An Obd2 To Can Converter bridges the gap between older OBD2 protocols and modern CAN bus systems, enabling newer devices to communicate with pre-2008 vehicles. At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we empower automotive enthusiasts and professionals with the knowledge and tools necessary to navigate the complexities of vehicle diagnostics. Discover how this technology simplifies vehicle communication, enhances diagnostic capabilities, and ensures compatibility across a wide range of automotive systems.
Contents
- 1. What Is an OBD2 to CAN Converter?
- 1.1. Defining the OBD2 to CAN Converter
- 1.2. Core Functionality of the Converter
- 1.3. Why Is This Conversion Needed?
- 1.4. Benefits of Using an OBD2 to CAN Converter
- 1.5. Common Applications in Automotive Diagnostics
- 2. How Does an OBD2 to CAN Converter Work?
- 2.1. Understanding OBD2 Protocols
- 2.2. The Role of the CAN Bus System
- 2.3. Step-by-Step Conversion Process
- 2.4. Key Components of an OBD2 to CAN Converter
- 2.5. Examples of Real-World Applications
- 3. Choosing the Right OBD2 to CAN Converter
- 3.1. Compatibility with Your Vehicle
- 3.2. Supported OBD2 Protocols
- 3.3. CAN Bus Speed and Standards
- 3.4. Build Quality and Durability
- 3.5. Ease of Use and Installation
- 3.6. Brand Reputation and Reviews
- 3.7. Price vs. Performance
- 3.8. Additional Features to Consider
- 4. Setting Up and Installing an OBD2 to CAN Converter
- 4.1. Gathering Necessary Tools and Equipment
- 4.2. Identifying the OBD2 Port in Your Vehicle
- 4.3. Connecting the Converter to the OBD2 Port
- 4.4. Connecting the Converter to the CAN Bus System
- 4.5. Configuring the Converter Settings
- 4.6. Testing the Connection
- 4.7. Troubleshooting Common Installation Issues
- 5. Common Issues and Troubleshooting
- 5.1. Communication Errors
- 5.2. Incorrect Data Readings
- 5.3. Converter Not Recognizing the Vehicle
- 5.4. Intermittent Connection Problems
- 5.5. Converter Freezing or Crashing
- 6. Advanced Tips and Tricks
- 6.1. Customizing Conversion Parameters
- 6.2. Using Data Logging Features
- 6.3. Integrating with Aftermarket Systems
- 6.4. Performing Advanced Diagnostics
- 6.5. Automating Tasks with Scripting
- 7. Maintaining Your OBD2 to CAN Converter
- 7.1. Cleaning and Storage
- 7.2. Inspecting Cables and Connectors
- 7.3. Updating Firmware
- 7.4. Protecting from Overvoltage
- 7.5. Regular Testing
- 8. The Future of OBD2 to CAN Conversion
- 8.1. Wireless Connectivity
- 8.2. Enhanced Data Security
- 8.3. Artificial Intelligence (AI) Integration
- 8.4. Real-Time Data Analysis
- 8.5. Integration with Smart Devices
- 9. OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN: Your Partner in Automotive Diagnostics
- 9.1. Our Commitment to Quality and Accuracy
- 9.2. Comprehensive Resources and Guides
- 9.3. Expert Support and Consultation
- 9.4. Exclusive Deals and Discounts
- 9.5. Success Stories from Our Community
- 10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 10.1. What is the difference between OBD2 and CAN bus?
- 10.2. Do I need an OBD2 to CAN converter for my car?
- 10.3. How do I know which OBD2 protocol my car uses?
- 10.4. Can I use an OBD2 scanner on a CAN bus system?
- 10.5. What is the CAN bus speed?
- 10.6. How do I update the firmware on my OBD2 to CAN converter?
- 10.7. Can an OBD2 to CAN converter improve my car’s performance?
- 10.8. What are the common OBD2 error codes?
- 10.9. Where can I buy an OBD2 to CAN converter?
- 10.10. How much does an OBD2 to CAN converter cost?
