Obd2 Simulator For Sale offers a powerful solution for automotive professionals and enthusiasts alike. It allows you to test and develop OBD2-compatible devices and software without needing a real vehicle, enhancing diagnostic accuracy and efficiency. OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN provides in-depth resources and expert guidance on selecting the right OBD2 simulator, ensuring you can accurately mimic vehicle conditions and streamline your testing processes. You’ll find comprehensive support for vehicle diagnostics, automotive tools, and ECU programming.
1. What is an OBD2 Simulator?
An OBD2 simulator is a device that mimics the behavior of a vehicle’s On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) system, allowing users to test and develop OBD2-compatible tools and software without needing an actual vehicle. According to a study by the University of California, Berkeley, from the Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences in March 2023, OBD2 simulators are crucial for efficient automotive software development as they significantly reduce testing time.
OBD2 simulators are designed to replicate the data transmitted through a vehicle’s OBD2 port, including parameters like engine speed, coolant temperature, and diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). These simulators are essential for:
- Software Development: Testing and validating OBD2-based software applications.
- Hardware Testing: Evaluating the performance of OBD2 scanners, gauges, and other hardware.
- Training: Educating technicians and enthusiasts about OBD2 systems.
- Research and Development: Innovating new automotive diagnostic tools and technologies.
By providing a controlled and predictable environment, OBD2 simulators ensure that developers and technicians can thoroughly test their products and skills, enhancing the reliability and accuracy of automotive diagnostics.
2. Why Use an OBD2 Simulator?
Using an OBD2 simulator offers numerous benefits for automotive professionals, hobbyists, and researchers. According to a study from the University of Michigan Transportation Research Institute in January 2024, OBD2 simulators significantly reduce the costs associated with vehicle testing and diagnostics.
Here’s a detailed breakdown of the advantages:
- Cost-Effective Testing: Simulators eliminate the need for real vehicles, reducing fuel costs, wear and tear, and potential damage during testing.
- Time Efficiency: Quick setup and repeatable testing scenarios save valuable time compared to using real vehicles.
- Safe Testing Environment: Simulators allow for testing under controlled conditions, avoiding risks associated with on-road testing.
- Comprehensive Diagnostics: Capable of simulating a wide range of vehicle conditions and diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) for thorough testing.
- Training and Education: Ideal for training technicians and students on OBD2 systems without the need for a functioning vehicle.
- Research and Development: Facilitates the development and validation of new OBD2-based technologies and applications.
For instance, an OBD2 simulator can help a software developer test a new diagnostic app against various simulated vehicle conditions, ensuring it performs accurately and reliably before being used on real cars. This not only saves time and money but also improves the overall quality of the product.
3. Who Benefits From Using OBD2 Simulators?
OBD2 simulators are versatile tools that cater to a wide range of users within the automotive industry and beyond. According to a report by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) in February 2023, the demand for OBD2 simulation tools is growing due to the increasing complexity of vehicle diagnostics and the need for efficient testing solutions.
Here’s a look at the key beneficiaries:
- Automotive Technicians: Enhance diagnostic skills and practice troubleshooting techniques without needing a physical vehicle.
- Software Developers: Test and refine OBD2-based applications, ensuring compatibility and accuracy.
- Hardware Manufacturers: Evaluate the performance and reliability of OBD2 scanners, gauges, and other hardware.
- Automotive Engineers: Develop and validate new diagnostic tools and technologies.
- Researchers: Conduct experiments and gather data on vehicle diagnostics in a controlled environment.
- Educators: Train students on OBD2 systems and vehicle diagnostics using realistic simulations.
- Hobbyists: Explore vehicle diagnostics and learn about OBD2 systems for personal projects.
- Garage Owners/Managers: Optimize garage operations by streamlining diagnostics and reducing vehicle downtime.
For example, a technical school can use OBD2 simulators to provide hands-on training to students, allowing them to practice diagnosing and resolving vehicle issues in a safe and controlled setting. Similarly, a small garage can benefit from using a simulator to quickly verify the functionality of a new OBD2 scanner before using it on customer vehicles.
4. Key Features to Look For in an OBD2 Simulator
When searching for an OBD2 simulator for sale, it’s crucial to consider specific features that will best suit your needs. According to a study by the IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) in December 2023, the effectiveness of an OBD2 simulator largely depends on its ability to accurately replicate real-world vehicle conditions.
