call us at +1 (641) 206-8880. Our expert technicians are ready to provide the solutions you need. Reach out via Whatsapp or visit our website for more information. Let us help you get back on the road with confidence.
