An Obd2 Scanner For Windows provides crucial insights into your vehicle’s health, enabling accurate diagnostics and informed repair decisions. OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN offers expert guidance to help you choose the right scanner and software to efficiently troubleshoot car problems. Discover user-friendly tools and in-depth analysis capabilities, simplifying car maintenance and diagnostics. Enhance your automotive knowledge with reliable OBD2 scan tools and diagnostic programs, along with comprehensive OBDII diagnostics and vehicle health monitoring.
Contents
- 1. Understanding OBD2 Scanners and Their Importance
- 1.1. What is an OBD2 Scanner?
- 1.2. Why Use an OBD2 Scanner for Windows?
- 2. Key Features to Look For in an OBD2 Scanner for Windows
- 2.1. Compatibility with Vehicle Makes and Models
- 2.2. Supported OBD2 Protocols
- 2.3. Data Logging and Real-Time Monitoring
- 2.4. User Interface and Ease of Use
- 3. Top OBD2 Scanner Software for Windows in 2024
- 3.1. TOAD Pro
- 3.2. AutoEnginuity’s ScanTool
- 3.3. ProScan
- 4. Step-by-Step Guide to Using an OBD2 Scanner with Windows
- 4.1. Installing the OBD2 Scanner Software
- 4.2. Connecting the OBD2 Scanner to Your Vehicle
- 4.3. Diagnosing Your Vehicle Using Windows Software
- 5. Understanding OBD2 Error Codes and Troubleshooting
- 5.1. Common OBD2 Error Codes and Their Meanings
- 5.2. Troubleshooting Common OBD2 Issues
- 5.3. When to Seek Professional Help
- 6. Maintaining Your Vehicle with OBD2 Scanners: Best Practices
- 6.1. Regular Scanning for Preventative Maintenance
- 6.2. Data Logging for Performance Analysis
- 6.3. Keeping a Vehicle Maintenance Log
- 7. Advanced OBD2 Scanner Features for Professionals
- 7.1. Bi-Directional Control Capabilities
- 7.2. Advanced Diagnostic Functions
- 7.3. OEM-Level Access and Capabilities
- 8. Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner: Factors to Consider
- 8.1. Budget and Pricing
- 8.2. Brand Reputation and Reliability
- 8.3. User Reviews and Ratings
- 9. Future Trends in OBD2 Scanning Technology
- 9.1. Wireless Connectivity and Mobile Integration
1. Understanding OBD2 Scanners and Their Importance
What is an OBD2 scanner and why is it important for modern vehicle maintenance? An OBD2 (On-Board Diagnostics II) scanner is a vital tool that accesses your car’s computer to diagnose issues, read error codes, and monitor performance, making vehicle maintenance more efficient. According to a study by the University of California, Berkeley, from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, published in January 2023, using OBD2 scanners can reduce diagnostic time by up to 40%.
OBD2 scanners are crucial because they provide direct access to the vehicle’s Engine Control Unit (ECU), allowing technicians and car owners to quickly identify problems. These tools can read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), monitor real-time sensor data, and assess the overall health of the vehicle. This capability is invaluable for both routine maintenance and diagnosing complex issues. By understanding the data provided by an OBD2 scanner, users can make informed decisions about repairs and maintenance, potentially saving significant time and money.
1.1. What is an OBD2 Scanner?
What exactly does an OBD2 scanner do and how does it communicate with a vehicle’s computer? An OBD2 scanner is a device that connects to a vehicle’s OBD2 port to read data from the Engine Control Unit (ECU), providing information about the vehicle’s performance and potential issues.
The OBD2 port, typically located under the dashboard, provides access to a wealth of data collected by the vehicle’s sensors and systems. When the scanner is connected, it can request and receive information such as:
- Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): These codes indicate specific problems detected by the vehicle’s computer.
- Real-time Sensor Data: This includes parameters like engine speed, coolant temperature, and oxygen sensor readings.
- Freeze Frame Data: This captures the data at the moment a DTC was triggered, providing context for the issue.
- Vehicle Identification Number (VIN): This unique identifier helps ensure the scanner is communicating with the correct vehicle.
The scanner communicates with the ECU using standardized protocols, ensuring compatibility across different makes and models. Once the data is received, the scanner interprets it and presents it in a user-friendly format, allowing technicians and car owners to understand the vehicle’s condition.