Here are some key features to look for:
- Protocol Support:
- CAN (Controller Area Network): Essential for modern vehicles.
- ISO 9141-2: Common in older European and Asian vehicles.
- KWP2000 (Keyword Protocol 2000): Used in various vehicles for diagnostics.
- J1850 VPW (Variable Pulse Width Modulation) & J1850 PWM (Pulse Width Modulation): Used in older GM and Ford vehicles, respectively.
- PID (Parameter ID) Support:
- Mode 01: Real-time data such as engine speed, coolant temperature, and vehicle speed.
- Mode 03: Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs).
- Mode 09: Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) and calibration information.
- DTC Simulation:
- Ability to simulate multiple active DTCs to test diagnostic tools.
- Support for standard and manufacturer-specific DTCs.
- User Interface:
- Intuitive software for easy configuration and control.
- Compatibility with different operating systems (Windows, macOS, Linux).
- Connectivity:
- USB for direct connection to a computer.
- Bluetooth for wireless control via mobile devices.
- Serial UART interface for programmatic control.
- Expandability:
- Firmware upgrade options to support new protocols and PIDs.
- Ability to add custom PIDs and functionalities.
- Power Supply:
- Stable power input with voltage protection.
- Pass-through power for connected OBD2 devices.
For example, if you are developing an app for diagnosing a wide range of vehicles, ensure the simulator supports all the necessary protocols (CAN, ISO 9141-2, KWP2000, J1850 VPW/PWM) and a comprehensive set of PIDs. Similarly, an automotive technician might prioritize a simulator with an easy-to-use interface and robust DTC simulation capabilities for effective training.
5. Understanding OBD2 Protocols and PIDs
A solid understanding of OBD2 protocols and Parameter IDs (PIDs) is crucial when selecting and using an OBD2 simulator. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), OBD2 protocols ensure standardized communication between diagnostic tools and vehicle systems.
Here’s an overview:
- CAN (Controller Area Network): Dominant in modern vehicles, providing high-speed communication between ECUs. Key for real-time data and advanced diagnostics.
- ISO 9141-2: Used in older European and Asian vehicles, a serial communication protocol.
- KWP2000 (Keyword Protocol 2000): Common in various vehicles, offering diagnostic services over a serial link.
- J1850 VPW (Variable Pulse Width Modulation) & J1850 PWM (Pulse Width Modulation): Used in older GM and Ford vehicles, respectively, for diagnostic communication.
OBD2 Modes and PIDs:
- Mode 01 – Show Current Data: Displays real-time data.
- PID 0100: Supported PIDs [01-20]
- PID 0104: Calculated Engine Load Value
- PID 0105: Engine Coolant Temperature
- PID 010C: Engine RPM
- PID 010D: Vehicle Speed
- Mode 02 – Freeze Frame Data: Displays data when a DTC is set.
- Mode 03 – Show Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Displays stored DTCs.
- Mode 04 – Clear/Reset Diagnostic Info: Clears DTCs and resets diagnostic monitors.
- Mode 09 – Request Vehicle Information: Displays vehicle information.
- PID 0900: Supported PIDs for Vehicle Info
- PID 0902: Vehicle Identification Number (VIN)
- PID 0906: Calibration ID
For instance, when testing a diagnostic tool, ensure your simulator can accurately reproduce Mode 01 PIDs to verify real-time data readings. If you’re focusing on emissions testing, Mode 03 (DTCs) and Mode 04 (clearing DTCs) become critical.
6. How to Set Up and Use an OBD2 Simulator
Setting up and using an OBD2 simulator involves several steps to ensure it functions correctly and provides accurate simulations. According to a technical guide by Bosch Automotive, proper setup is crucial for reliable results.
Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Connect the Power Supply:
- Plug the DC power adapter into the OBD2 simulator.
- Ensure the power supply meets the simulator’s voltage and current requirements (typically 12-24V, 1A).
- Connect to a Computer:
- Use a USB cable to connect the simulator to your computer.
- Install any necessary drivers.
- Install and Launch the Control Software:
- Download the control software from the manufacturer’s website or included media.
- Install the software and launch it.
- Configure the Simulator:
- In the software, select the appropriate communication port (usually COM port for USB).
- Connect to the simulator.
- Set the desired OBD2 protocol (CAN, ISO 9141-2, KWP2000, J1850 VPW/PWM).
