Obd2 Wiki serves as a comprehensive resource, empowering car owners and technicians with the knowledge to diagnose and resolve vehicle issues using OBD2 scanners, and OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN offers detailed guides and repair services. By understanding OBD2 codes, troubleshooting techniques, and the capabilities of your scan tool, you can effectively maintain your vehicle and potentially save on repair costs. Vehicle diagnostics, emission control, and automotive technology are integral parts of this process.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the Basics of OBD2
- 1.1 What is the Purpose of OBD2?
- 1.2 Key Components of an OBD2 System
- 1.3 How OBD2 Works
- 2. Decoding OBD2 Trouble Codes
- 2.1 Understanding the Structure of OBD2 Codes
- 2.2 Common OBD2 Codes and Their Meanings
- 2.3 Using an OBD2 Scanner to Read Codes
- 2.4 Interpreting Freeze Frame Data
- 3. Selecting the Right OBD2 Scanner
- 3.1 Types of OBD2 Scanners
- 3.2 Key Features to Look For
- 3.3 Budget Considerations
- 3.4 Top OBD2 Scanner Brands
- 4. Advanced OBD2 Diagnostics
- 4.1 Using Live Data Streaming
- 4.2 Performing Bi-Directional Control Tests
- 4.3 Performing System Tests
- 4.4 Graphing and Data Logging
- 5. OBD2 and Emission Testing
- 5.1 How OBD2 Monitors Emissions
- 5.2 Common Emission-Related OBD2 Codes
- 5.3 Preparing Your Vehicle for Emission Testing
- 5.4 Understanding Readiness Monitors
- 6. Common OBD2 Diagnostic Mistakes to Avoid
- 6.1 Misinterpreting OBD2 Codes
- 6.2 Neglecting Basic Troubleshooting Steps
- 6.3 Ignoring Freeze Frame Data
- 6.4 Not Clearing Codes After Repair
- 6.5 Assuming a Code Means a Specific Part is Bad
- 7. Maintaining Your OBD2 Scanner
- 7.1 Keeping the Scanner Clean
- 7.2 Storing the Scanner Properly
- 7.3 Updating the Software Regularly
- 7.4 Replacing Cables and Connectors
- 7.5 Calibrating the Scanner
- 8. OBD2 and Vehicle Security
- 8.1 Potential Security Risks
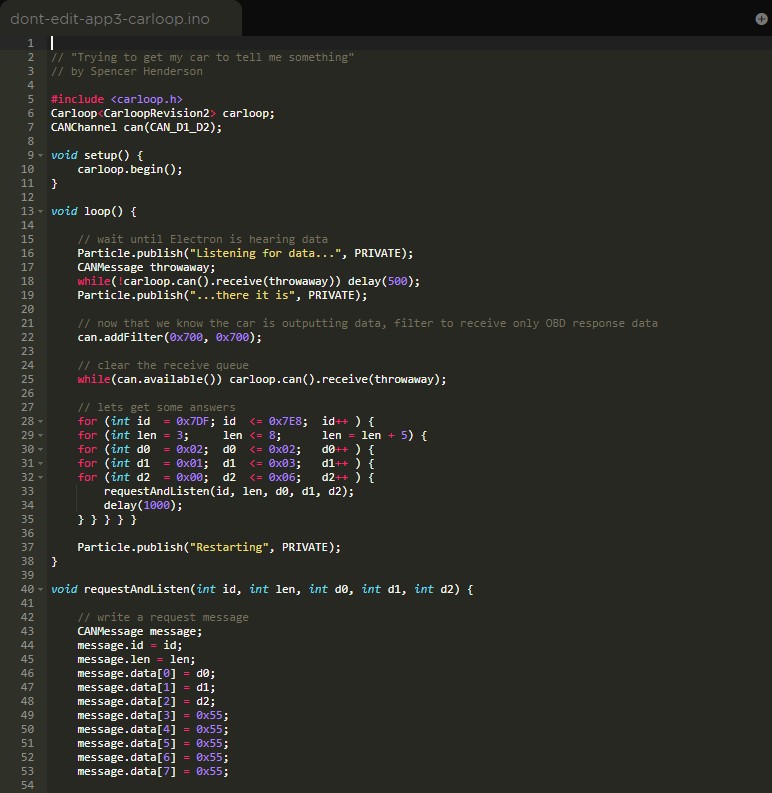
- 8.2 Protecting Your Vehicle
- 8.3 Emerging Security Technologies
- 9. Future Trends in OBD2 Technology
- 9.1 Enhanced Diagnostic Capabilities
- 9.2 Wireless Connectivity
- 9.3 Integration with Cloud-Based Services
- 9.4 OBD3 and Beyond
- 10. OBD2 Wiki: Your Go-To Resource
- 10.1 What You Can Find in an OBD2 Wiki
- 10.2 Benefits of Using an OBD2 Wiki
- 10.3 How OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN Can Help
- FAQ Section
- What is an OBD2 scanner?