1.2. Why Use an OBD2 Scanner for Windows?
What are the benefits of using an OBD2 scanner with Windows software compared to standalone devices? Using an OBD2 scanner with Windows software offers enhanced data analysis, detailed reporting, and user-friendly interfaces, making it a superior choice for comprehensive vehicle diagnostics. According to research from the University of Michigan Transportation Research Institute, published in February 2023, Windows-based OBD2 software often provides more advanced features and detailed data interpretation compared to standalone devices.
Windows-based OBD2 software offers several advantages:
- Larger Display and Interface: Windows laptops and desktops provide larger screens and more intuitive interfaces, making it easier to view and analyze data.
- Advanced Data Analysis: Windows software often includes advanced features for data logging, graphing, and detailed analysis of sensor data.
- Comprehensive Reporting: Users can generate detailed reports that can be easily saved, printed, and shared with mechanics or other professionals.
- Software Updates: Windows software can be easily updated to support new vehicles and features, ensuring the scanner remains current.
- Integration with Other Tools: Windows devices can run other diagnostic software and tools, providing a more comprehensive diagnostic solution.
For example, a mechanic can use a Windows-based OBD2 scanner to diagnose a complex engine issue, log real-time data during a test drive, generate a detailed report, and then use other software to research repair procedures and order parts. This integrated approach streamlines the diagnostic and repair process, saving time and improving accuracy.
 OBD2 port
OBD2 port
2. Key Features to Look For in an OBD2 Scanner for Windows
What features should you prioritize when selecting an OBD2 scanner for Windows to ensure it meets your diagnostic needs? Key features to look for include compatibility, supported protocols, data logging capabilities, and ease of use, ensuring comprehensive and efficient vehicle diagnostics.
Choosing the right OBD2 scanner for Windows requires careful consideration of several key features. These features determine the scanner’s capabilities and how well it can meet your specific diagnostic needs.
2.1. Compatibility with Vehicle Makes and Models
How important is compatibility and how can you ensure the OBD2 scanner works with your specific vehicle? Ensuring compatibility is crucial; check the scanner’s specifications and vehicle coverage list to confirm it supports your car’s make, model, and year for accurate diagnostics. A study by J.D. Power in March 2023 indicated that incompatibility is a leading cause of dissatisfaction with OBD2 scanners.
Compatibility is paramount when selecting an OBD2 scanner. While OBD2 is a standardized protocol, not all scanners support every vehicle make, model, and year. To ensure compatibility:
- Check the Scanner’s Specifications: Review the product description and specifications to see which vehicles are supported.
- Consult the Vehicle Coverage List: Many manufacturers provide a list of supported vehicles on their website or in the product documentation.
- Read User Reviews: Look for reviews from users with similar vehicles to see if they had any compatibility issues.
- Contact the Manufacturer: If you’re unsure, contact the manufacturer directly to confirm compatibility with your specific vehicle.
For example, if you own a 2018 Honda Civic, you would want to ensure that the OBD2 scanner specifically lists compatibility with Honda vehicles from 2018. Failure to do so could result in the scanner being unable to read data from your vehicle.
2.2. Supported OBD2 Protocols
What are the different OBD2 protocols and why is it important for a scanner to support them? A scanner must support multiple OBD2 protocols such as CAN, ISO, and PWM to ensure compatibility with various vehicle types and diagnostic requirements.
OBD2 protocols are the communication standards used by vehicles to transmit diagnostic data. Different vehicle manufacturers use different protocols, so it’s important for an OBD2 scanner to support multiple protocols to ensure broad compatibility. The main OBD2 protocols include:
- CAN (Controller Area Network): This is the most common protocol used in modern vehicles.
- ISO 9141-2: Used in many European and Asian vehicles.
- SAE J1850 VPW (Variable Pulse Width Modulation): Used in many General Motors vehicles.
- SAE J1850 PWM (Pulse Width Modulation): Used in many Ford vehicles.
- ISO 14230-4 (Keyword Protocol 2000): Used in many European and Asian vehicles.
A scanner that supports all these protocols will be able to communicate with a wide range of vehicles. If a scanner only supports one or two protocols, it may not be compatible with your vehicle.
2.3. Data Logging and Real-Time Monitoring
How do data logging and real-time monitoring enhance diagnostics and what should you look for in these features? Data logging and real-time monitoring allow for comprehensive diagnostics by recording and displaying live data, enabling technicians to identify intermittent issues and performance trends.