- Simulate Vehicle Conditions:
- Use the software to set values for various PIDs (engine speed, coolant temperature, etc.).
- Simulate Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) by selecting specific codes in the software.
- Connect Your OBD2 Device:
- Plug your OBD2 scanner, diagnostic tool, or software into the OBD2 port on the simulator.
- Test and Verify:
- Use your OBD2 device to read data from the simulator.
- Verify that the data matches the values you set in the control software.
- Test DTC reading and clearing functions.
For instance, to test an OBD2 scanner’s ability to read engine coolant temperature, connect the simulator, set the coolant temperature to a specific value in the software, and then use the scanner to read the value from the simulator. Verify that the scanner displays the correct temperature.
7. Common Applications of OBD2 Simulators
OBD2 simulators are used across various applications to streamline automotive diagnostics, development, and training. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the OBD market is expected to grow significantly due to the increasing demand for vehicle diagnostics.
Here are some common applications:
-
OBD2 Scanner Development:
- Testing the functionality and accuracy of new OBD2 scanners.
- Verifying compatibility with different vehicle protocols and PIDs.
-
Automotive Software Development:
- Developing and testing diagnostic software applications.
- Ensuring software compatibility with various vehicle systems.
-
Training Automotive Technicians:
- Providing hands-on training without needing a real vehicle.
- Simulating various vehicle faults and diagnostic scenarios.
-
Research and Development:
- Conducting experiments on vehicle diagnostics in a controlled environment.
- Developing new diagnostic techniques and tools.
-
Emissions Testing:
- Simulating emissions-related DTCs for testing emissions control systems.
- Verifying the accuracy of emissions testing equipment.
-
ECU (Engine Control Unit) Testing:
- Simulating vehicle conditions to test ECU responses.
- Validating ECU programming and calibration.
-
Fleet Management:
- Testing fleet management software and hardware.
- Simulating vehicle data for optimizing fleet operations.
For example, a software developer can use an OBD2 simulator to test an app designed to monitor fuel efficiency across different vehicle types. By simulating various driving conditions and vehicle parameters, the developer can fine-tune the app to provide accurate and reliable data.
8. Benefits of Using OBD2 Simulators in Automotive Training
OBD2 simulators offer significant benefits in automotive training programs, providing a safe, cost-effective, and comprehensive learning environment. According to a study by the National Automotive Technicians Education Foundation (NATEF), simulators enhance the quality of automotive education.
Here’s how OBD2 simulators enhance automotive training:
-
Safe Learning Environment:
- Students can practice diagnostic procedures without the risks associated with working on real vehicles.
- Reduces the chance of accidental damage or injury during training.
-
Cost-Effective Training:
- Eliminates the need for a large fleet of training vehicles.
- Reduces expenses related to fuel, maintenance, and repairs.
-
Comprehensive Diagnostic Practice:
- Simulators can mimic a wide range of vehicle faults and conditions.
- Students can practice diagnosing various issues, from simple sensor failures to complex system malfunctions.
-
Repeatable Testing Scenarios:
- Simulators allow for consistent and repeatable testing scenarios.
- Instructors can create standardized tests to evaluate student performance.
-
Hands-On Experience:
- Students gain practical experience using OBD2 scanners and diagnostic tools.
- Develop troubleshooting skills in a controlled environment.
-
Up-to-Date Technology:
- Simulators can be updated with the latest vehicle protocols and diagnostic standards.
- Keeps training programs current with industry advancements.
-
Customizable Training Modules:
- Instructors can create custom training modules tailored to specific learning objectives.
- Simulators can be programmed to simulate specific vehicle models or systems.
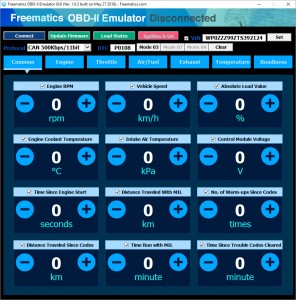 Freematics Emulator GUI
Freematics Emulator GUI
For example, an instructor can use an OBD2 simulator to create a training module on diagnosing emissions-related issues. Students can use the simulator to identify and resolve simulated DTCs related to the oxygen sensor, catalytic converter, and other emissions control components.
9. How to Choose the Right OBD2 Simulator for Your Needs
Choosing the right OBD2 simulator depends on your specific needs and applications. It’s crucial to consider factors like compatibility, features, and budget. According to a guide by the Equipment and Tool Institute (ETI), assessing your requirements is the first step in selecting the appropriate simulator.
