The OBD2 port location is crucial for effective vehicle diagnostics, and OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN offers expert insights to simplify this process. This article provides a comprehensive guide to understanding and locating the OBD2 port, ensuring you can easily access and utilize its diagnostic capabilities for vehicle maintenance and repair, using car diagnostic tools, automotive diagnostic systems, and vehicle computer interface.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the OBD2 Port: The Gateway to Your Vehicle’s Health
- 2. Pinpointing the OBD2 Port Location: A Practical Guide
- 3. Understanding the OBD2 Connector and Pinout: A Technical Overview
- 4. The Significance of the OBD2 Port: Unlocking Vehicle Diagnostics
- 5. Step-by-Step Guide: How to Use the OBD2 Port for Vehicle Diagnostics
- 6. Advanced Diagnostics: Taking Vehicle Insights to the Next Level
- 7. Common Issues and Troubleshooting: Addressing OBD2 Port Problems
- 8. OBD2 Port Standardization: Ensuring Compatibility and Ease of Use
- 9. Multiple OBD2 Ports: Understanding Vehicle Configurations
- 10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About OBD2 Ports
- Conclusion: Empowering Vehicle Owners with OBD2 Knowledge
1. Understanding the OBD2 Port: The Gateway to Your Vehicle’s Health
What is an OBD2 port? The OBD2 (On-Board Diagnostics II) port is a standardized interface in modern vehicles that provides access to the vehicle’s computer system for diagnostics and monitoring. It serves as a gateway to retrieve valuable data about your vehicle’s performance, emission system, and overall health. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), all cars and light trucks manufactured for sale in the United States after January 1, 1996, are required to have an OBD2 port. This standardization ensures that any compatible scan tool can communicate with the vehicle’s computer, regardless of the make or model.
Why is the OBD2 port so important? The OBD2 port allows mechanics and vehicle owners to diagnose problems quickly and accurately. By connecting an OBD2 scanner, you can read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) that indicate specific issues within the vehicle’s systems. This capability is invaluable for identifying problems ranging from minor sensor malfunctions to more severe engine or transmission failures. Moreover, the OBD2 port provides real-time data, allowing for monitoring of various parameters such as engine temperature, speed, and fuel consumption. This information can be used to optimize vehicle performance and prevent potential issues before they escalate, enhancing vehicle health monitoring and diagnostic data retrieval.
2. Pinpointing the OBD2 Port Location: A Practical Guide
Where Is The Obd2 Port Located in my car? The OBD2 port’s location is generally consistent across most vehicles, but it can vary depending on the make, model, and year. Typically, it is found inside the passenger compartment. It’s almost always within easy reach of the driver, usually under the dashboard. Specifically, you can check these common locations:
- Under the Dashboard: This is the most common location. Look beneath the steering column or in the area around the driver’s knees.
- Near the Center Console: Some vehicles have the OBD2 port located in the center console area, either in the front or on the side.
- Behind an Ashtray or Panel: In some models, the port might be hidden behind a small panel or ashtray that needs to be opened or removed.
To quickly find the OBD2 port, check your vehicle’s owner’s manual. Most manuals include a diagram showing the exact location of the port. If you don’t have the manual, you can search online for “[year] [make] [model] OBD2 port location”. Websites like OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN also offer resources to help you locate the port for various vehicles. Remember, the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) mandates that the OBD2 port must be located within 24 inches of the driver’s seat, making it relatively easy to find.
 Typical OBD2 port locations under the dashboard
Typical OBD2 port locations under the dashboard
3. Understanding the OBD2 Connector and Pinout: A Technical Overview
What is the OBD2 connector and pinout configuration? The OBD2 connector is a standardized 16-pin (2×8) J1962 connector used to interface with the vehicle’s computer. Each pin serves a specific function, enabling communication between the scan tool and the vehicle’s systems. Understanding the pinout configuration is essential for advanced diagnostics and custom applications. The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) define the standards for the OBD2 connector and pinout, ensuring interoperability across different vehicles and scan tools.