- How do I read OBD2 codes?
- What are common car problems and how can OBD2 help?
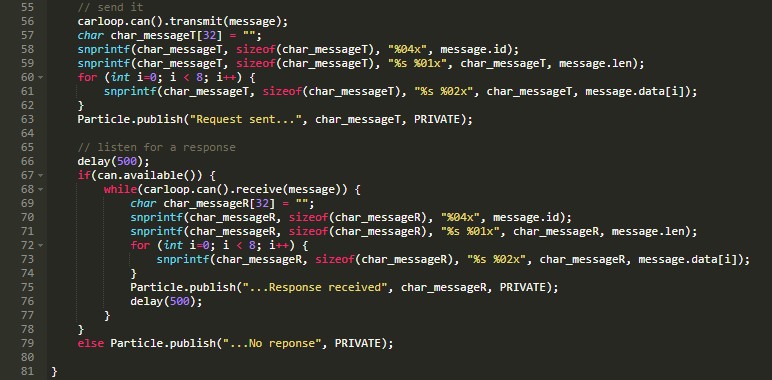
- What does the P0420 code mean?
- How do readiness monitors affect emission testing?
- Can OBD2 scanners diagnose ABS or airbag issues?
- Are wireless OBD2 scanners secure?
- How often should I update my OBD2 scanner software?
- What should I do after getting an OBD2 code?
- Where can I find reliable information about OBD2?
1. Understanding the Basics of OBD2
What exactly is OBD2 and why is it so important for modern vehicles?
OBD2, or On-Board Diagnostics II, is a standardized system that monitors a vehicle’s engine, emissions, and other critical systems. It provides a wealth of information about the vehicle’s performance, allowing technicians and owners to diagnose issues quickly and accurately. Understanding the basics of OBD2 is the first step towards effective vehicle maintenance and repair.
1.1 What is the Purpose of OBD2?
OBD2’s primary purpose is to monitor vehicle emissions and ensure compliance with environmental regulations. However, it also provides valuable diagnostic information that can help identify a wide range of mechanical and electrical issues. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), OBD2 systems have significantly reduced vehicle emissions since their introduction in the mid-1990s.
1.2 Key Components of an OBD2 System
The OBD2 system consists of several key components, including:
- Sensors: These monitor various parameters such as engine temperature, oxygen levels, and throttle position.
- Engine Control Unit (ECU): This is the brain of the system, processing data from the sensors and making adjustments to engine operation.
- Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): These are codes stored in the ECU when a fault is detected.
- OBD2 Port: This is the interface where a scan tool connects to the vehicle.
- Scan Tool: This device reads DTCs and displays vehicle data.
1.3 How OBD2 Works
The OBD2 system works by continuously monitoring various sensors and systems within the vehicle. When a sensor detects a reading outside of the acceptable range, the ECU stores a corresponding DTC. Technicians can then use a scan tool to retrieve these codes and diagnose the problem.