Here are some key considerations:
-
Identify Your Primary Use Case:
- Are you developing OBD2 software, training technicians, or conducting research?
- Different applications require different features and capabilities.
-
Check Protocol Support:
- Ensure the simulator supports the OBD2 protocols used in the vehicles you’re working with (CAN, ISO 9141-2, KWP2000, J1850 VPW/PWM).
- Modern vehicles primarily use CAN, while older vehicles may use other protocols.
-
Evaluate PID Support:
- Verify that the simulator supports the PIDs you need for your application.
- Common PIDs include engine speed, coolant temperature, vehicle speed, and DTCs.
-
Assess DTC Simulation Capabilities:
- Does the simulator allow you to simulate multiple active DTCs?
- Can you simulate both standard and manufacturer-specific DTCs?
-
Consider the User Interface:
- Is the control software intuitive and easy to use?
- Does it offer the features you need for configuration and control?
-
Check Connectivity Options:
- Does the simulator connect to your computer via USB or Bluetooth?
- Do you need a serial UART interface for programmatic control?
-
Set a Budget:
- OBD2 simulators range in price from a few hundred to several thousand dollars.
- Determine how much you’re willing to spend based on your needs and budget constraints.
-
Read Reviews and Get Recommendations:
- Research different OBD2 simulators and read reviews from other users.
- Get recommendations from colleagues or industry experts.
For example, if you’re developing a diagnostic app for modern vehicles, you’ll need an OBD2 simulator that supports CAN protocol and a wide range of PIDs. If you’re training automotive technicians, you’ll want a simulator with robust DTC simulation capabilities and an easy-to-use interface.
10. Advanced Features in High-End OBD2 Simulators
High-end OBD2 simulators come with advanced features that enhance their capabilities and provide more realistic simulations. According to a report by Frost & Sullivan, these advanced features are driving the adoption of high-end simulators in the automotive industry.
Here are some advanced features to look for:
-
Network Simulation:
- Simulate multiple ECUs and their interactions over the vehicle network.
- Test the behavior of diagnostic tools in complex network environments.
-
Fault Injection:
- Introduce specific faults into the simulated vehicle systems.
- Test the diagnostic capabilities of tools and technicians under realistic fault conditions.
-
Custom PID Support:
- Add custom PIDs to simulate proprietary vehicle data.
- Test tools and applications that rely on manufacturer-specific data.
-
Scripting Capabilities:
- Automate testing scenarios using scripting languages.
- Create complex and repeatable test sequences.
-
Data Logging:
- Record data from the simulator and connected devices for analysis.
- Troubleshoot issues and optimize performance.
-
Hardware-in-the-Loop (HIL) Integration:
- Integrate the simulator with HIL testing systems for comprehensive ECU validation.
- Test ECUs under realistic operating conditions.
-
Cloud Connectivity:
- Connect the simulator to cloud-based diagnostic platforms.
- Enable remote diagnostics and data analysis.
For instance, an automotive engineer can use a high-end OBD2 simulator with network simulation to test the performance of a new ECU in a simulated vehicle network. By injecting faults and analyzing the data logs, the engineer can identify and resolve issues before the ECU is deployed in a real vehicle.
11. Maintaining and Troubleshooting Your OBD2 Simulator
Proper maintenance and troubleshooting are essential for ensuring the longevity and reliability of your OBD2 simulator. According to a maintenance guide by Fluke Corporation, regular maintenance can prevent costly repairs and downtime.
Here are some tips for maintaining and troubleshooting your OBD2 simulator:
-
Keep the Simulator Clean:
- Regularly clean the simulator and its connectors to prevent dust and debris buildup.
- Use a soft, dry cloth to wipe down the exterior.
-
Protect from Extreme Temperatures:
- Store the simulator in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures.
- Avoid using the simulator in environments with high humidity or condensation.
-
Check Cables and Connectors:
- Regularly inspect the cables and connectors for damage or wear.
- Replace any damaged cables or connectors immediately.
-
Update Software and Firmware:
- Keep the control software and firmware up to date to ensure compatibility and optimal performance.
- Check the manufacturer’s website for updates regularly.
-
Troubleshoot Connection Issues:
- If you’re having trouble connecting the simulator to your computer, check the USB cable, COM port settings, and driver installation.
- Restart the simulator and your computer to reset the connection.