What are the key pins and their functions? Here’s a brief overview of some of the key pins:
- Pin 4: Chassis Ground: Provides a common ground for the vehicle’s electrical system.
- Pin 5: Signal Ground: Provides a ground reference for the diagnostic signals.
- Pin 6: CAN High (J-2284): Used for Controller Area Network (CAN) communication, which is the primary communication protocol in modern vehicles.
- Pin 7: ISO 9141-2 K-Line: Used for ISO 9141-2 communication, an older protocol still used in some vehicles.
- Pin 10: SAE J1850 Bus-: Used for SAE J1850 communication, another older protocol used primarily in Ford vehicles.
- Pin 14: CAN Low (J-2284): Used for CAN communication.
- Pin 15: ISO 9141-2 L-Line: Used for ISO 9141-2 communication.
- Pin 16: Battery Power: Provides power to the scan tool.
The CAN bus, connected through pins 6 and 14, is crucial for many diagnostic processes as outlined by the ISO 15765-4 standard, enabling efficient and reliable data transmission. Pins 4 and 5 provide grounding, ensuring safe and accurate data transmission, while pins 2 and 10 communicate with the SAE J1850 BUS+, facilitating direct communication with the vehicle’s main computer. The configuration and standardization of the OBD2 connector, supported by organizations like the European Automobile Manufacturers Association (ACEA), ensures compatibility and ease of use in vehicle diagnostics.
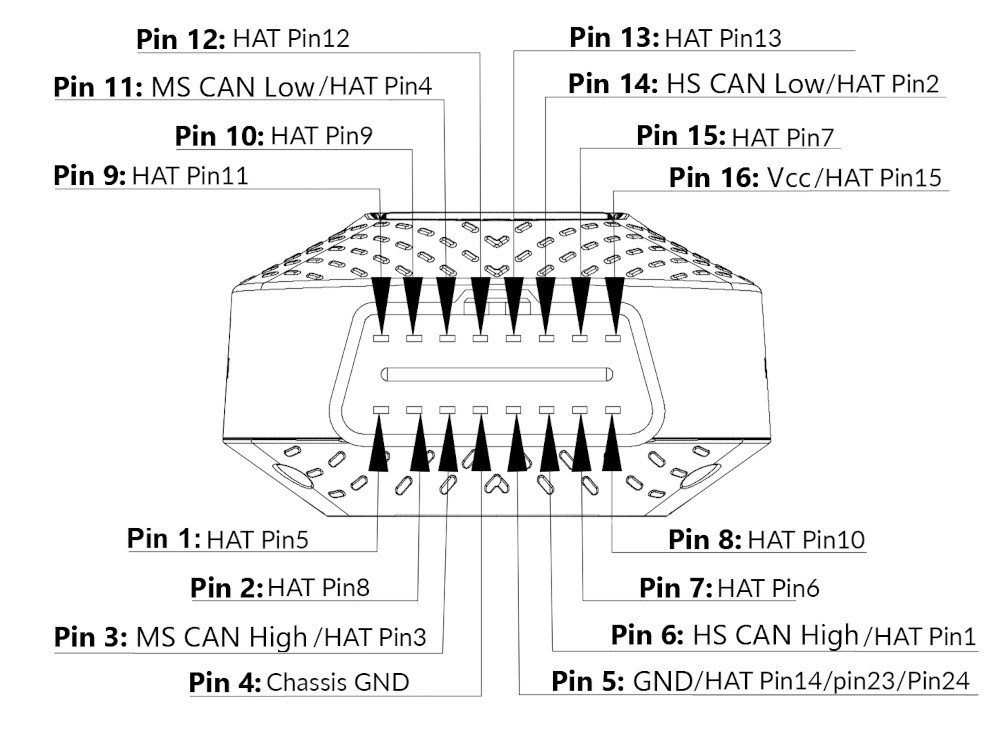 OBD2 connector pinouts
OBD2 connector pinouts
4. The Significance of the OBD2 Port: Unlocking Vehicle Diagnostics
Why is the OBD2 diagnostic port important? The OBD2 diagnostic port is essential for gaining insights into your car’s engine, emission system, and more, allowing for comprehensive self-diagnosis and reporting capabilities. It aids in troubleshooting and ensures vehicles meet emissions standards, playing a crucial role in automotive maintenance. According to a study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), accurate and timely diagnostics through the OBD2 port can reduce repair costs by up to 40%.