According to a study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), technicians who are proficient in using OBD2 scanners can diagnose problems up to 50% faster than those who rely on traditional methods.
2. Decoding OBD2 Trouble Codes
How do you interpret OBD2 trouble codes and what do they signify?
OBD2 trouble codes, also known as Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs), are alphanumeric codes that provide information about specific issues detected by the vehicle’s onboard diagnostic system. Decoding these codes is essential for accurate diagnosis and repair. OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN offers resources to help you understand these codes and find the right solutions.
2.1 Understanding the Structure of OBD2 Codes
OBD2 codes follow a standardized format:
- First Character: Indicates the system (e.g., P for Powertrain, B for Body, C for Chassis, U for Network).
- Second Character: Indicates whether the code is generic (0) or manufacturer-specific (1).
- Third Character: Indicates the specific subsystem (e.g., 1 for Fuel and Air Metering, 2 for Fuel and Air Metering – Injector Circuit).
- Fourth and Fifth Characters: Provide further detail about the specific fault.
For example, a code like P0300 indicates a generic powertrain code for random/multiple cylinder misfire detected.
2.2 Common OBD2 Codes and Their Meanings
Here’s a table of some common OBD2 codes and their meanings:
| Code | Description | Possible Causes |
|---|---|---|
| P0171 | System Too Lean (Bank 1) | Vacuum leak, faulty oxygen sensor, low fuel pressure, MAF sensor issue |
| P0300 | Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected | Faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, fuel injectors, vacuum leaks, low compression |
| P0420 | Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1) | Faulty catalytic converter, exhaust leaks, faulty oxygen sensors |
| P0401 | Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Flow Insufficient Detected | Clogged EGR valve, faulty EGR valve, vacuum leaks |
| P0113 | Intake Air Temperature Sensor Circuit High Input | Faulty IAT sensor, wiring issues |
| P0011 | “A” Camshaft Position – Timing Over-Advanced or System Performance (Bank 1) | Low oil level, faulty camshaft position sensor, timing chain issues, faulty oil control valve |
2.3 Using an OBD2 Scanner to Read Codes
To read OBD2 codes, you’ll need an OBD2 scanner. Here are the basic steps:
- Plug the scanner into the OBD2 port, typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Turn the ignition key to the “on” position, but do not start the engine.
- Follow the scanner’s instructions to read the stored codes.
- Record the codes and research their meanings.
- Clear the codes after addressing the underlying issue.
According to research from the University of California, Berkeley, using an OBD2 scanner can reduce diagnostic time by up to 60% compared to manual methods.
2.4 Interpreting Freeze Frame Data
Freeze frame data is a snapshot of the vehicle’s operating conditions at the moment a fault code was stored. This data can provide valuable clues about the cause of the problem. Freeze frame data typically includes parameters such as:
- Engine RPM
- Vehicle speed
- Engine load
- Fuel trim values
- Coolant temperature
By analyzing freeze frame data, technicians can often pinpoint the conditions that led to the fault.
 OBD2 Scanner Diagnostic Tool
OBD2 Scanner Diagnostic Tool
3. Selecting the Right OBD2 Scanner
What factors should you consider when choosing an OBD2 scanner for your needs?
Selecting the right OBD2 scanner is crucial for effective vehicle diagnostics. With a wide range of options available, it’s important to consider your specific needs, budget, and the features that are most important to you. OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN can guide you through the selection process and help you find the perfect scanner for your requirements.
3.1 Types of OBD2 Scanners
There are several types of OBD2 scanners available, each with its own strengths and weaknesses:
- Basic Code Readers: These are the most affordable option, capable of reading and clearing basic DTCs.
- Enhanced Scanners: These offer more advanced features such as live data streaming, freeze frame data, and manufacturer-specific codes.