1. What Is an OBD2 to CAN Converter?
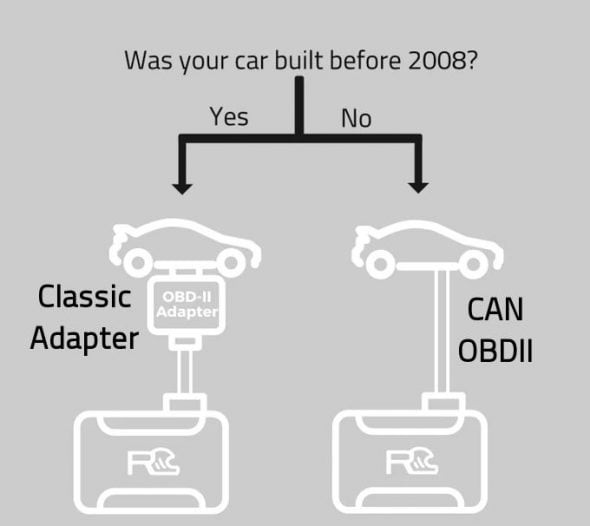
An OBD2 to CAN converter is a device that translates data between older OBD2 (On-Board Diagnostics II) protocols and the modern CAN (Controller Area Network) bus systems used in most vehicles manufactured after 2008. According to a study by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) in 2010, CAN bus systems offer faster data transmission speeds and improved reliability compared to older OBD2 protocols. These converters enable newer diagnostic tools and devices designed for CAN bus systems to work with older vehicles that use protocols like J1850 PWM, J1850 VPW, ISO 9141-2, and ISO 14230-4.
1.1. Defining the OBD2 to CAN Converter
An OBD2 to CAN converter serves as a communication bridge, allowing devices designed for modern CAN bus systems to interact with vehicles using older OBD2 protocols. This ensures compatibility and expands the usability of advanced diagnostic tools.
1.2. Core Functionality of the Converter
The primary function of an OBD2 to CAN converter is to translate the data transmitted via older OBD2 protocols into a format that can be understood by devices expecting CAN bus communication. This involves converting electrical signals and data formats to ensure seamless interaction.
1.3. Why Is This Conversion Needed?
The conversion is necessary because vehicles manufactured before 2008 often use different OBD2 protocols that are not directly compatible with newer diagnostic tools and systems designed for CAN bus communication. The CAN bus system, introduced to enhance data transmission speed and reliability, became mandatory in the US for all vehicles in 2008, as stated by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in their 2005 report on vehicle emissions standards.
1.4. Benefits of Using an OBD2 to CAN Converter
Using an OBD2 to CAN converter offers several benefits:
- Compatibility: Allows modern diagnostic tools to work with older vehicles.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Eliminates the need for separate diagnostic tools for different vehicle types.
- Efficiency: Streamlines the diagnostic process by providing a unified interface.
- Versatility: Enables the use of advanced features available in modern diagnostic equipment.
1.5. Common Applications in Automotive Diagnostics
OBD2 to CAN converters are commonly used in:
- Automotive Repair Shops: To diagnose a wide range of vehicles, both old and new.
- Vehicle Tuning: To read and modify ECU data in older vehicles using modern tuning software.
- Data Logging: To collect vehicle performance data for analysis and improvement.
- DIY Car Enthusiasts: To perform diagnostics and maintenance on their own vehicles.
2. How Does an OBD2 to CAN Converter Work?
An OBD2 to CAN converter functions by intercepting data transmitted through older OBD2 protocols, translating it into CAN bus format, and then transmitting it to the diagnostic tool or device. This process involves several key steps and components.
2.1. Understanding OBD2 Protocols
OBD2 protocols are communication standards used by vehicles to transmit diagnostic data. Common OBD2 protocols include:
- J1850 PWM (Pulse Width Modulation): Used primarily by Ford vehicles.
- J1850 VPW (Variable Pulse Width): Used mainly by General Motors vehicles.
- ISO 9141-2: Used by European and Asian vehicles.
- ISO 14230-4 (KWP2000): An international standard used by various manufacturers.
These protocols transmit data at different rates and use different encoding methods, making direct communication with CAN bus systems impossible.
2.2. The Role of the CAN Bus System
The CAN bus system is a robust communication network that allows various electronic control units (ECUs) within a vehicle to communicate with each other without a host computer. As detailed in a Bosch report from 1986, CAN bus systems offer high-speed data transmission, noise immunity, and error detection capabilities, making them ideal for modern automotive applications.
2.3. Step-by-Step Conversion Process
The conversion process typically involves these steps:
- Data Reception: The OBD2 to CAN converter receives data from the vehicle’s OBD2 port using one of the older protocols (e.g., J1850 PWM).
- Protocol Decoding: The converter decodes the received data to extract the relevant diagnostic information, such as engine RPM, temperature, and fault codes.
- Data Translation: The decoded data is translated into a CAN bus compatible format, which includes reformatting the data structure and converting electrical signal levels.
- CAN Bus Transmission: The translated data is transmitted over the CAN bus to the connected diagnostic tool or device.