How does the OBD2 port enhance vehicle maintenance? The OBD2 port allows for comprehensive self-diagnosis and reporting capabilities, aiding in troubleshooting and ensuring vehicles meet emissions standards. By connecting an OBD2 scanner, you can access a wealth of information about your vehicle’s performance and identify potential issues before they become major problems. This proactive approach to maintenance can save you time and money in the long run. For example, monitoring the engine temperature through the OBD2 port can alert you to a potential cooling system issue, preventing overheating and costly engine damage. Similarly, tracking fuel consumption can help you identify inefficiencies and optimize your driving habits for better fuel economy.
The OBD2 port also plays a critical role in ensuring that vehicles meet emissions standards. Many states require vehicles to pass an emissions test as part of their registration process. The OBD2 system monitors the components of the emission system, such as the catalytic converter and oxygen sensors, and alerts you to any malfunctions that could cause the vehicle to fail the test. Addressing these issues promptly can help you avoid costly fines and ensure that your vehicle is environmentally compliant, aligning with standards set by the California Air Resources Board (CARB).
5. Step-by-Step Guide: How to Use the OBD2 Port for Vehicle Diagnostics
How can I use the OBD2 port for vehicle diagnostics? Using the OBD2 port is straightforward. Simply plug a compatible scanner into the OBD2 port to communicate with the car’s computer system and read fault codes that indicate vehicle issues. If your car was manufactured after 1996, it is required by law to have an OBD2 port, making vehicle diagnostic tools accessible and easy to use.
What are the steps to follow? Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to use the OBD2 port for vehicle diagnostics:
- Locate the OBD2 Port: Refer to your vehicle’s owner’s manual or search online to find the exact location of the OBD2 port. It is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Plug in the OBD2 Scanner: Connect the OBD2 scanner to the port. Ensure that the connection is secure.
- Turn on the Ignition: Turn the ignition key to the “on” position without starting the engine. This provides power to the vehicle’s computer system and the OBD2 scanner.
- Read the Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Follow the instructions on the OBD2 scanner to read the DTCs. The scanner will display a list of codes that indicate specific issues within the vehicle’s systems.
- Interpret the DTCs: Use the scanner’s manual or an online resource like OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN to interpret the DTCs. Each code corresponds to a specific problem, such as a faulty sensor, a malfunctioning component, or an emission system issue.
- Clear the DTCs (Optional): After addressing the issues indicated by the DTCs, you can use the scanner to clear the codes. However, it’s essential to ensure that the problems have been resolved before clearing the codes, as they may reappear if the underlying issues persist.
By following these steps, you can effectively use the OBD2 port to diagnose and troubleshoot vehicle issues, making vehicle diagnostics simple and efficient.
6. Advanced Diagnostics: Taking Vehicle Insights to the Next Level
How can I take vehicle diagnostics to the next level? While your car’s OBD2 port gives you some basic information, you can go deeper by connecting advanced devices like the AutoPi CAN-FD Pro. It works with your OBD2 port to give you faster, more detailed insights into your vehicle’s performance, enhancing vehicle computer interface capabilities.
What are the benefits of using advanced diagnostic tools? Advanced diagnostic tools like the AutoPi CAN-FD Pro provide a range of benefits, including:
- Faster Data Retrieval: These tools offer faster data transfer rates, allowing you to retrieve diagnostic information more quickly.
- Detailed Insights: They provide more detailed insights into your vehicle’s performance, including parameters that are not accessible with basic OBD2 scanners.