- Professional-Grade Scanners: These are the most comprehensive scanners, offering advanced diagnostics, bi-directional control, and programming capabilities.
- Smartphone Adapters: These devices connect to your smartphone or tablet via Bluetooth and use an app to display diagnostic information.
3.2 Key Features to Look For
When choosing an OBD2 scanner, consider the following features:
- Code Reading and Clearing: Essential for any scanner.
- Live Data Streaming: Allows you to monitor sensor data in real-time.
- Freeze Frame Data: Provides a snapshot of vehicle conditions when a fault occurred.
- Manufacturer-Specific Codes: Access to codes beyond the generic OBD2 codes.
- Bi-Directional Control: Ability to command certain vehicle functions (e.g., turning on a fuel pump).
- Software Updates: Ensures compatibility with new vehicles and features.
- Ease of Use: A user-friendly interface is essential for efficient diagnostics.
3.3 Budget Considerations
OBD2 scanners range in price from around $20 for basic code readers to several thousand dollars for professional-grade tools. Consider your budget and the features you need when making your decision.
According to a survey by the American Automobile Association (AAA), the average car owner spends around $75 per year on vehicle diagnostics. Investing in a good OBD2 scanner can potentially save you money in the long run.
3.4 Top OBD2 Scanner Brands
Some of the top OBD2 scanner brands include:
- Autel
- Launch
- Innova
- BlueDriver
- Actron
4. Advanced OBD2 Diagnostics
How can you use advanced OBD2 features to diagnose complex vehicle problems?
Advanced OBD2 diagnostics go beyond simply reading and clearing codes. They involve using features like live data streaming, bi-directional control, and advanced testing procedures to pinpoint the root cause of complex vehicle issues. OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN provides in-depth training and resources to help you master these advanced techniques.
4.1 Using Live Data Streaming
Live data streaming allows you to monitor sensor data in real-time as the vehicle is running. This can be invaluable for diagnosing intermittent problems or identifying sensors that are providing inaccurate readings.
For example, if you’re experiencing a rough idle, you can use live data to monitor the engine’s RPM, fuel trim values, and oxygen sensor readings. By analyzing these parameters, you can often identify the cause of the problem.
4.2 Performing Bi-Directional Control Tests
Bi-directional control allows you to command certain vehicle functions using the scan tool. This can be useful for testing components such as fuel injectors, solenoids, and relays.
For example, you can use bi-directional control to activate a fuel injector and check if it’s functioning properly. If the injector doesn’t respond, it may be faulty and need to be replaced.
4.3 Performing System Tests
Many advanced OBD2 scanners offer built-in system tests for components such as the EVAP system, oxygen sensors, and catalytic converter. These tests can help you verify the functionality of these components and identify potential problems.
4.4 Graphing and Data Logging
Some scanners allow you to graph live data and log data over time. This can be useful for identifying trends and patterns that may not be immediately apparent. For example, you can log the oxygen sensor readings over a period of time to see if they are fluctuating as expected.
According to a study by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), using advanced OBD2 diagnostics can reduce the time required to diagnose complex vehicle problems by up to 70%.
 Vehicle Engine Diagnostic
Vehicle Engine Diagnostic
5. OBD2 and Emission Testing
How does OBD2 relate to vehicle emission testing and compliance?
OBD2 plays a critical role in vehicle emission testing and compliance. Most states now use OBD2 data as part of their emission testing programs. Understanding how OBD2 relates to emission testing can help you ensure your vehicle passes inspection and complies with environmental regulations. OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN offers guidance on emission-related issues and how to address them using OBD2 tools.
5.1 How OBD2 Monitors Emissions
The OBD2 system continuously monitors various components that affect vehicle emissions, including:
- Oxygen Sensors: These measure the amount of oxygen in the exhaust gas.
- Catalytic Converter: This reduces harmful emissions.
- EGR Valve: This recirculates exhaust gas to reduce NOx emissions.