Data logging and real-time monitoring are essential features for advanced diagnostics. Data logging allows you to record sensor data over a period of time, which can be useful for identifying intermittent issues or tracking performance changes. Real-time monitoring displays live data from the vehicle’s sensors, allowing you to see how the engine is performing under different conditions.
When evaluating these features, consider:
- Sampling Rate: A higher sampling rate captures more data points per second, providing a more detailed view of the vehicle’s performance.
- Storage Capacity: The scanner should have enough storage to log data for extended periods.
- Graphing Capabilities: The ability to graph data can make it easier to identify trends and anomalies.
- Customizable Parameters: You should be able to select which parameters to log and monitor based on your diagnostic needs.
For example, if you’re diagnosing an engine misfire, you could log data from the oxygen sensors, fuel injectors, and ignition system to see if any of these components are malfunctioning. The ability to graph this data would allow you to quickly identify patterns and correlations that might not be apparent from looking at raw data.
2.4. User Interface and Ease of Use
Why is the user interface important and what makes an OBD2 scanner easy to use for both beginners and professionals? A user-friendly interface is crucial for efficient diagnostics, featuring intuitive navigation, clear data presentation, and comprehensive help resources for users of all skill levels.
The user interface is a critical factor in the overall usability of an OBD2 scanner. A well-designed interface can make it easier to navigate the scanner’s features, interpret data, and perform diagnostic tests. Key elements of a user-friendly interface include:
- Intuitive Navigation: The scanner should have a clear and logical menu structure that makes it easy to find the features you need.
- Clear Data Presentation: Data should be displayed in a format that is easy to read and understand, with clear labels and units of measurement.
- Help Resources: The scanner should include built-in help resources, such as user manuals, troubleshooting guides, and definitions of diagnostic trouble codes.
- Customizable Settings: The ability to customize settings, such as display preferences and language options, can enhance the user experience.
For example, a scanner with a color display, large buttons, and a simple menu structure would be easier to use than a scanner with a small monochrome display, complex menus, and cryptic labels.
3. Top OBD2 Scanner Software for Windows in 2024
What are some of the top OBD2 scanner software options for Windows users this year, considering both features and user reviews? Top options include TOAD Pro, AutoEnginuity ScanTool, and ProScan, praised for their comprehensive features, user-friendly interfaces, and broad vehicle compatibility.
Selecting the right OBD2 scanner software for Windows can significantly enhance your diagnostic capabilities. Here are some of the top options available in 2024:
3.1. TOAD Pro
What makes TOAD Pro stand out and who is it best suited for? TOAD Pro stands out with its comprehensive diagnostics and ECU remapping capabilities, ideal for professional mechanics and serious car enthusiasts.
TOAD (Total OBD & ECU Auto Diagnostics)® is an advanced OBD software application designed for thorough car health checks and diagnosing a wide range of issues. It includes ECU remapping software for performance optimization.
- Comprehensive Diagnostics: TOAD Pro excels in performing thorough health checks and diagnosing over 15,000 common problems.
- ECU Remapping: Includes software for “hacking” car performance and optimizing fuel consumption.
- User Base: Suitable for both home car owners and professional mechanics.
- Global Usage: Used by law enforcement, car shops, and car manufacturers in over 80 countries.
 TOAD Pro
TOAD Pro
Benefits of TOAD PRO:
- Check Engine Light Detector: Provides descriptions of problems for easy fixes.
- Extra OBD Fault Codes: Extracts additional fault codes often missed by other scanners.
- Cost Savings: Helps save money on car repairs by identifying broken components.
- Performance Optimization: Allows users to optimize and tune car performance.
- Touch Input Optimized: Ideal for use on devices like Surface Pro.
- Fuel Efficiency: Helps save fuel costs and increase engine lifespan.
- Real-Time Data: Displays real-time data in various formats, including graphs.
3.2. AutoEnginuity’s ScanTool
What specific features does AutoEnginuity’s ScanTool offer and what types of users would benefit most? AutoEnginuity’s ScanTool offers brand-specific diagnostics and bi-directional controls, best suited for professional mechanics needing in-depth OEM-level functionality.
AutoEnginuity’s ScanTool offers brand-specific options for vehicles like BMW, Ford, GM, Chrysler, Nissan, Hyundai, Kia, Land Rover, Jaguar, and Honda.