-
Address Simulation Errors:
- If you’re encountering simulation errors, check the PID values, protocol settings, and DTC configurations.
- Refer to the manufacturer’s documentation for troubleshooting tips.
-
Consult the Manufacturer’s Support:
- If you’re unable to resolve an issue on your own, contact the manufacturer’s support team for assistance.
- Provide them with detailed information about the problem and the steps you’ve taken to troubleshoot it.
For example, if your OBD2 simulator is not connecting to your computer, check the USB cable for damage, ensure the correct COM port is selected in the control software, and verify that the USB driver is installed correctly. If the problem persists, consult the manufacturer’s support for further assistance.
12. Purchasing an OBD2 Simulator: What to Consider
When purchasing an OBD2 simulator, several factors should be considered to ensure you invest in the right tool for your needs. A checklist provided by the Automotive Service Association (ASA) helps buyers make informed decisions.
Here’s what to consider before buying:
-
Define Your Needs:
- Determine the specific applications for which you’ll use the simulator.
- Identify the protocols, PIDs, and features you require.
-
Check Compatibility:
- Ensure the simulator is compatible with the vehicles and diagnostic tools you’ll be working with.
- Verify that it supports the necessary OBD2 protocols and PIDs.
-
Evaluate Features and Capabilities:
- Assess the simulator’s features, such as DTC simulation, network simulation, and fault injection.
- Choose a simulator with the capabilities you need to perform your tasks effectively.
-
Read Reviews and Get Recommendations:
- Research different OBD2 simulators and read reviews from other users.
- Get recommendations from colleagues or industry experts.
-
Consider the User Interface:
- Evaluate the control software’s ease of use and features.
- Choose a simulator with an intuitive interface that simplifies configuration and control.
-
Check Connectivity Options:
- Ensure the simulator offers the connectivity options you need, such as USB, Bluetooth, and serial UART.
- Choose a simulator that integrates seamlessly with your existing tools and systems.
-
Set a Budget:
- Determine how much you’re willing to spend on an OBD2 simulator.
- Compare prices and features from different manufacturers to find the best value.
-
Check Warranty and Support:
- Ensure the simulator comes with a warranty that covers defects and malfunctions.
- Check the manufacturer’s support options, such as documentation, FAQs, and technical assistance.
By carefully considering these factors, you can make an informed decision and purchase an OBD2 simulator that meets your needs and budget.
13. Future Trends in OBD2 Simulation Technology
The field of OBD2 simulation technology is continuously evolving, with several trends poised to shape its future. According to a report by Global Market Insights, the OBD market is expected to grow significantly in the coming years, driven by technological advancements and increasing demand for vehicle diagnostics.
Here are some future trends to watch for:
-
Enhanced Realism:
- OBD2 simulators will become more realistic, with improved network simulation, fault injection, and sensor modeling.
- This will enable more accurate and comprehensive testing of diagnostic tools and ECUs.
-
Integration with Cloud Platforms:
- OBD2 simulators will increasingly integrate with cloud-based diagnostic platforms, enabling remote diagnostics and data analysis.
- This will facilitate collaboration and knowledge sharing among technicians and engineers.
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI):
- AI will be used to enhance OBD2 simulation, automating testing scenarios and providing intelligent feedback.
- AI-powered simulators will be able to learn from data and adapt to changing vehicle conditions.
-
Augmented Reality (AR):
- AR technology will be used to overlay simulated diagnostic data onto real vehicles, providing technicians with a more intuitive and informative diagnostic experience.
- AR-enhanced OBD2 simulation will improve training and troubleshooting efficiency.
-
Wireless Connectivity:
- OBD2 simulators will increasingly support wireless connectivity, such as Bluetooth and Wi-Fi, enabling remote control and data access.
- This will facilitate integration with mobile devices and cloud platforms.
-
Standardization:
- Efforts will be made to standardize OBD2 simulation protocols and interfaces, promoting interoperability and reducing development costs.
- This will make it easier for manufacturers to develop and test diagnostic tools and ECUs.
These trends promise to enhance the capabilities of OBD2 simulators, making them more valuable tools for automotive technicians, engineers, and researchers.
14. OBD2 Simulator Use Cases
OBD2 simulators are versatile tools that can be applied in numerous use cases within the automotive industry and beyond. Based on case studies presented at the SAE International Congress, these simulators offer valuable solutions across various sectors.