2.4. Key Components of an OBD2 to CAN Converter
The key components of an OBD2 to CAN converter include:
- Microcontroller: Responsible for managing the conversion process, decoding OBD2 protocols, and encoding CAN bus messages.
- OBD2 Interface: Hardware interface that connects to the vehicle’s OBD2 port and receives data.
- CAN Bus Interface: Hardware interface that transmits the translated data over the CAN bus.
- Power Supply: Provides the necessary power to operate the converter.
- Firmware: Software that controls the microcontroller and defines the conversion logic.
2.5. Examples of Real-World Applications
- Retrofitting Modern Diagnostic Tools: Allows a modern OBD2 scanner to be used on a 2006 Ford Mustang (J1850 PWM protocol).
- Using Advanced Tuning Software: Enables the use of advanced ECU tuning software on a 2004 Chevrolet Corvette (J1850 VPW protocol).
- Integrating Aftermarket Systems: Facilitates the integration of aftermarket performance monitoring systems in older vehicles.
 OBD2 Port Diagram
OBD2 Port Diagram
3. Choosing the Right OBD2 to CAN Converter
Selecting the appropriate OBD2 to CAN converter is crucial for ensuring compatibility and optimal performance. Consider these factors when making your choice.
3.1. Compatibility with Your Vehicle
Ensure the converter supports the OBD2 protocol used by your vehicle. Check your vehicle’s manual or consult with a mechanic to determine the correct protocol.
3.2. Supported OBD2 Protocols
Verify that the converter supports all the necessary OBD2 protocols, including J1850 PWM, J1850 VPW, ISO 9141-2, and ISO 14230-4. A versatile converter will be compatible with a wider range of vehicles.
3.3. CAN Bus Speed and Standards
Check the CAN bus speed supported by the converter. Most modern diagnostic tools use a standard CAN bus speed of 500 kbps, but older systems may use different speeds. Confirm compatibility with your diagnostic equipment.
3.4. Build Quality and Durability
Opt for a converter with robust build quality and durable components to withstand the harsh conditions of automotive environments. Look for converters with rugged enclosures and reliable connectors.
3.5. Ease of Use and Installation
Choose a converter that is easy to install and use. Simple plug-and-play devices are ideal for both professionals and DIY users. Clear documentation and user-friendly interfaces can also enhance the user experience.
3.6. Brand Reputation and Reviews
Research the brand reputation and read customer reviews before making a purchase. A reputable brand is more likely to offer reliable products and good customer support.
3.7. Price vs. Performance
Balance the price of the converter with its performance and features. While cheaper options may be tempting, investing in a higher-quality converter can save you time and frustration in the long run.
3.8. Additional Features to Consider
- Firmware Upgradability: Allows the converter to be updated with the latest protocols and features.
- Data Logging Capabilities: Enables the converter to record vehicle performance data for later analysis.
- Customizable Settings: Provides options to adjust the conversion process for specific applications.
4. Setting Up and Installing an OBD2 to CAN Converter
Proper setup and installation are essential for ensuring the OBD2 to CAN converter functions correctly. Follow these steps for a seamless installation process.
4.1. Gathering Necessary Tools and Equipment
Before starting the installation, gather the necessary tools and equipment, including:
- OBD2 to CAN converter
- OBD2 cable
- CAN bus connector
- Diagnostic tool or device
- Vehicle’s manual
- Screwdriver (if needed)
4.2. Identifying the OBD2 Port in Your Vehicle
The OBD2 port is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side. Refer to your vehicle’s manual for the exact location.
4.3. Connecting the Converter to the OBD2 Port
Plug the OBD2 cable into the vehicle’s OBD2 port. Ensure the connection is secure.
4.4. Connecting the Converter to the CAN Bus System
Connect the CAN bus connector to the diagnostic tool or device. Verify that the CAN bus speed settings match the requirements of the converter and the diagnostic tool.
4.5. Configuring the Converter Settings
Configure the converter settings according to the manufacturer’s instructions. This may involve selecting the appropriate OBD2 protocol and CAN bus speed.
4.6. Testing the Connection
Turn on the vehicle’s ignition and the diagnostic tool. Verify that the diagnostic tool is receiving data from the vehicle. Check for any error messages or communication issues.
4.7. Troubleshooting Common Installation Issues
If you encounter any issues during the installation process, try these troubleshooting tips:
- Check the OBD2 Connection: Ensure the OBD2 cable is securely plugged into the vehicle’s OBD2 port.
- Verify CAN Bus Settings: Confirm that the CAN bus speed settings are correct.
- Update Firmware: Update the converter’s firmware to the latest version.