- Real-Time Monitoring: They enable real-time monitoring of various vehicle systems, allowing you to track performance and identify potential issues as they arise.
- Customization: Advanced tools often allow for customization, enabling you to tailor the diagnostic process to your specific needs.
The AutoPi device helps you keep track of important car systems, like the engine and emissions. If you want deeper insights into how your car is really doing, the AutoPi CAN-FD Pro is the perfect upgrade to your OBD2 projects. According to a report by Grand View Research, the market for advanced automotive diagnostic tools is expected to grow significantly in the coming years, driven by the increasing complexity of modern vehicles and the demand for more accurate and efficient diagnostic solutions.
7. Common Issues and Troubleshooting: Addressing OBD2 Port Problems
What if I can’t find the OBD2 location? If you are unable to locate the OBD2 port, refer to your vehicle’s owner’s manual or search online for your specific vehicle’s diagnostic connector location. Alternatively, you can consult with a qualified mechanic or technician who can help you locate the port.
What are some common issues with the OBD2 port? While the OBD2 port is designed to be robust and reliable, it can sometimes experience issues that prevent it from functioning correctly. Some common problems include:
- Damaged Connector: The OBD2 port connector can become damaged due to physical wear and tear, corrosion, or improper use.
- Bent or Broken Pins: The pins inside the OBD2 port can become bent or broken, preventing proper connection with the scan tool.
- Wiring Issues: The wiring connected to the OBD2 port can become damaged, resulting in poor communication or no communication at all.
- Software Glitches: In rare cases, software glitches in the vehicle’s computer system can prevent the OBD2 port from functioning correctly.
How can I troubleshoot these issues? Here are some steps you can take to troubleshoot common OBD2 port problems:
- Inspect the Connector: Check the OBD2 port connector for any signs of damage, such as cracks, corrosion, or bent pins.
- Check the Wiring: Inspect the wiring connected to the OBD2 port for any signs of damage, such as cuts, fraying, or loose connections.
- Test the Power and Ground: Use a multimeter to test the power and ground pins on the OBD2 port to ensure that they are functioning correctly.
- Try a Different Scan Tool: If you are experiencing communication issues, try using a different scan tool to rule out the possibility of a faulty scanner.
- Consult a Professional: If you are unable to resolve the issues yourself, consult with a qualified mechanic or technician who can diagnose and repair the OBD2 port.
8. OBD2 Port Standardization: Ensuring Compatibility and Ease of Use
Are all OBD2 ports the same? Yes, all OBD2 ports and connectors follow the same standardization, ensuring compatibility across different vehicles and scan tools. This standardization is mandated by regulatory bodies like the EPA in the United States and the European Union, and supported by organizations like the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO).
Why is standardization important? Standardization ensures that any compatible scan tool can communicate with the vehicle’s computer, regardless of the make or model. This makes it easier for mechanics and vehicle owners to diagnose and troubleshoot issues. Without standardization, each vehicle manufacturer could use a different type of connector and communication protocol, making it much more difficult and expensive to diagnose vehicle problems. The standardization of the OBD2 port also promotes innovation and competition in the automotive diagnostic tools market, leading to the development of more advanced and affordable solutions.
According to a report by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), the standardization of the OBD2 port has significantly improved the accuracy and efficiency of vehicle diagnostics, leading to safer and more reliable vehicles.
9. Multiple OBD2 Ports: Understanding Vehicle Configurations
How many OBD2 ports does a car have? Typically, a standard passenger car has one OBD2 port, located within easy reach of the driver. However, some commercial vehicles and heavy-duty trucks may have multiple OBD2 ports or additional diagnostic connectors for specific systems.
Why might a vehicle have multiple ports? In some cases, a vehicle may have multiple OBD2 ports to provide access to different vehicle systems. For example, a hybrid vehicle may have one OBD2 port for the engine and transmission systems and another port for the hybrid system components. Similarly, some heavy-duty trucks may have additional diagnostic connectors for the anti-lock braking system (ABS) or the electronic stability control (ESC) system. These additional ports are typically used by specialized diagnostic tools and technicians who have specific knowledge of the vehicle’s systems.