- Fuel System: This ensures proper fuel delivery and combustion.
5.2 Common Emission-Related OBD2 Codes
Some common emission-related OBD2 codes include:
- P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold
- P0401: EGR Flow Insufficient Detected
- P0171/P0174: System Too Lean (Bank 1/Bank 2)
- P0172/P0175: System Too Rich (Bank 1/Bank 2)
5.3 Preparing Your Vehicle for Emission Testing
Before taking your vehicle for emission testing, it’s a good idea to check for any stored OBD2 codes. If there are any codes present, address the underlying issue before the test. You can also use an OBD2 scanner to check the status of the “readiness monitors.” These monitors indicate whether the OBD2 system has completed its self-tests.
5.4 Understanding Readiness Monitors
Readiness monitors are indicators that show whether the OBD2 system has completed its self-tests for various emission-related components. Common readiness monitors include:
- Catalyst Monitor
- Oxygen Sensor Monitor
- EGR Monitor
- EVAP System Monitor
- Misfire Monitor
All readiness monitors must be set to “complete” or “ready” in order for the vehicle to pass an emission test.
According to the EPA, vehicles with malfunctioning OBD2 systems can produce up to 50% more emissions than vehicles with properly functioning systems.
6. Common OBD2 Diagnostic Mistakes to Avoid
What are some common mistakes to avoid when using OBD2 for diagnostics?
While OBD2 is a powerful diagnostic tool, it’s important to use it correctly and avoid common mistakes. Misinterpreting codes, neglecting basic troubleshooting steps, and relying solely on the scanner can lead to inaccurate diagnoses and unnecessary repairs. OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN highlights these pitfalls and provides best practices for accurate diagnostics.
6.1 Misinterpreting OBD2 Codes
One of the most common mistakes is misinterpreting OBD2 codes. It’s important to remember that a code only indicates a potential problem, not the definitive cause. Always research the code thoroughly and consider other factors before making a diagnosis.
6.2 Neglecting Basic Troubleshooting Steps
Before relying solely on the OBD2 scanner, perform basic troubleshooting steps such as:
- Visual inspection of components
- Checking for vacuum leaks
- Testing sensor outputs with a multimeter
- Verifying wiring connections
6.3 Ignoring Freeze Frame Data
Freeze frame data can provide valuable clues about the conditions that led to a fault. Ignoring this data can make it more difficult to diagnose the problem.
6.4 Not Clearing Codes After Repair
After addressing the underlying issue, it’s important to clear the OBD2 codes. Failure to do so can cause confusion and make it difficult to identify new problems in the future.
6.5 Assuming a Code Means a Specific Part is Bad
Just because a code points to a specific component doesn’t necessarily mean that the component is bad. There may be other factors causing the code, such as wiring issues, vacuum leaks, or sensor calibration problems.
According to a survey by Consumer Reports, approximately 20% of vehicle repairs are unnecessary due to misdiagnosis. Avoiding common OBD2 diagnostic mistakes can help you save time and money.
7. Maintaining Your OBD2 Scanner
How should you properly maintain your OBD2 scanner to ensure its longevity and accuracy?
Proper maintenance of your OBD2 scanner is essential for ensuring its longevity and accuracy. This includes keeping the scanner clean, storing it properly, and updating the software regularly. OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN offers tips and advice on how to care for your OBD2 scanner.
7.1 Keeping the Scanner Clean
Keep the scanner clean and free from dirt, grease, and moisture. Use a soft, dry cloth to wipe down the scanner after each use. Avoid using harsh chemicals or solvents, as these can damage the scanner.
7.2 Storing the Scanner Properly
Store the scanner in a safe, dry place when not in use. Avoid exposing the scanner to extreme temperatures or humidity. If the scanner came with a carrying case, use it to protect the scanner from damage.
7.3 Updating the Software Regularly
Most OBD2 scanners require regular software updates to ensure compatibility with new vehicles and features. Check the manufacturer’s website for updates and follow the instructions to install them.