- Consult the Manual: Refer to the converter’s manual for troubleshooting guidance.
5. Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Even with proper setup, you may encounter issues while using an OBD2 to CAN converter. Here are some common problems and how to resolve them.
5.1. Communication Errors
Problem: The diagnostic tool fails to communicate with the vehicle.
Solution:
- Check OBD2 Connection: Ensure the OBD2 cable is securely connected.
- Verify Protocol Settings: Confirm that the correct OBD2 protocol is selected in the converter settings.
- Inspect Wiring: Check for any damaged or loose wires in the OBD2 and CAN bus connections.
- Test with Another Vehicle: Try the converter with another vehicle to rule out vehicle-specific issues.
5.2. Incorrect Data Readings
Problem: The diagnostic tool displays inaccurate or inconsistent data.
Solution:
- Calibrate the Converter: Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to calibrate the converter.
- Update Firmware: Update the converter’s firmware to the latest version to ensure accurate data translation.
- Check Sensor Data: Verify that the vehicle’s sensors are functioning correctly.
- Compare with Known Values: Compare the data readings with known values from a reliable source.
5.3. Converter Not Recognizing the Vehicle
Problem: The converter fails to recognize the vehicle’s OBD2 protocol.
Solution:
- Verify Vehicle Protocol: Confirm the vehicle’s OBD2 protocol using the vehicle’s manual or a diagnostic tool.
- Select Correct Protocol: Manually select the correct OBD2 protocol in the converter settings.
- Test with Another Vehicle: Try the converter with another vehicle to rule out vehicle-specific issues.
5.4. Intermittent Connection Problems
Problem: The connection between the converter and the diagnostic tool is unstable.
Solution:
- Secure Connections: Ensure all connections are secure and free from corrosion.
- Replace Cables: Replace any damaged or worn cables.
- Check Power Supply: Verify that the converter is receiving a stable power supply.
- Minimize Interference: Keep the converter away from sources of electromagnetic interference.
5.5. Converter Freezing or Crashing
Problem: The converter stops responding or crashes during operation.
Solution:
- Restart the Converter: Disconnect and reconnect the power supply to restart the converter.
- Update Firmware: Update the converter’s firmware to the latest version to fix any software bugs.
- Check for Overheating: Ensure the converter is not overheating. Provide adequate ventilation if necessary.
- Contact Support: Contact the manufacturer’s support team for further assistance.
6. Advanced Tips and Tricks
For advanced users, here are some tips and tricks to maximize the performance and versatility of your OBD2 to CAN converter.
6.1. Customizing Conversion Parameters
Some converters allow you to customize the conversion parameters, such as data filtering and scaling. Experiment with these settings to optimize the data output for your specific applications.
6.2. Using Data Logging Features
Take advantage of the data logging features to record vehicle performance data for later analysis. This can be useful for identifying performance issues, tuning the engine, and monitoring vehicle health.
6.3. Integrating with Aftermarket Systems
Integrate the converter with aftermarket systems, such as performance monitors, gauges, and data acquisition systems. This allows you to display real-time vehicle data and enhance the functionality of your aftermarket equipment.
6.4. Performing Advanced Diagnostics
Use the converter to perform advanced diagnostics, such as reading and clearing diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), monitoring sensor data, and performing actuator tests. This can help you troubleshoot complex vehicle issues and perform more thorough repairs.
6.5. Automating Tasks with Scripting
Automate repetitive tasks using scripting languages, such as Python or Lua. This can streamline the diagnostic process and improve efficiency.
7. Maintaining Your OBD2 to CAN Converter
Proper maintenance is essential for ensuring the longevity and reliability of your OBD2 to CAN converter. Follow these guidelines to keep your converter in top condition.
7.1. Cleaning and Storage
Keep the converter clean and free from dust, dirt, and moisture. Store it in a dry, protected environment when not in use.
7.2. Inspecting Cables and Connectors
Regularly inspect the cables and connectors for damage, wear, and corrosion. Replace any damaged or worn components.
7.3. Updating Firmware
Keep the converter’s firmware up to date to ensure compatibility with the latest vehicles and diagnostic tools. Check the manufacturer’s website for firmware updates.
7.4. Protecting from Overvoltage
Protect the converter from overvoltage by using a surge protector or voltage regulator. This can prevent damage from electrical spikes.
7.5. Regular Testing
Test the converter regularly to ensure it is functioning correctly. This can help you identify any potential issues before they become major problems.
8. The Future of OBD2 to CAN Conversion
The field of OBD2 to CAN conversion is constantly evolving, with new technologies and applications emerging. Here are some trends to watch for in the future.