It’s important to note that while some vehicles may have multiple diagnostic connectors, they are not all OBD2 compliant. Some connectors may use proprietary communication protocols or be designed for specific diagnostic functions. Therefore, it’s essential to consult the vehicle’s owner’s manual or a qualified technician to determine the correct diagnostic procedure for each system.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About OBD2 Ports
Here are some frequently asked questions about OBD2 ports:
-
What is an OBD2 scanner? An OBD2 scanner is a diagnostic tool that connects to the OBD2 port and allows you to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and monitor vehicle performance parameters.
-
How do I read OBD2 codes? You can read OBD2 codes by connecting an OBD2 scanner to the OBD2 port and following the instructions on the scanner to retrieve the DTCs.
-
What are common OBD2 error codes? Some common OBD2 error codes include P0300 (random/multiple cylinder misfire detected), P0171 (system too lean), and P0420 (catalyst system efficiency below threshold).
-
Can I use any OBD2 scanner on my car? Yes, all OBD2 scanners are designed to be compatible with any vehicle that has an OBD2 port. However, some scanners may offer more advanced features or be better suited for specific vehicle makes or models.
-
What does the check engine light mean? The check engine light indicates that the vehicle’s computer has detected a problem with one or more of its systems. The OBD2 system stores a DTC that corresponds to the specific problem.
-
How do I reset the check engine light? You can reset the check engine light by connecting an OBD2 scanner to the OBD2 port and using the scanner’s erase codes function. However, it’s essential to address the underlying issues before resetting the light, as it may reappear if the problems persist.
-
Where can I find a list of OBD2 codes? You can find a list of OBD2 codes on websites like OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN or in the scanner’s manual.
-
What is the difference between OBD1 and OBD2? OBD1 is an older diagnostic system that was used in vehicles manufactured before 1996. OBD2 is a more advanced and standardized system that is used in all cars and light trucks manufactured for sale in the United States after January 1, 1996.
-
Can the OBD2 port be used for anything other than diagnostics? Yes, the OBD2 port can also be used for other purposes, such as monitoring vehicle performance, tracking fuel consumption, and customizing vehicle settings.
-
What are the benefits of using an OBD2 scanner? The benefits of using an OBD2 scanner include:
- Identifying vehicle problems quickly and accurately
- Saving time and money on repairs
- Monitoring vehicle performance
- Ensuring that vehicles meet emissions standards
- Customizing vehicle settings
 Keywords about the OBD2 connector and why its important as a gateway
Keywords about the OBD2 connector and why its important as a gateway
Conclusion: Empowering Vehicle Owners with OBD2 Knowledge
The OBD2 diagnostic port is more than just a plug in your car; it’s a portal to understanding your vehicle’s health and status. The next time you find yourself with a dashboard warning light, remember the power of the OBD2 port at your fingertips. Embrace the capabilities of the OBD2 port to keep your vehicle running smoothly and efficiently, using advanced diagnostic techniques and automotive maintenance.
At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we understand the challenges you face as automotive technicians, shop owners, and car enthusiasts. The constant need to update your knowledge, the physical demands of the job, and the pressure to deliver accurate and timely repairs can be overwhelming. That’s why we’re here to help. Our comprehensive resources, expert guidance, and advanced diagnostic tools are designed to make your job easier and more efficient.
Ready to take control of your vehicle’s diagnostics and ensure peak performance?
- Contact us today for personalized assistance with OBD2 scanner selection and usage.
- Call us at +1 (641) 206-8880 or reach out via WhatsApp for immediate support.
- Visit our website at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for detailed guides and exclusive offers.
- Find us at 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States for in-person consultations.
Explore our range of OBD2 tools and automotive data loggers to keep your vehicle in top condition, and start leveraging the power of advanced diagnostics today. Let OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN be your trusted partner in automotive diagnostics and repair.
Discover Now!