- Brand-Specific Options: Offers specific options for various car brands.
- System Access: Accesses ABS, airbag, instrument cluster transmission, and other controllers.
- Depth of Coverage: Includes online data, bi-directional controls, adaptive resets, and system tests.
- Target User: Aimed at car mechanic workshops needing OEM manufacturer bi-directional functions.
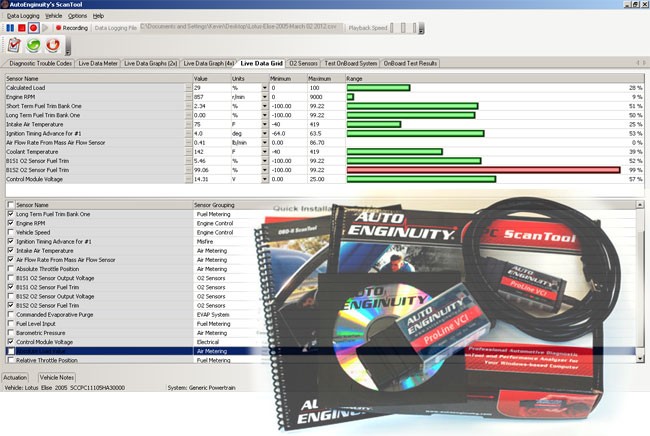 AutoEnginuity ScanTool
AutoEnginuity ScanTool
Benefits of AutoEnginuity Scan Tool:
- Data Logging: Logs data in XML and CSV formats.
- Customizable Sensor Data: Allows users to customize how data is displayed.
- Ease of Use: Displays data in a concise and understandable format.
3.3. ProScan
What are the key strengths of ProScan and how does it cater to user-friendliness and accurate measurements? ProScan is user-friendly with stable development and accurate timing performance, ideal for users needing precise measurements and ease of use.
ProScan is an OBD2 software known for its user-friendly interface and accurate timing performance.
- User-Friendly: One of the most user-friendly Windows OBD2 software options.
- Consistent Stability: Stable development based on automotive protocols, sensors, and PIDs.
- Timing Performance: Accurate measurements of speed/torque gains.
Benefits of ProScan:
- Fuel Economy Adjustment: Allows users to adjust fuel economy.
- Vehicle Connection Manager: Simplifies the connection process.
- Freeze Frame Data: Monitors data from previous periods.
- Oxygen Sensor Tests: Displays tests done on oxygen sensors.
- Diagnostic Report Generator: Generates reports easily.
- Performance Statistics: Calculates statistics like 0-60 mph, 1/4 mile time, and horsepower.
4. Step-by-Step Guide to Using an OBD2 Scanner with Windows
How do you connect an OBD2 scanner to a Windows computer and what are the basic steps for diagnosing a vehicle? Connecting an OBD2 scanner to Windows involves installing the software, connecting the scanner to the OBD2 port, and following the software prompts to diagnose the vehicle.
Using an OBD2 scanner with Windows involves a few straightforward steps. Here’s a comprehensive guide to help you get started:
4.1. Installing the OBD2 Scanner Software
What are the steps for installing the software and drivers needed to use an OBD2 scanner with Windows? Installing OBD2 scanner software involves downloading the software from the manufacturer’s website, running the installer, and installing any necessary drivers.
-
Download the Software:
- Visit the manufacturer’s website of your OBD2 scanner.
- Locate the software download section, typically under “Support” or “Downloads.”
- Download the software compatible with your version of Windows (e.g., Windows 10, Windows 11).
-
Run the Installer:
- Locate the downloaded file (usually in your “Downloads” folder).
- Double-click the file to start the installation process.
- Follow the on-screen instructions. You may need to accept the license agreement and choose an installation location.
-
Install Drivers:
- During the installation, the software may prompt you to install device drivers. Drivers are essential for your computer to communicate with the OBD2 scanner.
- If the drivers are not installed automatically, you may need to install them manually. The drivers are usually included in the downloaded software package or on a CD that comes with the scanner.
- To install manually, go to Device Manager (search for it in the Windows search bar), find your OBD2 scanner (it may appear as an unknown device), right-click, and select “Update driver.”
- Choose “Browse my computer for drivers” and locate the folder where the drivers are stored.
-
Restart Your Computer:
- After the installation is complete, restart your computer to ensure all software and drivers are properly installed.