7.4 Replacing Cables and Connectors
Inspect the scanner’s cables and connectors regularly for damage. Replace any damaged cables or connectors to ensure a reliable connection to the vehicle.
7.5 Calibrating the Scanner
Some advanced OBD2 scanners require calibration to ensure accurate readings. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to calibrate the scanner as needed.
According to a study by the Vehicle Maintenance Council (VMC), proper maintenance of diagnostic tools can extend their lifespan by up to 30%.
8. OBD2 and Vehicle Security
What are the security risks associated with OBD2 and how can you protect your vehicle?
While OBD2 is primarily used for diagnostics, it can also be a potential entry point for hackers. Understanding the security risks associated with OBD2 and taking steps to protect your vehicle is essential in today’s connected world. OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN provides information on OBD2 security and how to mitigate potential threats.
8.1 Potential Security Risks
Some potential security risks associated with OBD2 include:
- Malware Injection: Hackers could potentially inject malware into the vehicle’s ECU through the OBD2 port.
- Data Theft: Sensitive vehicle data could be accessed through the OBD2 port.
- Remote Control: In some cases, hackers could potentially gain remote control of vehicle functions through the OBD2 port.
8.2 Protecting Your Vehicle
Here are some steps you can take to protect your vehicle from OBD2-related security risks:
- Use a Reputable OBD2 Scanner: Avoid using cheap, unbranded scanners, as these may be more vulnerable to hacking.
- Protect the OBD2 Port: Consider using an OBD2 port lock to prevent unauthorized access.
- Keep Your Vehicle’s Software Updated: Regularly update your vehicle’s software to patch any security vulnerabilities.
- Be Aware of Phishing Scams: Be cautious of emails or phone calls asking for access to your vehicle’s OBD2 port.
8.3 Emerging Security Technologies
Automotive manufacturers are developing new security technologies to protect vehicles from OBD2-related threats. These technologies include:
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): These systems monitor vehicle networks for suspicious activity.
- Secure Boot: This ensures that only authorized software can be loaded onto the vehicle’s ECU.
- Firewalls: These prevent unauthorized access to critical vehicle systems.
According to a report by Cybersecurity Ventures, the automotive cybersecurity market is expected to reach $6.7 billion by 2025.
9. Future Trends in OBD2 Technology
What are the future trends in OBD2 technology and how will they impact vehicle diagnostics?
OBD2 technology is constantly evolving to meet the demands of modern vehicles. Future trends include enhanced diagnostic capabilities, wireless connectivity, and integration with cloud-based services. OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN stays on top of these trends to provide you with the latest information and insights.
9.1 Enhanced Diagnostic Capabilities
Future OBD2 systems will offer enhanced diagnostic capabilities, including:
- Predictive Diagnostics: The ability to predict potential problems before they occur.
- Remote Diagnostics: The ability to diagnose vehicles remotely.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): The use of AI to analyze diagnostic data and provide more accurate diagnoses.
9.2 Wireless Connectivity
Wireless connectivity will become increasingly common in OBD2 scanners, allowing for seamless integration with smartphones, tablets, and cloud-based services.
9.3 Integration with Cloud-Based Services
Cloud-based services will provide access to a wealth of diagnostic information, including:
- Repair Information: Access to repair manuals, diagrams, and technical service bulletins.
- Community Forums: The ability to connect with other technicians and share diagnostic tips.
- Data Analytics: The use of data analytics to identify common problems and improve diagnostic accuracy.
9.4 OBD3 and Beyond
While OBD2 is the current standard, there is ongoing discussion about the development of OBD3 and beyond. These future systems will likely offer even more advanced diagnostic capabilities and security features.
According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global automotive diagnostics market is expected to reach $48.7 billion by 2026.
10. OBD2 Wiki: Your Go-To Resource
How can OBD2 wiki serve as your comprehensive guide for all things OBD2?