8.1. Wireless Connectivity
Wireless connectivity, such as Bluetooth and Wi-Fi, is becoming increasingly common in OBD2 to CAN converters. This allows for easier integration with mobile devices and cloud-based diagnostic platforms.
8.2. Enhanced Data Security
Enhanced data security measures are being implemented to protect against unauthorized access and data breaches. This is especially important for connected vehicle applications.
8.3. Artificial Intelligence (AI) Integration
AI is being used to improve the accuracy and efficiency of data translation. AI-powered converters can automatically identify and adapt to different OBD2 protocols, making them more versatile and user-friendly.
8.4. Real-Time Data Analysis
Real-time data analysis capabilities are being integrated into converters, allowing users to monitor vehicle performance and identify potential issues in real-time.
8.5. Integration with Smart Devices
Converters are being integrated with smart devices, such as smartphones and tablets, to provide users with a more convenient and intuitive diagnostic experience.
9. OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN: Your Partner in Automotive Diagnostics
At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we are dedicated to providing you with the knowledge, tools, and support you need to excel in automotive diagnostics. Whether you’re a professional mechanic or a DIY enthusiast, we have the resources to help you succeed.
9.1. Our Commitment to Quality and Accuracy
We are committed to providing high-quality, accurate information on OBD2 to CAN conversion and other automotive diagnostic topics. Our team of experts works hard to ensure that our content is up-to-date, reliable, and easy to understand.
9.2. Comprehensive Resources and Guides
We offer a wide range of resources and guides to help you learn about OBD2 to CAN conversion and other automotive diagnostic topics. Our resources include articles, tutorials, videos, and product reviews.
9.3. Expert Support and Consultation
Our team of experts is available to provide support and consultation on OBD2 to CAN conversion and other automotive diagnostic topics. We can help you choose the right converter, troubleshoot installation issues, and optimize your diagnostic processes.
9.4. Exclusive Deals and Discounts
We offer exclusive deals and discounts on OBD2 to CAN converters and other automotive diagnostic tools. Check our website regularly for the latest offers.
9.5. Success Stories from Our Community
Join our community of automotive enthusiasts and professionals and share your success stories. Learn from others and get inspired to achieve your diagnostic goals.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
10.1. What is the difference between OBD2 and CAN bus?
OBD2 is a diagnostic protocol, while CAN bus is a communication network. OBD2 defines the types of data that can be accessed, while CAN bus provides the physical layer for transmitting that data.
10.2. Do I need an OBD2 to CAN converter for my car?
You need an OBD2 to CAN converter if you want to use a modern diagnostic tool on a vehicle that uses an older OBD2 protocol (pre-2008).
10.3. How do I know which OBD2 protocol my car uses?
Check your vehicle’s manual or consult with a mechanic. You can also use a diagnostic tool to identify the OBD2 protocol.
10.4. Can I use an OBD2 scanner on a CAN bus system?
Yes, most modern OBD2 scanners are designed to work with CAN bus systems.
10.5. What is the CAN bus speed?
The standard CAN bus speed is 500 kbps, but some older systems may use different speeds.
10.6. How do I update the firmware on my OBD2 to CAN converter?
Check the manufacturer’s website for firmware updates and follow the instructions provided.
10.7. Can an OBD2 to CAN converter improve my car’s performance?
No, an OBD2 to CAN converter does not directly improve your car’s performance. However, it can help you diagnose and troubleshoot performance issues.
10.8. What are the common OBD2 error codes?
Common OBD2 error codes include P0300 (Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected), P0171 (System Too Lean), and P0420 (Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold).
10.9. Where can I buy an OBD2 to CAN converter?
You can buy an OBD2 to CAN converter from automotive parts stores, online retailers, and directly from the manufacturer.
10.10. How much does an OBD2 to CAN converter cost?
The cost of an OBD2 to CAN converter varies depending on the features and brand. Prices typically range from $50 to $200.
Understanding and utilizing an OBD2 to CAN converter can greatly enhance your ability to diagnose and maintain vehicles, bridging the gap between older and newer technologies. By choosing the right converter, setting it up correctly, and keeping it well-maintained, you can unlock a wealth of diagnostic information and ensure your vehicle runs smoothly.
Are you facing challenges with diagnosing your older vehicle using modern OBD2 scanners? Do you want to unlock the full potential of your car’s diagnostic capabilities? Contact us at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN today for expert guidance and support. Call us at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN. Our address is 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States. Let us help you simplify your automotive diagnostics and keep your vehicle running at its best!