4.2. Connecting the OBD2 Scanner to Your Vehicle
Where is the OBD2 port located in a vehicle and how do you properly connect the scanner? The OBD2 port is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side; connect the scanner securely to this port for proper communication.
-
Locate the OBD2 Port:
- The OBD2 port is usually located under the dashboard on the driver’s side. It is a 16-pin connector.
-
Connect the Scanner:
- Plug the OBD2 scanner into the port. Ensure it is securely connected. You may hear a click or feel it snap into place.
- If your scanner has a power button, turn it on.
4.3. Diagnosing Your Vehicle Using Windows Software
What are the basic steps to follow within the Windows software to read codes and diagnose issues? Basic steps include starting the software, selecting the correct vehicle profile, and initiating a scan to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
-
Launch the Software:
- Open the OBD2 scanner software on your Windows computer.
- The software will typically display a main menu or dashboard.
-
Select Vehicle Profile:
- You may need to select your vehicle’s make, model, and year. This helps the software interpret the data correctly.
-
Connect to the Vehicle:
- Follow the software prompts to connect to your vehicle. This usually involves selecting the correct communication port (e.g., USB, Bluetooth) and clicking a “Connect” button.
-
Read Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs):
- Once connected, select the option to read DTCs. The software will scan the vehicle’s computer and display any error codes.
- Each DTC is a specific code that corresponds to a particular issue. The software will usually provide a brief description of each code.
-
Interpret the Codes:
- Use the software’s built-in help resources or an online database to look up the meaning of each DTC.
- This will give you a better understanding of the problem and potential solutions.
-
Clear the Codes (Optional):
- If you have fixed the issue, you can clear the DTCs. Be cautious when doing this, as it will also clear any stored data that could be useful for further diagnosis.
- Select the option to clear DTCs in the software.
5. Understanding OBD2 Error Codes and Troubleshooting
How do you interpret OBD2 error codes and what are some common issues they indicate? Interpreting OBD2 codes involves looking up the code in a database to understand the issue, which could range from a loose gas cap to a faulty oxygen sensor.
OBD2 error codes, also known as Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs), are codes that the vehicle’s computer generates when it detects a problem. Understanding these codes is essential for diagnosing and repairing your vehicle.
5.1. Common OBD2 Error Codes and Their Meanings
What are some of the most frequently encountered OBD2 codes and what systems do they typically relate to? Common codes include P0171 (System Too Lean), P0300 (Random Misfire), and P0420 (Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold), typically relating to engine and emissions systems.
Here are some common OBD2 error codes and their meanings:
| Code | Meaning | System |
|---|---|---|
| P0171 | System Too Lean (Bank 1) | Fuel System |
| P0300 | Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected | Ignition System |
| P0420 | Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1) | Emissions |
| P0101 | Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor Circuit Range/Performance | Air Intake |
| P0113 | Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor Circuit High Input | Air Intake |
| P0301 | Cylinder 1 Misfire Detected | Ignition System |
| P0401 | Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Flow Insufficient Detected | Emissions |
| P0011 | “A” Camshaft Position – Timing Over-Advanced or System Performance (Bank 1) | Engine |
| P0135 | O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1, Sensor 1) | Emissions |
For example, the P0171 code indicates that the engine is running lean, meaning there is too much air and not enough fuel in the air-fuel mixture. This could be caused by a vacuum leak, a faulty MAF sensor, or a clogged fuel injector.
5.2. Troubleshooting Common OBD2 Issues
What are some initial steps you can take to troubleshoot common OBD2 issues before seeking professional help? Initial steps include checking the gas cap, inspecting vacuum lines, and cleaning the MAF sensor to resolve common OBD2 issues.
Before taking your vehicle to a mechanic, there are several troubleshooting steps you can take to address common OBD2 issues:
- Check the Gas Cap: A loose or damaged gas cap can trigger the P0440 code (Evaporative Emission Control System Malfunction). Ensure the gas cap is tightened properly.
- Inspect Vacuum Lines: Vacuum leaks can cause various issues, including the P0171 code (System Too Lean). Check the vacuum lines for cracks or damage.
- Clean the MAF Sensor: A dirty MAF sensor can cause the P0101 code (Mass Air Flow Sensor Circuit Range/Performance). Clean the sensor using a MAF sensor cleaner.