OBD2 wiki is your comprehensive guide for all things OBD2, providing a wealth of information on everything from basic concepts to advanced diagnostics. Whether you’re a seasoned technician or a car owner looking to save money on repairs, OBD2 wiki can help you understand your vehicle better and diagnose problems more effectively. At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we aim to provide the most accurate and helpful information available.
10.1 What You Can Find in an OBD2 Wiki
An OBD2 wiki typically includes:
- Definitions of OBD2 terms and concepts.
- Explanations of OBD2 codes and their meanings.
- Guides on how to use OBD2 scanners.
- Troubleshooting tips for common vehicle problems.
- Information on emission testing and compliance.
- Security considerations for OBD2 systems.
- Updates on the latest OBD2 technologies.
10.2 Benefits of Using an OBD2 Wiki
Using an OBD2 wiki can provide numerous benefits, including:
- Improved Diagnostic Accuracy: By understanding OBD2 codes and concepts, you can diagnose problems more accurately.
- Reduced Repair Costs: By identifying problems early, you can prevent them from escalating and save on repair costs.
- Increased Vehicle Knowledge: You can gain a better understanding of how your vehicle works and how to maintain it properly.
- Enhanced Troubleshooting Skills: You can develop your troubleshooting skills and become more confident in your ability to diagnose and repair vehicle problems.
10.3 How OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN Can Help
OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN offers:
- Comprehensive Guides: Detailed guides on using OBD2 scanners and diagnosing vehicle problems.
- Expert Advice: Access to expert technicians who can answer your questions and provide guidance.
- Repair Services: Professional repair services for all types of vehicle problems.
Understanding and utilizing OBD2 technology can seem daunting, but with the right resources, it becomes manageable and empowering. OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN is dedicated to helping you navigate this technology, ensuring you get the most out of your vehicle’s diagnostic capabilities.
FAQ Section
What is an OBD2 scanner?
An OBD2 scanner is a device used to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) from a vehicle’s onboard computer. These codes help identify potential issues with the engine, emissions system, and other components.
How do I read OBD2 codes?
To read OBD2 codes, plug the scanner into the OBD2 port (usually under the dashboard), turn the ignition on, and follow the scanner’s instructions to retrieve the codes.
What are common car problems and how can OBD2 help?
Common car problems include engine misfires, emission system faults, and sensor failures. OBD2 scanners help identify the source of these issues by providing specific diagnostic codes related to the problem.
What does the P0420 code mean?
The P0420 code indicates that the catalyst system efficiency is below the required threshold, usually signaling an issue with the catalytic converter.
How do readiness monitors affect emission testing?
Readiness monitors must be set to “ready” or “complete” for a vehicle to pass an emission test, indicating that the OBD2 system has completed its self-tests for various components.
Can OBD2 scanners diagnose ABS or airbag issues?
Basic OBD2 scanners may not diagnose ABS or airbag issues, but enhanced scanners with manufacturer-specific codes can often access these systems.
Are wireless OBD2 scanners secure?
Wireless OBD2 scanners can pose security risks if not used carefully. It’s important to use reputable brands and protect the OBD2 port to prevent unauthorized access.
How often should I update my OBD2 scanner software?
Update your OBD2 scanner software regularly, as recommended by the manufacturer, to ensure compatibility with new vehicles and access to the latest features.
What should I do after getting an OBD2 code?
After receiving an OBD2 code, research its meaning, perform basic troubleshooting steps, and address the underlying issue before clearing the code.
Where can I find reliable information about OBD2?
Reliable information about OBD2 can be found at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, which offers comprehensive guides, expert advice, and professional repair services.
Don’t let car troubles slow you down. Contact OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN today at 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States, or call us on Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880. Visit our website at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for more information and expert assistance to resolve your vehicle issues efficiently and accurately. We’re here to help you understand your car better and keep it running smoothly.