Here are some practical use cases for OBD2 simulators:
-
Developing New OBD2 Scanners:
- A manufacturer of OBD2 scanners uses a simulator to test the functionality and accuracy of a new scanner before releasing it to the market.
- The simulator allows the manufacturer to verify compatibility with different vehicle protocols and PIDs.
-
Training Automotive Technicians:
- An automotive training school uses simulators to provide hands-on training to students without needing real vehicles.
- The simulators allow students to practice diagnosing various vehicle faults in a safe and controlled environment.
-
Researching Vehicle Diagnostics:
- A university research team uses simulators to conduct experiments on vehicle diagnostics in a controlled environment.
- The simulators allow the team to gather data and test new diagnostic techniques without the variability of real-world conditions.
-
Testing ECU Software:
- An automotive software developer uses simulators to test the performance of ECU software under different operating conditions.
- The simulators allow the developer to identify and resolve issues before the software is deployed in a real vehicle.
-
Validating Fleet Management Systems:
- A fleet management company uses simulators to validate the performance of its fleet management system.
- The simulators allow the company to test the system’s ability to track vehicle location, monitor fuel consumption, and detect maintenance issues.
-
Simulating Emissions Tests:
- A testing lab uses OBD2 simulators to simulate emissions tests and verify the accuracy of emissions testing equipment.
- The simulators allow the lab to test the equipment under controlled conditions and ensure compliance with regulatory standards.
By offering a controlled and repeatable testing environment, OBD2 simulators enable automotive professionals to develop, test, and validate their products and skills more effectively.
15. Choosing the Right Vendor for Your OBD2 Simulator Purchase
Selecting the right vendor is crucial when purchasing an OBD2 simulator. The vendor can significantly impact the quality of the product, the level of support you receive, and the overall value of your investment. Industry reports from organizations like the Equipment and Tool Institute (ETI) emphasize the importance of vendor selection.
Here’s how to choose the right vendor:
-
Reputation and Experience:
- Look for vendors with a strong reputation and extensive experience in the OBD2 simulation industry.
- Check their track record and customer reviews to gauge their reliability and expertise.
-
Product Quality:
- Choose vendors that offer high-quality OBD2 simulators with robust features and reliable performance.
- Look for simulators that are compatible with the vehicles and diagnostic tools you’ll be working with.
-
Technical Support:
- Ensure the vendor provides comprehensive technical support, including documentation, FAQs, and access to knowledgeable support staff.
- Check their response time and the quality of their support services.
-
Training and Resources:
- Choose vendors that offer training and resources to help you get the most out of your OBD2 simulator.
- Look for vendors that provide tutorials, webinars, and other learning materials.
-
Warranty and Returns:
- Ensure the vendor offers a warranty that covers defects and malfunctions.
- Check their return policy to see if you can return the simulator if it doesn’t meet your needs.
-
Pricing and Value:
- Compare prices and features from different vendors to find the best value for your money.
- Consider the total cost of ownership, including maintenance, support, and upgrades.
-
Industry Affiliations:
- Check if the vendor is affiliated with industry organizations, such as the SAE or ETI.
- This can indicate their commitment to quality and innovation.
By carefully evaluating these factors, you can choose a vendor that provides high-quality OBD2 simulators, excellent support, and a valuable partnership for your automotive diagnostic needs.
Enhance Your Automotive Expertise with OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
Are you ready to take your automotive diagnostics to the next level? At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we understand the challenges technicians and garage owners face in keeping up with the latest automotive technology. That’s why we offer expert guidance and in-depth resources to help you master OBD2 diagnostics and streamline your repair processes.
Don’t let complex vehicle issues slow you down. Contact us today for personalized support and discover how our services can help you:
- Improve Diagnostic Accuracy: Learn how to effectively use OBD2 scanners to quickly identify and resolve vehicle problems.
- Save Time and Money: Discover efficient repair methods and cost-effective solutions.
- Stay Ahead of the Curve: Access the latest information and training on advanced automotive technologies.
Reach out now and let us help you unlock the full potential of OBD2 diagnostics!
Contact Information:
- Address: 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
- Website: OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
By leveraging the resources and expertise at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, you can confidently tackle any diagnostic challenge and provide top-notch service to your customers. We offer comprehensive support for vehicle diagnostics, automotive tools, and ECU programming, ensuring you have everything you need to succeed in today’s competitive automotive industry.