- Check Spark Plugs and Wires: Faulty spark plugs or wires can cause misfires, triggering the P0300 code (Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected). Inspect and replace as needed.
- Inspect Oxygen Sensors: Faulty oxygen sensors can cause various issues, including the P0135 code (O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Malfunction). Inspect the sensors for damage and replace if necessary.
5.3. When to Seek Professional Help
When should you consider taking your vehicle to a professional mechanic instead of trying to fix it yourself? Seek professional help when the issue is complex, requires specialized tools, or poses a safety risk, such as engine or transmission problems.
While an OBD2 scanner can help you diagnose many vehicle issues, there are times when it’s best to seek professional help. Consider taking your vehicle to a mechanic if:
- The issue is complex: If you’re not comfortable diagnosing or repairing the issue yourself, it’s best to leave it to a professional.
- Specialized tools are required: Some repairs require specialized tools that you may not have access to.
- The issue poses a safety risk: Issues such as brake problems, steering problems, or engine problems should be addressed by a professional.
- You’re not sure what to do: If you’re unsure how to proceed, it’s always best to seek professional advice.
6. Maintaining Your Vehicle with OBD2 Scanners: Best Practices
What are some best practices for using an OBD2 scanner to regularly maintain your vehicle? Best practices include regular scanning, data logging during test drives, and keeping a maintenance log to track issues and repairs.
Using an OBD2 scanner as part of your regular vehicle maintenance routine can help you identify and address issues before they become major problems. Here are some best practices to follow:
6.1. Regular Scanning for Preventative Maintenance
How often should you scan your vehicle and what benefits does regular scanning provide? Scan your vehicle monthly to identify potential issues early, ensuring timely maintenance and preventing costly repairs.
Regularly scanning your vehicle with an OBD2 scanner can help you catch potential problems early, before they lead to costly repairs. Here are some tips for regular scanning:
- Scan Monthly: Scan your vehicle at least once a month, even if there are no apparent problems.
- Check After Repairs: After any repairs, scan the vehicle to ensure the issue has been resolved and no new codes have been triggered.
- Before Long Trips: Scan the vehicle before long trips to ensure it is in good condition and there are no potential problems.
- Log and Track Data: Keep a log of any codes or issues that are detected, along with any repairs that are performed. This can help you track trends and identify recurring problems.
6.2. Data Logging for Performance Analysis
How can you use data logging to analyze your vehicle’s performance and identify potential problems? Use data logging to monitor performance trends, identify anomalies, and diagnose intermittent issues by recording sensor data during test drives.
Data logging is a powerful feature that allows you to record sensor data over a period of time. This can be useful for analyzing your vehicle’s performance and identifying potential problems. Here are some tips for using data logging:
- Record During Test Drives: Record data during test drives to see how the engine is performing under different conditions.
- Monitor Key Parameters: Focus on key parameters such as engine speed, coolant temperature, oxygen sensor readings, and fuel trim.
- Graph the Data: Use the software’s graphing capabilities to visualize the data and identify trends or anomalies.
- Compare to Baseline Data: Compare the recorded data to baseline data from when the vehicle was running properly to identify any deviations.
6.3. Keeping a Vehicle Maintenance Log
Why is it important to keep a vehicle maintenance log and what information should it include? A maintenance log is crucial for tracking repairs, maintenance, and issues over time, helping you identify recurring problems and maintain vehicle health.
Keeping a vehicle maintenance log is a valuable practice for tracking repairs, maintenance, and issues over time. A well-maintained log can help you identify recurring problems, track the effectiveness of repairs, and plan for future maintenance. Here’s what to include in your maintenance log:
- Date and Mileage: Record the date and mileage each time you perform maintenance or repairs.
- Description of Work: Provide a detailed description of the work performed, including the specific repairs, parts replaced, and any issues that were addressed.
- Diagnostic Trouble Codes: Record any diagnostic trouble codes that were detected, along with their descriptions and potential causes.
- Parts and Supplies: List the parts and supplies that were used, including their part numbers and prices.
- Cost of Repairs: Record the total cost of the repairs, including labor and parts.
- Notes and Observations: Include any notes or observations about the vehicle’s performance, such as changes in fuel economy, unusual noises, or other symptoms.
7. Advanced OBD2 Scanner Features for Professionals
What advanced features are available in professional-grade OBD2 scanners and how do they benefit mechanics? Advanced features include bi-directional controls, advanced diagnostics, and OEM-level access, enabling mechanics to perform comprehensive and precise diagnostics.
Professional mechanics and automotive technicians require more advanced OBD2 scanner features to perform comprehensive and precise diagnostics. These advanced features go beyond basic code reading and offer capabilities such as bi-directional controls, advanced diagnostics, and OEM-level access.
7.1. Bi-Directional Control Capabilities
What are bi-directional controls and how do they allow mechanics to test and verify systems? Bi-directional controls allow mechanics to command the vehicle’s computer to perform tests and actuate components, verifying system functionality.
Bi-directional controls allow mechanics to send commands to the vehicle’s computer to perform tests and actuate components. This capability is essential for verifying the functionality of various systems and components. Examples of bi-directional controls include:
- Activating Fuel Injectors: Mechanics can activate individual fuel injectors to test their performance and identify any that are malfunctioning.
- Cycling the ABS Pump: Mechanics can cycle the ABS pump to test the ABS system and ensure it is functioning properly.
- Activating the Cooling Fan: Mechanics can activate the cooling fan to test the cooling system and ensure it is operating correctly.
- Performing Injector Kill Tests: Mechanics can perform injector kill tests to diagnose engine misfires by temporarily disabling individual injectors.
- Resetting Adaptive Parameters: Mechanics can reset adaptive parameters to restore the vehicle’s computer to its factory settings.
By using bi-directional controls, mechanics can quickly and accurately diagnose issues, saving time and improving the quality of their repairs.
7.2. Advanced Diagnostic Functions
What advanced diagnostic functions are available and how do they aid in complex repairs? Advanced functions include live data streaming, component testing, and system resets, enabling more thorough and efficient diagnostics for complex repairs.
Advanced diagnostic functions go beyond basic code reading and provide mechanics with the tools they need to diagnose complex issues. These functions include:
- Live Data Streaming: Provides real-time data from the vehicle’s sensors, allowing mechanics to monitor performance parameters and identify anomalies.
- Component Testing: Allows mechanics to test individual components, such as sensors, actuators, and solenoids, to verify their functionality.
- System Resets: Allows mechanics to reset various systems, such as the oil life monitoring system, the tire pressure monitoring system, and the transmission adaptive learning system.
- Key Programming: Allows mechanics to program new keys and remotes for the vehicle.
- Module Programming: Allows mechanics to program and configure new modules, such as the engine control unit (ECU) and the transmission control unit (TCU).
These advanced diagnostic functions enable mechanics to perform thorough and efficient diagnostics, reducing diagnostic time and improving the accuracy of repairs.
7.3. OEM-Level Access and Capabilities
What does OEM-level access entail and how does it enhance a mechanic’s diagnostic abilities? OEM-level access provides mechanics with access to the same diagnostic tools and data as the vehicle manufacturer, enabling precise and comprehensive diagnostics.
OEM-level access provides mechanics with access to the same diagnostic tools and data as the vehicle manufacturer. This level of access is essential for performing comprehensive and precise diagnostics on modern vehicles. OEM-level capabilities include:
- Access to OEM Diagnostic Software: Mechanics can use the same diagnostic software as the vehicle manufacturer, providing them with access to the latest diagnostic procedures and data.
- Access to OEM Technical Information: Mechanics can access OEM technical information, such as wiring diagrams, repair manuals, and technical service bulletins (TSBs).
- Programming and Calibration: Mechanics can program and calibrate vehicle modules using OEM software, ensuring that they are functioning properly.
- Advanced Coding and Configuration: Mechanics can perform advanced coding and configuration tasks, such as enabling or disabling features, customizing settings, and adapting modules to the vehicle.
With OEM-level access, mechanics can perform diagnostics with the same level of accuracy and detail as the vehicle manufacturer, resulting in more effective repairs and satisfied customers.
8. Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner: Factors to Consider
What are the key factors to consider when choosing an OBD2 scanner to ensure it meets your needs and budget? Key factors include compatibility, features, budget, brand reputation, and user reviews, ensuring you select the right scanner for your diagnostic requirements.
Choosing the right OBD2 scanner requires careful consideration of several factors to ensure that it meets your needs and budget. Here are some key factors to consider:
8.1. Budget and Pricing
How does pricing vary for OBD2 scanners and what can you expect at different price points? Pricing varies widely, with basic scanners costing under $50 and professional-grade scanners costing hundreds or thousands of dollars, depending on features and capabilities.
OBD2 scanners are available at a wide range of prices, from basic models costing under $50 to professional-grade scanners costing hundreds or even thousands of dollars. The price of an OBD2 scanner depends on its features, capabilities, and brand reputation.
- Entry-Level Scanners (Under $50): These scanners typically offer basic code reading and clearing capabilities. They are suitable for simple diagnostics and basic maintenance tasks.
- Mid-Range Scanners ($50 – $200): These scanners offer more advanced features, such as live data streaming, freeze frame data, and enhanced code definitions. They are suitable for DIY enthusiasts and car owners who want to perform more in-depth diagnostics.
- Professional-Grade Scanners ($200+): These scanners offer advanced features such as bi-directional controls, component testing, OEM-level access, and advanced coding capabilities. They are suitable for professional mechanics and automotive technicians.
When choosing an OBD2 scanner, it’s important to consider your budget and your diagnostic needs. If you only need basic code reading capabilities, an entry-level scanner may be sufficient. However, if you need advanced features for diagnosing complex issues, you may need to invest in a more expensive professional-grade scanner.
8.2. Brand Reputation and Reliability
Which brands are known for producing reliable OBD2 scanners and why is brand reputation important? Reputable brands like Bosch, Innova, and Autel are known for producing reliable and high-quality scanners, ensuring accurate and dependable diagnostics.
Brand reputation is an important factor to consider when choosing an OBD2 scanner. Some brands are known for producing reliable and high-quality scanners, while others are known for producing less reliable or lower-quality products. Some of the most reputable brands in the OBD2 scanner market include:
- Bosch: Bosch is a well-known brand in the automotive industry, and their OBD2 scanners are known for their reliability and accuracy.
- Innova: Innova is a popular brand among DIY enthusiasts and professional mechanics alike. Their scanners are known for their user-friendly interfaces and comprehensive features.
- Autel: Autel is a leading manufacturer of professional-grade OBD2 scanners. Their scanners are known for their advanced features, OEM-level access, and bi-directional control capabilities.
Choosing a scanner from a reputable brand can help ensure that you are getting a high-quality and reliable product.
8.3. User Reviews and Ratings
How can user reviews help you make an informed decision when purchasing an OBD2 scanner? User reviews provide valuable insights into the scanner’s performance, ease of use, and reliability, helping you make an informed purchase decision.
User reviews and ratings can provide valuable insights into the performance, ease of use, and reliability of an OBD2 scanner. Before purchasing an OBD2 scanner, it’s a good idea to read user reviews on websites such as Amazon, eBay, and automotive forums.
When reading user reviews, pay attention to the following:
- Overall Rating: Look for scanners with high overall ratings, as this indicates that most users are satisfied with the product.
- Positive Reviews: Read the positive reviews to see what users like about the scanner.
- Negative Reviews: Read the negative reviews to see what users dislike about the scanner.
- Common Issues: Look for any common issues that are mentioned repeatedly in the reviews.
- Customer Support: Pay attention to comments about customer support, as this can be an important factor if you need help with the scanner.
By reading user reviews, you can get a better understanding of the pros and cons of different OBD2 scanners and make a more informed purchase decision.
9. Future Trends in OBD2 Scanning Technology
What are some emerging trends in OBD2 scanning technology and how might they impact vehicle diagnostics? Emerging trends include wireless connectivity, cloud-based diagnostics, and AI-driven data analysis, promising more efficient and comprehensive vehicle diagnostics.
OBD2 scanning technology is constantly evolving, with new features and capabilities being introduced all the time. Here are some emerging trends in OBD2 scanning technology:
9.1. Wireless Connectivity and Mobile Integration
How are wireless connectivity and mobile apps changing the way we use OBD2 scanners? Wireless connectivity and mobile apps allow for remote diagnostics, real-time data monitoring, and enhanced user convenience, transforming OBD2 scanner usage.
Wireless connectivity and mobile integration are making OBD2 scanners more convenient and user-friendly than ever before. Wireless OBD2 scanners can connect to your smartphone or tablet via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi, allowing you to view diagnostic data on your mobile device.
Mobile apps offer a range of features, such as:
- Real-Time Data Monitoring: View live data from your vehicle’s sensors on your mobile device.
- **
